Yanyong Zhang
On the Entropy Dynamics in Reinforcement Fine-Tuning of Large Language Models
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Entropy serves as a critical metric for measuring the diversity of outputs generated by large language models (LLMs), providing valuable insights into their exploration capabilities. While recent studies increasingly focus on monitoring and adjusting entropy to better balance exploration and exploitation in reinforcement fine-tuning (RFT), a principled understanding of entropy dynamics during this process is yet to be thoroughly investigated. In this paper, we establish a theoretical framework for analyzing the entropy dynamics during the RFT process, which begins with a discriminant expression that quantifies entropy change under a single logit update. This foundation enables the derivation of a first-order expression for entropy change, which can be further extended to the update formula of Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO). The corollaries and insights drawn from the theoretical analysis inspire the design of entropy control methods, and also offer a unified lens for interpreting various entropy-based methods in existing studies. We provide empirical evidence to support the main conclusions of our analysis and demonstrate the effectiveness of the derived entropy-discriminator clipping methods. This study yields novel insights into RFT training dynamics, providing theoretical support and practical strategies for optimizing the exploration-exploitation balance during LLM fine-tuning.
ConsisDrive: Identity-Preserving Driving World Models for Video Generation by Instance Mask
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Autonomous driving relies on robust models trained on large-scale, high-quality multi-view driving videos. Although world models provide a cost-effective solution for generating realistic driving data, they often suffer from identity drift, where the same object changes its appearance or category across frames due to the absence of instance-level temporal constraints. We introduce ConsisDrive, an identity-preserving driving world model designed to enforce temporal consistency at the instance level. Our framework incorporates two key components: (1) Instance-Masked Attention, which applies instance identity masks and trajectory masks within attention blocks to ensure that visual tokens interact only with their corresponding instance features across spatial and temporal dimensions, thereby preserving object identity consistency; and (2) Instance-Masked Loss, which adaptively emphasizes foreground regions with probabilistic instance masking, reducing background noise while maintaining overall scene fidelity. By integrating these mechanisms, ConsisDrive achieves state-of-the-art driving video generation quality and demonstrates significant improvements in downstream autonomous driving tasks on the nuScenes dataset. Our project page is https://shanpoyang654.github.io/ConsisDrive/page.html.
InstaDrive: Instance-Aware Driving World Models for Realistic and Consistent Video Generation
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Autonomous driving relies on robust models trained on high-quality, large-scale multi-view driving videos. While world models offer a cost-effective solution for generating realistic driving videos, they struggle to maintain instance-level temporal consistency and spatial geometric fidelity. To address these challenges, we propose InstaDrive, a novel framework that enhances driving video realism through two key advancements: (1) Instance Flow Guider, which extracts and propagates instance features across frames to enforce temporal consistency, preserving instance identity over time. (2) Spatial Geometric Aligner, which improves spatial reasoning, ensures precise instance positioning, and explicitly models occlusion hierarchies. By incorporating these instance-aware mechanisms, InstaDrive achieves state-of-the-art video generation quality and enhances downstream autonomous driving tasks on the nuScenes dataset. Additionally, we utilize CARLA's autopilot to procedurally and stochastically simulate rare but safety-critical driving scenarios across diverse maps and regions, enabling rigorous safety evaluation for autonomous systems. Our project page is https://shanpoyang654.github.io/InstaDrive/page.html.
Environment-Aware Adaptive Pruning with Interleaved Inference Orchestration for Vision-Language-Action Models
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:While Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models hold promise in embodied intelligence, their large parameter counts lead to substantial inference latency that hinders real-time manipulation, motivating parameter sparsification. However, as the environment evolves during VLA execution, the optimal sparsity patterns change accordingly. Static pruning lacks the adaptability required for environment dynamics, whereas fixed-interval dynamic layer pruning suffers from coarse granularity and high retraining overheads. To bridge this gap, we propose EcoVLA, a training-free, plug-and-play adaptive pruning framework that supports orthogonal combination with existing VLA acceleration methods. EcoVLA comprises two components: Environment-aware Adaptive Pruning (EAP) and Interleaved Inference Orchestration ($I^2O$). EAP is a lightweight adaptive channel pruning method that incorporates the temporal consistency of the physical environment to update sparsity patterns. $I^2O$ leverages the FLOPs bubbles inherent in VLA inference to schedule the pruning method in parallel, ensuring negligible impact on latency. Evaluated on diverse VLA models and benchmarks, EcoVLA delivers state-of-the-art performance, achieving up to 1.60$\times$ speedup with only a 0.4% drop in success rate, and further reaches 2.18$\times$ speedup with only a 0.5% degradation when combined with token pruning. We further validate the effectiveness of EcoVLA on real-world robots.
Latent Shadows: The Gaussian-Discrete Duality in Masked Diffusion
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Masked discrete diffusion is a dominant paradigm for high-quality language modeling where tokens are iteratively corrupted to a mask state, yet its inference efficiency is bottlenecked by the lack of deterministic sampling tools. While diffusion duality enables deterministic distillation for uniform models, these approaches generally underperform masked models and rely on complex integral operators. Conversely, in the masked domain, prior methods typically assume the absence of deterministic trajectories, forcing a reliance on stochastic distillation. To bridge this gap, we establish explicit Masked Diffusion Duality, proving that the masked process arises as the projection of a continuous Gaussian process via a novel maximum-value index preservation mechanism. Furthermore, we introduce Masked Consistency Distillation (MCD), a principled framework that leverages this duality to analytically construct the deterministic coupled trajectories required for consistency distillation, bypassing numerical ODE solvers. This result strictly improves upon prior stochastic distillation methods, achieving a 16$\times$ inference speedup without compromising generation quality. Our findings not only provide a solid theoretical foundation connecting masked and continuous diffusion, but also unlock the full potential of consistency distillation for high-performance discrete generation. Our code is available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/MCD-70FD.
Rethinking Popularity Bias in Collaborative Filtering via Analytical Vector Decomposition
Dec 24, 2025



Abstract:Popularity bias fundamentally undermines the personalization capabilities of collaborative filtering (CF) models, causing them to disproportionately recommend popular items while neglecting users' genuine preferences for niche content. While existing approaches treat this as an external confounding factor, we reveal that popularity bias is an intrinsic geometric artifact of Bayesian Pairwise Ranking (BPR) optimization in CF models. Through rigorous mathematical analysis, we prove that BPR systematically organizes item embeddings along a dominant "popularity direction" where embedding magnitudes directly correlate with interaction frequency. This geometric distortion forces user embeddings to simultaneously handle two conflicting tasks-expressing genuine preference and calibrating against global popularity-trapping them in suboptimal configurations that favor popular items regardless of individual tastes. We propose Directional Decomposition and Correction (DDC), a universally applicable framework that surgically corrects this embedding geometry through asymmetric directional updates. DDC guides positive interactions along personalized preference directions while steering negative interactions away from the global popularity direction, disentangling preference from popularity at the geometric source. Extensive experiments across multiple BPR-based architectures demonstrate that DDC significantly outperforms state-of-the-art debiasing methods, reducing training loss to less than 5% of heavily-tuned baselines while achieving superior recommendation quality and fairness. Code is available in https://github.com/LingFeng-Liu-AI/DDC.
TransLLM: A Unified Multi-Task Foundation Framework for Urban Transportation via Learnable Prompting
Aug 20, 2025Abstract:Urban transportation systems encounter diverse challenges across multiple tasks, such as traffic forecasting, electric vehicle (EV) charging demand prediction, and taxi dispatch. Existing approaches suffer from two key limitations: small-scale deep learning models are task-specific and data-hungry, limiting their generalizability across diverse scenarios, while large language models (LLMs), despite offering flexibility through natural language interfaces, struggle with structured spatiotemporal data and numerical reasoning in transportation domains. To address these limitations, we propose TransLLM, a unified foundation framework that integrates spatiotemporal modeling with large language models through learnable prompt composition. Our approach features a lightweight spatiotemporal encoder that captures complex dependencies via dilated temporal convolutions and dual-adjacency graph attention networks, seamlessly interfacing with LLMs through structured embeddings. A novel instance-level prompt routing mechanism, trained via reinforcement learning, dynamically personalizes prompts based on input characteristics, moving beyond fixed task-specific templates. The framework operates by encoding spatiotemporal patterns into contextual representations, dynamically composing personalized prompts to guide LLM reasoning, and projecting the resulting representations through specialized output layers to generate task-specific predictions. Experiments across seven datasets and three tasks demonstrate the exceptional effectiveness of TransLLM in both supervised and zero-shot settings. Compared to ten baseline models, it delivers competitive performance on both regression and planning problems, showing strong generalization and cross-task adaptability. Our code is available at https://github.com/BiYunying/TransLLM.
\(X\)-evolve: Solution space evolution powered by large language models
Aug 11, 2025



Abstract:While combining large language models (LLMs) with evolutionary algorithms (EAs) shows promise for solving complex optimization problems, current approaches typically evolve individual solutions, often incurring high LLM call costs. We introduce \(X\)-evolve, a paradigm-shifting method that instead evolves solution spaces \(X\) (sets of individual solutions) - subsets of the overall search space \(S\). In \(X\)-evolve, LLMs generate tunable programs wherein certain code snippets, designated as parameters, define a tunable solution space. A score-based search algorithm then efficiently explores this parametrically defined space, guided by feedback from objective function scores. This strategy enables broader and more efficient exploration, which can potentially accelerate convergence at a much lower search cost, requiring up to two orders of magnitude fewer LLM calls than prior leading methods. We demonstrate \(X\)-evolve's efficacy across three distinct hard optimization problems. For the cap set problem, we discover a larger partial admissible set, establishing a new tighter asymptotic lower bound for the cap set constant (\(C \ge 2.2203\)). In information theory, we uncover a larger independent set for the 15-vertex cycle graph (\(\mathcal{C}_{15}^{\boxtimes 5}\), size 19,946), thereby raising the known lower bound on its Shannon capacity. Furthermore, for the NP-hard online bin packing problem, we generate heuristics that consistently outperform standard strategies across established benchmarks. By evolving solution spaces, our method considerably improves search effectiveness, making it possible to tackle high-dimensional problems that were previously computationally prohibitive.
VLMPlanner: Integrating Visual Language Models with Motion Planning
Jul 27, 2025Abstract:Integrating large language models (LLMs) into autonomous driving motion planning has recently emerged as a promising direction, offering enhanced interpretability, better controllability, and improved generalization in rare and long-tail scenarios. However, existing methods often rely on abstracted perception or map-based inputs, missing crucial visual context, such as fine-grained road cues, accident aftermath, or unexpected obstacles, which are essential for robust decision-making in complex driving environments. To bridge this gap, we propose VLMPlanner, a hybrid framework that combines a learning-based real-time planner with a vision-language model (VLM) capable of reasoning over raw images. The VLM processes multi-view images to capture rich, detailed visual information and leverages its common-sense reasoning capabilities to guide the real-time planner in generating robust and safe trajectories. Furthermore, we develop the Context-Adaptive Inference Gate (CAI-Gate) mechanism that enables the VLM to mimic human driving behavior by dynamically adjusting its inference frequency based on scene complexity, thereby achieving an optimal balance between planning performance and computational efficiency. We evaluate our approach on the large-scale, challenging nuPlan benchmark, with comprehensive experimental results demonstrating superior planning performance in scenarios with intricate road conditions and dynamic elements. Code will be available.
Position: Intelligent Science Laboratory Requires the Integration of Cognitive and Embodied AI
Jun 24, 2025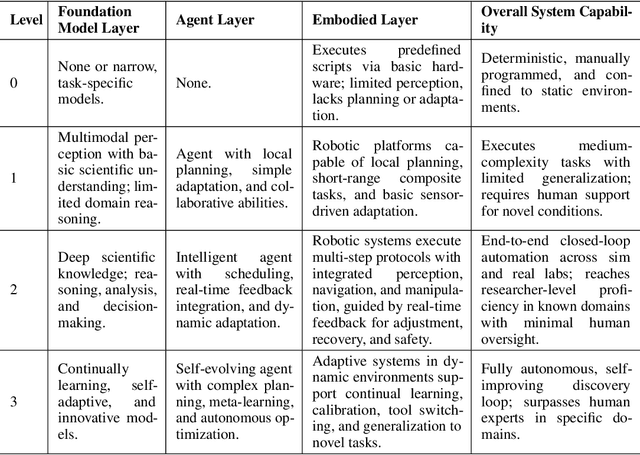
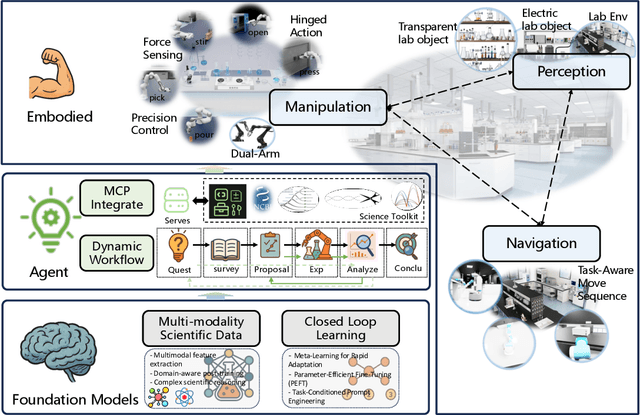
Abstract:Scientific discovery has long been constrained by human limitations in expertise, physical capability, and sleep cycles. The recent rise of AI scientists and automated laboratories has accelerated both the cognitive and operational aspects of research. However, key limitations persist: AI systems are often confined to virtual environments, while automated laboratories lack the flexibility and autonomy to adaptively test new hypotheses in the physical world. Recent advances in embodied AI, such as generalist robot foundation models, diffusion-based action policies, fine-grained manipulation learning, and sim-to-real transfer, highlight the promise of integrating cognitive and embodied intelligence. This convergence opens the door to closed-loop systems that support iterative, autonomous experimentation and the possibility of serendipitous discovery. In this position paper, we propose the paradigm of Intelligent Science Laboratories (ISLs): a multi-layered, closed-loop framework that deeply integrates cognitive and embodied intelligence. ISLs unify foundation models for scientific reasoning, agent-based workflow orchestration, and embodied agents for robust physical experimentation. We argue that such systems are essential for overcoming the current limitations of scientific discovery and for realizing the full transformative potential of AI-driven science.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge