Yao Li
Task Vector in TTS: Toward Emotionally Expressive Dialectal Speech Synthesis
Dec 21, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in text-to-speech (TTS) have yielded remarkable improvements in naturalness and intelligibility. Building on these achievements, research has increasingly shifted toward enhancing the expressiveness of generated speech, such as dialectal and emotional TTS. However, cross-style synthesis combining both dialect and emotion remains challenging and largely unexplored, mainly due to the scarcity of dialectal data with emotional labels. To address this, we propose Hierarchical Expressive Vector (HE-Vector), a two-stage method for Emotional Dialectal TTS. In the first stage, we construct different task vectors to model dialectal and emotional styles independently, and then enhance single-style synthesis by adjusting their weights, a method we refer to as Expressive Vector (E-Vector). For the second stage, we hierarchically integrate these vectors to achieve controllable emotionally expressive dialect synthesis without requiring jointly labeled data, corresponding to Hierarchical Expressive Vector (HE-Vector). Experimental results demonstrate that HE-Vectors achieve superior performance in dialect synthesis, and promising results in synthesizing emotionally expressive dialectal speech in a zero-shot setting.
PDAC: Efficient Coreset Selection for Continual Learning via Probability Density Awareness
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:Rehearsal-based Continual Learning (CL) maintains a limited memory buffer to store replay samples for knowledge retention, making these approaches heavily reliant on the quality of the stored samples. Current Rehearsal-based CL methods typically construct the memory buffer by selecting a representative subset (referred to as coresets), aiming to approximate the training efficacy of the full dataset with minimal storage overhead. However, mainstream Coreset Selection (CS) methods generally formulate the CS problem as a bi-level optimization problem that relies on numerous inner and outer iterations to solve, leading to substantial computational cost thus limiting their practical efficiency. In this paper, we aim to provide a more efficient selection logic and scheme for coreset construction. To this end, we first analyze the Mean Squared Error (MSE) between the buffer-trained model and the Bayes-optimal model through the perspective of localized error decomposition to investigate the contribution of samples from different regions to MSE suppression. Further theoretical and experimental analyses demonstrate that samples with high probability density play a dominant role in error suppression. Inspired by this, we propose the Probability Density-Aware Coreset (PDAC) method. PDAC leverages the Projected Gaussian Mixture (PGM) model to estimate each sample's joint density, enabling efficient density-prioritized buffer selection. Finally, we introduce the streaming Expectation Maximization (EM) algorithm to enhance the adaptability of PGM parameters to streaming data, yielding Streaming PDAC (SPDAC) for streaming scenarios. Extensive comparative experiments show that our methods outperforms other baselines across various CL settings while ensuring favorable efficiency.
Towards Frequency-Adaptive Learning for SAR Despeckling
Nov 08, 2025Abstract:Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) images are inherently corrupted by speckle noise, limiting their utility in high-precision applications. While deep learning methods have shown promise in SAR despeckling, most methods employ a single unified network to process the entire image, failing to account for the distinct speckle statistics associated with different spatial physical characteristics. It often leads to artifacts, blurred edges, and texture distortion. To address these issues, we propose SAR-FAH, a frequency-adaptive heterogeneous despeckling model based on a divide-and-conquer architecture. First, wavelet decomposition is used to separate the image into frequency sub-bands carrying different intrinsic characteristics. Inspired by their differing noise characteristics, we design specialized sub-networks for different frequency components. The tailored approach leverages statistical variations across frequencies, improving edge and texture preservation while suppressing noise. Specifically, for the low-frequency part, denoising is formulated as a continuous dynamic system via neural ordinary differential equations, ensuring structural fidelity and sufficient smoothness that prevents artifacts. For high-frequency sub-bands rich in edges and textures, we introduce an enhanced U-Net with deformable convolutions for noise suppression and enhanced features. Extensive experiments on synthetic and real SAR images validate the superior performance of the proposed model in noise removal and structural preservation.
SymCode: A Neurosymbolic Approach to Mathematical Reasoning via Verifiable Code Generation
Oct 29, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) often struggle with complex mathematical reasoning, where prose-based generation leads to unverified and arithmetically unsound solutions. Current prompting strategies like Chain of Thought still operate within this unreliable medium, lacking a mechanism for deterministic verification. To address these limitations, we introduce SymCode, a neurosymbolic framework that reframes mathematical problem-solving as a task of verifiable code generation using the SymPy library. We evaluate SymCode on challenging benchmarks, including MATH-500 and OlympiadBench, demonstrating significant accuracy improvements of up to 13.6 percentage points over baselines. Our analysis shows that SymCode is not only more token-efficient but also fundamentally shifts model failures from opaque logical fallacies towards transparent, programmatic errors. By grounding LLM reasoning in a deterministic symbolic engine, SymCode represents a key step towards more accurate and trustworthy AI in formal domains.
In-Loop Filtering Using Learned Look-Up Tables for Video Coding
Sep 11, 2025Abstract:In-loop filtering (ILF) is a key technology in video coding standards to reduce artifacts and enhance visual quality. Recently, neural network-based ILF schemes have achieved remarkable coding gains, emerging as a powerful candidate for next-generation video coding standards. However, the use of deep neural networks (DNN) brings significant computational and time complexity or high demands for dedicated hardware, making it challenging for general use. To address this limitation, we study a practical ILF solution by adopting look-up tables (LUTs). After training a DNN with a restricted reference range for ILF, all possible inputs are traversed, and the output values of the DNN are cached into LUTs. During the coding process, the filtering process is performed by simply retrieving the filtered pixel through locating the input pixels and interpolating between the cached values, instead of relying on heavy inference computations. In this paper, we propose a universal LUT-based ILF framework, termed LUT-ILF++. First, we introduce the cooperation of multiple kinds of filtering LUTs and propose a series of customized indexing mechanisms to enable better filtering reference perception with limited storage consumption. Second, we propose the cross-component indexing mechanism to enable the filtering of different color components jointly. Third, in order to make our solution practical for coding uses, we propose the LUT compaction scheme to enable the LUT pruning, achieving a lower storage cost of the entire solution. The proposed framework is implemented in the VVC reference software. Experimental results show that the proposed framework achieves on average 0.82%/2.97%/1.63% and 0.85%/4.11%/2.06% bitrate reduction for common test sequences, under the AI and RA configurations, respectively. Compared to DNN-based solutions, our proposed solution has much lower time complexity and storage cost.
Single Index Bandits: Generalized Linear Contextual Bandits with Unknown Reward Functions
Jun 15, 2025Abstract:Generalized linear bandits have been extensively studied due to their broad applicability in real-world online decision-making problems. However, these methods typically assume that the expected reward function is known to the users, an assumption that is often unrealistic in practice. Misspecification of this link function can lead to the failure of all existing algorithms. In this work, we address this critical limitation by introducing a new problem of generalized linear bandits with unknown reward functions, also known as single index bandits. We first consider the case where the unknown reward function is monotonically increasing, and propose two novel and efficient algorithms, STOR and ESTOR, that achieve decent regrets under standard assumptions. Notably, our ESTOR can obtain the nearly optimal regret bound $\tilde{O}_T(\sqrt{T})$ in terms of the time horizon $T$. We then extend our methods to the high-dimensional sparse setting and show that the same regret rate can be attained with the sparsity index. Next, we introduce GSTOR, an algorithm that is agnostic to general reward functions, and establish regret bounds under a Gaussian design assumption. Finally, we validate the efficiency and effectiveness of our algorithms through experiments on both synthetic and real-world datasets.
Enhancing Speech-to-Speech Dialogue Modeling with End-to-End Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Apr 27, 2025


Abstract:In recent years, end-to-end speech-to-speech (S2S) dialogue systems have garnered increasing research attention due to their advantages over traditional cascaded systems, including achieving lower latency and more natural integration of nonverbal cues such as emotion and speaker identity. However, these end-to-end systems face key challenges, particularly in incorporating external knowledge, a capability commonly addressed by Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) in text-based large language models (LLMs). The core difficulty lies in the modality gap between input speech and retrieved textual knowledge, which hinders effective integration. To address this issue, we propose a novel end-to-end RAG framework that directly retrieves relevant textual knowledge from speech queries, eliminating the need for intermediate speech-to-text conversion via techniques like ASR. Experimental results demonstrate that our method significantly improves the performance of end-to-end S2S dialogue systems while achieving higher retrieval efficiency. Although the overall performance still lags behind cascaded models, our framework offers a promising direction for enhancing knowledge integration in end-to-end S2S systems. We will release the code and dataset to support reproducibility and promote further research in this area.
DMAGaze: Gaze Estimation Based on Feature Disentanglement and Multi-Scale Attention
Apr 15, 2025Abstract:Gaze estimation, which predicts gaze direction, commonly faces the challenge of interference from complex gaze-irrelevant information in face images. In this work, we propose DMAGaze, a novel gaze estimation framework that exploits information from facial images in three aspects: gaze-relevant global features (disentangled from facial image), local eye features (extracted from cropped eye patch), and head pose estimation features, to improve overall performance. Firstly, we design a new continuous mask-based Disentangler to accurately disentangle gaze-relevant and gaze-irrelevant information in facial images by achieving the dual-branch disentanglement goal through separately reconstructing the eye and non-eye regions. Furthermore, we introduce a new cascaded attention module named Multi-Scale Global Local Attention Module (MS-GLAM). Through a customized cascaded attention structure, it effectively focuses on global and local information at multiple scales, further enhancing the information from the Disentangler. Finally, the global gaze-relevant features disentangled by the upper face branch, combined with head pose and local eye features, are passed through the detection head for high-precision gaze estimation. Our proposed DMAGaze has been extensively validated on two mainstream public datasets, achieving state-of-the-art performance.
Quantum Lipschitz Bandits
Apr 03, 2025Abstract:The Lipschitz bandit is a key variant of stochastic bandit problems where the expected reward function satisfies a Lipschitz condition with respect to an arm metric space. With its wide-ranging practical applications, various Lipschitz bandit algorithms have been developed, achieving the cumulative regret lower bound of order $\tilde O(T^{(d_z+1)/(d_z+2)})$ over time horizon $T$. Motivated by recent advancements in quantum computing and the demonstrated success of quantum Monte Carlo in simpler bandit settings, we introduce the first quantum Lipschitz bandit algorithms to address the challenges of continuous action spaces and non-linear reward functions. Specifically, we first leverage the elimination-based framework to propose an efficient quantum Lipschitz bandit algorithm named Q-LAE. Next, we present novel modifications to the classical Zooming algorithm, which results in a simple quantum Lipschitz bandit method, Q-Zooming. Both algorithms exploit the computational power of quantum methods to achieve an improved regret bound of $\tilde O(T^{d_z/(d_z+1)})$. Comprehensive experiments further validate our improved theoretical findings, demonstrating superior empirical performance compared to existing Lipschitz bandit methods.
Beyond Non-Expert Demonstrations: Outcome-Driven Action Constraint for Offline Reinforcement Learning
Apr 03, 2025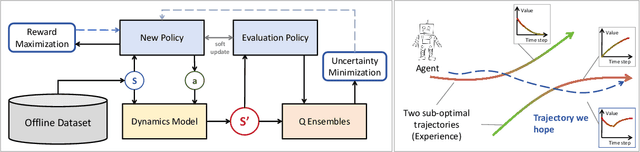
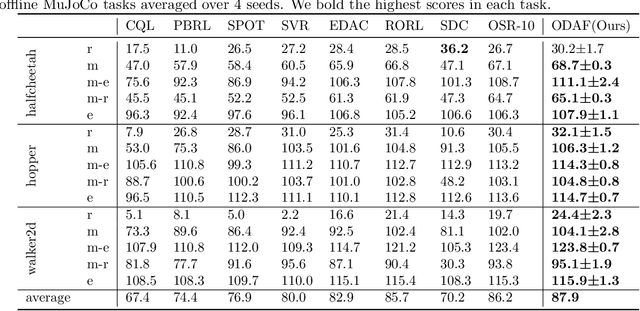
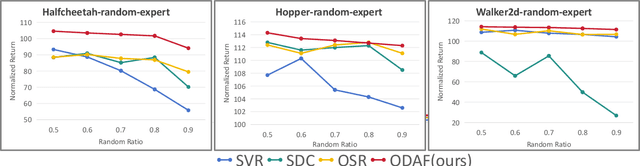
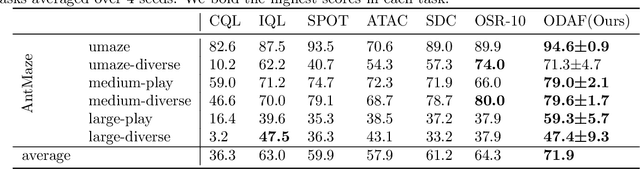
Abstract:We address the challenge of offline reinforcement learning using realistic data, specifically non-expert data collected through sub-optimal behavior policies. Under such circumstance, the learned policy must be safe enough to manage distribution shift while maintaining sufficient flexibility to deal with non-expert (bad) demonstrations from offline data.To tackle this issue, we introduce a novel method called Outcome-Driven Action Flexibility (ODAF), which seeks to reduce reliance on the empirical action distribution of the behavior policy, hence reducing the negative impact of those bad demonstrations.To be specific, a new conservative reward mechanism is developed to deal with distribution shift by evaluating actions according to whether their outcomes meet safety requirements - remaining within the state support area, rather than solely depending on the actions' likelihood based on offline data.Besides theoretical justification, we provide empirical evidence on widely used MuJoCo and various maze benchmarks, demonstrating that our ODAF method, implemented using uncertainty quantification techniques, effectively tolerates unseen transitions for improved "trajectory stitching," while enhancing the agent's ability to learn from realistic non-expert data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge