Jing Lyu
Reshaping Action Error Distributions for Reliable Vision-Language-Action Models
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:In robotic manipulation, vision-language-action (VLA) models have emerged as a promising paradigm for learning generalizable and scalable robot policies. Most existing VLA frameworks rely on standard supervised objectives, typically cross-entropy for discrete actions and mean squared error (MSE) for continuous action regression, which impose strong pointwise constraints on individual predictions. In this work, we focus on continuous-action VLA models and move beyond conventional MSE-based regression by reshaping action error distributions during training. Drawing on information-theoretic principles, we introduce Minimum Error Entropy (MEE) into modern VLA architectures and propose a trajectory-level MEE objective, together with two weighted variants, combined with MSE for continuous-action VLA training. We evaluate our approaches across standard, few-shot, and noisy settings on multiple representative VLA architectures, using simulation benchmarks such as LIBERO and SimplerEnv as well as real-world robotic manipulation tasks. Experimental results demonstrate consistent improvements in success rates and robustness across these settings. Under imbalanced data regimes, the gains persist within a well-characterized operating range, while incurring negligible additional training cost and no impact on inference efficiency. We further provide theoretical analyses that explain why MEE-based supervision is effective and characterize its practical range. Project Page: https://cognition2actionlab.github.io/VLA-TMEE.github.io/
ObjEmbed: Towards Universal Multimodal Object Embeddings
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Aligning objects with corresponding textual descriptions is a fundamental challenge and a realistic requirement in vision-language understanding. While recent multimodal embedding models excel at global image-text alignment, they often struggle with fine-grained alignment between image regions and specific phrases. In this work, we present ObjEmbed, a novel MLLM embedding model that decomposes the input image into multiple regional embeddings, each corresponding to an individual object, along with global embeddings. It supports a wide range of visual understanding tasks like visual grounding, local image retrieval, and global image retrieval. ObjEmbed enjoys three key properties: (1) Object-Oriented Representation: It captures both semantic and spatial aspects of objects by generating two complementary embeddings for each region: an object embedding for semantic matching and an IoU embedding that predicts localization quality. The final object matching score combines semantic similarity with the predicted IoU, enabling more accurate retrieval. (2) Versatility: It seamlessly handles both region-level and image-level tasks. (3) Efficient Encoding: All objects in an image, along with the full image, are encoded in a single forward pass for high efficiency. Superior performance on 18 diverse benchmarks demonstrates its strong semantic discrimination.
Latent Reasoning VLA: Latent Thinking and Prediction for Vision-Language-Action Models
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models benefit from chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning, but existing approaches incur high inference overhead and rely on discrete reasoning representations that mismatch continuous perception and control. We propose Latent Reasoning VLA (\textbf{LaRA-VLA}), a unified VLA framework that internalizes multi-modal CoT reasoning into continuous latent representations for embodied action. LaRA-VLA performs unified reasoning and prediction in latent space, eliminating explicit CoT generation at inference time and enabling efficient, action-oriented control. To realize latent embodied reasoning, we introduce a curriculum-based training paradigm that progressively transitions from explicit textual and visual CoT supervision to latent reasoning, and finally adapts latent reasoning dynamics to condition action generation. We construct two structured CoT datasets and evaluate LaRA-VLA on both simulation benchmarks and long-horizon real-robot manipulation tasks. Experimental results show that LaRA-VLA consistently outperforms state-of-the-art VLA methods while reducing inference latency by up to 90\% compared to explicit CoT-based approaches, demonstrating latent reasoning as an effective and efficient paradigm for real-time embodied control. Project Page: \href{https://loveju1y.github.io/Latent-Reasoning-VLA/}{LaRA-VLA Website}.
WeDetect: Fast Open-Vocabulary Object Detection as Retrieval
Dec 13, 2025Abstract:Open-vocabulary object detection aims to detect arbitrary classes via text prompts. Methods without cross-modal fusion layers (non-fusion) offer faster inference by treating recognition as a retrieval problem, \ie, matching regions to text queries in a shared embedding space. In this work, we fully explore this retrieval philosophy and demonstrate its unique advantages in efficiency and versatility through a model family named WeDetect: (1) State-of-the-art performance. WeDetect is a real-time detector with a dual-tower architecture. We show that, with well-curated data and full training, the non-fusion WeDetect surpasses other fusion models and establishes a strong open-vocabulary foundation. (2) Fast backtrack of historical data. WeDetect-Uni is a universal proposal generator based on WeDetect. We freeze the entire detector and only finetune an objectness prompt to retrieve generic object proposals across categories. Importantly, the proposal embeddings are class-specific and enable a new application, object retrieval, supporting retrieval objects in historical data. (3) Integration with LMMs for referring expression comprehension (REC). We further propose WeDetect-Ref, an LMM-based object classifier to handle complex referring expressions, which retrieves target objects from the proposal list extracted by WeDetect-Uni. It discards next-token prediction and classifies objects in a single forward pass. Together, the WeDetect family unifies detection, proposal generation, object retrieval, and REC under a coherent retrieval framework, achieving state-of-the-art performance across 15 benchmarks with high inference efficiency.
Single Index Bandits: Generalized Linear Contextual Bandits with Unknown Reward Functions
Jun 15, 2025Abstract:Generalized linear bandits have been extensively studied due to their broad applicability in real-world online decision-making problems. However, these methods typically assume that the expected reward function is known to the users, an assumption that is often unrealistic in practice. Misspecification of this link function can lead to the failure of all existing algorithms. In this work, we address this critical limitation by introducing a new problem of generalized linear bandits with unknown reward functions, also known as single index bandits. We first consider the case where the unknown reward function is monotonically increasing, and propose two novel and efficient algorithms, STOR and ESTOR, that achieve decent regrets under standard assumptions. Notably, our ESTOR can obtain the nearly optimal regret bound $\tilde{O}_T(\sqrt{T})$ in terms of the time horizon $T$. We then extend our methods to the high-dimensional sparse setting and show that the same regret rate can be attained with the sparsity index. Next, we introduce GSTOR, an algorithm that is agnostic to general reward functions, and establish regret bounds under a Gaussian design assumption. Finally, we validate the efficiency and effectiveness of our algorithms through experiments on both synthetic and real-world datasets.
Instruction-augmented Multimodal Alignment for Image-Text and Element Matching
Apr 16, 2025Abstract:With the rapid advancement of text-to-image (T2I) generation models, assessing the semantic alignment between generated images and text descriptions has become a significant research challenge. Current methods, including those based on Visual Question Answering (VQA), still struggle with fine-grained assessments and precise quantification of image-text alignment. This paper presents an improved evaluation method named Instruction-augmented Multimodal Alignment for Image-Text and Element Matching (iMatch), which evaluates image-text semantic alignment by fine-tuning multimodal large language models. We introduce four innovative augmentation strategies: First, the QAlign strategy creates a precise probabilistic mapping to convert discrete scores from multimodal large language models into continuous matching scores. Second, a validation set augmentation strategy uses pseudo-labels from model predictions to expand training data, boosting the model's generalization performance. Third, an element augmentation strategy integrates element category labels to refine the model's understanding of image-text matching. Fourth, an image augmentation strategy employs techniques like random lighting to increase the model's robustness. Additionally, we propose prompt type augmentation and score perturbation strategies to further enhance the accuracy of element assessments. Our experimental results show that the iMatch method significantly surpasses existing methods, confirming its effectiveness and practical value. Furthermore, our iMatch won first place in the CVPR NTIRE 2025 Text to Image Generation Model Quality Assessment - Track 1 Image-Text Alignment.
Assessing Attendance by Peer Information
Jun 06, 2021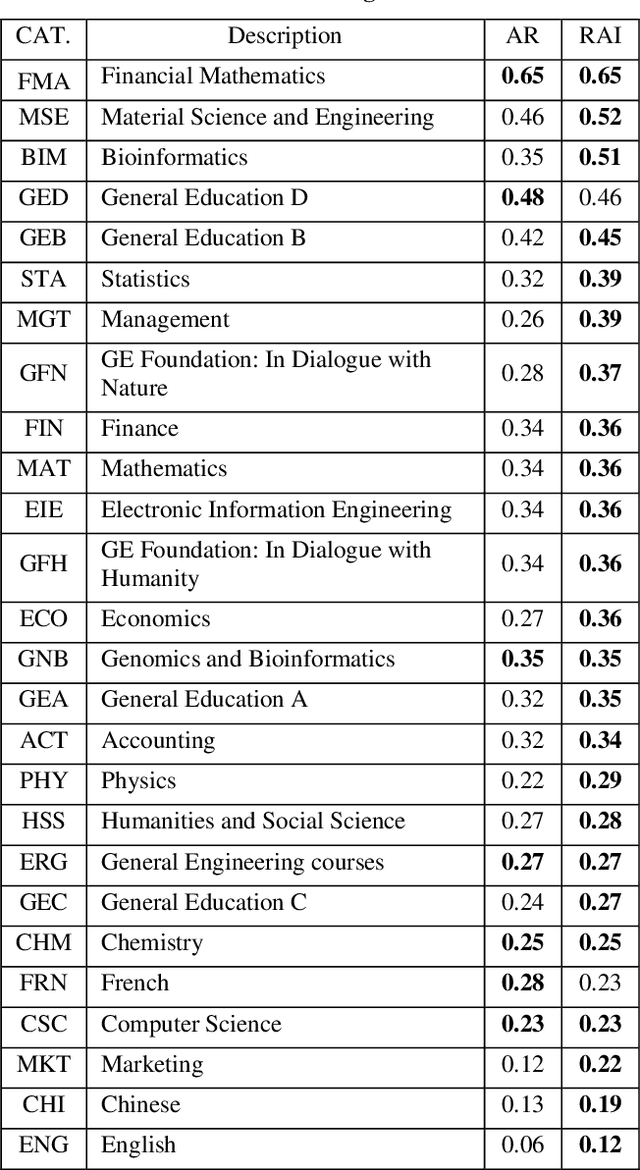
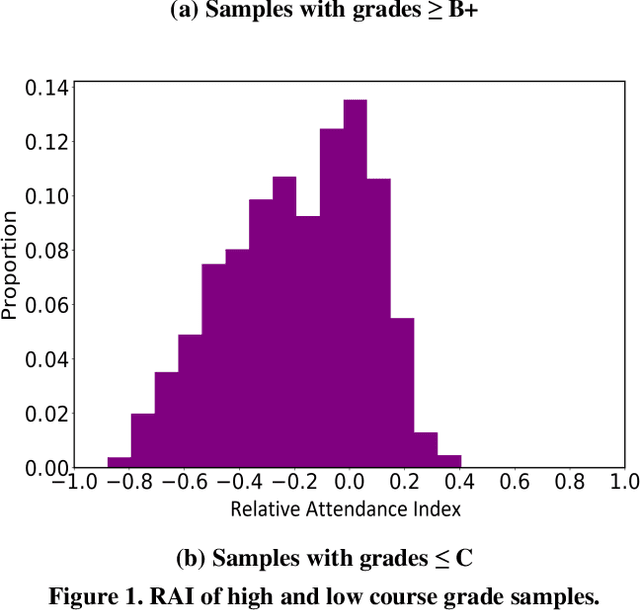
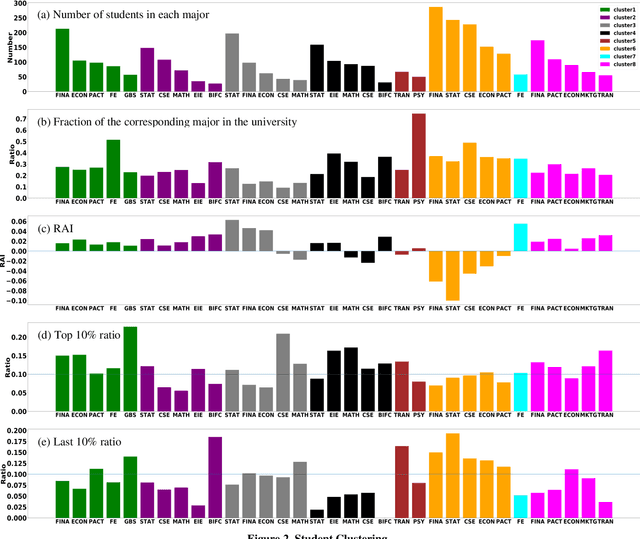
Abstract:Attendance rate is an important indicator of students' study motivation, behavior and Psychological status; However, the heterogeneous nature of student attendance rates due to the course registration difference or the online/offline difference in a blended learning environment makes it challenging to compare attendance rates. In this paper, we propose a novel method called Relative Attendance Index (RAI) to measure attendance rates, which reflects students' efforts on attending courses. While traditional attendance focuses on the record of a single person or course, relative attendance emphasizes peer attendance information of relevant individuals or courses, making the comparisons of attendance more justified. Experimental results on real-life data show that RAI can indeed better reflect student engagement.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge