Junda Lu
NanoControl: A Lightweight Framework for Precise and Efficient Control in Diffusion Transformer
Aug 14, 2025Abstract:Diffusion Transformers (DiTs) have demonstrated exceptional capabilities in text-to-image synthesis. However, in the domain of controllable text-to-image generation using DiTs, most existing methods still rely on the ControlNet paradigm originally designed for UNet-based diffusion models. This paradigm introduces significant parameter overhead and increased computational costs. To address these challenges, we propose the Nano Control Diffusion Transformer (NanoControl), which employs Flux as the backbone network. Our model achieves state-of-the-art controllable text-to-image generation performance while incurring only a 0.024\% increase in parameter count and a 0.029\% increase in GFLOPs, thus enabling highly efficient controllable generation. Specifically, rather than duplicating the DiT backbone for control, we design a LoRA-style (low-rank adaptation) control module that directly learns control signals from raw conditioning inputs. Furthermore, we introduce a KV-Context Augmentation mechanism that integrates condition-specific key-value information into the backbone in a simple yet highly effective manner, facilitating deep fusion of conditional features. Extensive benchmark experiments demonstrate that NanoControl significantly reduces computational overhead compared to conventional control approaches, while maintaining superior generation quality and achieving improved controllability.
NTIRE 2025 challenge on Text to Image Generation Model Quality Assessment
May 22, 2025Abstract:This paper reports on the NTIRE 2025 challenge on Text to Image (T2I) generation model quality assessment, which will be held in conjunction with the New Trends in Image Restoration and Enhancement Workshop (NTIRE) at CVPR 2025. The aim of this challenge is to address the fine-grained quality assessment of text-to-image generation models. This challenge evaluates text-to-image models from two aspects: image-text alignment and image structural distortion detection, and is divided into the alignment track and the structural track. The alignment track uses the EvalMuse-40K, which contains around 40K AI-Generated Images (AIGIs) generated by 20 popular generative models. The alignment track has a total of 371 registered participants. A total of 1,883 submissions are received in the development phase, and 507 submissions are received in the test phase. Finally, 12 participating teams submitted their models and fact sheets. The structure track uses the EvalMuse-Structure, which contains 10,000 AI-Generated Images (AIGIs) with corresponding structural distortion mask. A total of 211 participants have registered in the structure track. A total of 1155 submissions are received in the development phase, and 487 submissions are received in the test phase. Finally, 8 participating teams submitted their models and fact sheets. Almost all methods have achieved better results than baseline methods, and the winning methods in both tracks have demonstrated superior prediction performance on T2I model quality assessment.
Instruction-augmented Multimodal Alignment for Image-Text and Element Matching
Apr 16, 2025Abstract:With the rapid advancement of text-to-image (T2I) generation models, assessing the semantic alignment between generated images and text descriptions has become a significant research challenge. Current methods, including those based on Visual Question Answering (VQA), still struggle with fine-grained assessments and precise quantification of image-text alignment. This paper presents an improved evaluation method named Instruction-augmented Multimodal Alignment for Image-Text and Element Matching (iMatch), which evaluates image-text semantic alignment by fine-tuning multimodal large language models. We introduce four innovative augmentation strategies: First, the QAlign strategy creates a precise probabilistic mapping to convert discrete scores from multimodal large language models into continuous matching scores. Second, a validation set augmentation strategy uses pseudo-labels from model predictions to expand training data, boosting the model's generalization performance. Third, an element augmentation strategy integrates element category labels to refine the model's understanding of image-text matching. Fourth, an image augmentation strategy employs techniques like random lighting to increase the model's robustness. Additionally, we propose prompt type augmentation and score perturbation strategies to further enhance the accuracy of element assessments. Our experimental results show that the iMatch method significantly surpasses existing methods, confirming its effectiveness and practical value. Furthermore, our iMatch won first place in the CVPR NTIRE 2025 Text to Image Generation Model Quality Assessment - Track 1 Image-Text Alignment.
Dataset Distillation via Adversarial Prediction Matching
Dec 14, 2023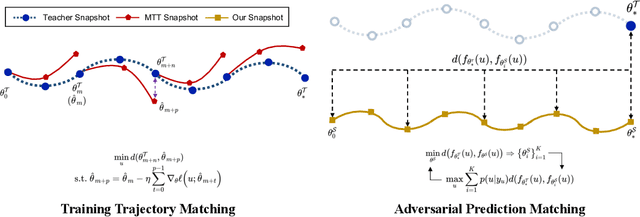
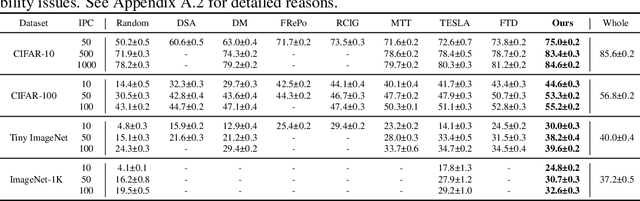
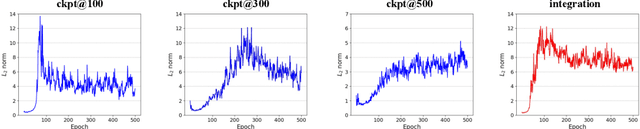
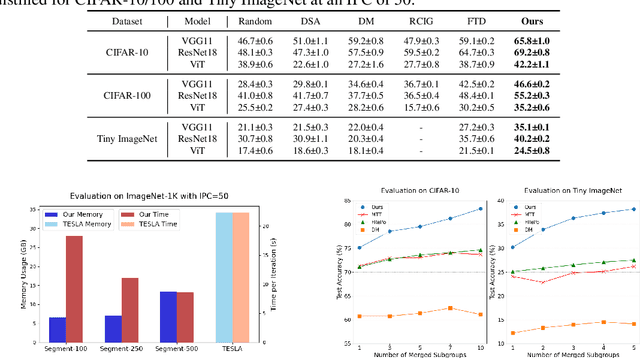
Abstract:Dataset distillation is the technique of synthesizing smaller condensed datasets from large original datasets while retaining necessary information to persist the effect. In this paper, we approach the dataset distillation problem from a novel perspective: we regard minimizing the prediction discrepancy on the real data distribution between models, which are respectively trained on the large original dataset and on the small distilled dataset, as a conduit for condensing information from the raw data into the distilled version. An adversarial framework is proposed to solve the problem efficiently. In contrast to existing distillation methods involving nested optimization or long-range gradient unrolling, our approach hinges on single-level optimization. This ensures the memory efficiency of our method and provides a flexible tradeoff between time and memory budgets, allowing us to distil ImageNet-1K using a minimum of only 6.5GB of GPU memory. Under the optimal tradeoff strategy, it requires only 2.5$\times$ less memory and 5$\times$ less runtime compared to the state-of-the-art. Empirically, our method can produce synthetic datasets just 10% the size of the original, yet achieve, on average, 94% of the test accuracy of models trained on the full original datasets including ImageNet-1K, significantly surpassing state-of-the-art. Additionally, extensive tests reveal that our distilled datasets excel in cross-architecture generalization capabilities.
DialogBench: Evaluating LLMs as Human-like Dialogue Systems
Nov 03, 2023Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable breakthroughs in new dialogue capabilities, refreshing human's impressions on dialogue systems. The long-standing goal of dialogue systems is to be human-like enough to establish long-term connections with users by satisfying the need for communication, affection and social belonging. Therefore, there has been an urgent need to evaluate LLMs as human-like dialogue systems. In this paper, we propose DialogBench, a dialogue evaluation benchmark that currently contains $12$ dialogue tasks to assess the capabilities of LLMs as human-like dialogue systems should have. Specifically, we prompt GPT-4 to generate evaluation instances for each task. We first design the basic prompt based on widely-used design principles and further mitigate the existing biases to generate higher-quality evaluation instances. Our extensive test over $28$ LLMs (including pre-trained and supervised instruction-tuning) shows that instruction fine-tuning benefits improve the human likeness of LLMs to a certain extent, but there is still much room to improve those capabilities for most LLMs as human-like dialogue systems. In addition, experimental results also indicate that LLMs perform differently in various abilities that human-like dialogue systems should have. We will publicly release DialogBench, along with the associated evaluation code for the broader research community.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge