Bo Cheng
CTA-Flux: Integrating Chinese Cultural Semantics into High-Quality English Text-to-Image Communities
Aug 20, 2025Abstract:We proposed the Chinese Text Adapter-Flux (CTA-Flux). An adaptation method fits the Chinese text inputs to Flux, a powerful text-to-image (TTI) generative model initially trained on the English corpus. Despite the notable image generation ability conditioned on English text inputs, Flux performs poorly when processing non-English prompts, particularly due to linguistic and cultural biases inherent in predominantly English-centric training datasets. Existing approaches, such as translating non-English prompts into English or finetuning models for bilingual mappings, inadequately address culturally specific semantics, compromising image authenticity and quality. To address this issue, we introduce a novel method to bridge Chinese semantic understanding with compatibility in English-centric TTI model communities. Existing approaches relying on ControlNet-like architectures typically require a massive parameter scale and lack direct control over Chinese semantics. In comparison, CTA-flux leverages MultiModal Diffusion Transformer (MMDiT) to control the Flux backbone directly, significantly reducing the number of parameters while enhancing the model's understanding of Chinese semantics. This integration significantly improves the generation quality and cultural authenticity without extensive retraining of the entire model, thus maintaining compatibility with existing text-to-image plugins such as LoRA, IP-Adapter, and ControlNet. Empirical evaluations demonstrate that CTA-flux supports Chinese and English prompts and achieves superior image generation quality, visual realism, and faithful depiction of Chinese semantics.
NanoControl: A Lightweight Framework for Precise and Efficient Control in Diffusion Transformer
Aug 14, 2025Abstract:Diffusion Transformers (DiTs) have demonstrated exceptional capabilities in text-to-image synthesis. However, in the domain of controllable text-to-image generation using DiTs, most existing methods still rely on the ControlNet paradigm originally designed for UNet-based diffusion models. This paradigm introduces significant parameter overhead and increased computational costs. To address these challenges, we propose the Nano Control Diffusion Transformer (NanoControl), which employs Flux as the backbone network. Our model achieves state-of-the-art controllable text-to-image generation performance while incurring only a 0.024\% increase in parameter count and a 0.029\% increase in GFLOPs, thus enabling highly efficient controllable generation. Specifically, rather than duplicating the DiT backbone for control, we design a LoRA-style (low-rank adaptation) control module that directly learns control signals from raw conditioning inputs. Furthermore, we introduce a KV-Context Augmentation mechanism that integrates condition-specific key-value information into the backbone in a simple yet highly effective manner, facilitating deep fusion of conditional features. Extensive benchmark experiments demonstrate that NanoControl significantly reduces computational overhead compared to conventional control approaches, while maintaining superior generation quality and achieving improved controllability.
Align, Don't Divide: Revisiting the LoRA Architecture in Multi-Task Learning
Aug 07, 2025Abstract:Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) is essential for adapting Large Language Models (LLMs). In practice, LLMs are often required to handle a diverse set of tasks from multiple domains, a scenario naturally addressed by multi-task learning (MTL). Within this MTL context, a prevailing trend involves LoRA variants with multiple adapters or heads, which advocate for structural diversity to capture task-specific knowledge. Our findings present a direct challenge to this paradigm. We first show that a simplified multi-head architecture with high inter-head similarity substantially outperforms complex multi-adapter and multi-head systems. This leads us to question the multi-component paradigm itself, and we further demonstrate that a standard single-adapter LoRA, with a sufficiently increased rank, also achieves highly competitive performance. These results lead us to a new hypothesis: effective MTL generalization hinges on learning robust shared representations, not isolating task-specific features. To validate this, we propose Align-LoRA, which incorporates an explicit loss to align task representations within the shared adapter space. Experiments confirm that Align-LoRA significantly surpasses all baselines, establishing a simpler yet more effective paradigm for adapting LLMs to multiple tasks. The code is available at https://github.com/jinda-liu/Align-LoRA.
FLUX-Makeup: High-Fidelity, Identity-Consistent, and Robust Makeup Transfer via Diffusion Transformer
Aug 07, 2025
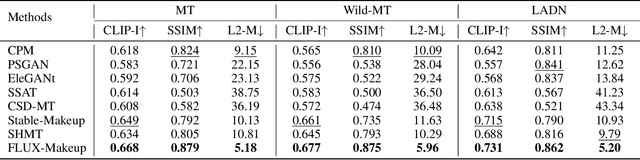
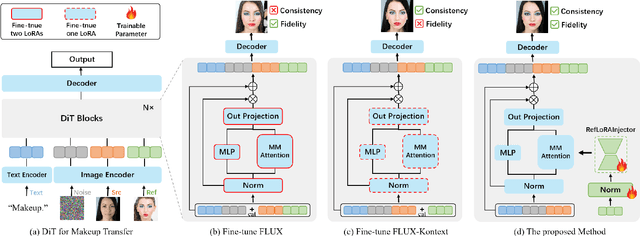
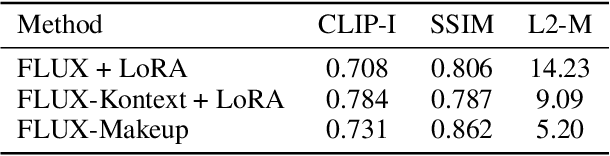
Abstract:Makeup transfer aims to apply the makeup style from a reference face to a target face and has been increasingly adopted in practical applications. Existing GAN-based approaches typically rely on carefully designed loss functions to balance transfer quality and facial identity consistency, while diffusion-based methods often depend on additional face-control modules or algorithms to preserve identity. However, these auxiliary components tend to introduce extra errors, leading to suboptimal transfer results. To overcome these limitations, we propose FLUX-Makeup, a high-fidelity, identity-consistent, and robust makeup transfer framework that eliminates the need for any auxiliary face-control components. Instead, our method directly leverages source-reference image pairs to achieve superior transfer performance. Specifically, we build our framework upon FLUX-Kontext, using the source image as its native conditional input. Furthermore, we introduce RefLoRAInjector, a lightweight makeup feature injector that decouples the reference pathway from the backbone, enabling efficient and comprehensive extraction of makeup-related information. In parallel, we design a robust and scalable data generation pipeline to provide more accurate supervision during training. The paired makeup datasets produced by this pipeline significantly surpass the quality of all existing datasets. Extensive experiments demonstrate that FLUX-Makeup achieves state-of-the-art performance, exhibiting strong robustness across diverse scenarios.
DLP: Dynamic Layerwise Pruning in Large Language Models
May 27, 2025Abstract:Pruning has recently been widely adopted to reduce the parameter scale and improve the inference efficiency of Large Language Models (LLMs). Mainstream pruning techniques often rely on uniform layerwise pruning strategies, which can lead to severe performance degradation at high sparsity levels. Recognizing the varying contributions of different layers in LLMs, recent studies have shifted their focus toward non-uniform layerwise pruning. However, these approaches often rely on pre-defined values, which can result in suboptimal performance. To overcome these limitations, we propose a novel method called Dynamic Layerwise Pruning (DLP). This approach adaptively determines the relative importance of each layer by integrating model weights with input activation information, assigning pruning rates accordingly. Experimental results show that DLP effectively preserves model performance at high sparsity levels across multiple LLMs. Specifically, at 70% sparsity, DLP reduces the perplexity of LLaMA2-7B by 7.79 and improves the average accuracy by 2.7% compared to state-of-the-art methods. Moreover, DLP is compatible with various existing LLM compression techniques and can be seamlessly integrated into Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT). We release the code at https://github.com/ironartisan/DLP to facilitate future research.
DialogueAgents: A Hybrid Agent-Based Speech Synthesis Framework for Multi-Party Dialogue
Apr 20, 2025Abstract:Speech synthesis is crucial for human-computer interaction, enabling natural and intuitive communication. However, existing datasets involve high construction costs due to manual annotation and suffer from limited character diversity, contextual scenarios, and emotional expressiveness. To address these issues, we propose DialogueAgents, a novel hybrid agent-based speech synthesis framework, which integrates three specialized agents -- a script writer, a speech synthesizer, and a dialogue critic -- to collaboratively generate dialogues. Grounded in a diverse character pool, the framework iteratively refines dialogue scripts and synthesizes speech based on speech review, boosting emotional expressiveness and paralinguistic features of the synthesized dialogues. Using DialogueAgent, we contribute MultiTalk, a bilingual, multi-party, multi-turn speech dialogue dataset covering diverse topics. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our framework and the high quality of the MultiTalk dataset. We release the dataset and code https://github.com/uirlx/DialogueAgents to facilitate future research on advanced speech synthesis models and customized data generation.
CEFW: A Comprehensive Evaluation Framework for Watermark in Large Language Models
Mar 24, 2025Abstract:Text watermarking provides an effective solution for identifying synthetic text generated by large language models. However, existing techniques often focus on satisfying specific criteria while ignoring other key aspects, lacking a unified evaluation. To fill this gap, we propose the Comprehensive Evaluation Framework for Watermark (CEFW), a unified framework that comprehensively evaluates watermarking methods across five key dimensions: ease of detection, fidelity of text quality, minimal embedding cost, robustness to adversarial attacks, and imperceptibility to prevent imitation or forgery. By assessing watermarks according to all these key criteria, CEFW offers a thorough evaluation of their practicality and effectiveness. Moreover, we introduce a simple and effective watermarking method called Balanced Watermark (BW), which guarantees robustness and imperceptibility through balancing the way watermark information is added. Extensive experiments show that BW outperforms existing methods in overall performance across all evaluation dimensions. We release our code to the community for future research. https://github.com/DrankXs/BalancedWatermark.
PlanGen: Towards Unified Layout Planning and Image Generation in Auto-Regressive Vision Language Models
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we propose a unified layout planning and image generation model, PlanGen, which can pre-plan spatial layout conditions before generating images. Unlike previous diffusion-based models that treat layout planning and layout-to-image as two separate models, PlanGen jointly models the two tasks into one autoregressive transformer using only next-token prediction. PlanGen integrates layout conditions into the model as context without requiring specialized encoding of local captions and bounding box coordinates, which provides significant advantages over the previous embed-and-pool operations on layout conditions, particularly when dealing with complex layouts. Unified prompting allows PlanGen to perform multitasking training related to layout, including layout planning, layout-to-image generation, image layout understanding, etc. In addition, PlanGen can be seamlessly expanded to layout-guided image manipulation thanks to the well-designed modeling, with teacher-forcing content manipulation policy and negative layout guidance. Extensive experiments verify the effectiveness of our PlanGen in multiple layoutrelated tasks, showing its great potential. Code is available at: https://360cvgroup.github.io/PlanGen.
NAMI: Efficient Image Generation via Progressive Rectified Flow Transformers
Mar 12, 2025Abstract:Flow-based transformer models for image generation have achieved state-of-the-art performance with larger model parameters, but their inference deployment cost remains high. To enhance inference performance while maintaining generation quality, we propose progressive rectified flow transformers. We divide the rectified flow into different stages according to resolution, using fewer transformer layers at the low-resolution stages to generate image layouts and concept contours, and progressively adding more layers as the resolution increases. Experiments demonstrate that our approach achieves fast convergence and reduces inference time while ensuring generation quality. The main contributions of this paper are summarized as follows: (1) We introduce progressive rectified flow transformers that enable multi-resolution training, accelerating model convergence; (2) NAMI leverages piecewise flow and spatial cascading of Diffusion Transformer (DiT) to rapidly generate images, reducing inference time by 40% to generate a 1024 resolution image; (3) We propose NAMI-1K benchmark to evaluate human preference performance, aiming to mitigate distributional bias and prevent data leakage from open-source benchmarks. The results show that our model is competitive with state-of-the-art models.
WISA: World Simulator Assistant for Physics-Aware Text-to-Video Generation
Mar 11, 2025Abstract:Recent rapid advancements in text-to-video (T2V) generation, such as SoRA and Kling, have shown great potential for building world simulators. However, current T2V models struggle to grasp abstract physical principles and generate videos that adhere to physical laws. This challenge arises primarily from a lack of clear guidance on physical information due to a significant gap between abstract physical principles and generation models. To this end, we introduce the World Simulator Assistant (WISA), an effective framework for decomposing and incorporating physical principles into T2V models. Specifically, WISA decomposes physical principles into textual physical descriptions, qualitative physical categories, and quantitative physical properties. To effectively embed these physical attributes into the generation process, WISA incorporates several key designs, including Mixture-of-Physical-Experts Attention (MoPA) and a Physical Classifier, enhancing the model's physics awareness. Furthermore, most existing datasets feature videos where physical phenomena are either weakly represented or entangled with multiple co-occurring processes, limiting their suitability as dedicated resources for learning explicit physical principles. We propose a novel video dataset, WISA-32K, collected based on qualitative physical categories. It consists of 32,000 videos, representing 17 physical laws across three domains of physics: dynamics, thermodynamics, and optics. Experimental results demonstrate that WISA can effectively enhance the compatibility of T2V models with real-world physical laws, achieving a considerable improvement on the VideoPhy benchmark. The visual exhibitions of WISA and WISA-32K are available in the https://360cvgroup.github.io/WISA/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge