CGMatch: A Different Perspective of Semi-supervised Learning
Paper and Code
Mar 04, 2025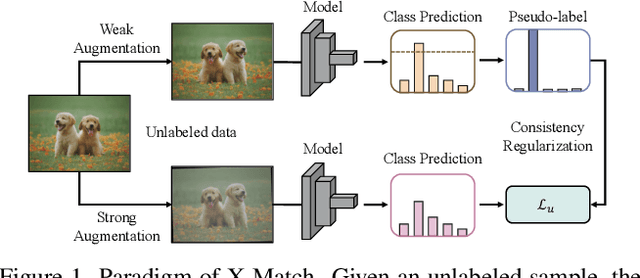
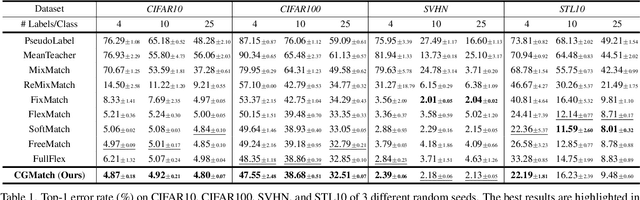
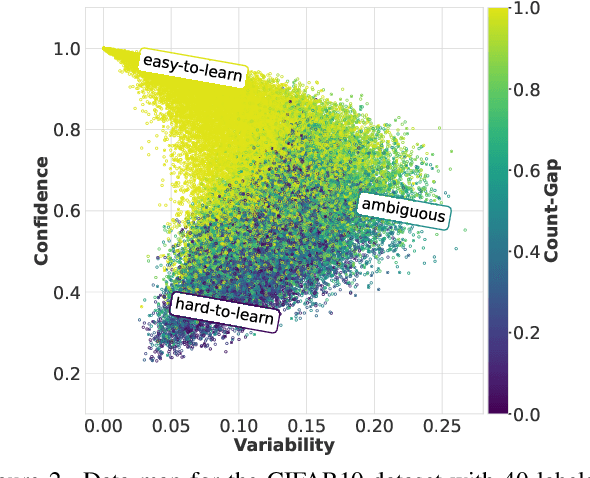

Semi-supervised learning (SSL) has garnered significant attention due to its ability to leverage limited labeled data and a large amount of unlabeled data to improve model generalization performance. Recent approaches achieve impressive successes by combining ideas from both consistency regularization and pseudo-labeling. However, these methods tend to underperform in the more realistic situations with relatively scarce labeled data. We argue that this issue arises because existing methods rely solely on the model's confidence, making them challenging to accurately assess the model's state and identify unlabeled examples contributing to the training phase when supervision information is limited, especially during the early stages of model training. In this paper, we propose a novel SSL model called CGMatch, which, for the first time, incorporates a new metric known as Count-Gap (CG). We demonstrate that CG is effective in discovering unlabeled examples beneficial for model training. Along with confidence, a commonly used metric in SSL, we propose a fine-grained dynamic selection (FDS) strategy. This strategy dynamically divides the unlabeled dataset into three subsets with different characteristics: easy-to-learn set, ambiguous set, and hard-to-learn set. By selective filtering subsets, and applying corresponding regularization with selected subsets, we mitigate the negative impact of incorrect pseudo-labels on model optimization and generalization. Extensive experimental results on several common SSL benchmarks indicate the effectiveness of CGMatch especially when the labeled data are particularly limited. Source code is available at https://github.com/BoCheng-96/CGMatch.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge