Liuzhuozheng Li
VAE-REPA: Variational Autoencoder Representation Alignment for Efficient Diffusion Training
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:Denoising-based diffusion transformers, despite their strong generation performance, suffer from inefficient training convergence. Existing methods addressing this issue, such as REPA (relying on external representation encoders) or SRA (requiring dual-model setups), inevitably incur heavy computational overhead during training due to external dependencies. To tackle these challenges, this paper proposes \textbf{\namex}, a lightweight intrinsic guidance framework for efficient diffusion training. \name leverages off-the-shelf pre-trained Variational Autoencoder (VAE) features: their reconstruction property ensures inherent encoding of visual priors like rich texture details, structural patterns, and basic semantic information. Specifically, \name aligns the intermediate latent features of diffusion transformers with VAE features via a lightweight projection layer, supervised by a feature alignment loss. This design accelerates training without extra representation encoders or dual-model maintenance, resulting in a simple yet effective pipeline. Extensive experiments demonstrate that \name improves both generation quality and training convergence speed compared to vanilla diffusion transformers, matches or outperforms state-of-the-art acceleration methods, and incurs merely 4\% extra GFLOPs with zero additional cost for external guidance models.
Distribution Matching Distillation Meets Reinforcement Learning
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:Distribution Matching Distillation (DMD) distills a pre-trained multi-step diffusion model to a few-step one to improve inference efficiency. However, the performance of the latter is often capped by the former. To circumvent this dilemma, we propose DMDR, a novel framework that combines Reinforcement Learning (RL) techniques into the distillation process. We show that for the RL of the few-step generator, the DMD loss itself is a more effective regularization compared to the traditional ones. In turn, RL can help to guide the mode coverage process in DMD more effectively. These allow us to unlock the capacity of the few-step generator by conducting distillation and RL simultaneously. Meanwhile, we design the dynamic distribution guidance and dynamic renoise sampling training strategies to improve the initial distillation process. The experiments demonstrate that DMDR can achieve leading visual quality, prompt coherence among few-step methods, and even exhibit performance that exceeds the multi-step teacher.
CTA-Flux: Integrating Chinese Cultural Semantics into High-Quality English Text-to-Image Communities
Aug 20, 2025Abstract:We proposed the Chinese Text Adapter-Flux (CTA-Flux). An adaptation method fits the Chinese text inputs to Flux, a powerful text-to-image (TTI) generative model initially trained on the English corpus. Despite the notable image generation ability conditioned on English text inputs, Flux performs poorly when processing non-English prompts, particularly due to linguistic and cultural biases inherent in predominantly English-centric training datasets. Existing approaches, such as translating non-English prompts into English or finetuning models for bilingual mappings, inadequately address culturally specific semantics, compromising image authenticity and quality. To address this issue, we introduce a novel method to bridge Chinese semantic understanding with compatibility in English-centric TTI model communities. Existing approaches relying on ControlNet-like architectures typically require a massive parameter scale and lack direct control over Chinese semantics. In comparison, CTA-flux leverages MultiModal Diffusion Transformer (MMDiT) to control the Flux backbone directly, significantly reducing the number of parameters while enhancing the model's understanding of Chinese semantics. This integration significantly improves the generation quality and cultural authenticity without extensive retraining of the entire model, thus maintaining compatibility with existing text-to-image plugins such as LoRA, IP-Adapter, and ControlNet. Empirical evaluations demonstrate that CTA-flux supports Chinese and English prompts and achieves superior image generation quality, visual realism, and faithful depiction of Chinese semantics.
NanoControl: A Lightweight Framework for Precise and Efficient Control in Diffusion Transformer
Aug 14, 2025Abstract:Diffusion Transformers (DiTs) have demonstrated exceptional capabilities in text-to-image synthesis. However, in the domain of controllable text-to-image generation using DiTs, most existing methods still rely on the ControlNet paradigm originally designed for UNet-based diffusion models. This paradigm introduces significant parameter overhead and increased computational costs. To address these challenges, we propose the Nano Control Diffusion Transformer (NanoControl), which employs Flux as the backbone network. Our model achieves state-of-the-art controllable text-to-image generation performance while incurring only a 0.024\% increase in parameter count and a 0.029\% increase in GFLOPs, thus enabling highly efficient controllable generation. Specifically, rather than duplicating the DiT backbone for control, we design a LoRA-style (low-rank adaptation) control module that directly learns control signals from raw conditioning inputs. Furthermore, we introduce a KV-Context Augmentation mechanism that integrates condition-specific key-value information into the backbone in a simple yet highly effective manner, facilitating deep fusion of conditional features. Extensive benchmark experiments demonstrate that NanoControl significantly reduces computational overhead compared to conventional control approaches, while maintaining superior generation quality and achieving improved controllability.
FLUX-Makeup: High-Fidelity, Identity-Consistent, and Robust Makeup Transfer via Diffusion Transformer
Aug 07, 2025
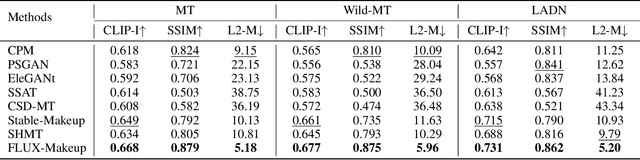
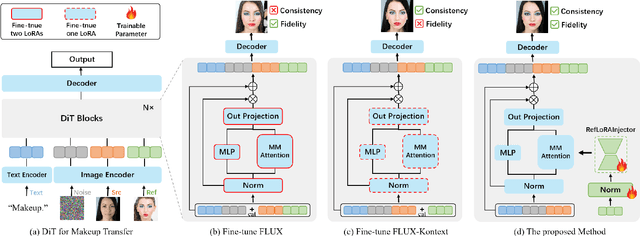
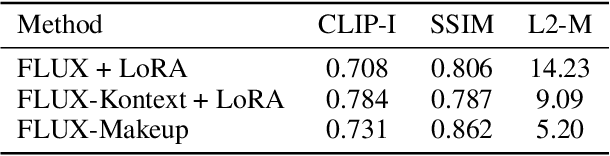
Abstract:Makeup transfer aims to apply the makeup style from a reference face to a target face and has been increasingly adopted in practical applications. Existing GAN-based approaches typically rely on carefully designed loss functions to balance transfer quality and facial identity consistency, while diffusion-based methods often depend on additional face-control modules or algorithms to preserve identity. However, these auxiliary components tend to introduce extra errors, leading to suboptimal transfer results. To overcome these limitations, we propose FLUX-Makeup, a high-fidelity, identity-consistent, and robust makeup transfer framework that eliminates the need for any auxiliary face-control components. Instead, our method directly leverages source-reference image pairs to achieve superior transfer performance. Specifically, we build our framework upon FLUX-Kontext, using the source image as its native conditional input. Furthermore, we introduce RefLoRAInjector, a lightweight makeup feature injector that decouples the reference pathway from the backbone, enabling efficient and comprehensive extraction of makeup-related information. In parallel, we design a robust and scalable data generation pipeline to provide more accurate supervision during training. The paired makeup datasets produced by this pipeline significantly surpass the quality of all existing datasets. Extensive experiments demonstrate that FLUX-Makeup achieves state-of-the-art performance, exhibiting strong robustness across diverse scenarios.
No Other Representation Component Is Needed: Diffusion Transformers Can Provide Representation Guidance by Themselves
May 05, 2025Abstract:Recent studies have demonstrated that learning a meaningful internal representation can both accelerate generative training and enhance generation quality of the diffusion transformers. However, existing approaches necessitate to either introduce an additional and complex representation training framework or rely on a large-scale, pre-trained representation foundation model to provide representation guidance during the original generative training process. In this study, we posit that the unique discriminative process inherent to diffusion transformers enables them to offer such guidance without requiring external representation components. We therefore propose Self-Representation A}lignment (SRA), a simple yet straightforward method that obtain representation guidance through a self-distillation manner. Specifically, SRA aligns the output latent representation of the diffusion transformer in earlier layer with higher noise to that in later layer with lower noise to progressively enhance the overall representation learning during only generative training process. Experimental results indicate that applying SRA to DiTs and SiTs yields consistent performance improvements. Moreover, SRA not only significantly outperforms approaches relying on auxiliary, complex representation training frameworks but also achieves performance comparable to methods that heavily dependent on powerful external representation priors.
Vision-Language Model Fine-Tuning via Simple Parameter-Efficient Modification
Sep 25, 2024Abstract:Recent advances in fine-tuning Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have witnessed the success of prompt tuning and adapter tuning, while the classic model fine-tuning on inherent parameters seems to be overlooked. It is believed that fine-tuning the parameters of VLMs with few-shot samples corrupts the pre-trained knowledge since fine-tuning the CLIP model even degrades performance. In this paper, we revisit this viewpoint, and propose a new perspective: fine-tuning the specific parameters instead of all will uncover the power of classic model fine-tuning on VLMs. Through our meticulous study, we propose ClipFit, a simple yet effective method to fine-tune CLIP without introducing any overhead of extra parameters. We demonstrate that by only fine-tuning the specific bias terms and normalization layers, ClipFit can improve the performance of zero-shot CLIP by 7.27\% average harmonic mean accuracy. Lastly, to understand how fine-tuning in CLIPFit affects the pre-trained models, we conducted extensive experimental analyses w.r.t. changes in internal parameters and representations. We found that low-level text bias layers and the first layer normalization layer change much more than other layers. The code is available at \url{https://github.com/minglllli/CLIPFit}.
Structure Gaussian SLAM with Manhattan World Hypothesis
May 30, 2024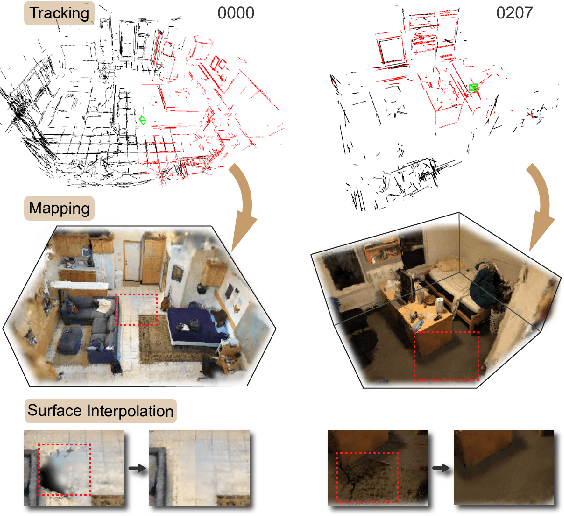

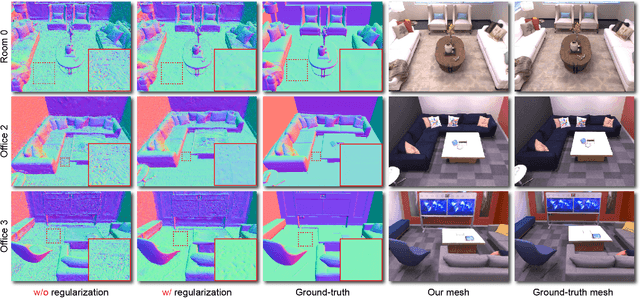
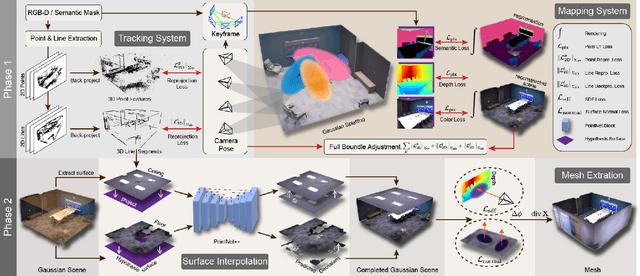
Abstract:Gaussian SLAM systems have made significant advancements in improving the efficiency and fidelity of real-time reconstructions. However, these systems often encounter incomplete reconstructions in complex indoor environments, characterized by substantial holes due to unobserved geometry caused by obstacles or limited view angles. To address this challenge, we present Manhattan Gaussian SLAM (MG-SLAM), an RGB-D system that leverages the Manhattan World hypothesis to enhance geometric accuracy and completeness. By seamlessly integrating fused line segments derived from structured scenes, MG-SLAM ensures robust tracking in textureless indoor areas. Moreover, The extracted lines and planar surface assumption allow strategic interpolation of new Gaussians in regions of missing geometry, enabling efficient scene completion. Extensive experiments conducted on both synthetic and real-world scenes demonstrate that these advancements enable our method to achieve state-of-the-art performance, marking a substantial improvement in the capabilities of Gaussian SLAM systems.
CEIR: Concept-based Explainable Image Representation Learning
Dec 17, 2023Abstract:In modern machine learning, the trend of harnessing self-supervised learning to derive high-quality representations without label dependency has garnered significant attention. However, the absence of label information, coupled with the inherently high-dimensional nature, improves the difficulty for the interpretation of learned representations. Consequently, indirect evaluations become the popular metric for evaluating the quality of these features, leading to a biased validation of the learned representation rationale. To address these challenges, we introduce a novel approach termed Concept-based Explainable Image Representation (CEIR). Initially, using the Concept-based Model (CBM) incorporated with pretrained CLIP and concepts generated by GPT-4, we project input images into a concept vector space. Subsequently, a Variational Autoencoder (VAE) learns the latent representation from these projected concepts, which serves as the final image representation. Due to the capability of the representation to encapsulate high-level, semantically relevant concepts, the model allows for attributions to a human-comprehensible concept space. This not only enhances interpretability but also preserves the robustness essential for downstream tasks. For instance, our method exhibits state-of-the-art unsupervised clustering performance on benchmarks such as CIFAR10, CIFAR100, and STL10. Furthermore, capitalizing on the universality of human conceptual understanding, CEIR can seamlessly extract the related concept from open-world images without fine-tuning. This offers a fresh approach to automatic label generation and label manipulation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge