Yanning Zhang
Knowing the Unknown: Interpretable Open-World Object Detection via Concept Decomposition Model
Feb 24, 2026Abstract:Open-world object detection (OWOD) requires incrementally detecting known categories while reliably identifying unknown objects. Existing methods primarily focus on improving unknown recall, yet overlook interpretability, often leading to known-unknown confusion and reduced prediction reliability. This paper aims to make the entire OWOD framework interpretable, enabling the detector to truly "knowing the unknown". To this end, we propose a concept-driven InterPretable OWOD framework(IPOW) by introducing a Concept Decomposition Model (CDM) for OWOD, which explicitly decomposes the coupled RoI features in Faster R-CNN into discriminative, shared, and background concepts. Discriminative concepts identify the most discriminative features to enlarge the distances between known categories, while shared and background concepts, due to their strong generalization ability, can be readily transferred to detect unknown categories. Leveraging the interpretable framework, we identify that known-unknown confusion arises when unknown objects fall into the discriminative space of known classes. To address this, we propose Concept-Guided Rectification (CGR) to further resolve such confusion. Extensive experiments show that IPOW significantly improves unknown recall while mitigating confusion, and provides concept-level interpretability for both known and unknown predictions.
YOLO-IOD: Towards Real Time Incremental Object Detection
Dec 28, 2025Abstract:Current methods for incremental object detection (IOD) primarily rely on Faster R-CNN or DETR series detectors; however, these approaches do not accommodate the real-time YOLO detection frameworks. In this paper, we first identify three primary types of knowledge conflicts that contribute to catastrophic forgetting in YOLO-based incremental detectors: foreground-background confusion, parameter interference, and misaligned knowledge distillation. Subsequently, we introduce YOLO-IOD, a real-time Incremental Object Detection (IOD) framework that is constructed upon the pretrained YOLO-World model, facilitating incremental learning via a stage-wise parameter-efficient fine-tuning process. Specifically, YOLO-IOD encompasses three principal components: 1) Conflict-Aware Pseudo-Label Refinement (CPR), which mitigates the foreground-background confusion by leveraging the confidence levels of pseudo labels and identifying potential objects relevant to future tasks. 2) Importancebased Kernel Selection (IKS), which identifies and updates the pivotal convolution kernels pertinent to the current task during the current learning stage. 3) Cross-Stage Asymmetric Knowledge Distillation (CAKD), which addresses the misaligned knowledge distillation conflict by transmitting the features of the student target detector through the detection heads of both the previous and current teacher detectors, thereby facilitating asymmetric distillation between existing and newly introduced categories. We further introduce LoCo COCO, a more realistic benchmark that eliminates data leakage across stages. Experiments on both conventional and LoCo COCO benchmarks show that YOLO-IOD achieves superior performance with minimal forgetting.
GMODiff: One-Step Gain Map Refinement with Diffusion Priors for HDR Reconstruction
Dec 18, 2025

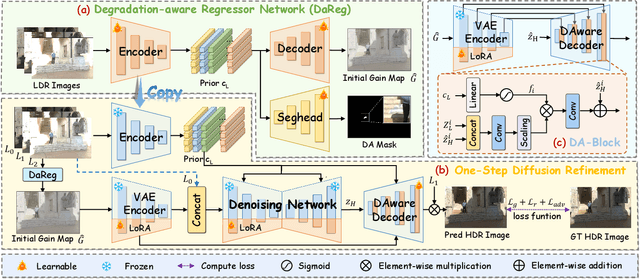

Abstract:Pre-trained Latent Diffusion Models (LDMs) have recently shown strong perceptual priors for low-level vision tasks, making them a promising direction for multi-exposure High Dynamic Range (HDR) reconstruction. However, directly applying LDMs to HDR remains challenging due to: (1) limited dynamic-range representation caused by 8-bit latent compression, (2) high inference cost from multi-step denoising, and (3) content hallucination inherent to generative nature. To address these challenges, we introduce GMODiff, a gain map-driven one-step diffusion framework for multi-exposure HDR reconstruction. Instead of reconstructing full HDR content, we reformulate HDR reconstruction as a conditionally guided Gain Map (GM) estimation task, where the GM encodes the extended dynamic range while retaining the same bit depth as LDR images. We initialize the denoising process from an informative regression-based estimate rather than pure noise, enabling the model to generate high-quality GMs in a single denoising step. Furthermore, recognizing that regression-based models excel in content fidelity while LDMs favor perceptual quality, we leverage regression priors to guide both the denoising process and latent decoding of the LDM, suppressing hallucinations while preserving structural accuracy. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our GMODiff performs favorably against several state-of-the-art methods and is 100 faster than previous LDM-based methods.
SOMA: Feature Gradient Enhanced Affine-Flow Matching for SAR-Optical Registration
Nov 17, 2025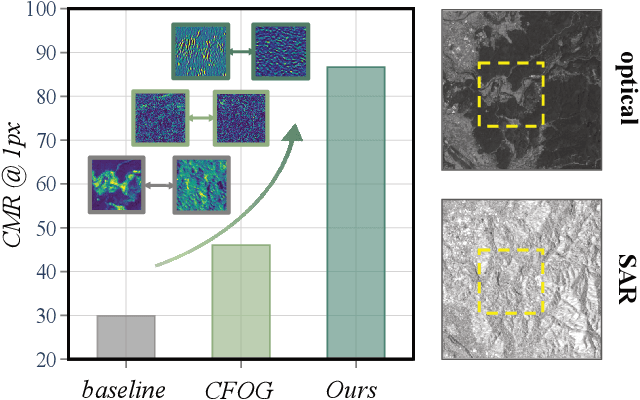
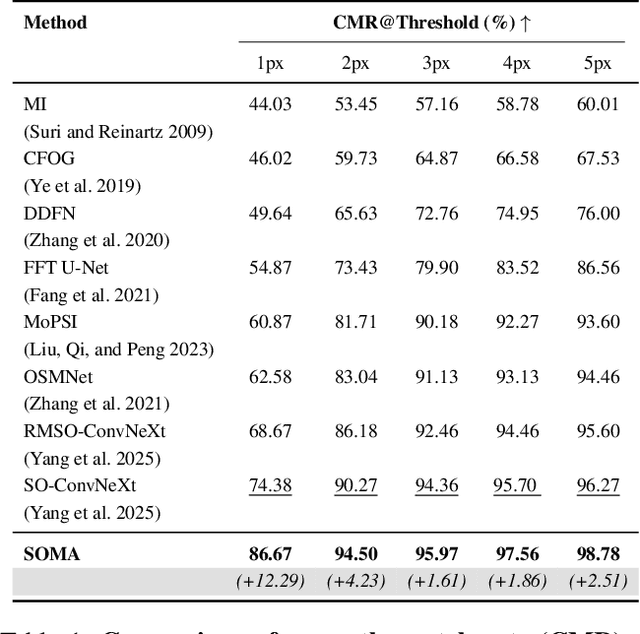
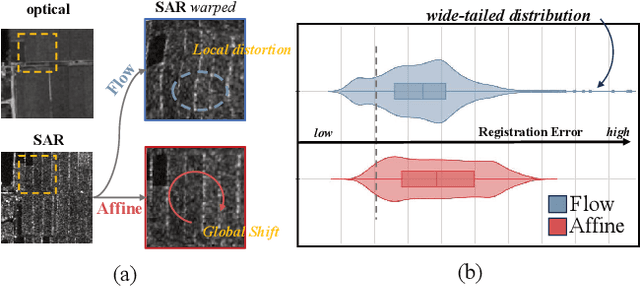
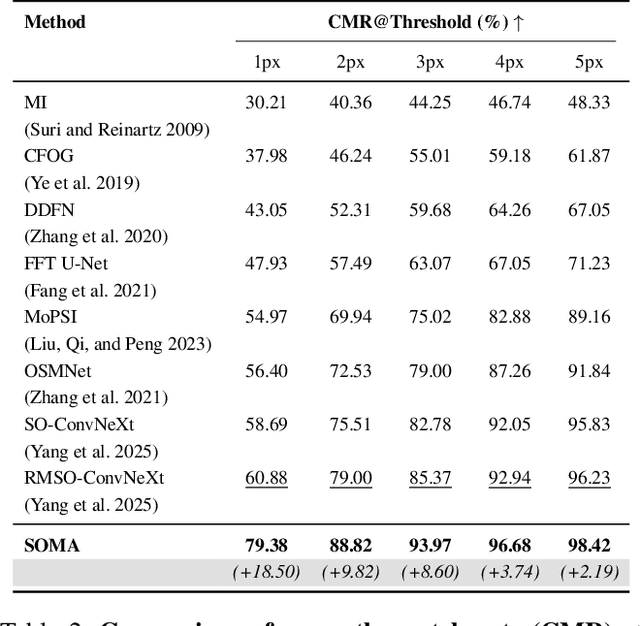
Abstract:Achieving pixel-level registration between SAR and optical images remains a challenging task due to their fundamentally different imaging mechanisms and visual characteristics. Although deep learning has achieved great success in many cross-modal tasks, its performance on SAR-Optical registration tasks is still unsatisfactory. Gradient-based information has traditionally played a crucial role in handcrafted descriptors by highlighting structural differences. However, such gradient cues have not been effectively leveraged in deep learning frameworks for SAR-Optical image matching. To address this gap, we propose SOMA, a dense registration framework that integrates structural gradient priors into deep features and refines alignment through a hybrid matching strategy. Specifically, we introduce the Feature Gradient Enhancer (FGE), which embeds multi-scale, multi-directional gradient filters into the feature space using attention and reconstruction mechanisms to boost feature distinctiveness. Furthermore, we propose the Global-Local Affine-Flow Matcher (GLAM), which combines affine transformation and flow-based refinement within a coarse-to-fine architecture to ensure both structural consistency and local accuracy. Experimental results demonstrate that SOMA significantly improves registration precision, increasing the CMR@1px by 12.29% on the SEN1-2 dataset and 18.50% on the GFGE_SO dataset. In addition, SOMA exhibits strong robustness and generalizes well across diverse scenes and resolutions.
FreDFT: Frequency Domain Fusion Transformer for Visible-Infrared Object Detection
Nov 14, 2025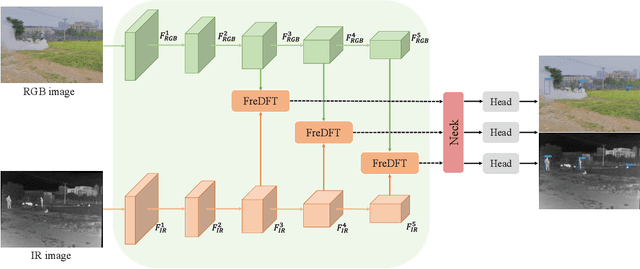

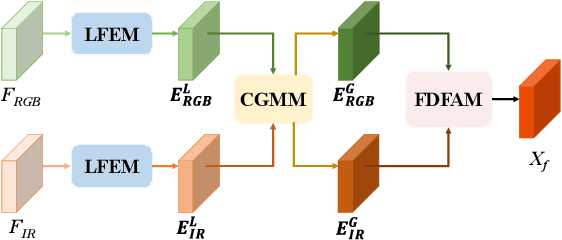
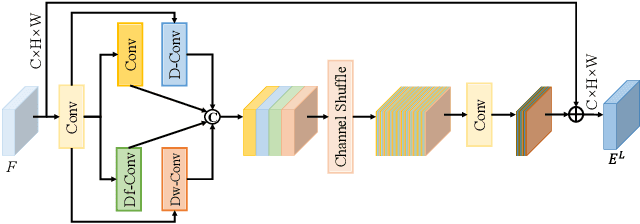
Abstract:Visible-infrared object detection has gained sufficient attention due to its detection performance in low light, fog, and rain conditions. However, visible and infrared modalities captured by different sensors exist the information imbalance problem in complex scenarios, which can cause inadequate cross-modal fusion, resulting in degraded detection performance. \textcolor{red}{Furthermore, most existing methods use transformers in the spatial domain to capture complementary features, ignoring the advantages of developing frequency domain transformers to mine complementary information.} To solve these weaknesses, we propose a frequency domain fusion transformer, called FreDFT, for visible-infrared object detection. The proposed approach employs a novel multimodal frequency domain attention (MFDA) to mine complementary information between modalities and a frequency domain feed-forward layer (FDFFL) via a mixed-scale frequency feature fusion strategy is designed to better enhance multimodal features. To eliminate the imbalance of multimodal information, a cross-modal global modeling module (CGMM) is constructed to perform pixel-wise inter-modal feature interaction in a spatial and channel manner. Moreover, a local feature enhancement module (LFEM) is developed to strengthen multimodal local feature representation and promote multimodal feature fusion by using various convolution layers and applying a channel shuffle. Extensive experimental results have verified that our proposed FreDFT achieves excellent performance on multiple public datasets compared with other state-of-the-art methods. The code of our FreDFT is linked at https://github.com/WenCongWu/FreDFT.
Multi-level Collaborative Distillation Meets Global Workspace Model: A Unified Framework for OCIL
Aug 12, 2025Abstract:Online Class-Incremental Learning (OCIL) enables models to learn continuously from non-i.i.d. data streams and samples of the data streams can be seen only once, making it more suitable for real-world scenarios compared to offline learning. However, OCIL faces two key challenges: maintaining model stability under strict memory constraints and ensuring adaptability to new tasks. Under stricter memory constraints, current replay-based methods are less effective. While ensemble methods improve adaptability (plasticity), they often struggle with stability. To overcome these challenges, we propose a novel approach that enhances ensemble learning through a Global Workspace Model (GWM)-a shared, implicit memory that guides the learning of multiple student models. The GWM is formed by fusing the parameters of all students within each training batch, capturing the historical learning trajectory and serving as a dynamic anchor for knowledge consolidation. This fused model is then redistributed periodically to the students to stabilize learning and promote cross-task consistency. In addition, we introduce a multi-level collaborative distillation mechanism. This approach enforces peer-to-peer consistency among students and preserves historical knowledge by aligning each student with the GWM. As a result, student models remain adaptable to new tasks while maintaining previously learned knowledge, striking a better balance between stability and plasticity. Extensive experiments on three standard OCIL benchmarks show that our method delivers significant performance improvement for several OCIL models across various memory budgets.
HVI-CIDNet+: Beyond Extreme Darkness for Low-Light Image Enhancement
Jul 09, 2025Abstract:Low-Light Image Enhancement (LLIE) aims to restore vivid content and details from corrupted low-light images. However, existing standard RGB (sRGB) color space-based LLIE methods often produce color bias and brightness artifacts due to the inherent high color sensitivity. While Hue, Saturation, and Value (HSV) color space can decouple brightness and color, it introduces significant red and black noise artifacts. To address this problem, we propose a new color space for LLIE, namely Horizontal/Vertical-Intensity (HVI), defined by the HV color map and learnable intensity. The HV color map enforces small distances for the red coordinates to remove red noise artifacts, while the learnable intensity compresses the low-light regions to remove black noise artifacts. Additionally, we introduce the Color and Intensity Decoupling Network+ (HVI-CIDNet+), built upon the HVI color space, to restore damaged content and mitigate color distortion in extremely dark regions. Specifically, HVI-CIDNet+ leverages abundant contextual and degraded knowledge extracted from low-light images using pre-trained vision-language models, integrated via a novel Prior-guided Attention Block (PAB). Within the PAB, latent semantic priors can promote content restoration, while degraded representations guide precise color correction, both particularly in extremely dark regions through the meticulously designed cross-attention fusion mechanism. Furthermore, we construct a Region Refinement Block that employs convolution for information-rich regions and self-attention for information-scarce regions, ensuring accurate brightness adjustments. Comprehensive results from benchmark experiments demonstrate that the proposed HVI-CIDNet+ outperforms the state-of-the-art methods on 10 datasets.
Prompt-Free Conditional Diffusion for Multi-object Image Augmentation
Jul 08, 2025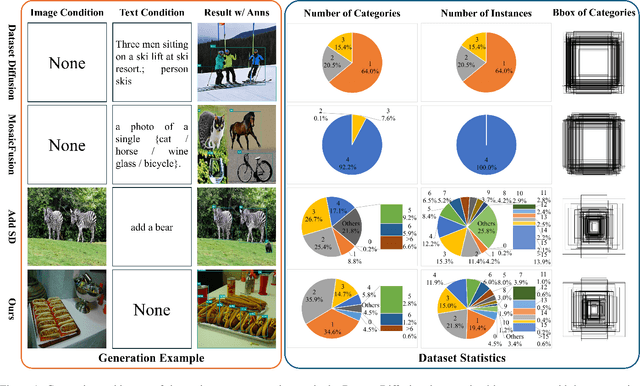
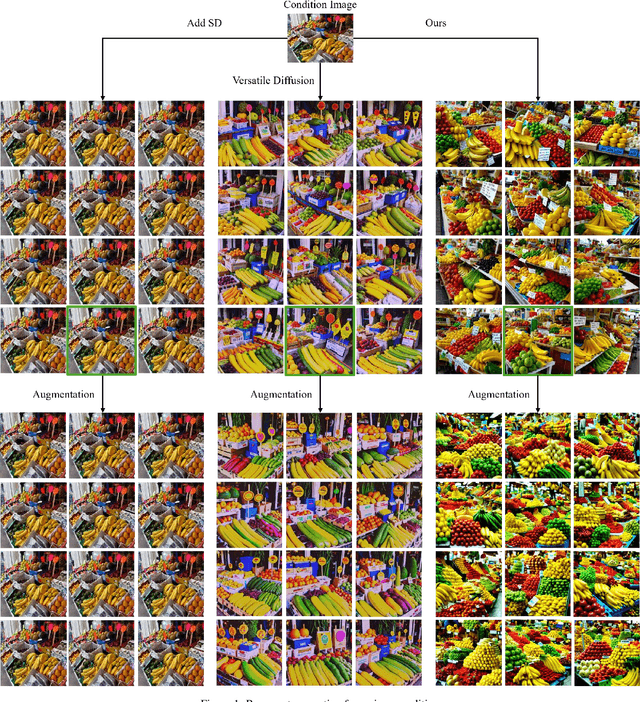
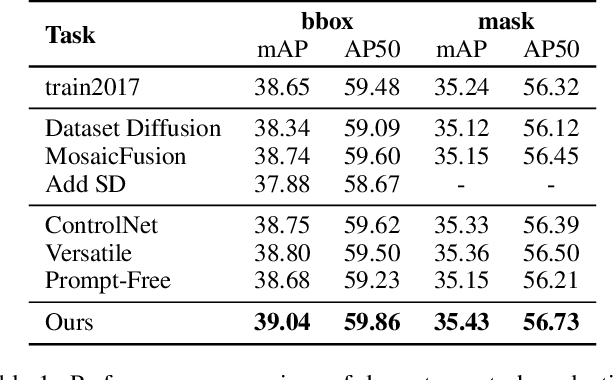
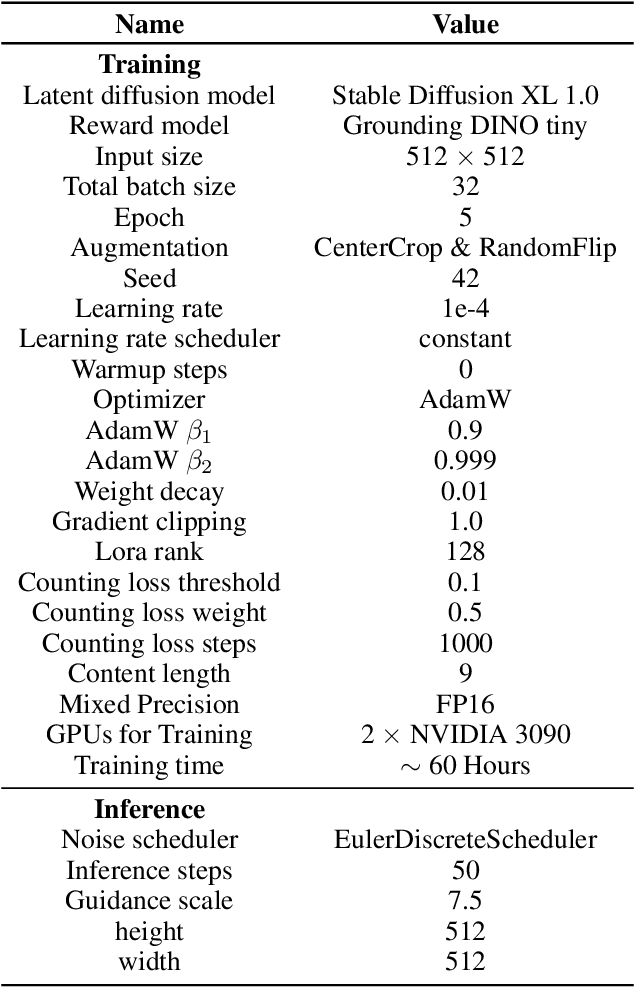

Abstract:Diffusion models has underpinned much recent advances of dataset augmentation in various computer vision tasks. However, when involving generating multi-object images as real scenarios, most existing methods either rely entirely on text condition, resulting in a deviation between the generated objects and the original data, or rely too much on the original images, resulting in a lack of diversity in the generated images, which is of limited help to downstream tasks. To mitigate both problems with one stone, we propose a prompt-free conditional diffusion framework for multi-object image augmentation. Specifically, we introduce a local-global semantic fusion strategy to extract semantics from images to replace text, and inject knowledge into the diffusion model through LoRA to alleviate the category deviation between the original model and the target dataset. In addition, we design a reward model based counting loss to assist the traditional reconstruction loss for model training. By constraining the object counts of each category instead of pixel-by-pixel constraints, bridging the quantity deviation between the generated data and the original data while improving the diversity of the generated data. Experimental results demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method over several representative state-of-the-art baselines and showcase strong downstream task gain and out-of-domain generalization capabilities. Code is available at \href{https://github.com/00why00/PFCD}{here}.
Language Embedding Meets Dynamic Graph: A New Exploration for Neural Architecture Representation Learning
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:Neural Architecture Representation Learning aims to transform network models into feature representations for predicting network attributes, playing a crucial role in deploying and designing networks for real-world applications. Recently, inspired by the success of transformers, transformer-based models integrated with Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have achieved significant progress in representation learning. However, current methods still have some limitations. First, existing methods overlook hardware attribute information, which conflicts with the current trend of diversified deep learning hardware and limits the practical applicability of models. Second, current encoding approaches rely on static adjacency matrices to represent topological structures, failing to capture the structural differences between computational nodes, which ultimately compromises encoding effectiveness. In this paper, we introduce LeDG-Former, an innovative framework that addresses these limitations through the synergistic integration of language-based semantic embedding and dynamic graph representation learning. Specifically, inspired by large language models (LLMs), we propose a language embedding framework where both neural architectures and hardware platform specifications are projected into a unified semantic space through tokenization and LLM processing, enabling zero-shot prediction across different hardware platforms for the first time. Then, we propose a dynamic graph-based transformer for modeling neural architectures, resulting in improved neural architecture modeling performance. On the NNLQP benchmark, LeDG-Former surpasses previous methods, establishing a new SOTA while demonstrating the first successful cross-hardware latency prediction capability. Furthermore, our framework achieves superior performance on the cell-structured NAS-Bench-101 and NAS-Bench-201 datasets.
Adaptive Spatial Augmentation for Semi-supervised Semantic Segmentation
May 29, 2025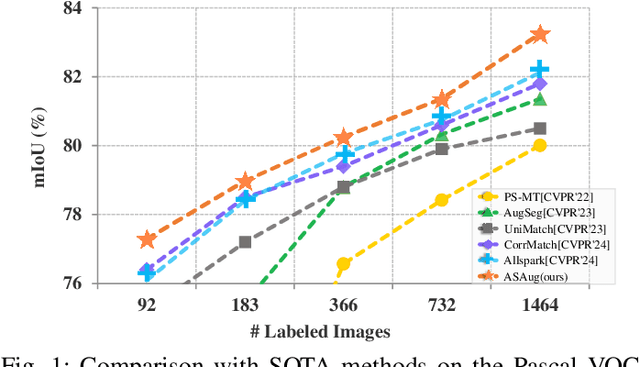
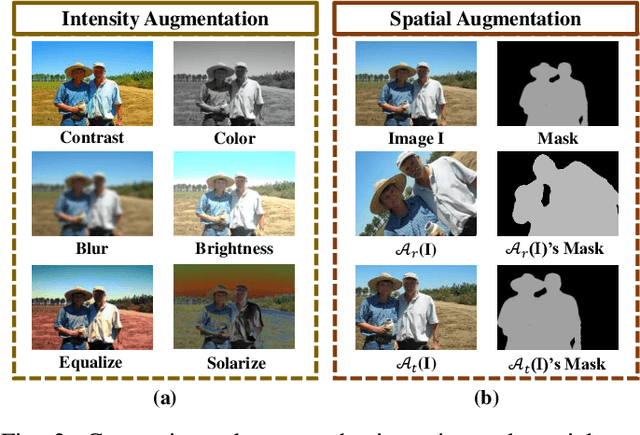
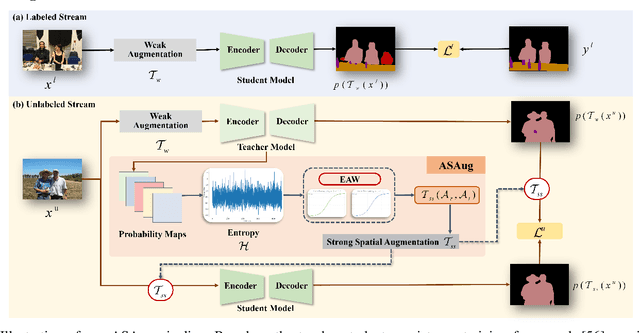
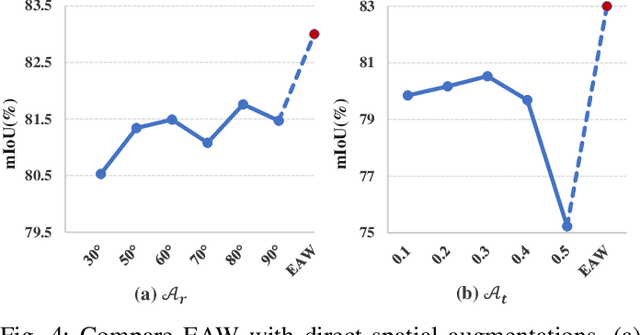
Abstract:In semi-supervised semantic segmentation (SSSS), data augmentation plays a crucial role in the weak-to-strong consistency regularization framework, as it enhances diversity and improves model generalization. Recent strong augmentation methods have primarily focused on intensity-based perturbations, which have minimal impact on the semantic masks. In contrast, spatial augmentations like translation and rotation have long been acknowledged for their effectiveness in supervised semantic segmentation tasks, but they are often ignored in SSSS. In this work, we demonstrate that spatial augmentation can also contribute to model training in SSSS, despite generating inconsistent masks between the weak and strong augmentations. Furthermore, recognizing the variability among images, we propose an adaptive augmentation strategy that dynamically adjusts the augmentation for each instance based on entropy. Extensive experiments show that our proposed Adaptive Spatial Augmentation (\textbf{ASAug}) can be integrated as a pluggable module, consistently improving the performance of existing methods and achieving state-of-the-art results on benchmark datasets such as PASCAL VOC 2012, Cityscapes, and COCO.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge