Jiang Wu
Styles + Persona-plug = Customized LLMs
Jan 10, 2026Abstract:We discover a previously overlooked challenge in personalized text generation: personalization methods are increasingly applied under explicit style instructions, yet their behavior under such constraints remains poorly understood. To balance implicit personalization and explicit style, we formulate personalization as a distributional residual and propose PsPLUG, a lightweight soft-prompt plug-in trained with style-conditioned preference contrasts. Across LaMP benchmark, our framework improves persona alignment, maintains stylistic fidelity, and outperforms retrieval-based and soft-prompt baselines with minimal computation. These results show that residual modeling provides a simple and principled foundation for controllable, style-aware LLM personalization.
CARD: Cluster-level Adaptation with Reward-guided Decoding for Personalized Text Generation
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:Adapting large language models to individual users remains challenging due to the tension between fine-grained personalization and scalable deployment. We present CARD, a hierarchical framework that achieves effective personalization through progressive refinement. CARD first clusters users according to shared stylistic patterns and learns cluster-specific LoRA adapters, enabling robust generalization and strong low-resource performance. To capture individual differences within each cluster, we propose an implicit preference learning mechanism that contrasts user-authored text with cluster-level generations, allowing the model to infer user-specific style preferences without manual annotation. At inference time, CARD injects personalization exclusively at decoding via lightweight user preference vectors and low-rank logit corrections, while keeping the base model frozen. Experiments on the LaMP and LongLaMP benchmarks show that CARD achieves competitive or superior generation quality compared to state-of-the-art baselines, while significantly improving efficiency and scalability for practical personalized text generation.
GUITester: Enabling GUI Agents for Exploratory Defect Discovery
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Exploratory GUI testing is essential for software quality but suffers from high manual costs. While Multi-modal Large Language Model (MLLM) agents excel in navigation, they fail to autonomously discover defects due to two core challenges: \textit{Goal-Oriented Masking}, where agents prioritize task completion over reporting anomalies, and \textit{Execution-Bias Attribution}, where system defects are misidentified as agent errors. To address these, we first introduce \textbf{GUITestBench}, the first interactive benchmark for this task, featuring 143 tasks across 26 defects. We then propose \textbf{GUITester}, a multi-agent framework that decouples navigation from verification via two modules: (i) a \textit{Planning-Execution Module (PEM)} that proactively probes for defects via embedded testing intents, and (ii) a \textit{Hierarchical Reflection Module (HRM)} that resolves attribution ambiguity through interaction history analysis. GUITester achieves an F1-score of 48.90\% (Pass@3) on GUITestBench, outperforming state-of-the-art baselines (33.35\%). Our work demonstrates the feasibility of autonomous exploratory testing and provides a robust foundation for future GUI quality assurance~\footnote{Our code is now available in~\href{https://github.com/ADaM-BJTU/GUITestBench}{https://github.com/ADaM-BJTU/GUITestBench}}.
Smartphone monitoring of smiling as a behavioral proxy of well-being in everyday life
Dec 10, 2025Abstract:Subjective well-being is a cornerstone of individual and societal health, yet its scientific measurement has traditionally relied on self-report methods prone to recall bias and high participant burden. This has left a gap in our understanding of well-being as it is expressed in everyday life. We hypothesized that candid smiles captured during natural smartphone interactions could serve as a scalable, objective behavioral correlate of positive affect. To test this, we analyzed 405,448 video clips passively recorded from 233 consented participants over one week. Using a deep learning model to quantify smile intensity, we identified distinct diurnal and daily patterns. Daily patterns of smile intensity across the week showed strong correlation with national survey data on happiness (r=0.92), and diurnal rhythms documented close correspondence with established results from the day reconstruction method (r=0.80). Higher daily mean smile intensity was significantly associated with more physical activity (Beta coefficient = 0.043, 95% CI [0.001, 0.085]) and greater light exposure (Beta coefficient = 0.038, [0.013, 0.063]), whereas no significant effects were found for smartphone use. These findings suggest that passive smartphone sensing could serve as a powerful, ecologically valid methodology for studying the dynamics of affective behavior and open the door to understanding this behavior at a population scale.
MinerU2.5: A Decoupled Vision-Language Model for Efficient High-Resolution Document Parsing
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:We introduce MinerU2.5, a 1.2B-parameter document parsing vision-language model that achieves state-of-the-art recognition accuracy while maintaining exceptional computational efficiency. Our approach employs a coarse-to-fine, two-stage parsing strategy that decouples global layout analysis from local content recognition. In the first stage, the model performs efficient layout analysis on downsampled images to identify structural elements, circumventing the computational overhead of processing high-resolution inputs. In the second stage, guided by the global layout, it performs targeted content recognition on native-resolution crops extracted from the original image, preserving fine-grained details in dense text, complex formulas, and tables. To support this strategy, we developed a comprehensive data engine that generates diverse, large-scale training corpora for both pretraining and fine-tuning. Ultimately, MinerU2.5 demonstrates strong document parsing ability, achieving state-of-the-art performance on multiple benchmarks, surpassing both general-purpose and domain-specific models across various recognition tasks, while maintaining significantly lower computational overhead.
TransMPC: Transformer-based Explicit MPC with Variable Prediction Horizon
Sep 09, 2025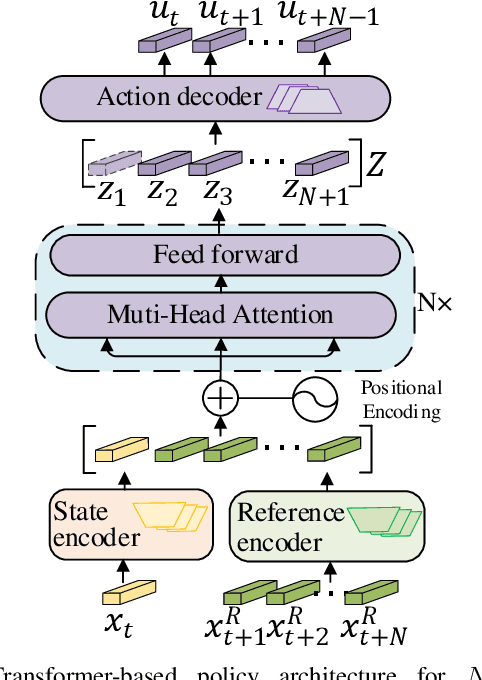
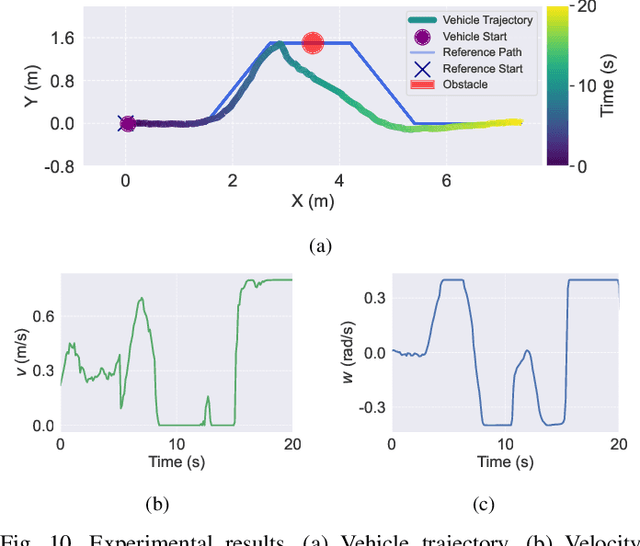
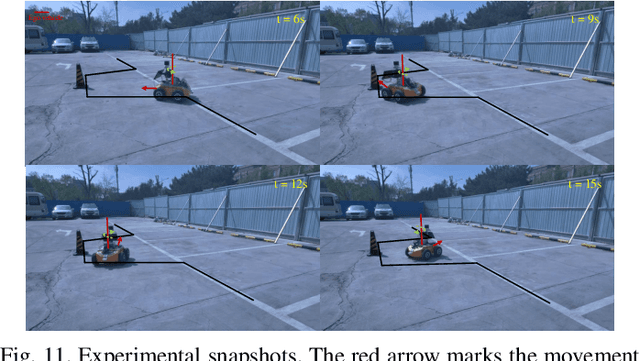
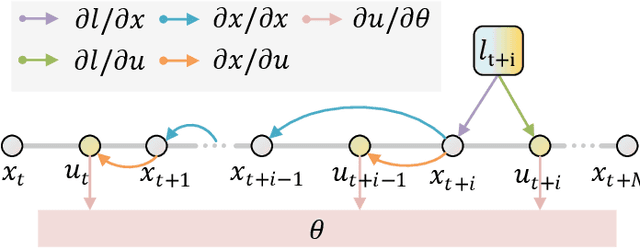
Abstract:Traditional online Model Predictive Control (MPC) methods often suffer from excessive computational complexity, limiting their practical deployment. Explicit MPC mitigates online computational load by pre-computing control policies offline; however, existing explicit MPC methods typically rely on simplified system dynamics and cost functions, restricting their accuracy for complex systems. This paper proposes TransMPC, a novel Transformer-based explicit MPC algorithm capable of generating highly accurate control sequences in real-time for complex dynamic systems. Specifically, we formulate the MPC policy as an encoder-only Transformer leveraging bidirectional self-attention, enabling simultaneous inference of entire control sequences in a single forward pass. This design inherently accommodates variable prediction horizons while ensuring low inference latency. Furthermore, we introduce a direct policy optimization framework that alternates between sampling and learning phases. Unlike imitation-based approaches dependent on precomputed optimal trajectories, TransMPC directly optimizes the true finite-horizon cost via automatic differentiation. Random horizon sampling combined with a replay buffer provides independent and identically distributed (i.i.d.) training samples, ensuring robust generalization across varying states and horizon lengths. Extensive simulations and real-world vehicle control experiments validate the effectiveness of TransMPC in terms of solution accuracy, adaptability to varying horizons, and computational efficiency.
Middo: Model-Informed Dynamic Data Optimization for Enhanced LLM Fine-Tuning via Closed-Loop Learning
Aug 29, 2025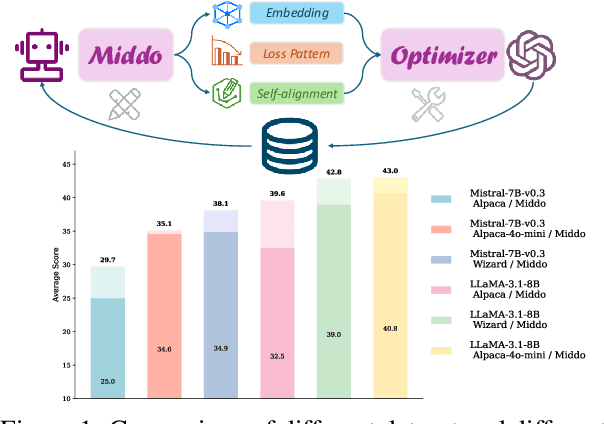
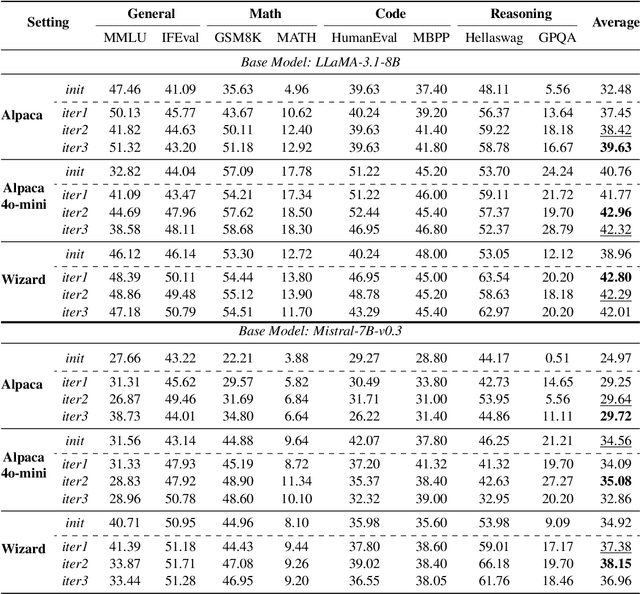
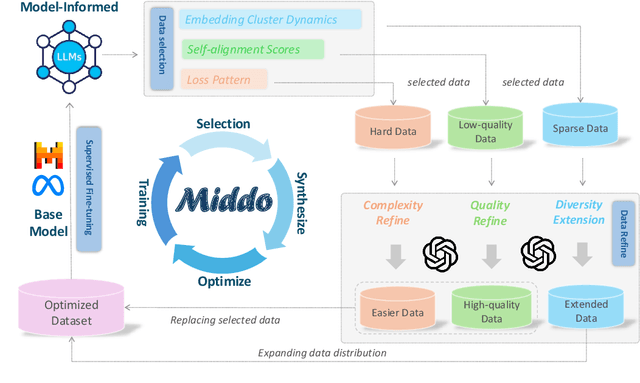
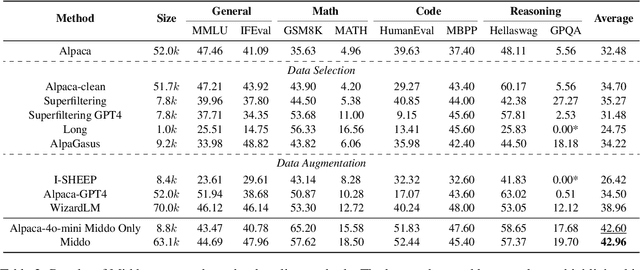
Abstract:Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) Large Language Models (LLM) fundamentally rely on high-quality training data. While data selection and data synthesis are two common strategies to improve data quality, existing approaches often face limitations in static dataset curation that fail to adapt to evolving model capabilities. In this paper, we introduce Middo, a self-evolving Model-informed dynamic data optimization framework that uses model-aware data selection and context-preserving data refinement. Unlike conventional one-off filtering/synthesis methods, our framework establishes a closed-loop optimization system: (1) A self-referential diagnostic module proactively identifies suboptimal samples through tri-axial model signals - loss patterns (complexity), embedding cluster dynamics (diversity), and self-alignment scores (quality); (2) An adaptive optimization engine then transforms suboptimal samples into pedagogically valuable training points while preserving semantic integrity; (3) This optimization process continuously evolves with model capability through dynamic learning principles. Experiments on multiple benchmarks demonstrate that our \method consistently enhances the quality of seed data and boosts LLM's performance with improving accuracy by 7.15% on average while maintaining the original dataset scale. This work establishes a new paradigm for sustainable LLM training through dynamic human-AI co-evolution of data and models. Our datasets, models, and code are coming soon.
GTR-CoT: Graph Traversal as Visual Chain of Thought for Molecular Structure Recognition
Jun 09, 2025



Abstract:Optical Chemical Structure Recognition (OCSR) is crucial for digitizing chemical knowledge by converting molecular images into machine-readable formats. While recent vision-language models (VLMs) have shown potential in this task, their image-captioning approach often struggles with complex molecular structures and inconsistent annotations. To overcome these challenges, we introduce GTR-Mol-VLM, a novel framework featuring two key innovations: (1) the \textit{Graph Traversal as Visual Chain of Thought} mechanism that emulates human reasoning by incrementally parsing molecular graphs through sequential atom-bond predictions, and (2) the data-centric principle of \textit{Faithfully Recognize What You've Seen}, which addresses the mismatch between abbreviated structures in images and their expanded annotations. To support model development, we constructed GTR-CoT-1.3M, a large-scale instruction-tuning dataset with meticulously corrected annotations, and introduced MolRec-Bench, the first benchmark designed for a fine-grained evaluation of graph-parsing accuracy in OCSR. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that GTR-Mol-VLM achieves superior results compared to specialist models, chemistry-domain VLMs, and commercial general-purpose VLMs. Notably, in scenarios involving molecular images with functional group abbreviations, GTR-Mol-VLM outperforms the second-best baseline by approximately 14 percentage points, both in SMILES-based and graph-based metrics. We hope that this work will drive OCSR technology to more effectively meet real-world needs, thereby advancing the fields of cheminformatics and AI for Science. We will release GTR-CoT at https://github.com/opendatalab/GTR-CoT.
Evaluating Large Language Model with Knowledge Oriented Language Specific Simple Question Answering
May 22, 2025



Abstract:We introduce KoLasSimpleQA, the first benchmark evaluating the multilingual factual ability of Large Language Models (LLMs). Inspired by existing research, we created the question set with features such as single knowledge point coverage, absolute objectivity, unique answers, and temporal stability. These questions enable efficient evaluation using the LLM-as-judge paradigm, testing both the LLMs' factual memory and self-awareness ("know what they don't know"). KoLasSimpleQA expands existing research in two key dimensions: (1) Breadth (Multilingual Coverage): It includes 9 languages, supporting global applicability evaluation. (2) Depth (Dual Domain Design): It covers both the general domain (global facts) and the language-specific domain (such as history, culture, and regional traditions) for a comprehensive assessment of multilingual capabilities. We evaluated mainstream LLMs, including traditional LLM and emerging Large Reasoning Models. Results show significant performance differences between the two domains, particularly in performance metrics, ranking, calibration, and robustness. This highlights the need for targeted evaluation and optimization in multilingual contexts. We hope KoLasSimpleQA will help the research community better identify LLM capability boundaries in multilingual contexts and provide guidance for model optimization. We will release KoLasSimpleQA at https://github.com/opendatalab/KoLasSimpleQA .
Sparse2DGS: Geometry-Prioritized Gaussian Splatting for Surface Reconstruction from Sparse Views
Apr 29, 2025Abstract:We present a Gaussian Splatting method for surface reconstruction using sparse input views. Previous methods relying on dense views struggle with extremely sparse Structure-from-Motion points for initialization. While learning-based Multi-view Stereo (MVS) provides dense 3D points, directly combining it with Gaussian Splatting leads to suboptimal results due to the ill-posed nature of sparse-view geometric optimization. We propose Sparse2DGS, an MVS-initialized Gaussian Splatting pipeline for complete and accurate reconstruction. Our key insight is to incorporate the geometric-prioritized enhancement schemes, allowing for direct and robust geometric learning under ill-posed conditions. Sparse2DGS outperforms existing methods by notable margins while being ${2}\times$ faster than the NeRF-based fine-tuning approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge