Zhipeng Ma
Uncovering Causal Drivers of Energy Efficiency for Industrial Process in Foundry via Time-Series Causal Inference
Nov 17, 2025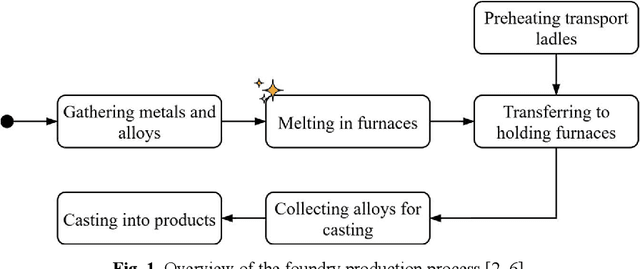
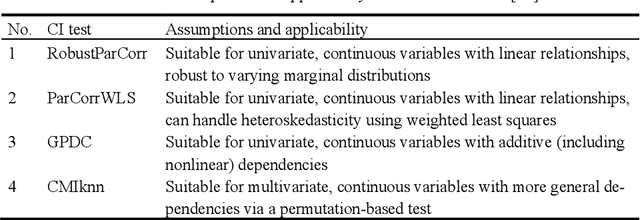
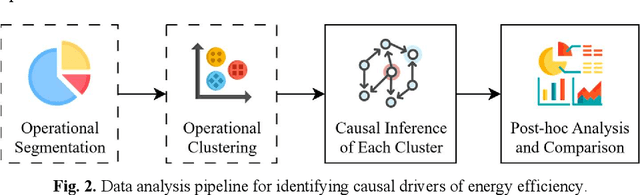
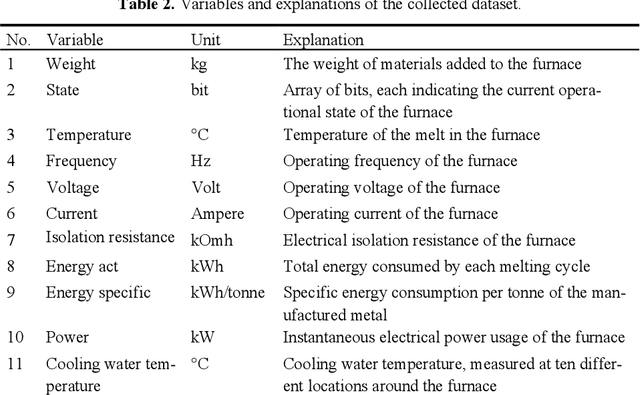
Abstract:Improving energy efficiency in industrial foundry processes is a critical challenge, as these operations are highly energy-intensive and marked by complex interdependencies among process variables. Correlation-based analyses often fail to distinguish true causal drivers from spurious associations, limiting their usefulness for decision-making. This paper applies a time-series causal inference framework to identify the operational factors that directly affect energy efficiency in induction furnace melting. Using production data from a Danish foundry, the study integrates time-series clustering to segment melting cycles into distinct operational modes with the PCMCI+ algorithm, a state-of-the-art causal discovery method, to uncover cause-effect relationships within each mode. Across clusters, robust causal relations among energy consumption, furnace temperature, and material weight define the core drivers of efficiency, while voltage consistently influences cooling water temperature with a delayed response. Cluster-specific differences further distinguish operational regimes: efficient clusters are characterized by stable causal structures, whereas inefficient ones exhibit reinforcing feedback loops and atypical dependencies. The contributions of this study are twofold. First, it introduces an integrated clustering-causal inference pipeline as a methodological innovation for analyzing energy-intensive processes. Second, it provides actionable insights that enable foundry operators to optimize performance, reduce energy consumption, and lower emissions.
Discovering Operational Patterns Using Image-Based Convolutional Clustering and Composite Evaluation: A Case Study in Foundry Melting Processes
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Industrial process monitoring increasingly relies on sensor-generated time-series data, yet the lack of labels, high variability, and operational noise make it difficult to extract meaningful patterns using conventional methods. Existing clustering techniques either rely on fixed distance metrics or deep models designed for static data, limiting their ability to handle dynamic, unstructured industrial sequences. Addressing this gap, this paper proposes a novel framework for unsupervised discovery of operational modes in univariate time-series data using image-based convolutional clustering with composite internal evaluation. The proposed framework improves upon existing approaches in three ways: (1) raw time-series sequences are transformed into grayscale matrix representations via overlapping sliding windows, allowing effective feature extraction using a deep convolutional autoencoder; (2) the framework integrates both soft and hard clustering outputs and refines the selection through a two-stage strategy; and (3) clustering performance is objectively evaluated by a newly developed composite score, S_eva, which combines normalized Silhouette, Calinski-Harabasz, and Davies-Bouldin indices. Applied to over 3900 furnace melting operations from a Nordic foundry, the method identifies seven explainable operational patterns, revealing significant differences in energy consumption, thermal dynamics, and production duration. Compared to classical and deep clustering baselines, the proposed approach achieves superior overall performance, greater robustness, and domain-aligned explainability. The framework addresses key challenges in unsupervised time-series analysis, such as sequence irregularity, overlapping modes, and metric inconsistency, and provides a generalizable solution for data-driven diagnostics and energy optimization in industrial systems.
Multi-Agent Multimodal Large Language Model Framework for Automated Interpretation of Fuel Efficiency Analytics in Public Transportation
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Enhancing fuel efficiency in public transportation requires the integration of complex multimodal data into interpretable, decision-relevant insights. However, traditional analytics and visualization methods often yield fragmented outputs that demand extensive human interpretation, limiting scalability and consistency. This study presents a multi-agent framework that leverages multimodal large language models (LLMs) to automate data narration and energy insight generation. The framework coordinates three specialized agents, including a data narration agent, an LLM-as-a-judge agent, and an optional human-in-the-loop evaluator, to iteratively transform analytical artifacts into coherent, stakeholder-oriented reports. The system is validated through a real-world case study on public bus transportation in Northern Jutland, Denmark, where fuel efficiency data from 4006 trips are analyzed using Gaussian Mixture Model clustering. Comparative experiments across five state-of-the-art LLMs and three prompting paradigms identify GPT-4.1 mini with Chain-of-Thought prompting as the optimal configuration, achieving 97.3% narrative accuracy while balancing interpretability and computational cost. The findings demonstrate that multi-agent orchestration significantly enhances factual precision, coherence, and scalability in LLM-based reporting. The proposed framework establishes a replicable and domain-adaptive methodology for AI-driven narrative generation and decision support in energy informatics.
GRAIT: Gradient-Driven Refusal-Aware Instruction Tuning for Effective Hallucination Mitigation
Feb 09, 2025Abstract:Refusal-Aware Instruction Tuning (RAIT) aims to enhance Large Language Models (LLMs) by improving their ability to refuse responses to questions beyond their knowledge, thereby reducing hallucinations and improving reliability. Effective RAIT must address two key challenges: firstly, effectively reject unknown questions to minimize hallucinations; secondly, avoid over-refusal to ensure questions that can be correctly answered are not rejected, thereby maintain the helpfulness of LLM outputs. In this paper, we address the two challenges by deriving insightful observations from the gradient-based perspective, and proposing the Gradient-driven Refusal Aware Instruction Tuning Framework GRAIT: (1) employs gradient-driven sample selection to effectively minimize hallucinations and (2) introduces an adaptive weighting mechanism during fine-tuning to reduce the risk of over-refusal, achieving the balance between accurate refusals and maintaining useful responses. Experimental evaluations on open-ended and multiple-choice question answering tasks demonstrate that GRAIT significantly outperforms existing RAIT methods in the overall performance. The source code and data will be available at https://github.com/opendatalab/GRAIT .
DataPro -- A Standardized Data Understanding and Processing Procedure: A Case Study of an Eco-Driving Project
Jan 21, 2025Abstract:A systematic pipeline for data processing and knowledge discovery is essential to extracting knowledge from big data and making recommendations for operational decision-making. The CRISP-DM model is the de-facto standard for developing data-mining projects in practice. However, advancements in data processing technologies require enhancements to this framework. This paper presents the DataPro (a standardized data understanding and processing procedure) model, which extends CRISP-DM and emphasizes the link between data scientists and stakeholders by adding the "technical understanding" and "implementation" phases. Firstly, the "technical understanding" phase aligns business demands with technical requirements, ensuring the technical team's accurate comprehension of business goals. Next, the "implementation" phase focuses on the practical application of developed data science models, ensuring theoretical models are effectively applied in business contexts. Furthermore, clearly defining roles and responsibilities in each phase enhances management and communication among all participants. Afterward, a case study on an eco-driving data science project for fuel efficiency analysis in the Danish public transportation sector illustrates the application of the DataPro model. By following the proposed framework, the project identified key business objectives, translated them into technical requirements, and developed models that provided actionable insights for reducing fuel consumption. Finally, the model is evaluated qualitatively, demonstrating its superiority over other data science procedures.
Utilize the Flow before Stepping into the Same River Twice: Certainty Represented Knowledge Flow for Refusal-Aware Instruction Tuning
Oct 09, 2024



Abstract:Refusal-Aware Instruction Tuning (RAIT) enables Large Language Models (LLMs) to refuse to answer unknown questions. By modifying responses of unknown questions in the training data to refusal responses such as "I don't know", RAIT enhances the reliability of LLMs and reduces their hallucination. Generally, RAIT modifies training samples based on the correctness of the initial LLM's response. However, this crude approach can cause LLMs to excessively refuse answering questions they could have correctly answered, the problem we call over-refusal. In this paper, we explore two primary causes of over-refusal: Static conflict emerges when the RAIT data is constructed solely on correctness criteria, causing similar samples in the LLM's feature space to be assigned different labels (original vs. modified "I don't know"). Dynamic conflict occurs due to the changes of LLM's knowledge state during fine-tuning, which transforms previous unknown questions into knowns, while the training data, which is constructed based on the initial LLM, remains unchanged. These conflicts cause the trained LLM to misclassify known questions as unknown, resulting in over-refusal. To address this issue, we introduce Certainty Represented Knowledge Flow for Refusal-Aware Instructions Construction (CRaFT). CRaFT centers on two main contributions: First, we additionally incorporate response certainty to selectively filter and modify data, reducing static conflicts. Second, we implement preliminary rehearsal training to characterize changes in the LLM's knowledge state, which helps mitigate dynamic conflicts during the fine-tuning process. We conducted extensive experiments on open-ended question answering and multiple-choice question task. Experiment results show that CRaFT can improve LLM's overall performance during the RAIT process. Source code and training data will be released at Github.
A Scoping Review of Energy-Efficient Driving Behaviors and Applied State-of-the-Art AI Methods
Mar 04, 2024
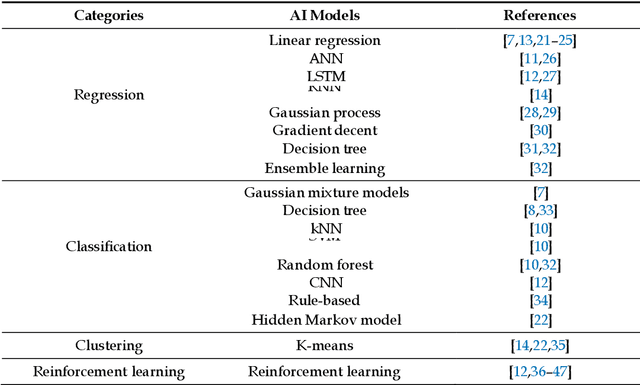
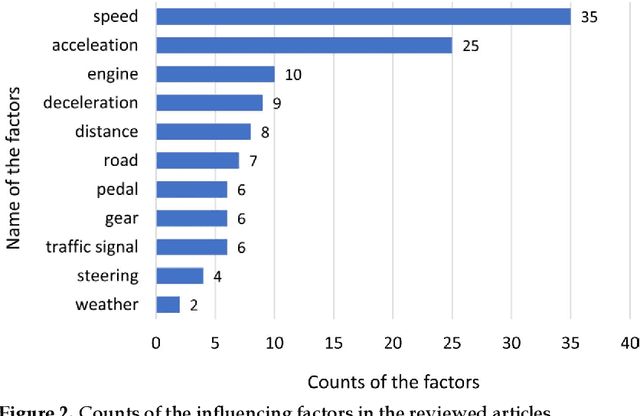
Abstract:The transportation sector remains a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions. The understanding of energy-efficient driving behaviors and utilization of energy-efficient driving strategies are essential to reduce vehicles' fuel consumption. However, there is no comprehensive investigation into energy-efficient driving behaviors and strategies. Furthermore, many state-of-the-art AI models have been applied for the analysis of eco-friendly driving styles, but no overview is available. To fill the gap, this paper conducts a thorough literature review on ecological driving behaviors and styles and analyzes the driving factors influencing energy consumption and state-of-the-art methodologies. With a thorough scoping review process, the methodological and related data are compared. The results show that the factors that impact driving behaviors can be summarized into eleven features including speed, acceleration, deceleration, pedal, and so on. This paper finds that supervised/unsupervised learning algorithms and reinforcement learning frameworks have been popularly used to model the vehicle's energy consumption with multi-dimensional data. Furthermore, the literature shows that the driving data are collected from either simulators or real-world experiments, and the real-world data are mainly stored and transmitted by meters, controller area networks, onboard data services, smartphones, and additional sensors installed in the vehicle. Based on driving behavior factors, driver characteristics, and safety rules, this paper recommends nine energy-efficient driving styles including four guidelines for the drivers' selection and adjustment of the vehicle parameters, three recommendations for the energy-efficient driving styles in different driving scenarios, and two subjective suggestions for different types of drivers and employers.
A Novel Hybrid Feature Importance and Feature Interaction Detection Framework for Predictive Optimization in Industry 4.0 Applications
Mar 04, 2024Abstract:Advanced machine learning algorithms are increasingly utilized to provide data-based prediction and decision-making support in Industry 4.0. However, the prediction accuracy achieved by the existing models is insufficient to warrant practical implementation in real-world applications. This is because not all features present in real-world datasets possess a direct relevance to the predictive analysis being conducted. Consequently, the careful incorporation of select features has the potential to yield a substantial positive impact on the outcome. To address the research gap, this paper proposes a novel hybrid framework that combines the feature importance detector - local interpretable model-agnostic explanations (LIME) and the feature interaction detector - neural interaction detection (NID), to improve prediction accuracy. By applying the proposed framework, unnecessary features can be eliminated, and interactions are encoded to generate a more conducive dataset for predictive purposes. Subsequently, the proposed model is deployed to refine the prediction of electricity consumption in foundry processing. The experimental outcomes reveal an augmentation of up to 9.56% in the R2 score, and a diminution of up to 24.05% in the root mean square error.
A Data-Driven Two-Phase Multi-Split Causal Ensemble Model for Time Series
Mar 04, 2024



Abstract:Causal inference is a fundamental research topic for discovering the cause-effect relationships in many disciplines. However, not all algorithms are equally well-suited for a given dataset. For instance, some approaches may only be able to identify linear relationships, while others are applicable for non-linearities. Algorithms further vary in their sensitivity to noise and their ability to infer causal information from coupled vs. non-coupled time series. Therefore, different algorithms often generate different causal relationships for the same input. To achieve a more robust causal inference result, this publication proposes a novel data-driven two-phase multi-split causal ensemble model to combine the strengths of different causality base algorithms. In comparison to existing approaches, the proposed ensemble method reduces the influence of noise through a data partitioning scheme in the first phase. To achieve this, the data are initially divided into several partitions and the base algorithms are applied to each partition. Subsequently, Gaussian mixture models are used to identify the causal relationships derived from the different partitions that are likely to be valid. In the second phase, the identified relationships from each base algorithm are then merged based on three combination rules. The proposed ensemble approach is evaluated using multiple metrics, among them a newly developed evaluation index for causal ensemble approaches. We perform experiments using three synthetic datasets with different volumes and complexity, which are specifically designed to test causality detection methods under different circumstances while knowing the ground truth causal relationships. In these experiments, our causality ensemble outperforms each of its base algorithms. In practical applications, the use of the proposed method could hence lead to more robust and reliable causality results.
More Than Routing: Joint GPS and Route Modeling for Refine Trajectory Representation Learning
Feb 25, 2024



Abstract:Trajectory representation learning plays a pivotal role in supporting various downstream tasks. Traditional methods in order to filter the noise in GPS trajectories tend to focus on routing-based methods used to simplify the trajectories. However, this approach ignores the motion details contained in the GPS data, limiting the representation capability of trajectory representation learning. To fill this gap, we propose a novel representation learning framework that Joint GPS and Route Modelling based on self-supervised technology, namely JGRM. We consider GPS trajectory and route as the two modes of a single movement observation and fuse information through inter-modal information interaction. Specifically, we develop two encoders, each tailored to capture representations of route and GPS trajectories respectively. The representations from the two modalities are fed into a shared transformer for inter-modal information interaction. Eventually, we design three self-supervised tasks to train the model. We validate the effectiveness of the proposed method on two real datasets based on extensive experiments. The experimental results demonstrate that JGRM outperforms existing methods in both road segment representation and trajectory representation tasks. Our source code is available at Anonymous Github.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge