Zheng Ma
SSI-DM: Singularity Skipping Inversion of Diffusion Models
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Inverting real images into the noise space is essential for editing tasks using diffusion models, yet existing methods produce non-Gaussian noise with poor editability due to the inaccuracy in early noising steps. We identify the root cause: a mathematical singularity that renders inversion fundamentally ill-posed. We propose Singularity Skipping Inversion of Diffusion Models (SSI-DM), which bypasses this singular region by adding small noise before standard inversion. This simple approach produces inverted noise with natural Gaussian properties while maintaining reconstruction fidelity. As a plug-and-play technique compatible with general diffusion models, our method achieves superior performance on public image datasets for reconstruction and interpolation tasks, providing a principled and efficient solution to diffusion model inversion.
Empowering Small Language Models with Factual Hallucination-Aware Reasoning for Financial Classification
Jan 04, 2026Abstract:Small language models (SLMs) are increasingly used for financial classification due to their fast inference and local deployability. However, compared with large language models, SLMs are more prone to factual hallucinations in reasoning and exhibit weaker classification performance. This raises a natural question: Can mitigating factual hallucinations improve SLMs' financial classification? To address this, we propose a three-step pipeline named AAAI (Association Identification, Automated Detection, and Adaptive Inference). Experiments on three representative SLMs reveal that: (1) factual hallucinations are positively correlated with misclassifications; (2) encoder-based verifiers effectively detect factual hallucinations; and (3) incorporating feedback on factual errors enables SLMs' adaptive inference that enhances classification performance. We hope this pipeline contributes to trustworthy and effective applications of SLMs in finance.
Towards Multiple Missing Values-resistant Unsupervised Graph Anomaly Detection
Nov 13, 2025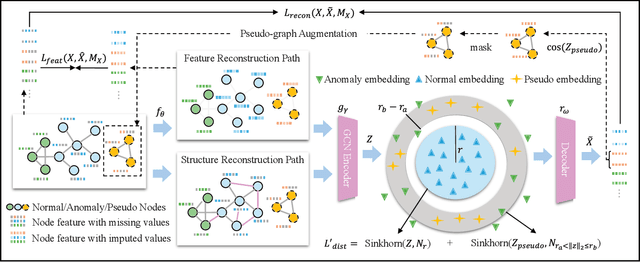
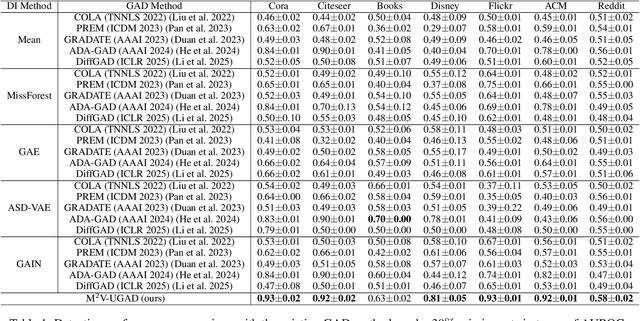
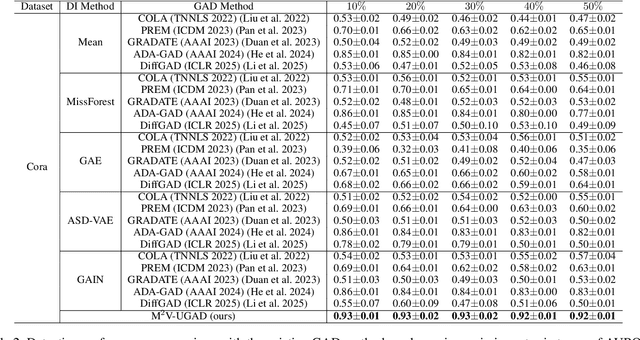
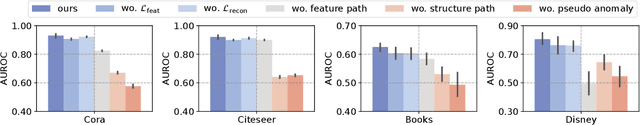
Abstract:Unsupervised graph anomaly detection (GAD) has received increasing attention in recent years, which aims to identify data anomalous patterns utilizing only unlabeled node information from graph-structured data. However, prevailing unsupervised GAD methods typically presuppose complete node attributes and structure information, a condition hardly satisfied in real-world scenarios owing to privacy, collection errors or dynamic node arrivals. Existing standard imputation schemes risk "repairing" rare anomalous nodes so that they appear normal, thereby introducing imputation bias into the detection process. In addition, when both node attributes and edges are missing simultaneously, estimation errors in one view can contaminate the other, causing cross-view interference that further undermines the detection performance. To overcome these challenges, we propose M$^2$V-UGAD, a multiple missing values-resistant unsupervised GAD framework on incomplete graphs. Specifically, a dual-pathway encoder is first proposed to independently reconstruct missing node attributes and graph structure, thereby preventing errors in one view from propagating to the other. The two pathways are then fused and regularized in a joint latent space so that normals occupy a compact inner manifold while anomalies reside on an outer shell. Lastly, to mitigate imputation bias, we sample latent codes just outside the normal region and decode them into realistic node features and subgraphs, providing hard negative examples that sharpen the decision boundary. Experiments on seven public benchmarks demonstrate that M$^2$V-UGAD consistently outperforms existing unsupervised GAD methods across varying missing rates.
Towards Effective Open-set Graph Class-incremental Learning
Jul 23, 2025Abstract:Graph class-incremental learning (GCIL) allows graph neural networks (GNNs) to adapt to evolving graph analytical tasks by incrementally learning new class knowledge while retaining knowledge of old classes. Existing GCIL methods primarily focus on a closed-set assumption, where all test samples are presumed to belong to previously known classes. Such an assumption restricts their applicability in real-world scenarios, where unknown classes naturally emerge during inference, and are absent during training. In this paper, we explore a more challenging open-set graph class-incremental learning scenario with two intertwined challenges: catastrophic forgetting of old classes, which impairs the detection of unknown classes, and inadequate open-set recognition, which destabilizes the retention of learned knowledge. To address the above problems, a novel OGCIL framework is proposed, which utilizes pseudo-sample embedding generation to effectively mitigate catastrophic forgetting and enable robust detection of unknown classes. To be specific, a prototypical conditional variational autoencoder is designed to synthesize node embeddings for old classes, enabling knowledge replay without storing raw graph data. To handle unknown classes, we employ a mixing-based strategy to generate out-of-distribution (OOD) samples from pseudo in-distribution and current node embeddings. A novel prototypical hypersphere classification loss is further proposed, which anchors in-distribution embeddings to their respective class prototypes, while repelling OOD embeddings away. Instead of assigning all unknown samples into one cluster, our proposed objective function explicitly models them as outliers through prototype-aware rejection regions, ensuring a robust open-set recognition. Extensive experiments on five benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of OGCIL over existing GCIL and open-set GNN methods.
Cognitive-Radio Functionality: A Novel Configuration for STAR-RIS assisted RSMA Networks
May 30, 2025Abstract:Cognitive radio rate-splitting multiple access (CR-RSMA) has emerged as a promising multiple access framework that can efficiently manage interference and adapt dynamically to heterogeneous quality-of-service (QoS) requirements. To effectively support such demanding access schemes, programmable wireless environments have attracted considerable attention, especially through simultaneously transmitting and reflecting reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (STAR-RISs), which can enable full-space control of signal propagation in asymmetric user deployments. In this paper, we propose the cognitive radio (CR) functionality for STAR-RIS-assisted CR-RSMA systems, leveraging the unique capability of the STAR-RIS to combine element and power splitting for adaptive control of transmission and reflection in CR scenarios. Specifically, the proposed CR functionality partitions the STAR-RIS into two regions independently controlling the transmission and reflection of signals, simultaneously ensuring the required QoS for the primary user and enhancing the performance of the secondary user. To accurately characterize the system performance, we derive analytical expressions for the ergodic rate of the secondary user and the outage rate of the primary user under Nakagami-m fading. Finally, simulation results show that the proposed approach effectively manages interference, guarantees the QoS of the primary user, and significantly improves the throughput of the secondary user, highlighting STAR-RIS as an efficient solution for CR-RSMA-based services.
DeepRTE: Pre-trained Attention-based Neural Network for Radiative Tranfer
May 29, 2025Abstract:In this study, we propose a novel neural network approach, termed DeepRTE, to address the steady-state Radiative Transfer Equation (RTE). The RTE is a differential-integral equation that governs the propagation of radiation through a participating medium, with applications spanning diverse domains such as neutron transport, atmospheric radiative transfer, heat transfer, and optical imaging. Our proposed DeepRTE framework leverages pre-trained attention-based neural networks to solve the RTE with high accuracy and computational efficiency. The efficacy of the proposed approach is substantiated through comprehensive numerical experiments.
Extract, Match, and Score: An Evaluation Paradigm for Long Question-context-answer Triplets in Financial Analysis
Mar 20, 2025Abstract:The rapid advancement of large language models (LLMs) has sparked widespread adoption across diverse applications, making robust evaluation frameworks crucial for assessing their performance. While conventional evaluation metrics remain applicable for shorter texts, their efficacy diminishes when evaluating the quality of long-form answers. This limitation is particularly critical in real-world scenarios involving extended questions, extensive context, and long-form answers, such as financial analysis or regulatory compliance. In this paper, we use a practical financial use case to illustrate applications that handle "long question-context-answer triplets". We construct a real-world financial dataset comprising long triplets and demonstrate the inadequacies of traditional metrics. To address this, we propose an effective Extract, Match, and Score (EMS) evaluation approach tailored to the complexities of long-form LLMs' outputs, providing practitioners with a reliable methodology for assessing LLMs' performance in complex real-world scenarios.
Exploring the Reliability of Self-explanation and its Relationship with Classification in Language Model-driven Financial Analysis
Mar 20, 2025Abstract:Language models (LMs) have exhibited exceptional versatility in reasoning and in-depth financial analysis through their proprietary information processing capabilities. Previous research focused on evaluating classification performance while often overlooking explainability or pre-conceived that refined explanation corresponds to higher classification accuracy. Using a public dataset in finance domain, we quantitatively evaluated self-explanations by LMs, focusing on their factuality and causality. We identified the statistically significant relationship between the accuracy of classifications and the factuality or causality of self-explanations. Our study built an empirical foundation for approximating classification confidence through self-explanations and for optimizing classification via proprietary reasoning.
CapArena: Benchmarking and Analyzing Detailed Image Captioning in the LLM Era
Mar 16, 2025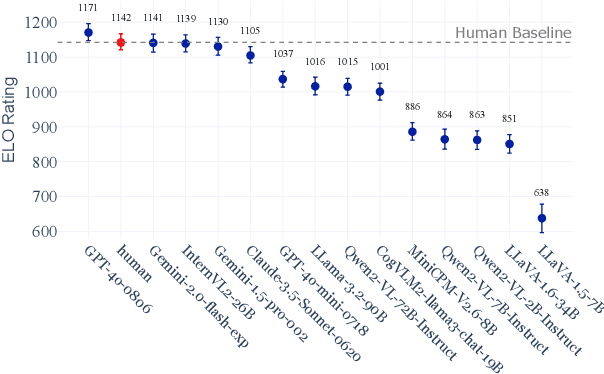

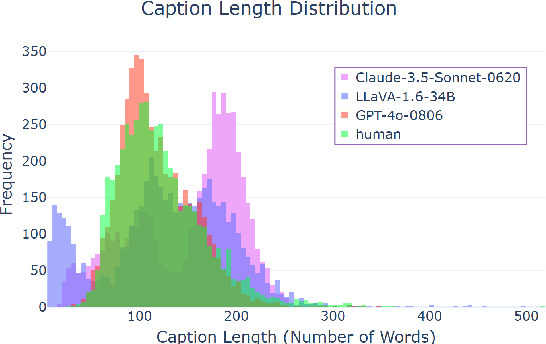
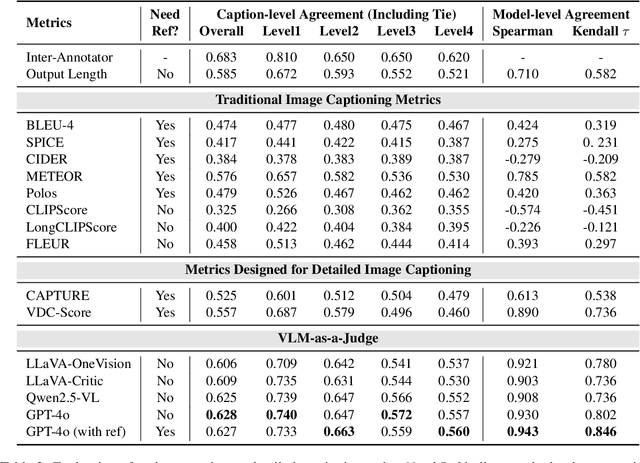
Abstract:Image captioning has been a longstanding challenge in vision-language research. With the rise of LLMs, modern Vision-Language Models (VLMs) generate detailed and comprehensive image descriptions. However, benchmarking the quality of such captions remains unresolved. This paper addresses two key questions: (1) How well do current VLMs actually perform on image captioning, particularly compared to humans? We built CapArena, a platform with over 6000 pairwise caption battles and high-quality human preference votes. Our arena-style evaluation marks a milestone, showing that leading models like GPT-4o achieve or even surpass human performance, while most open-source models lag behind. (2) Can automated metrics reliably assess detailed caption quality? Using human annotations from CapArena, we evaluate traditional and recent captioning metrics, as well as VLM-as-a-Judge. Our analysis reveals that while some metrics (e.g., METEOR) show decent caption-level agreement with humans, their systematic biases lead to inconsistencies in model ranking. In contrast, VLM-as-a-Judge demonstrates robust discernment at both the caption and model levels. Building on these insights, we release CapArena-Auto, an accurate and efficient automated benchmark for detailed captioning, achieving 94.3% correlation with human rankings at just $4 per test. Data and resources will be open-sourced at https://caparena.github.io.
Semi-supervised Anomaly Detection with Extremely Limited Labels in Dynamic Graphs
Jan 25, 2025Abstract:Semi-supervised graph anomaly detection (GAD) has recently received increasing attention, which aims to distinguish anomalous patterns from graphs under the guidance of a moderate amount of labeled data and a large volume of unlabeled data. Although these proposed semi-supervised GAD methods have achieved great success, their superior performance will be seriously degraded when the provided labels are extremely limited due to some unpredictable factors. Besides, the existing methods primarily focus on anomaly detection in static graphs, and little effort was paid to consider the continuous evolution characteristic of graphs over time (dynamic graphs). To address these challenges, we propose a novel GAD framework (EL$^{2}$-DGAD) to tackle anomaly detection problem in dynamic graphs with extremely limited labels. Specifically, a transformer-based graph encoder model is designed to more effectively preserve evolving graph structures beyond the local neighborhood. Then, we incorporate an ego-context hypersphere classification loss to classify temporal interactions according to their structure and temporal neighborhoods while ensuring the normal samples are mapped compactly against anomalous data. Finally, the above loss is further augmented with an ego-context contrasting module which utilizes unlabeled data to enhance model generalization. Extensive experiments on four datasets and three label rates demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method in comparison to the existing GAD methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge