Yingzhu Zhao
Extract, Match, and Score: An Evaluation Paradigm for Long Question-context-answer Triplets in Financial Analysis
Mar 20, 2025Abstract:The rapid advancement of large language models (LLMs) has sparked widespread adoption across diverse applications, making robust evaluation frameworks crucial for assessing their performance. While conventional evaluation metrics remain applicable for shorter texts, their efficacy diminishes when evaluating the quality of long-form answers. This limitation is particularly critical in real-world scenarios involving extended questions, extensive context, and long-form answers, such as financial analysis or regulatory compliance. In this paper, we use a practical financial use case to illustrate applications that handle "long question-context-answer triplets". We construct a real-world financial dataset comprising long triplets and demonstrate the inadequacies of traditional metrics. To address this, we propose an effective Extract, Match, and Score (EMS) evaluation approach tailored to the complexities of long-form LLMs' outputs, providing practitioners with a reliable methodology for assessing LLMs' performance in complex real-world scenarios.
A Unified Speaker Adaptation Approach for ASR
Oct 16, 2021

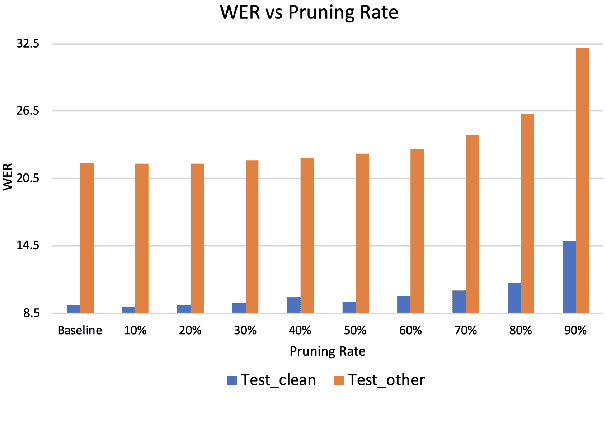

Abstract:Transformer models have been used in automatic speech recognition (ASR) successfully and yields state-of-the-art results. However, its performance is still affected by speaker mismatch between training and test data. Further finetuning a trained model with target speaker data is the most natural approach for adaptation, but it takes a lot of compute and may cause catastrophic forgetting to the existing speakers. In this work, we propose a unified speaker adaptation approach consisting of feature adaptation and model adaptation. For feature adaptation, we employ a speaker-aware persistent memory model which generalizes better to unseen test speakers by making use of speaker i-vectors to form a persistent memory. For model adaptation, we use a novel gradual pruning method to adapt to target speakers without changing the model architecture, which to the best of our knowledge, has never been explored in ASR. Specifically, we gradually prune less contributing parameters on model encoder to a certain sparsity level, and use the pruned parameters for adaptation, while freezing the unpruned parameters to keep the original model performance. We conduct experiments on the Librispeech dataset. Our proposed approach brings relative 2.74-6.52% word error rate (WER) reduction on general speaker adaptation. On target speaker adaptation, our method outperforms the baseline with up to 20.58% relative WER reduction, and surpasses the finetuning method by up to relative 2.54%. Besides, with extremely low-resource adaptation data (e.g., 1 utterance), our method could improve the WER by relative 6.53% with only a few epochs of training.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge