Bin Ma
Univ. Western Ontario
Beyond Lips: Integrating Gesture and Lip Cues for Robust Audio-visual Speaker Extraction
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Most audio-visual speaker extraction methods rely on synchronized lip recording to isolate the speech of a target speaker from a multi-talker mixture. However, in natural human communication, co-speech gestures are also temporally aligned with speech, often emphasizing specific words or syllables. These gestures provide complementary visual cues that can be especially valuable when facial or lip regions are occluded or distant. In this work, we move beyond lip-centric approaches and propose SeLG, a model that integrates both lip and upper-body gesture information for robust speaker extraction. SeLG features a cross-attention-based fusion mechanism that enables each visual modality to query and selectively attend to relevant speech features in the mixture. To improve the alignment of gesture representations with speech dynamics, SeLG also employs a contrastive InfoNCE loss that encourages gesture embeddings to align more closely with corresponding lip embeddings, which are more strongly correlated with speech. Experimental results on the YGD dataset, containing TED talks, demonstrate that the proposed contrastive learning strategy significantly improves gesture-based speaker extraction, and that our proposed SeLG model, by effectively fusing lip and gesture cues with an attention mechanism and InfoNCE loss, achieves superior performance compared to baselines, across both complete and partial (i.e., missing-modality) conditions.
LuSeeL: Language-queried Binaural Universal Sound Event Extraction and Localization
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Most universal sound extraction algorithms focus on isolating a target sound event from single-channel audio mixtures. However, the real world is three-dimensional, and binaural audio, which mimics human hearing, can capture richer spatial information, including sound source location. This spatial context is crucial for understanding and modeling complex auditory scenes, as it inherently informs sound detection and extraction. In this work, we propose a language-driven universal sound extraction network that isolates text-described sound events from binaural mixtures by effectively leveraging the spatial cues present in binaural signals. Additionally, we jointly predict the direction of arrival (DoA) of the target sound using spatial features from the extraction network. This dual-task approach exploits complementary location information to improve extraction performance while enabling accurate DoA estimation. Experimental results on the in-the-wild AudioCaps dataset show that our proposed LuSeeL model significantly outperforms single-channel and uni-task baselines.
E2E-AEC: Implementing an end-to-end neural network learning approach for acoustic echo cancellation
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:We propose a novel neural network-based end-to-end acoustic echo cancellation (E2E-AEC) method capable of streaming inference, which operates effectively without reliance on traditional linear AEC (LAEC) techniques and time delay estimation. Our approach includes several key strategies: First, we introduce and refine progressive learning to gradually enhance echo suppression. Second, our model employs knowledge transfer by initializing with a pre-trained LAECbased model, harnessing the insights gained from LAEC training. Third, we optimize the attention mechanism with a loss function applied on attention weights to achieve precise time alignment between the reference and microphone signals. Lastly, we incorporate voice activity detection to enhance speech quality and improve echo removal by masking the network output when near-end speech is absent. The effectiveness of our approach is validated through experiments conducted on public datasets.
FlowSE-GRPO: Training Flow Matching Speech Enhancement via Online Reinforcement Learning
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Generative speech enhancement offers a promising alternative to traditional discriminative methods by modeling the distribution of clean speech conditioned on noisy inputs. Post-training alignment via reinforcement learning (RL) effectively aligns generative models with human preferences and downstream metrics in domains such as natural language processing, but its use in speech enhancement remains limited, especially for online RL. Prior work explores offline methods like Direct Preference Optimization (DPO); online methods such as Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) remain largely uninvestigated. In this paper, we present the first successful integration of online GRPO into a flow-matching speech enhancement framework, enabling efficient post-training alignment to perceptual and task-oriented metrics with few update steps. Unlike prior GRPO work on Large Language Models, we adapt the algorithm to the continuous, time-series nature of speech and to the dynamics of flow-matching generative models. We show that optimizing a single reward yields rapid metric gains but often induces reward hacking that degrades audio fidelity despite higher scores. To mitigate this, we propose a multi-metric reward optimization strategy that balances competing objectives, substantially reducing overfitting and improving overall performance. Our experiments validate online GRPO for speech enhancement and provide practical guidance for RL-based post-training of generative audio models.
Diffusion Knows Transparency: Repurposing Video Diffusion for Transparent Object Depth and Normal Estimation
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Transparent objects remain notoriously hard for perception systems: refraction, reflection and transmission break the assumptions behind stereo, ToF and purely discriminative monocular depth, causing holes and temporally unstable estimates. Our key observation is that modern video diffusion models already synthesize convincing transparent phenomena, suggesting they have internalized the optical rules. We build TransPhy3D, a synthetic video corpus of transparent/reflective scenes: 11k sequences rendered with Blender/Cycles. Scenes are assembled from a curated bank of category-rich static assets and shape-rich procedural assets paired with glass/plastic/metal materials. We render RGB + depth + normals with physically based ray tracing and OptiX denoising. Starting from a large video diffusion model, we learn a video-to-video translator for depth (and normals) via lightweight LoRA adapters. During training we concatenate RGB and (noisy) depth latents in the DiT backbone and co-train on TransPhy3D and existing frame-wise synthetic datasets, yielding temporally consistent predictions for arbitrary-length input videos. The resulting model, DKT, achieves zero-shot SOTA on real and synthetic video benchmarks involving transparency: ClearPose, DREDS (CatKnown/CatNovel), and TransPhy3D-Test. It improves accuracy and temporal consistency over strong image/video baselines, and a normal variant sets the best video normal estimation results on ClearPose. A compact 1.3B version runs at ~0.17 s/frame. Integrated into a grasping stack, DKT's depth boosts success rates across translucent, reflective and diffuse surfaces, outperforming prior estimators. Together, these results support a broader claim: "Diffusion knows transparency." Generative video priors can be repurposed, efficiently and label-free, into robust, temporally coherent perception for challenging real-world manipulation.
FunAudio-ASR Technical Report
Sep 15, 2025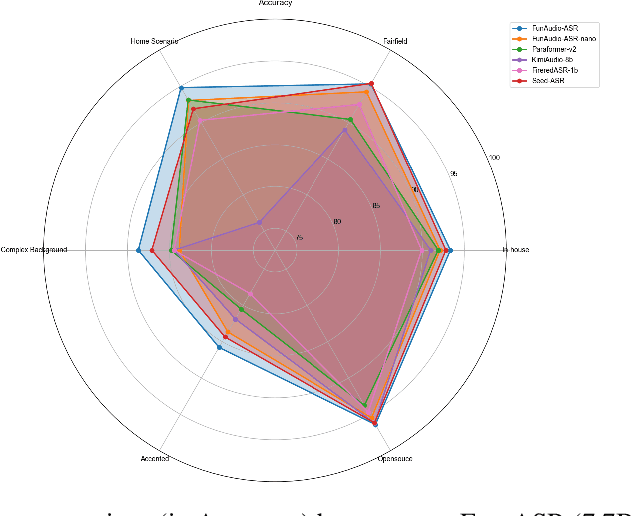
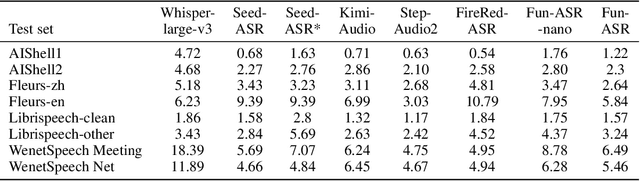
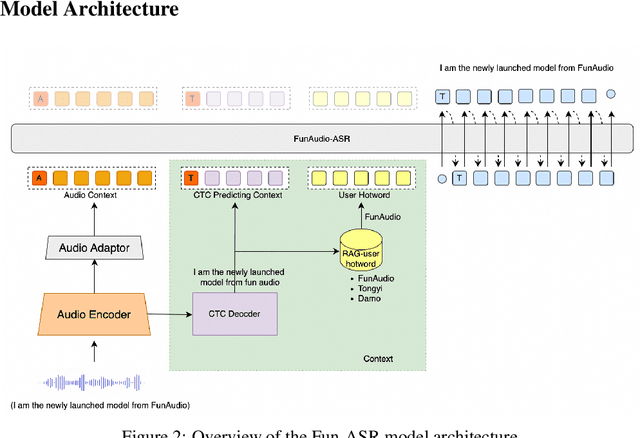
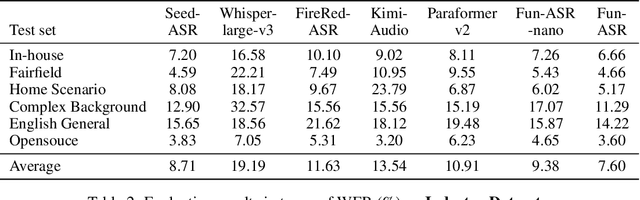
Abstract:In recent years, automatic speech recognition (ASR) has witnessed transformative advancements driven by three complementary paradigms: data scaling, model size scaling, and deep integration with large language models (LLMs). However, LLMs are prone to hallucination, which can significantly degrade user experience in real-world ASR applications. In this paper, we present FunAudio-ASR, a large-scale, LLM-based ASR system that synergistically combines massive data, large model capacity, LLM integration, and reinforcement learning to achieve state-of-the-art performance across diverse and complex speech recognition scenarios. Moreover, FunAudio-ASR is specifically optimized for practical deployment, with enhancements in streaming capability, noise robustness, code-switching, hotword customization, and satisfying other real-world application requirements. Experimental results show that while most LLM-based ASR systems achieve strong performance on open-source benchmarks, they often underperform on real industry evaluation sets. Thanks to production-oriented optimizations, FunAudio-ASR achieves SOTA performance on real application datasets, demonstrating its effectiveness and robustness in practical settings.
Insight Rumors: A Novel Textual Rumor Locating and Marking Model Leveraging Att_BiMamba2 Network
Aug 18, 2025Abstract:With the development of social media networks, rumor detection models have attracted more and more attention. Whereas, these models primarily focus on classifying contexts as rumors or not, lacking the capability to locate and mark specific rumor content. To address this limitation, this paper proposes a novel rumor detection model named Insight Rumors to locate and mark rumor content within textual data. Specifically, we propose the Bidirectional Mamba2 Network with Dot-Product Attention (Att_BiMamba2), a network that constructs a bidirectional Mamba2 model and applies dot-product attention to weight and combine the outputs from both directions, thereby enhancing the representation of high-dimensional rumor features. Simultaneously, a Rumor Locating and Marking module is designed to locate and mark rumors. The module constructs a skip-connection network to project high-dimensional rumor features onto low-dimensional label features. Moreover, Conditional Random Fields (CRF) is employed to impose strong constraints on the output label features, ensuring accurate rumor content location. Additionally, a labeled dataset for rumor locating and marking is constructed, with the effectiveness of the proposed model is evaluated through comprehensive experiments. Extensive experiments indicate that the proposed scheme not only detects rumors accurately but also locates and marks them in context precisely, outperforming state-of-the-art schemes that can only discriminate rumors roughly.
ClearerVoice-Studio: Bridging Advanced Speech Processing Research and Practical Deployment
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:This paper introduces ClearerVoice-Studio, an open-source, AI-powered speech processing toolkit designed to bridge cutting-edge research and practical application. Unlike broad platforms like SpeechBrain and ESPnet, ClearerVoice-Studio focuses on interconnected speech tasks of speech enhancement, separation, super-resolution, and multimodal target speaker extraction. A key advantage is its state-of-the-art pretrained models, including FRCRN with 3 million uses and MossFormer with 2.5 million uses, optimized for real-world scenarios. It also offers model optimization tools, multi-format audio support, the SpeechScore evaluation toolkit, and user-friendly interfaces, catering to researchers, developers, and end-users. Its rapid adoption attracting 3000 GitHub stars and 239 forks highlights its academic and industrial impact. This paper details ClearerVoice-Studio's capabilities, architectures, training strategies, benchmarks, community impact, and future plan. Source code is available at https://github.com/modelscope/ClearerVoice-Studio.
Plug-and-Play Co-Occurring Face Attention for Robust Audio-Visual Speaker Extraction
May 27, 2025Abstract:Audio-visual speaker extraction isolates a target speaker's speech from a mixture speech signal conditioned on a visual cue, typically using the target speaker's face recording. However, in real-world scenarios, other co-occurring faces are often present on-screen, providing valuable speaker activity cues in the scene. In this work, we introduce a plug-and-play inter-speaker attention module to process these flexible numbers of co-occurring faces, allowing for more accurate speaker extraction in complex multi-person environments. We integrate our module into two prominent models: the AV-DPRNN and the state-of-the-art AV-TFGridNet. Extensive experiments on diverse datasets, including the highly overlapped VoxCeleb2 and sparsely overlapped MISP, demonstrate that our approach consistently outperforms baselines. Furthermore, cross-dataset evaluations on LRS2 and LRS3 confirm the robustness and generalizability of our method.
ZenFlow: Enabling Stall-Free Offloading Training via Asynchronous Updates
May 18, 2025Abstract:Fine-tuning large language models (LLMs) often exceeds GPU memory limits, prompting systems to offload model states to CPU memory. However, existing offloaded training frameworks like ZeRO-Offload treat all parameters equally and update the full model on the CPU, causing severe GPU stalls, where fast, expensive GPUs sit idle waiting for slow CPU updates and limited-bandwidth PCIe transfers. We present ZenFlow, a new offloading framework that prioritizes important parameters and decouples updates between GPU and CPU. ZenFlow performs in-place updates of important gradients on GPU, while asynchronously offloading and accumulating less important ones on CPU, fully overlapping CPU work with GPU computation. To scale across GPUs, ZenFlow introduces a lightweight gradient selection method that exploits a novel spatial and temporal locality property of important gradients, avoiding costly global synchronization. ZenFlow achieves up to 5x end-to-end speedup, 2x lower PCIe traffic, and reduces GPU stalls by over 85 percent, all while preserving accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge