Shengkui Zhao
LuSeeL: Language-queried Binaural Universal Sound Event Extraction and Localization
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Most universal sound extraction algorithms focus on isolating a target sound event from single-channel audio mixtures. However, the real world is three-dimensional, and binaural audio, which mimics human hearing, can capture richer spatial information, including sound source location. This spatial context is crucial for understanding and modeling complex auditory scenes, as it inherently informs sound detection and extraction. In this work, we propose a language-driven universal sound extraction network that isolates text-described sound events from binaural mixtures by effectively leveraging the spatial cues present in binaural signals. Additionally, we jointly predict the direction of arrival (DoA) of the target sound using spatial features from the extraction network. This dual-task approach exploits complementary location information to improve extraction performance while enabling accurate DoA estimation. Experimental results on the in-the-wild AudioCaps dataset show that our proposed LuSeeL model significantly outperforms single-channel and uni-task baselines.
Beyond Lips: Integrating Gesture and Lip Cues for Robust Audio-visual Speaker Extraction
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Most audio-visual speaker extraction methods rely on synchronized lip recording to isolate the speech of a target speaker from a multi-talker mixture. However, in natural human communication, co-speech gestures are also temporally aligned with speech, often emphasizing specific words or syllables. These gestures provide complementary visual cues that can be especially valuable when facial or lip regions are occluded or distant. In this work, we move beyond lip-centric approaches and propose SeLG, a model that integrates both lip and upper-body gesture information for robust speaker extraction. SeLG features a cross-attention-based fusion mechanism that enables each visual modality to query and selectively attend to relevant speech features in the mixture. To improve the alignment of gesture representations with speech dynamics, SeLG also employs a contrastive InfoNCE loss that encourages gesture embeddings to align more closely with corresponding lip embeddings, which are more strongly correlated with speech. Experimental results on the YGD dataset, containing TED talks, demonstrate that the proposed contrastive learning strategy significantly improves gesture-based speaker extraction, and that our proposed SeLG model, by effectively fusing lip and gesture cues with an attention mechanism and InfoNCE loss, achieves superior performance compared to baselines, across both complete and partial (i.e., missing-modality) conditions.
FlowSE-GRPO: Training Flow Matching Speech Enhancement via Online Reinforcement Learning
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Generative speech enhancement offers a promising alternative to traditional discriminative methods by modeling the distribution of clean speech conditioned on noisy inputs. Post-training alignment via reinforcement learning (RL) effectively aligns generative models with human preferences and downstream metrics in domains such as natural language processing, but its use in speech enhancement remains limited, especially for online RL. Prior work explores offline methods like Direct Preference Optimization (DPO); online methods such as Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) remain largely uninvestigated. In this paper, we present the first successful integration of online GRPO into a flow-matching speech enhancement framework, enabling efficient post-training alignment to perceptual and task-oriented metrics with few update steps. Unlike prior GRPO work on Large Language Models, we adapt the algorithm to the continuous, time-series nature of speech and to the dynamics of flow-matching generative models. We show that optimizing a single reward yields rapid metric gains but often induces reward hacking that degrades audio fidelity despite higher scores. To mitigate this, we propose a multi-metric reward optimization strategy that balances competing objectives, substantially reducing overfitting and improving overall performance. Our experiments validate online GRPO for speech enhancement and provide practical guidance for RL-based post-training of generative audio models.
E2E-AEC: Implementing an end-to-end neural network learning approach for acoustic echo cancellation
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:We propose a novel neural network-based end-to-end acoustic echo cancellation (E2E-AEC) method capable of streaming inference, which operates effectively without reliance on traditional linear AEC (LAEC) techniques and time delay estimation. Our approach includes several key strategies: First, we introduce and refine progressive learning to gradually enhance echo suppression. Second, our model employs knowledge transfer by initializing with a pre-trained LAECbased model, harnessing the insights gained from LAEC training. Third, we optimize the attention mechanism with a loss function applied on attention weights to achieve precise time alignment between the reference and microphone signals. Lastly, we incorporate voice activity detection to enhance speech quality and improve echo removal by masking the network output when near-end speech is absent. The effectiveness of our approach is validated through experiments conducted on public datasets.
FunAudio-ASR Technical Report
Sep 15, 2025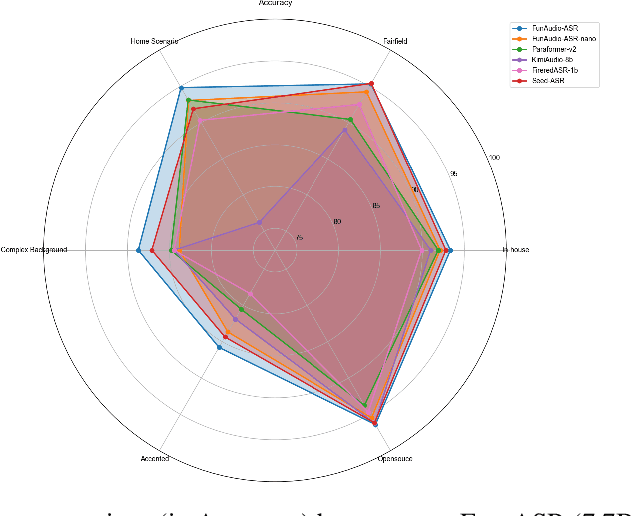
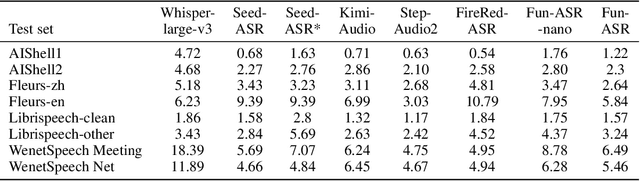
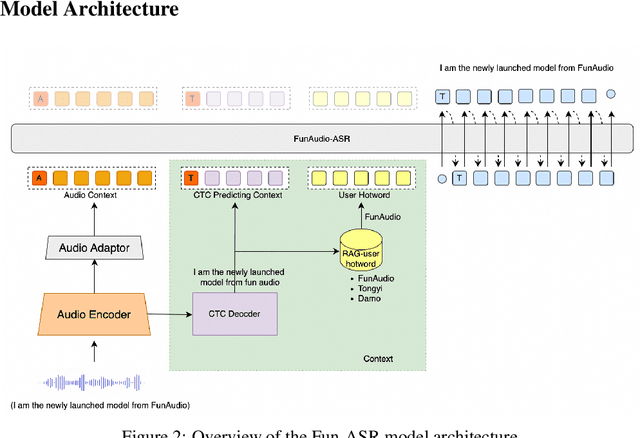
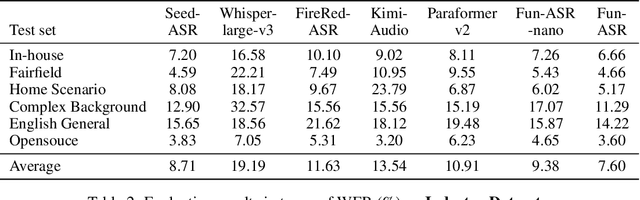
Abstract:In recent years, automatic speech recognition (ASR) has witnessed transformative advancements driven by three complementary paradigms: data scaling, model size scaling, and deep integration with large language models (LLMs). However, LLMs are prone to hallucination, which can significantly degrade user experience in real-world ASR applications. In this paper, we present FunAudio-ASR, a large-scale, LLM-based ASR system that synergistically combines massive data, large model capacity, LLM integration, and reinforcement learning to achieve state-of-the-art performance across diverse and complex speech recognition scenarios. Moreover, FunAudio-ASR is specifically optimized for practical deployment, with enhancements in streaming capability, noise robustness, code-switching, hotword customization, and satisfying other real-world application requirements. Experimental results show that while most LLM-based ASR systems achieve strong performance on open-source benchmarks, they often underperform on real industry evaluation sets. Thanks to production-oriented optimizations, FunAudio-ASR achieves SOTA performance on real application datasets, demonstrating its effectiveness and robustness in practical settings.
ClearerVoice-Studio: Bridging Advanced Speech Processing Research and Practical Deployment
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:This paper introduces ClearerVoice-Studio, an open-source, AI-powered speech processing toolkit designed to bridge cutting-edge research and practical application. Unlike broad platforms like SpeechBrain and ESPnet, ClearerVoice-Studio focuses on interconnected speech tasks of speech enhancement, separation, super-resolution, and multimodal target speaker extraction. A key advantage is its state-of-the-art pretrained models, including FRCRN with 3 million uses and MossFormer with 2.5 million uses, optimized for real-world scenarios. It also offers model optimization tools, multi-format audio support, the SpeechScore evaluation toolkit, and user-friendly interfaces, catering to researchers, developers, and end-users. Its rapid adoption attracting 3000 GitHub stars and 239 forks highlights its academic and industrial impact. This paper details ClearerVoice-Studio's capabilities, architectures, training strategies, benchmarks, community impact, and future plan. Source code is available at https://github.com/modelscope/ClearerVoice-Studio.
Plug-and-Play Co-Occurring Face Attention for Robust Audio-Visual Speaker Extraction
May 27, 2025Abstract:Audio-visual speaker extraction isolates a target speaker's speech from a mixture speech signal conditioned on a visual cue, typically using the target speaker's face recording. However, in real-world scenarios, other co-occurring faces are often present on-screen, providing valuable speaker activity cues in the scene. In this work, we introduce a plug-and-play inter-speaker attention module to process these flexible numbers of co-occurring faces, allowing for more accurate speaker extraction in complex multi-person environments. We integrate our module into two prominent models: the AV-DPRNN and the state-of-the-art AV-TFGridNet. Extensive experiments on diverse datasets, including the highly overlapped VoxCeleb2 and sparsely overlapped MISP, demonstrate that our approach consistently outperforms baselines. Furthermore, cross-dataset evaluations on LRS2 and LRS3 confirm the robustness and generalizability of our method.
Conditional Latent Diffusion-Based Speech Enhancement Via Dual Context Learning
Jan 17, 2025Abstract:Recently, the application of diffusion probabilistic models has advanced speech enhancement through generative approaches. However, existing diffusion-based methods have focused on the generation process in high-dimensional waveform or spectral domains, leading to increased generation complexity and slower inference speeds. Additionally, these methods have primarily modelled clean speech distributions, with limited exploration of noise distributions, thereby constraining the discriminative capability of diffusion models for speech enhancement. To address these issues, we propose a novel approach that integrates a conditional latent diffusion model (cLDM) with dual-context learning (DCL). Our method utilizes a variational autoencoder (VAE) to compress mel-spectrograms into a low-dimensional latent space. We then apply cLDM to transform the latent representations of both clean speech and background noise into Gaussian noise by the DCL process, and a parameterized model is trained to reverse this process, conditioned on noisy latent representations and text embeddings. By operating in a lower-dimensional space, the latent representations reduce the complexity of the generation process, while the DCL process enhances the model's ability to handle diverse and unseen noise environments. Our experiments demonstrate the strong performance of the proposed approach compared to existing diffusion-based methods, even with fewer iterative steps, and highlight the superior generalization capability of our models to out-of-domain noise datasets (https://github.com/modelscope/ClearerVoice-Studio).
HiFi-SR: A Unified Generative Transformer-Convolutional Adversarial Network for High-Fidelity Speech Super-Resolution
Jan 17, 2025



Abstract:The application of generative adversarial networks (GANs) has recently advanced speech super-resolution (SR) based on intermediate representations like mel-spectrograms. However, existing SR methods that typically rely on independently trained and concatenated networks may lead to inconsistent representations and poor speech quality, especially in out-of-domain scenarios. In this work, we propose HiFi-SR, a unified network that leverages end-to-end adversarial training to achieve high-fidelity speech super-resolution. Our model features a unified transformer-convolutional generator designed to seamlessly handle both the prediction of latent representations and their conversion into time-domain waveforms. The transformer network serves as a powerful encoder, converting low-resolution mel-spectrograms into latent space representations, while the convolutional network upscales these representations into high-resolution waveforms. To enhance high-frequency fidelity, we incorporate a multi-band, multi-scale time-frequency discriminator, along with a multi-scale mel-reconstruction loss in the adversarial training process. HiFi-SR is versatile, capable of upscaling any input speech signal between 4 kHz and 32 kHz to a 48 kHz sampling rate. Experimental results demonstrate that HiFi-SR significantly outperforms existing speech SR methods across both objective metrics and ABX preference tests, for both in-domain and out-of-domain scenarios (https://github.com/modelscope/ClearerVoice-Studio).
Emotional Dimension Control in Language Model-Based Text-to-Speech: Spanning a Broad Spectrum of Human Emotions
Sep 25, 2024Abstract:Current emotional text-to-speech (TTS) systems face challenges in mimicking a broad spectrum of human emotions due to the inherent complexity of emotions and limitations in emotional speech datasets and models. This paper proposes a TTS framework that facilitates control over pleasure, arousal, and dominance, and can synthesize a diversity of emotional styles without requiring any emotional speech data during TTS training. We train an emotional attribute predictor using only categorical labels from speech data, aligning with psychological research and incorporating anchored dimensionality reduction on self-supervised learning (SSL) features. The TTS framework converts text inputs into phonetic tokens via an autoregressive language model and uses pseudo-emotional dimensions to guide the parallel prediction of fine-grained acoustic details. Experiments conducted on the LibriTTS dataset demonstrate that our framework can synthesize speech with enhanced naturalness and a variety of emotional styles by effectively controlling emotional dimensions, even without the inclusion of any emotional speech during TTS training.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge