Tingting Wang
School of Communication and Information Engineering, Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Nanjing 2100023, China
Weighted Graph Clustering via Scale Contraction and Graph Structure Learning
Jan 24, 2026Abstract:Graph clustering aims to partition nodes into distinct clusters based on their similarity, thereby revealing relationships among nodes. Nevertheless, most existing methods do not fully utilize these edge weights. Leveraging edge weights in graph clustering tasks faces two critical challenges. (1) The introduction of edge weights may significantly increase storage space and training time, making it essential to reduce the graph scale while preserving nodes that are beneficial for the clustering task. (2) Edge weight information may inherently contain noise that negatively impacts clustering results. However, few studies can jointly optimize clustering and edge weights, which is crucial for mitigating the negative impact of noisy edges on clustering task. To address these challenges, we propose a contractile edge-weight-aware graph clustering network. Specifically, a cluster-oriented graph contraction module is designed to reduce the graph scale while preserving important nodes. An edge-weight-aware attention network is designed to identify and weaken noisy connections. In this way, we can more easily identify and mitigate the impact of noisy edges during the clustering process, thus enhancing clustering effectiveness. We conducted extensive experiments on three real-world weighted graph datasets. In particular, our model outperforms the best baseline, demonstrating its superior performance. Furthermore, experiments also show that the proposed graph contraction module can significantly reduce training time and storage space.
Investigating Self-regulated Learning Sequences within a Generative AI-based Intelligent Tutoring System
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:There has been a growing trend in employing generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) techniques to support learning. Moreover, scholars have reached a consensus on the critical role of self-regulated learning (SRL) in ensuring learning effectiveness within GenAI-assisted learning environments, making it essential to capture students' dynamic SRL patterns. In this study, we extracted students' interaction patterns with GenAI from trace data as they completed a problem-solving task within a GenAI-assisted intelligent tutoring system. Students' purpose of using GenAI was also analyzed from the perspective of information processing, i.e., information acquisition and information transformation. Using sequential and clustering analysis, this study classified participants into two groups based on their SRL sequences. These two groups differed in the frequency and temporal characteristics of GenAI use. In addition, most students used GenAI for information acquisition rather than information transformation, while the correlation between the purpose of using GenAI and learning performance was not statistically significant. Our findings inform both pedagogical design and the development of GenAI-assisted learning environments.
Plug-and-Play Co-Occurring Face Attention for Robust Audio-Visual Speaker Extraction
May 27, 2025Abstract:Audio-visual speaker extraction isolates a target speaker's speech from a mixture speech signal conditioned on a visual cue, typically using the target speaker's face recording. However, in real-world scenarios, other co-occurring faces are often present on-screen, providing valuable speaker activity cues in the scene. In this work, we introduce a plug-and-play inter-speaker attention module to process these flexible numbers of co-occurring faces, allowing for more accurate speaker extraction in complex multi-person environments. We integrate our module into two prominent models: the AV-DPRNN and the state-of-the-art AV-TFGridNet. Extensive experiments on diverse datasets, including the highly overlapped VoxCeleb2 and sparsely overlapped MISP, demonstrate that our approach consistently outperforms baselines. Furthermore, cross-dataset evaluations on LRS2 and LRS3 confirm the robustness and generalizability of our method.
HALO: Half Life-Based Outdated Fact Filtering in Temporal Knowledge Graphs
May 12, 2025Abstract:Outdated facts in temporal knowledge graphs (TKGs) result from exceeding the expiration date of facts, which negatively impact reasoning performance on TKGs. However, existing reasoning methods primarily focus on positive importance of historical facts, neglecting adverse effects of outdated facts. Besides, training on these outdated facts yields extra computational cost. To address these challenges, we propose an outdated fact filtering framework named HALO, which quantifies the temporal validity of historical facts by exploring the half-life theory to filter outdated facts in TKGs. HALO consists of three modules: the temporal fact attention module, the dynamic relation-aware encoder module, and the outdated fact filtering module. Firstly, the temporal fact attention module captures the evolution of historical facts over time to identify relevant facts. Secondly, the dynamic relation-aware encoder module is designed for efficiently predicting the half life of each fact. Finally, we construct a time decay function based on the half-life theory to quantify the temporal validity of facts and filter outdated facts. Experimental results show that HALO outperforms the state-of-the-art TKG reasoning methods on three public datasets, demonstrating its effectiveness in detecting and filtering outdated facts (Codes are available at https://github.com/yushuowiki/K-Half/tree/main ).
Weighted Graph Structure Learning with Attention Denoising for Node Classification
Mar 15, 2025Abstract:Node classification in graphs aims to predict the categories of unlabeled nodes by utilizing a small set of labeled nodes. However, weighted graphs often contain noisy edges and anomalous edge weights, which can distort fine-grained relationships between nodes and hinder accurate classification. We propose the Edge Weight-aware Graph Structure Learning (EWGSL) method, which combines weight learning and graph structure learning to address these issues. EWGSL improves node classification by redefining attention coefficients in graph attention networks to incorporate node features and edge weights. It also applies graph structure learning to sparsify attention coefficients and uses a modified InfoNCE loss function to enhance performance by adapting to denoised graph weights. Extensive experimental results show that EWGSL has an average Micro-F1 improvement of 17.8% compared with the best baseline.
Time-Graph Frequency Representation with Singular Value Decomposition for Neural Speech Enhancement
Dec 24, 2024Abstract:Time-frequency (T-F) domain methods for monaural speech enhancement have benefited from the success of deep learning. Recently, focus has been put on designing two-stream network models to predict amplitude mask and phase separately, or, coupling the amplitude and phase into Cartesian coordinates and constructing real and imaginary pairs. However, most methods suffer from the alignment modeling of amplitude and phase (real and imaginary pairs) in a two-stream network framework, which inevitably incurs performance restrictions. In this paper, we introduce a graph Fourier transform defined with the singular value decomposition (GFT-SVD), resulting in real-valued time-graph representation for neural speech enhancement. This real-valued representation-based GFT-SVD provides an ability to align the modeling of amplitude and phase, leading to avoiding recovering the target speech phase information. Our findings demonstrate the effects of real-valued time-graph representation based on GFT-SVD for neutral speech enhancement. The extensive speech enhancement experiments establish that the combination of GFT-SVD and DNN outperforms the combination of GFT with the eigenvector decomposition (GFT-EVD) and magnitude estimation UNet, and outperforms the short-time Fourier transform (STFT) and DNN, regarding objective intelligibility and perceptual quality. We release our source code at: https://github.com/Wangfighting0015/GFT\_project.
A Comprehensive Survey on Root Cause Analysis in (Micro) Services: Methodologies, Challenges, and Trends
Jul 23, 2024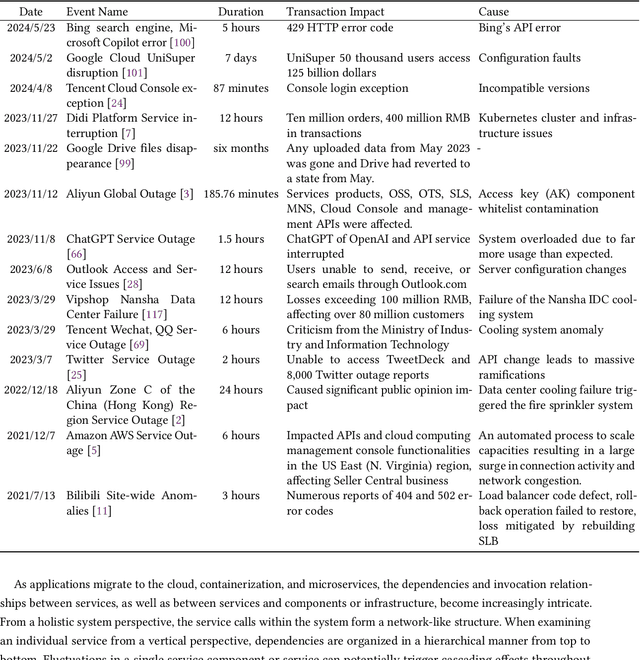
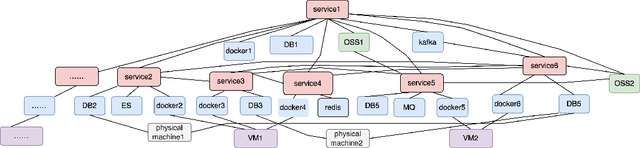
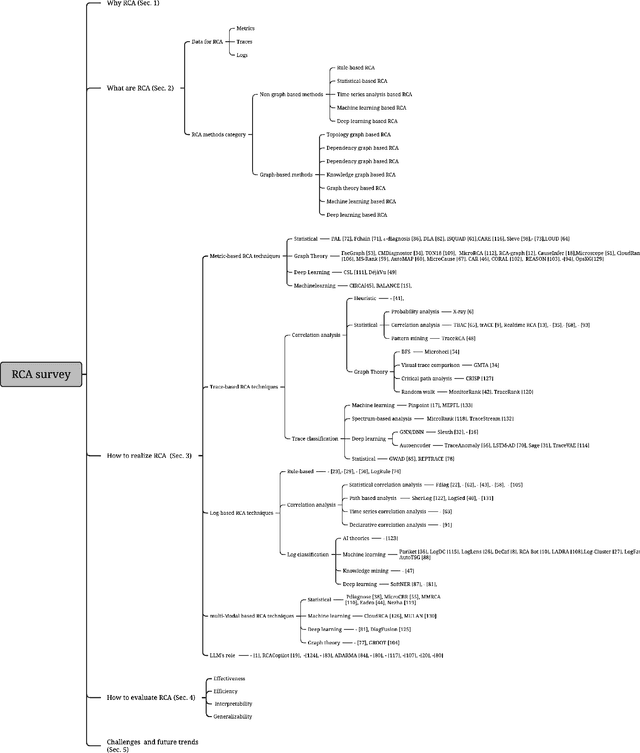
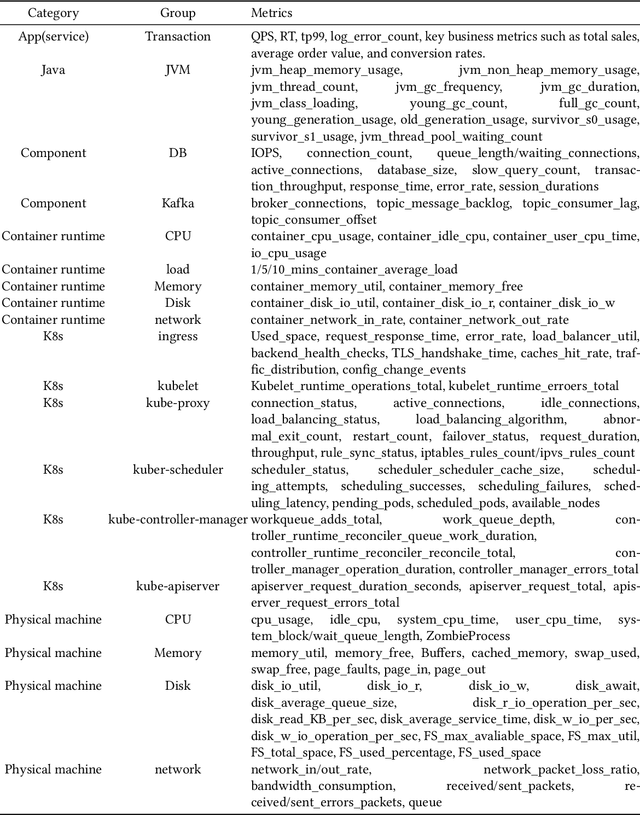
Abstract:The complex dependencies and propagative faults inherent in microservices, characterized by a dense network of interconnected services, pose significant challenges in identifying the underlying causes of issues. Prompt identification and resolution of disruptive problems are crucial to ensure rapid recovery and maintain system stability. Numerous methodologies have emerged to address this challenge, primarily focusing on diagnosing failures through symptomatic data. This survey aims to provide a comprehensive, structured review of root cause analysis (RCA) techniques within microservices, exploring methodologies that include metrics, traces, logs, and multi-model data. It delves deeper into the methodologies, challenges, and future trends within microservices architectures. Positioned at the forefront of AI and automation advancements, it offers guidance for future research directions.
Incorporating Higher-order Structural Information for Graph Clustering
Mar 19, 2024Abstract:Clustering holds profound significance in data mining. In recent years, graph convolutional network (GCN) has emerged as a powerful tool for deep clustering, integrating both graph structural information and node attributes. However, most existing methods ignore the higher-order structural information of the graph. Evidently, nodes within the same cluster can establish distant connections. Besides, recent deep clustering methods usually apply a self-supervised module to monitor the training process of their model, focusing solely on node attributes without paying attention to graph structure. In this paper, we propose a novel graph clustering network to make full use of graph structural information. To capture the higher-order structural information, we design a graph mutual infomax module, effectively maximizing mutual information between graph-level and node-level representations, and employ a trinary self-supervised module that includes modularity as a structural constraint. Our proposed model outperforms many state-of-the-art methods on various datasets, demonstrating its superiority.
KGroot: Enhancing Root Cause Analysis through Knowledge Graphs and Graph Convolutional Neural Networks
Feb 11, 2024


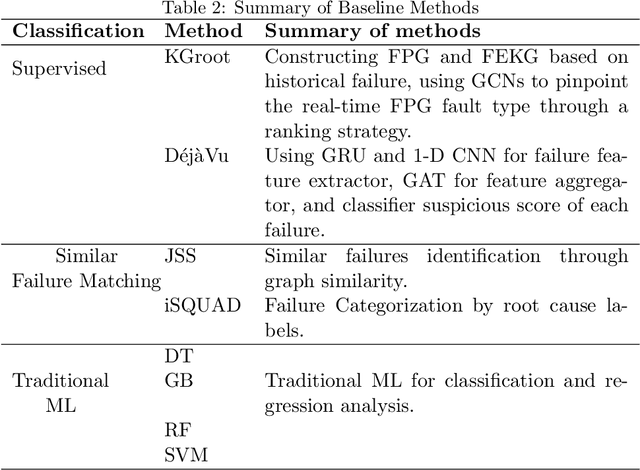
Abstract:Fault localization is challenging in online micro-service due to the wide variety of monitoring data volume, types, events and complex interdependencies in service and components. Faults events in services are propagative and can trigger a cascade of alerts in a short period of time. In the industry, fault localization is typically conducted manually by experienced personnel. This reliance on experience is unreliable and lacks automation. Different modules present information barriers during manual localization, making it difficult to quickly align during urgent faults. This inefficiency lags stability assurance to minimize fault detection and repair time. Though actionable methods aimed to automatic the process, the accuracy and efficiency are less than satisfactory. The precision of fault localization results is of paramount importance as it underpins engineers trust in the diagnostic conclusions, which are derived from multiple perspectives and offer comprehensive insights. Therefore, a more reliable method is required to automatically identify the associative relationships among fault events and propagation path. To achieve this, KGroot uses event knowledge and the correlation between events to perform root cause reasoning by integrating knowledge graphs and GCNs for RCA. FEKG is built based on historical data, an online graph is constructed in real-time when a failure event occurs, and the similarity between each knowledge graph and online graph is compared using GCNs to pinpoint the fault type through a ranking strategy. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate KGroot can locate the root cause with accuracy of 93.5% top 3 potential causes in second-level. This performance matches the level of real-time fault diagnosis in the industrial environment and significantly surpasses state-of-the-art baselines in RCA in terms of effectiveness and efficiency.
Three-Stage Cascade Framework for Blurry Video Frame Interpolation
Oct 09, 2023Abstract:Blurry video frame interpolation (BVFI) aims to generate high-frame-rate clear videos from low-frame-rate blurry videos, is a challenging but important topic in the computer vision community. Blurry videos not only provide spatial and temporal information like clear videos, but also contain additional motion information hidden in each blurry frame. However, existing BVFI methods usually fail to fully leverage all valuable information, which ultimately hinders their performance. In this paper, we propose a simple end-to-end three-stage framework to fully explore useful information from blurry videos. The frame interpolation stage designs a temporal deformable network to directly sample useful information from blurry inputs and synthesize an intermediate frame at an arbitrary time interval. The temporal feature fusion stage explores the long-term temporal information for each target frame through a bi-directional recurrent deformable alignment network. And the deblurring stage applies a transformer-empowered Taylor approximation network to recursively recover the high-frequency details. The proposed three-stage framework has clear task assignment for each module and offers good expandability, the effectiveness of which are demonstrated by various experimental results. We evaluate our model on four benchmarks, including the Adobe240 dataset, GoPro dataset, YouTube240 dataset and Sony dataset. Quantitative and qualitative results indicate that our model outperforms existing SOTA methods. Besides, experiments on real-world blurry videos also indicate the good generalization ability of our model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge