Faming Fang
First-order State Space Model for Lightweight Image Super-resolution
Sep 10, 2025
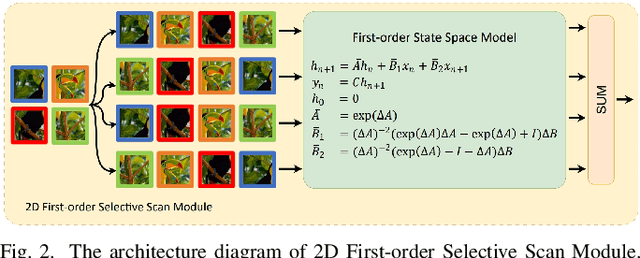
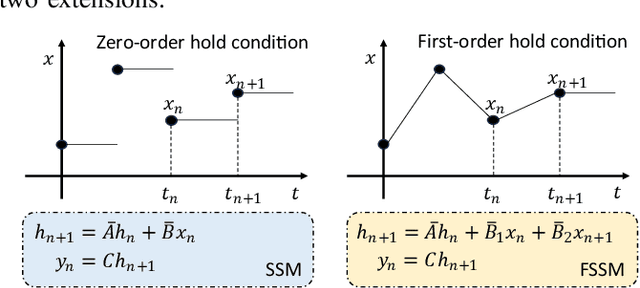

Abstract:State space models (SSMs), particularly Mamba, have shown promise in NLP tasks and are increasingly applied to vision tasks. However, most Mamba-based vision models focus on network architecture and scan paths, with little attention to the SSM module. In order to explore the potential of SSMs, we modified the calculation process of SSM without increasing the number of parameters to improve the performance on lightweight super-resolution tasks. In this paper, we introduce the First-order State Space Model (FSSM) to improve the original Mamba module, enhancing performance by incorporating token correlations. We apply a first-order hold condition in SSMs, derive the new discretized form, and analyzed cumulative error. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that FSSM improves the performance of MambaIR on five benchmark datasets without additionally increasing the number of parameters, and surpasses current lightweight SR methods, achieving state-of-the-art results.
* Accept by ICASSP 2025 (Oral)
Harmonizing knowledge Transfer in Neural Network with Unified Distillation
Sep 27, 2024Abstract:Knowledge distillation (KD), known for its ability to transfer knowledge from a cumbersome network (teacher) to a lightweight one (student) without altering the architecture, has been garnering increasing attention. Two primary categories emerge within KD methods: feature-based, focusing on intermediate layers' features, and logits-based, targeting the final layer's logits. This paper introduces a novel perspective by leveraging diverse knowledge sources within a unified KD framework. Specifically, we aggregate features from intermediate layers into a comprehensive representation, effectively gathering semantic information from different stages and scales. Subsequently, we predict the distribution parameters from this representation. These steps transform knowledge from the intermediate layers into corresponding distributive forms, thereby allowing for knowledge distillation through a unified distribution constraint at different stages of the network, ensuring the comprehensiveness and coherence of knowledge transfer. Numerous experiments were conducted to validate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
Three-Stage Cascade Framework for Blurry Video Frame Interpolation
Oct 09, 2023Abstract:Blurry video frame interpolation (BVFI) aims to generate high-frame-rate clear videos from low-frame-rate blurry videos, is a challenging but important topic in the computer vision community. Blurry videos not only provide spatial and temporal information like clear videos, but also contain additional motion information hidden in each blurry frame. However, existing BVFI methods usually fail to fully leverage all valuable information, which ultimately hinders their performance. In this paper, we propose a simple end-to-end three-stage framework to fully explore useful information from blurry videos. The frame interpolation stage designs a temporal deformable network to directly sample useful information from blurry inputs and synthesize an intermediate frame at an arbitrary time interval. The temporal feature fusion stage explores the long-term temporal information for each target frame through a bi-directional recurrent deformable alignment network. And the deblurring stage applies a transformer-empowered Taylor approximation network to recursively recover the high-frequency details. The proposed three-stage framework has clear task assignment for each module and offers good expandability, the effectiveness of which are demonstrated by various experimental results. We evaluate our model on four benchmarks, including the Adobe240 dataset, GoPro dataset, YouTube240 dataset and Sony dataset. Quantitative and qualitative results indicate that our model outperforms existing SOTA methods. Besides, experiments on real-world blurry videos also indicate the good generalization ability of our model.
Deep Unfolding Convolutional Dictionary Model for Multi-Contrast MRI Super-resolution and Reconstruction
Sep 03, 2023Abstract:Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) tasks often involve multiple contrasts. Recently, numerous deep learning-based multi-contrast MRI super-resolution (SR) and reconstruction methods have been proposed to explore the complementary information from the multi-contrast images. However, these methods either construct parameter-sharing networks or manually design fusion rules, failing to accurately model the correlations between multi-contrast images and lacking certain interpretations. In this paper, we propose a multi-contrast convolutional dictionary (MC-CDic) model under the guidance of the optimization algorithm with a well-designed data fidelity term. Specifically, we bulid an observation model for the multi-contrast MR images to explicitly model the multi-contrast images as common features and unique features. In this way, only the useful information in the reference image can be transferred to the target image, while the inconsistent information will be ignored. We employ the proximal gradient algorithm to optimize the model and unroll the iterative steps into a deep CDic model. Especially, the proximal operators are replaced by learnable ResNet. In addition, multi-scale dictionaries are introduced to further improve the model performance. We test our MC-CDic model on multi-contrast MRI SR and reconstruction tasks. Experimental results demonstrate the superior performance of the proposed MC-CDic model against existing SOTA methods. Code is available at https://github.com/lpcccc-cv/MC-CDic.
Deep Richardson-Lucy Deconvolution for Low-Light Image Deblurring
Aug 10, 2023

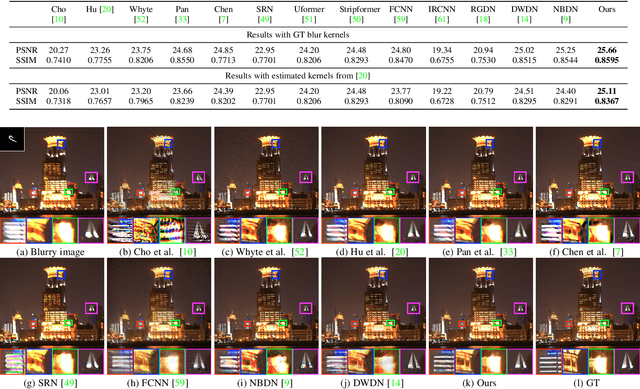

Abstract:Images taken under the low-light condition often contain blur and saturated pixels at the same time. Deblurring images with saturated pixels is quite challenging. Because of the limited dynamic range, the saturated pixels are usually clipped in the imaging process and thus cannot be modeled by the linear blur model. Previous methods use manually designed smooth functions to approximate the clipping procedure. Their deblurring processes often require empirically defined parameters, which may not be the optimal choices for different images. In this paper, we develop a data-driven approach to model the saturated pixels by a learned latent map. Based on the new model, the non-blind deblurring task can be formulated into a maximum a posterior (MAP) problem, which can be effectively solved by iteratively computing the latent map and the latent image. Specifically, the latent map is computed by learning from a map estimation network (MEN), and the latent image estimation process is implemented by a Richardson-Lucy (RL)-based updating scheme. To estimate high-quality deblurred images without amplified artifacts, we develop a prior estimation network (PEN) to obtain prior information, which is further integrated into the RL scheme. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method performs favorably against state-of-the-art algorithms both quantitatively and qualitatively on synthetic and real-world images.
Flow Guidance Deformable Compensation Network for Video Frame Interpolation
Nov 22, 2022Abstract:Motion-based video frame interpolation (VFI) methods have made remarkable progress with the development of deep convolutional networks over the past years. While their performance is often jeopardized by the inaccuracy of flow map estimation, especially in the case of large motion and occlusion. In this paper, we propose a flow guidance deformable compensation network (FGDCN) to overcome the drawbacks of existing motion-based methods. FGDCN decomposes the frame sampling process into two steps: a flow step and a deformation step. Specifically, the flow step utilizes a coarse-to-fine flow estimation network to directly estimate the intermediate flows and synthesizes an anchor frame simultaneously. To ensure the accuracy of the estimated flow, a distillation loss and a task-oriented loss are jointly employed in this step. Under the guidance of the flow priors learned in step one, the deformation step designs a pyramid deformable compensation network to compensate for the missing details of the flow step. In addition, a pyramid loss is proposed to supervise the model in both the image and frequency domain. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm achieves excellent performance on various datasets with fewer parameters.
Multiple Degradation and Reconstruction Network for Single Image Denoising via Knowledge Distillation
Apr 29, 2022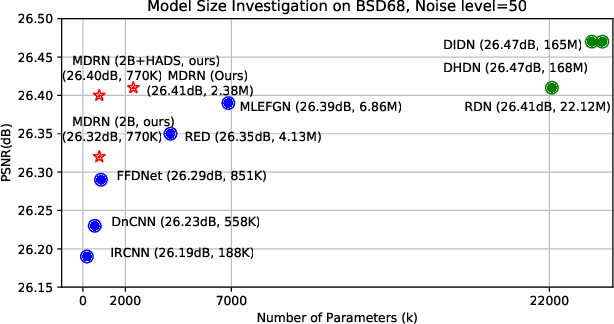
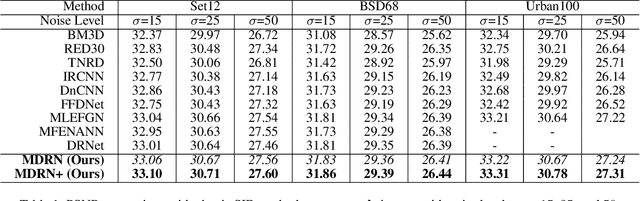
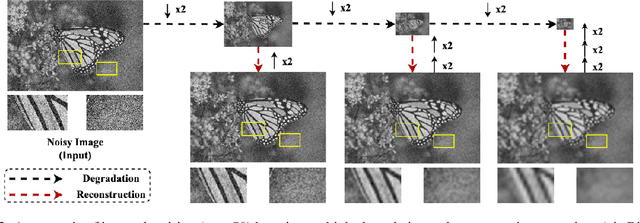
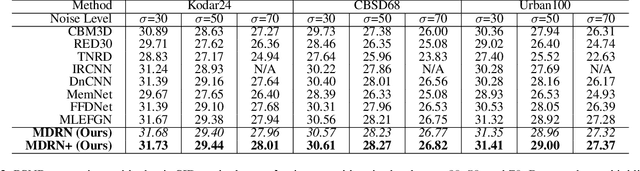
Abstract:Single image denoising (SID) has achieved significant breakthroughs with the development of deep learning. However, the proposed methods are often accompanied by plenty of parameters, which greatly limits their application scenarios. Different from previous works that blindly increase the depth of the network, we explore the degradation mechanism of the noisy image and propose a lightweight Multiple Degradation and Reconstruction Network (MDRN) to progressively remove noise. Meanwhile, we propose two novel Heterogeneous Knowledge Distillation Strategies (HMDS) to enable MDRN to learn richer and more accurate features from heterogeneous models, which make it possible to reconstruct higher-quality denoised images under extreme conditions. Extensive experiments show that our MDRN achieves favorable performance against other SID models with fewer parameters. Meanwhile, plenty of ablation studies demonstrate that the introduced HMDS can improve the performance of tiny models or the model under high noise levels, which is extremely useful for related applications.
Contrastive Learning for Local and Global Learning MRI Reconstruction
Nov 30, 2021
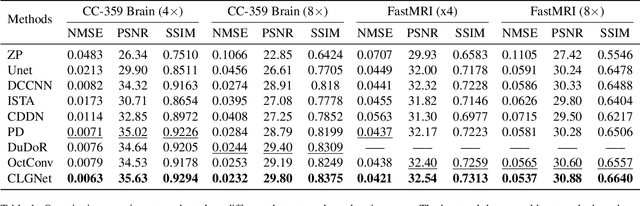
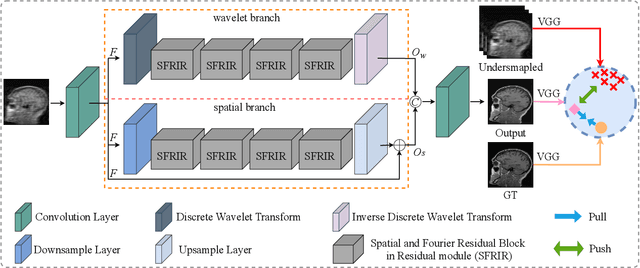
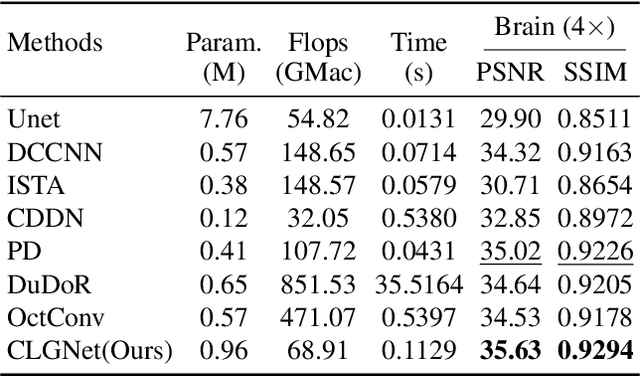
Abstract:Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is an important medical imaging modality, while it requires a long acquisition time. To reduce the acquisition time, various methods have been proposed. However, these methods failed to reconstruct images with a clear structure for two main reasons. Firstly, similar patches widely exist in MR images, while most previous deep learning-based methods ignore this property and only adopt CNN to learn local information. Secondly, the existing methods only use clear images to constrain the upper bound of the solution space, while the lower bound is not constrained, so that a better parameter of the network cannot be obtained. To address these problems, we propose a Contrastive Learning for Local and Global Learning MRI Reconstruction Network (CLGNet). Specifically, according to the Fourier theory, each value in the Fourier domain is calculated from all the values in Spatial domain. Therefore, we propose a Spatial and Fourier Layer (SFL) to simultaneously learn the local and global information in Spatial and Fourier domains. Moreover, compared with self-attention and transformer, the SFL has a stronger learning ability and can achieve better performance in less time. Based on the SFL, we design a Spatial and Fourier Residual block as the main component of our model. Meanwhile, to constrain the lower bound and upper bound of the solution space, we introduce contrastive learning, which can pull the result closer to the clear image and push the result further away from the undersampled image. Extensive experimental results on different datasets and acceleration rates demonstrate that the proposed CLGNet achieves new state-of-the-art results.
Structure-Preserving Deraining with Residue Channel Prior Guidance
Aug 20, 2021



Abstract:Single image deraining is important for many high-level computer vision tasks since the rain streaks can severely degrade the visibility of images, thereby affecting the recognition and analysis of the image. Recently, many CNN-based methods have been proposed for rain removal. Although these methods can remove part of the rain streaks, it is difficult for them to adapt to real-world scenarios and restore high-quality rain-free images with clear and accurate structures. To solve this problem, we propose a Structure-Preserving Deraining Network (SPDNet) with RCP guidance. SPDNet directly generates high-quality rain-free images with clear and accurate structures under the guidance of RCP but does not rely on any rain-generating assumptions. Specifically, we found that the RCP of images contains more accurate structural information than rainy images. Therefore, we introduced it to our deraining network to protect structure information of the rain-free image. Meanwhile, a Wavelet-based Multi-Level Module (WMLM) is proposed as the backbone for learning the background information of rainy images and an Interactive Fusion Module (IFM) is designed to make full use of RCP information. In addition, an iterative guidance strategy is proposed to gradually improve the accuracy of RCP, refining the result in a progressive path. Extensive experimental results on both synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrate that the proposed model achieves new state-of-the-art results. Code: https://github.com/Joyies/SPDNet
Feedback Network for Mutually Boosted Stereo Image Super-Resolution and Disparity Estimation
Jun 02, 2021



Abstract:Under stereo settings, the problem of image super-resolution (SR) and disparity estimation are interrelated that the result of each problem could help to solve the other. The effective exploitation of correspondence between different views facilitates the SR performance, while the high-resolution (HR) features with richer details benefit the correspondence estimation. According to this motivation, we propose a Stereo Super-Resolution and Disparity Estimation Feedback Network (SSRDE-FNet), which simultaneously handles the stereo image super-resolution and disparity estimation in a unified framework and interact them with each other to further improve their performance. Specifically, the SSRDE-FNet is composed of two dual recursive sub-networks for left and right views. Besides the cross-view information exploitation in the low-resolution (LR) space, HR representations produced by the SR process are utilized to perform HR disparity estimation with higher accuracy, through which the HR features can be aggregated to generate a finer SR result. Afterward, the proposed HR Disparity Information Feedback (HRDIF) mechanism delivers information carried by HR disparity back to previous layers to further refine the SR image reconstruction. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness and advancement of SSRDE-FNet.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge