Jinhao Liu
The Molecular Structure of Thought: Mapping the Topology of Long Chain-of-Thought Reasoning
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) often fail to learn effective long chain-of-thought (Long CoT) reasoning from human or non-Long-CoT LLMs imitation. To understand this, we propose that effective and learnable Long CoT trajectories feature stable molecular-like structures in unified view, which are formed by three interaction types: Deep-Reasoning (covalent-like), Self-Reflection (hydrogen-bond-like), and Self-Exploration (van der Waals-like). Analysis of distilled trajectories reveals these structures emerge from Long CoT fine-tuning, not keyword imitation. We introduce Effective Semantic Isomers and show that only bonds promoting fast entropy convergence support stable Long CoT learning, while structural competition impairs training. Drawing on these findings, we present Mole-Syn, a distribution-transfer-graph method that guides synthesis of effective Long CoT structures, boosting performance and RL stability across benchmarks.
The Universal Landscape of Human Reasoning
Oct 24, 2025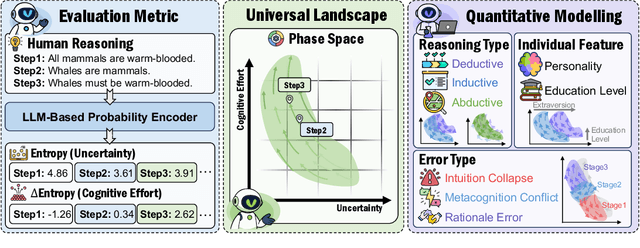
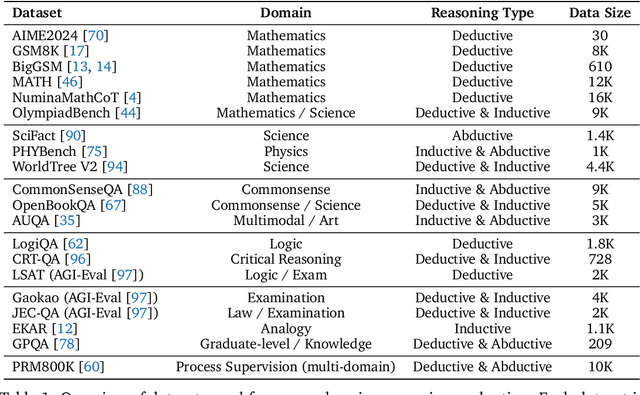
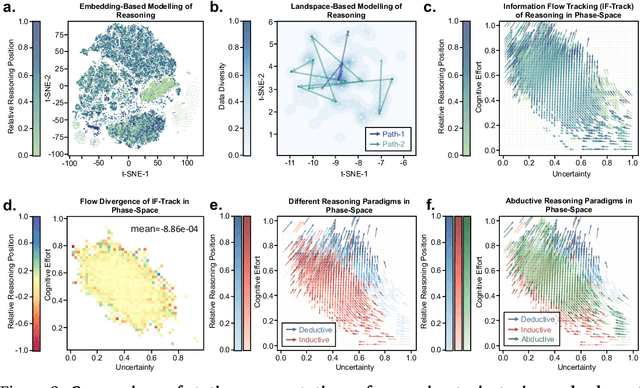
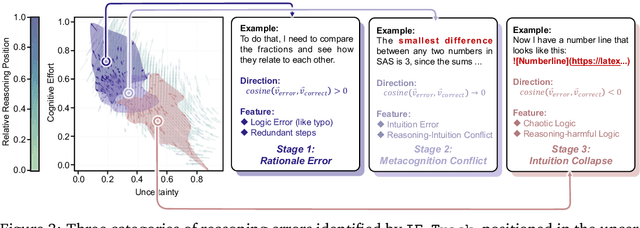
Abstract:Understanding how information is dynamically accumulated and transformed in human reasoning has long challenged cognitive psychology, philosophy, and artificial intelligence. Existing accounts, from classical logic to probabilistic models, illuminate aspects of output or individual modelling, but do not offer a unified, quantitative description of general human reasoning dynamics. To solve this, we introduce Information Flow Tracking (IF-Track), that uses large language models (LLMs) as probabilistic encoder to quantify information entropy and gain at each reasoning step. Through fine-grained analyses across diverse tasks, our method is the first successfully models the universal landscape of human reasoning behaviors within a single metric space. We show that IF-Track captures essential reasoning features, identifies systematic error patterns, and characterizes individual differences. Applied to discussion of advanced psychological theory, we first reconcile single- versus dual-process theories in IF-Track and discover the alignment of artificial and human cognition and how LLMs reshaping human reasoning process. This approach establishes a quantitative bridge between theory and measurement, offering mechanistic insights into the architecture of reasoning.
Beyond Surface Reasoning: Unveiling the True Long Chain-of-Thought Capacity of Diffusion Large Language Models
Oct 10, 2025Abstract:Recently, Diffusion Large Language Models (DLLMs) have offered high throughput and effective sequential reasoning, making them a competitive alternative to autoregressive LLMs (ALLMs). However, parallel decoding, which enables simultaneous token updates, conflicts with the causal order often required for rigorous reasoning. We first identify this conflict as the core Parallel-Sequential Contradiction (PSC). Behavioral analyses in both simple and complex reasoning tasks show that DLLMs exhibit genuine parallelism only for directly decidable outputs. As task difficulty increases, they revert to autoregressive-like behavior, a limitation exacerbated by autoregressive prompting, which nearly doubles the number of decoding steps with remasking without improving quality. Moreover, PSC restricts DLLMs' self-reflection, reasoning depth, and exploratory breadth. To further characterize PSC, we introduce three scaling dimensions for DLLMs: parallel, diffusion, and sequential. Empirically, while parallel scaling yields consistent improvements, diffusion and sequential scaling are constrained by PSC. Based on these findings, we propose several practical mitigations, parallel-oriented prompting, diffusion early stopping, and parallel scaling, to reduce PSC-induced ineffectiveness and inefficiencies.
AutoPR: Let's Automate Your Academic Promotion!
Oct 10, 2025Abstract:As the volume of peer-reviewed research surges, scholars increasingly rely on social platforms for discovery, while authors invest considerable effort in promoting their work to ensure visibility and citations. To streamline this process and reduce the reliance on human effort, we introduce Automatic Promotion (AutoPR), a novel task that transforms research papers into accurate, engaging, and timely public content. To enable rigorous evaluation, we release PRBench, a multimodal benchmark that links 512 peer-reviewed articles to high-quality promotional posts, assessing systems along three axes: Fidelity (accuracy and tone), Engagement (audience targeting and appeal), and Alignment (timing and channel optimization). We also introduce PRAgent, a multi-agent framework that automates AutoPR in three stages: content extraction with multimodal preparation, collaborative synthesis for polished outputs, and platform-specific adaptation to optimize norms, tone, and tagging for maximum reach. When compared to direct LLM pipelines on PRBench, PRAgent demonstrates substantial improvements, including a 604% increase in total watch time, a 438% rise in likes, and at least a 2.9x boost in overall engagement. Ablation studies show that platform modeling and targeted promotion contribute the most to these gains. Our results position AutoPR as a tractable, measurable research problem and provide a roadmap for scalable, impactful automated scholarly communication.
AI4Research: A Survey of Artificial Intelligence for Scientific Research
Jul 02, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), particularly in large language models (LLMs) such as OpenAI-o1 and DeepSeek-R1, have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in complex domains such as logical reasoning and experimental coding. Motivated by these advancements, numerous studies have explored the application of AI in the innovation process, particularly in the context of scientific research. These AI technologies primarily aim to develop systems that can autonomously conduct research processes across a wide range of scientific disciplines. Despite these significant strides, a comprehensive survey on AI for Research (AI4Research) remains absent, which hampers our understanding and impedes further development in this field. To address this gap, we present a comprehensive survey and offer a unified perspective on AI4Research. Specifically, the main contributions of our work are as follows: (1) Systematic taxonomy: We first introduce a systematic taxonomy to classify five mainstream tasks in AI4Research. (2) New frontiers: Then, we identify key research gaps and highlight promising future directions, focusing on the rigor and scalability of automated experiments, as well as the societal impact. (3) Abundant applications and resources: Finally, we compile a wealth of resources, including relevant multidisciplinary applications, data corpora, and tools. We hope our work will provide the research community with quick access to these resources and stimulate innovative breakthroughs in AI4Research.
RBF++: Quantifying and Optimizing Reasoning Boundaries across Measurable and Unmeasurable Capabilities for Chain-of-Thought Reasoning
May 19, 2025Abstract:Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning has proven effective in enhancing large language models (LLMs) on complex tasks, spurring research into its underlying mechanisms. However, two primary challenges remain for real-world applications: (1) the lack of quantitative metrics and actionable guidelines for evaluating and optimizing measurable boundaries of CoT capability, and (2) the absence of methods to assess boundaries of unmeasurable CoT capability, such as multimodal perception. To address these gaps, we introduce the Reasoning Boundary Framework++ (RBF++). To tackle the first challenge, we define the reasoning boundary (RB) as the maximum limit of CoT performance. We also propose a combination law for RBs, enabling quantitative analysis and offering actionable guidance across various CoT tasks. For the second challenge, particularly in multimodal scenarios, we introduce a constant assumption, which replaces unmeasurable RBs with scenario-specific constants. Additionally, we propose the reasoning boundary division mechanism, which divides unmeasurable RBs into two sub-boundaries, facilitating the quantification and optimization of both unmeasurable domain knowledge and multimodal perception capabilities. Extensive experiments involving 38 models across 13 tasks validate the feasibility of our framework in cross-modal settings. Additionally, we evaluate 10 CoT strategies, offer insights into optimization and decay from two complementary perspectives, and expand evaluation benchmarks for measuring RBs in LLM reasoning. We hope this work advances the understanding of RBs and optimization strategies in LLMs. Code and data are available at https://github.com/LightChen233/reasoning-boundary.
DLPO: Towards a Robust, Efficient, and Generalizable Prompt Optimization Framework from a Deep-Learning Perspective
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable success across diverse tasks, largely driven by well-designed prompts. However, crafting and selecting such prompts often requires considerable human effort, significantly limiting its scalability. To mitigate this, recent studies have explored automated prompt optimization as a promising solution. Despite these efforts, existing methods still face critical challenges in robustness, efficiency, and generalization. To systematically address these challenges, we first conduct an empirical analysis to identify the limitations of current reflection-based prompt optimization paradigm. Building on these insights, we propose 7 innovative approaches inspired by traditional deep learning paradigms for prompt optimization (DLPO), seamlessly integrating these concepts into text-based gradient optimization. Through these advancements, we progressively tackle the aforementioned challenges and validate our methods through extensive experimentation. We hope our study not only provides valuable guidance for future research but also offers a comprehensive understanding of the challenges and potential solutions in prompt optimization. Our code is available at https://github.com/sfasfaffa/DLPO.
Towards Reasoning Era: A Survey of Long Chain-of-Thought for Reasoning Large Language Models
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in reasoning with large language models (RLLMs), such as OpenAI-O1 and DeepSeek-R1, have demonstrated their impressive capabilities in complex domains like mathematics and coding. A central factor in their success lies in the application of long chain-of-thought (Long CoT) characteristics, which enhance reasoning abilities and enable the solution of intricate problems. However, despite these developments, a comprehensive survey on Long CoT is still lacking, limiting our understanding of its distinctions from traditional short chain-of-thought (Short CoT) and complicating ongoing debates on issues like "overthinking" and "test-time scaling." This survey seeks to fill this gap by offering a unified perspective on Long CoT. (1) We first distinguish Long CoT from Short CoT and introduce a novel taxonomy to categorize current reasoning paradigms. (2) Next, we explore the key characteristics of Long CoT: deep reasoning, extensive exploration, and feasible reflection, which enable models to handle more complex tasks and produce more efficient, coherent outcomes compared to the shallower Short CoT. (3) We then investigate key phenomena such as the emergence of Long CoT with these characteristics, including overthinking, and test-time scaling, offering insights into how these processes manifest in practice. (4) Finally, we identify significant research gaps and highlight promising future directions, including the integration of multi-modal reasoning, efficiency improvements, and enhanced knowledge frameworks. By providing a structured overview, this survey aims to inspire future research and further the development of logical reasoning in artificial intelligence.
ECM: A Unified Electronic Circuit Model for Explaining the Emergence of In-Context Learning and Chain-of-Thought in Large Language Model
Feb 05, 2025



Abstract:Recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) have led to significant successes across various applications, where the most noticeable is to a series of emerging capabilities, particularly in the areas of In-Context Learning (ICL) and Chain-of-Thought (CoT). To better understand and control model performance, many studies have begun investigating the underlying causes of these phenomena and their impact on task outcomes. However, existing explanatory frameworks predominantly focus on isolating and explaining ICL and CoT independently, leading to an incomplete understanding of their combined influence on model performance. To address this gap, we propose the Electronic Circuit Model (ECM), which provides a foundation for developing scalable, learnable policies and improving the management of AI-generated content. Specifically, ECM conceptualizes model behavior as an electronic circuit: ICL is represented as semantic magnetic field to providing an additional voltage following Faraday's Law, while CoT is modeled as series resistors to constrain the model output performance following Ohm's Law. Experimental results demonstrate that the ECM effectively predicts and explains LLM performance across a variety of prompting strategies. Furthermore, we apply ECM to advanced reasoning strategy optimization on a series of tasks, such as the International Olympiad in Informatics (IOI) and the International Mathematical Olympiad (IMO), achieving competitive performance that surpasses nearly 80% of top human competitors.
Flexible Active Safety Motion Control for Robotic Obstacle Avoidance: A CBF-Guided MPC Approach
May 20, 2024



Abstract:A flexible active safety motion (FASM) control approach is proposed for the avoidance of dynamic obstacles and the reference tracking in robot manipulators. The distinctive feature of the proposed method lies in its utilization of control barrier functions (CBF) to design flexible CBF-guided safety criteria (CBFSC) with dynamically optimized decay rates, thereby offering flexibility and active safety for robot manipulators in dynamic environments. First, discrete-time CBFs are employed to formulate the novel flexible CBFSC with dynamic decay rates for robot manipulators. Following that, the model predictive control (MPC) philosophy is applied, integrating flexible CBFSC as safety constraints into the receding-horizon optimization problem. Significantly, the decay rates of the designed CBFSC are incorporated as decision variables in the optimization problem, facilitating the dynamic enhancement of flexibility during the obstacle avoidance process. In particular, a novel cost function that integrates a penalty term is designed to dynamically adjust the safety margins of the CBFSC. Finally, experiments are conducted in various scenarios using a Universal Robots 5 (UR5) manipulator to validate the effectiveness of the proposed approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge