Jiannan Guan
The Universal Landscape of Human Reasoning
Oct 24, 2025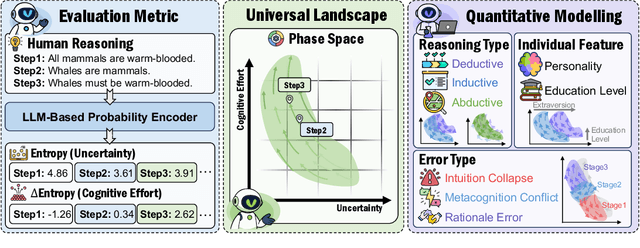
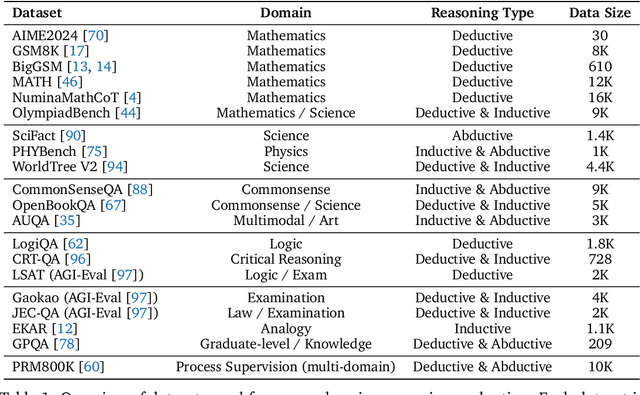
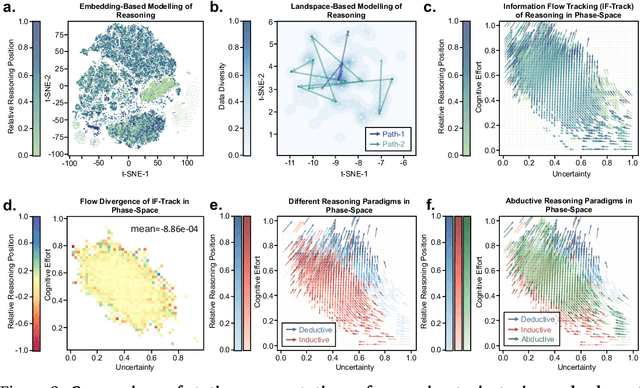
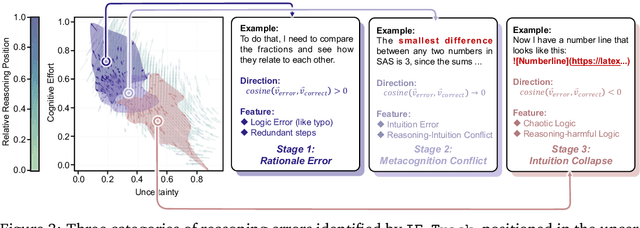
Abstract:Understanding how information is dynamically accumulated and transformed in human reasoning has long challenged cognitive psychology, philosophy, and artificial intelligence. Existing accounts, from classical logic to probabilistic models, illuminate aspects of output or individual modelling, but do not offer a unified, quantitative description of general human reasoning dynamics. To solve this, we introduce Information Flow Tracking (IF-Track), that uses large language models (LLMs) as probabilistic encoder to quantify information entropy and gain at each reasoning step. Through fine-grained analyses across diverse tasks, our method is the first successfully models the universal landscape of human reasoning behaviors within a single metric space. We show that IF-Track captures essential reasoning features, identifies systematic error patterns, and characterizes individual differences. Applied to discussion of advanced psychological theory, we first reconcile single- versus dual-process theories in IF-Track and discover the alignment of artificial and human cognition and how LLMs reshaping human reasoning process. This approach establishes a quantitative bridge between theory and measurement, offering mechanistic insights into the architecture of reasoning.
AutoPR: Let's Automate Your Academic Promotion!
Oct 10, 2025Abstract:As the volume of peer-reviewed research surges, scholars increasingly rely on social platforms for discovery, while authors invest considerable effort in promoting their work to ensure visibility and citations. To streamline this process and reduce the reliance on human effort, we introduce Automatic Promotion (AutoPR), a novel task that transforms research papers into accurate, engaging, and timely public content. To enable rigorous evaluation, we release PRBench, a multimodal benchmark that links 512 peer-reviewed articles to high-quality promotional posts, assessing systems along three axes: Fidelity (accuracy and tone), Engagement (audience targeting and appeal), and Alignment (timing and channel optimization). We also introduce PRAgent, a multi-agent framework that automates AutoPR in three stages: content extraction with multimodal preparation, collaborative synthesis for polished outputs, and platform-specific adaptation to optimize norms, tone, and tagging for maximum reach. When compared to direct LLM pipelines on PRBench, PRAgent demonstrates substantial improvements, including a 604% increase in total watch time, a 438% rise in likes, and at least a 2.9x boost in overall engagement. Ablation studies show that platform modeling and targeted promotion contribute the most to these gains. Our results position AutoPR as a tractable, measurable research problem and provide a roadmap for scalable, impactful automated scholarly communication.
AI4Research: A Survey of Artificial Intelligence for Scientific Research
Jul 02, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), particularly in large language models (LLMs) such as OpenAI-o1 and DeepSeek-R1, have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in complex domains such as logical reasoning and experimental coding. Motivated by these advancements, numerous studies have explored the application of AI in the innovation process, particularly in the context of scientific research. These AI technologies primarily aim to develop systems that can autonomously conduct research processes across a wide range of scientific disciplines. Despite these significant strides, a comprehensive survey on AI for Research (AI4Research) remains absent, which hampers our understanding and impedes further development in this field. To address this gap, we present a comprehensive survey and offer a unified perspective on AI4Research. Specifically, the main contributions of our work are as follows: (1) Systematic taxonomy: We first introduce a systematic taxonomy to classify five mainstream tasks in AI4Research. (2) New frontiers: Then, we identify key research gaps and highlight promising future directions, focusing on the rigor and scalability of automated experiments, as well as the societal impact. (3) Abundant applications and resources: Finally, we compile a wealth of resources, including relevant multidisciplinary applications, data corpora, and tools. We hope our work will provide the research community with quick access to these resources and stimulate innovative breakthroughs in AI4Research.
UFO-RL: Uncertainty-Focused Optimization for Efficient Reinforcement Learning Data Selection
May 18, 2025Abstract:Scaling RL for LLMs is computationally expensive, largely due to multi-sampling for policy optimization and evaluation, making efficient data selection crucial. Inspired by the Zone of Proximal Development (ZPD) theory, we hypothesize LLMs learn best from data within their potential comprehension zone. Addressing the limitation of conventional, computationally intensive multi-sampling methods for data assessment, we introduce UFO-RL. This novel framework uses a computationally efficient single-pass uncertainty estimation to identify informative data instances, achieving up to 185x faster data evaluation. UFO-RL leverages this metric to select data within the estimated ZPD for training. Experiments show that training with just 10% of data selected by UFO-RL yields performance comparable to or surpassing full-data training, reducing overall training time by up to 16x while enhancing stability and generalization. UFO-RL offers a practical and highly efficient strategy for scaling RL fine-tuning of LLMs by focusing learning on valuable data.
Towards Reasoning Era: A Survey of Long Chain-of-Thought for Reasoning Large Language Models
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in reasoning with large language models (RLLMs), such as OpenAI-O1 and DeepSeek-R1, have demonstrated their impressive capabilities in complex domains like mathematics and coding. A central factor in their success lies in the application of long chain-of-thought (Long CoT) characteristics, which enhance reasoning abilities and enable the solution of intricate problems. However, despite these developments, a comprehensive survey on Long CoT is still lacking, limiting our understanding of its distinctions from traditional short chain-of-thought (Short CoT) and complicating ongoing debates on issues like "overthinking" and "test-time scaling." This survey seeks to fill this gap by offering a unified perspective on Long CoT. (1) We first distinguish Long CoT from Short CoT and introduce a novel taxonomy to categorize current reasoning paradigms. (2) Next, we explore the key characteristics of Long CoT: deep reasoning, extensive exploration, and feasible reflection, which enable models to handle more complex tasks and produce more efficient, coherent outcomes compared to the shallower Short CoT. (3) We then investigate key phenomena such as the emergence of Long CoT with these characteristics, including overthinking, and test-time scaling, offering insights into how these processes manifest in practice. (4) Finally, we identify significant research gaps and highlight promising future directions, including the integration of multi-modal reasoning, efficiency improvements, and enhanced knowledge frameworks. By providing a structured overview, this survey aims to inspire future research and further the development of logical reasoning in artificial intelligence.
Can Large Language Models Understand You Better? An MBTI Personality Detection Dataset Aligned with Population Traits
Dec 17, 2024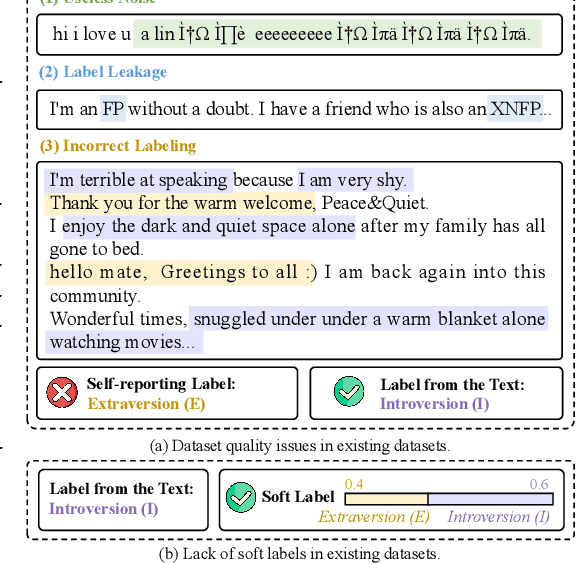
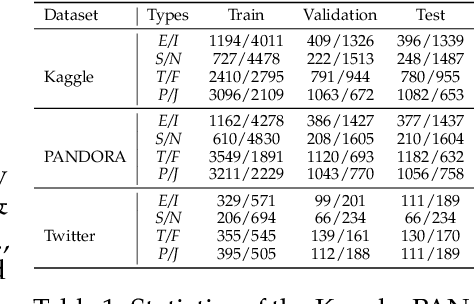
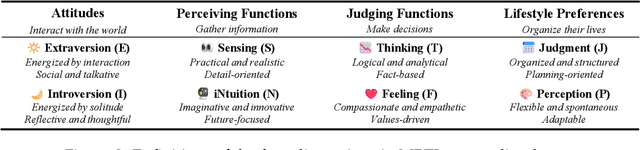
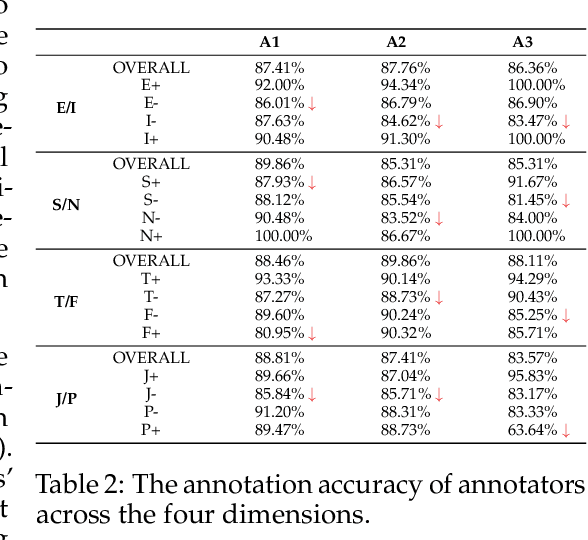
Abstract:The Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) is one of the most influential personality theories reflecting individual differences in thinking, feeling, and behaving. MBTI personality detection has garnered considerable research interest and has evolved significantly over the years. However, this task tends to be overly optimistic, as it currently does not align well with the natural distribution of population personality traits. Specifically, (1) the self-reported labels in existing datasets result in incorrect labeling issues, and (2) the hard labels fail to capture the full range of population personality distributions. In this paper, we optimize the task by constructing MBTIBench, the first manually annotated high-quality MBTI personality detection dataset with soft labels, under the guidance of psychologists. As for the first challenge, MBTIBench effectively solves the incorrect labeling issues, which account for 29.58% of the data. As for the second challenge, we estimate soft labels by deriving the polarity tendency of samples. The obtained soft labels confirm that there are more people with non-extreme personality traits. Experimental results not only highlight the polarized predictions and biases in LLMs as key directions for future research, but also confirm that soft labels can provide more benefits to other psychological tasks than hard labels. The code and data are available at https://github.com/Personality-NLP/MbtiBench.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge