Wenbin Zhang
Bifrost: Steering Strategic Trajectories to Bridge Contextual Gaps for Self-Improving Agents
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Autonomous agents excel in self-improvement through reflection and iterative refinement, which reuse successful task trajectories as in-context examples to assist subsequent reasoning. However, shifting across tasks often introduces a context mismatch. Hence, existing approaches either discard the trajectories or manipulate them using heuristics, leading to a non-negligible fine-tuning cost or unguaranteed performance. To bridge this gap, we reveal a context-trajectory correlation, where shifts of context are highly parallel with shifts of trajectory. Based on this finding, we propose BrIdge contextual gap FoR imprOvised trajectory STeering (Bifrost), a training-free method that leverages context differences to precisely guide the adaptation of previously solved trajectories towards the target task, mitigating the misalignment caused by context shifts. Our trajectory adaptation is conducted at the representation level using agent hidden states, ensuring trajectory transformation accurately aligns with the target context in a shared space. Across diverse benchmarks, Bifrost consistently outperforms existing trajectory reuse and finetuned self-improvement methods, demonstrating that agents can effectively leverage past experiences despite substantial context shifts.
Adaptive Speaker Embedding Self-Augmentation for Personal Voice Activity Detection with Short Enrollment Speech
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Personal Voice Activity Detection (PVAD) is crucial for identifying target speaker segments in the mixture, yet its performance heavily depends on the quality of speaker embeddings. A key practical limitation is the short enrollment speech--such as a wake-up word--which provides limited cues. This paper proposes a novel adaptive speaker embedding self-augmentation strategy that enhances PVAD performance by augmenting the original enrollment embeddings through additive fusion of keyframe embeddings extracted from mixed speech. Furthermore, we introduce a long-term adaptation strategy to iteratively refine embeddings during detection, mitigating speaker temporal variability. Experiments show significant gains in recall, precision, and F1-score under short enrollment conditions, matching full-length enrollment performance after five iterative updates. The source code is available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/ASE-PVAD-E5D6 .
Fairness-Aware Graph Representation Learning with Limited Demographic Information
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:Ensuring fairness in Graph Neural Networks is fundamental to promoting trustworthy and socially responsible machine learning systems. In response, numerous fair graph learning methods have been proposed in recent years. However, most of them assume full access to demographic information, a requirement rarely met in practice due to privacy, legal, or regulatory restrictions. To this end, this paper introduces a novel fair graph learning framework that mitigates bias in graph learning under limited demographic information. Specifically, we propose a mechanism guided by partial demographic data to generate proxies for demographic information and design a strategy that enforces consistent node embeddings across demographic groups. In addition, we develop an adaptive confidence strategy that dynamically adjusts each node's contribution to fairness and utility based on prediction confidence. We further provide theoretical analysis demonstrating that our framework, FairGLite, achieves provable upper bounds on group fairness metrics, offering formal guarantees for bias mitigation. Through extensive experiments on multiple datasets and fair graph learning frameworks, we demonstrate the framework's effectiveness in both mitigating bias and maintaining model utility.
AI Fairness Beyond Complete Demographics: Current Achievements and Future Directions
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Fairness in artificial intelligence (AI) has become a growing concern due to discriminatory outcomes in AI-based decision-making systems. While various methods have been proposed to mitigate bias, most rely on complete demographic information, an assumption often impractical due to legal constraints and the risk of reinforcing discrimination. This survey examines fairness in AI when demographics are incomplete, addressing the gap between traditional approaches and real-world challenges. We introduce a novel taxonomy of fairness notions in this setting, clarifying their relationships and distinctions. Additionally, we summarize existing techniques that promote fairness beyond complete demographics and highlight open research questions to encourage further progress in the field.
TSLA: A Task-Specific Learning Adaptation for Semantic Segmentation on Autonomous Vehicles Platform
Aug 17, 2025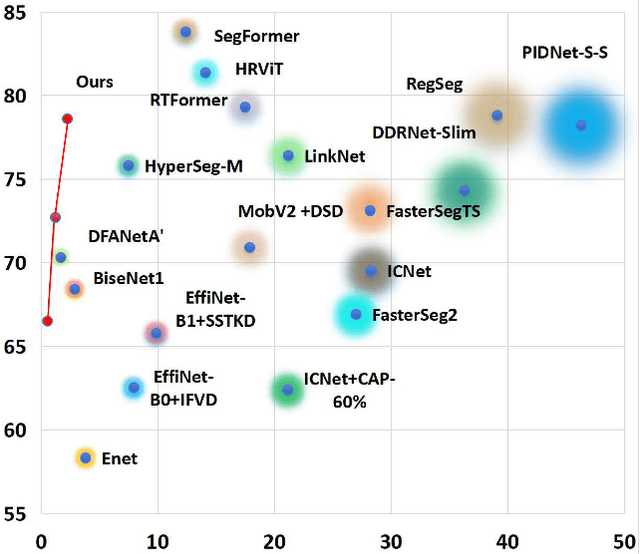
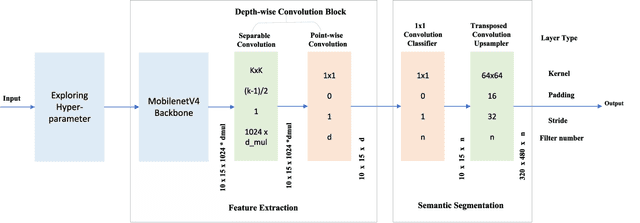
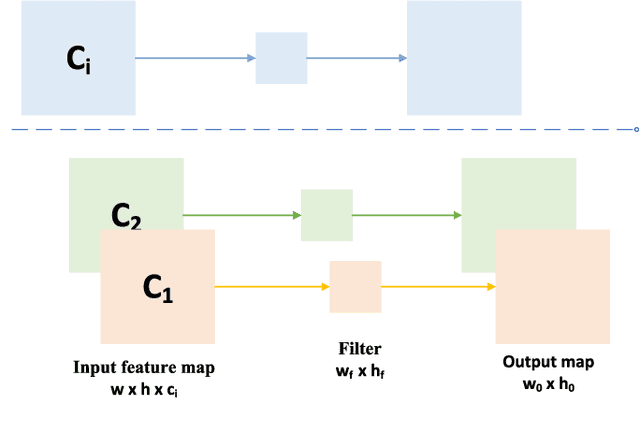
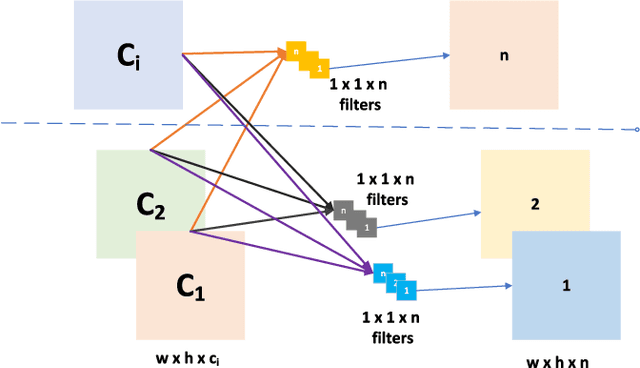
Abstract:Autonomous driving platforms encounter diverse driving scenarios, each with varying hardware resources and precision requirements. Given the computational limitations of embedded devices, it is crucial to consider computing costs when deploying on target platforms like the NVIDIA\textsuperscript{\textregistered} DRIVE PX 2. Our objective is to customize the semantic segmentation network according to the computing power and specific scenarios of autonomous driving hardware. We implement dynamic adaptability through a three-tier control mechanism -- width multiplier, classifier depth, and classifier kernel -- allowing fine-grained control over model components based on hardware constraints and task requirements. This adaptability facilitates broad model scaling, targeted refinement of the final layers, and scenario-specific optimization of kernel sizes, leading to improved resource allocation and performance. Additionally, we leverage Bayesian Optimization with surrogate modeling to efficiently explore hyperparameter spaces under tight computational budgets. Our approach addresses scenario-specific and task-specific requirements through automatic parameter search, accommodating the unique computational complexity and accuracy needs of autonomous driving. It scales its Multiply-Accumulate Operations (MACs) for Task-Specific Learning Adaptation (TSLA), resulting in alternative configurations tailored to diverse self-driving tasks. These TSLA customizations maximize computational capacity and model accuracy, optimizing hardware utilization.
RCR-Router: Efficient Role-Aware Context Routing for Multi-Agent LLM Systems with Structured Memory
Aug 06, 2025Abstract:Multi-agent large language model (LLM) systems have shown strong potential in complex reasoning and collaborative decision-making tasks. However, most existing coordination schemes rely on static or full-context routing strategies, which lead to excessive token consumption, redundant memory exposure, and limited adaptability across interaction rounds. We introduce RCR-Router, a modular and role-aware context routing framework designed to enable efficient, adaptive collaboration in multi-agent LLMs. To our knowledge, this is the first routing approach that dynamically selects semantically relevant memory subsets for each agent based on its role and task stage, while adhering to a strict token budget. A lightweight scoring policy guides memory selection, and agent outputs are iteratively integrated into a shared memory store to facilitate progressive context refinement. To better evaluate model behavior, we further propose an Answer Quality Score metric that captures LLM-generated explanations beyond standard QA accuracy. Experiments on three multi-hop QA benchmarks -- HotPotQA, MuSiQue, and 2WikiMultihop -- demonstrate that RCR-Router reduces token usage (up to 30%) while improving or maintaining answer quality. These results highlight the importance of structured memory routing and output-aware evaluation in advancing scalable multi-agent LLM systems.
End-to-End DOA-Guided Speech Extraction in Noisy Multi-Talker Scenarios
Jul 28, 2025Abstract:Target Speaker Extraction (TSE) plays a critical role in enhancing speech signals in noisy and multi-speaker environments. This paper presents an end-to-end TSE model that incorporates Direction of Arrival (DOA) and beamwidth embeddings to extract speech from a specified spatial region centered around the DOA. Our approach efficiently captures spatial and temporal features, enabling robust performance in highly complex scenarios with multiple simultaneous speakers. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed model not only significantly enhances the target speech within the defined beamwidth but also effectively suppresses interference from other directions, producing a clear and isolated target voice. Furthermore, the model achieves remarkable improvements in downstream Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) tasks, making it particularly suitable for real-world applications.
Preserving AUC Fairness in Learning with Noisy Protected Groups
May 24, 2025Abstract:The Area Under the ROC Curve (AUC) is a key metric for classification, especially under class imbalance, with growing research focus on optimizing AUC over accuracy in applications like medical image analysis and deepfake detection. This leads to fairness in AUC optimization becoming crucial as biases can impact protected groups. While various fairness mitigation techniques exist, fairness considerations in AUC optimization remain in their early stages, with most research focusing on improving AUC fairness under the assumption of clean protected groups. However, these studies often overlook the impact of noisy protected groups, leading to fairness violations in practice. To address this, we propose the first robust AUC fairness approach under noisy protected groups with fairness theoretical guarantees using distributionally robust optimization. Extensive experiments on tabular and image datasets show that our method outperforms state-of-the-art approaches in preserving AUC fairness. The code is in https://github.com/Purdue-M2/AUC_Fairness_with_Noisy_Groups.
Exploring the Vulnerability of the Content Moderation Guardrail in Large Language Models via Intent Manipulation
May 24, 2025Abstract:Intent detection, a core component of natural language understanding, has considerably evolved as a crucial mechanism in safeguarding large language models (LLMs). While prior work has applied intent detection to enhance LLMs' moderation guardrails, showing a significant success against content-level jailbreaks, the robustness of these intent-aware guardrails under malicious manipulations remains under-explored. In this work, we investigate the vulnerability of intent-aware guardrails and demonstrate that LLMs exhibit implicit intent detection capabilities. We propose a two-stage intent-based prompt-refinement framework, IntentPrompt, that first transforms harmful inquiries into structured outlines and further reframes them into declarative-style narratives by iteratively optimizing prompts via feedback loops to enhance jailbreak success for red-teaming purposes. Extensive experiments across four public benchmarks and various black-box LLMs indicate that our framework consistently outperforms several cutting-edge jailbreak methods and evades even advanced Intent Analysis (IA) and Chain-of-Thought (CoT)-based defenses. Specifically, our "FSTR+SPIN" variant achieves attack success rates ranging from 88.25% to 96.54% against CoT-based defenses on the o1 model, and from 86.75% to 97.12% on the GPT-4o model under IA-based defenses. These findings highlight a critical weakness in LLMs' safety mechanisms and suggest that intent manipulation poses a growing challenge to content moderation guardrails.
Structured Agent Distillation for Large Language Model
May 20, 2025



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) exhibit strong capabilities as decision-making agents by interleaving reasoning and actions, as seen in ReAct-style frameworks. Yet, their practical deployment is constrained by high inference costs and large model sizes. We propose Structured Agent Distillation, a framework that compresses large LLM-based agents into smaller student models while preserving both reasoning fidelity and action consistency. Unlike standard token-level distillation, our method segments trajectories into {[REASON]} and {[ACT]} spans, applying segment-specific losses to align each component with the teacher's behavior. This structure-aware supervision enables compact agents to better replicate the teacher's decision process. Experiments on ALFWorld, HotPotQA-ReAct, and WebShop show that our approach consistently outperforms token-level and imitation learning baselines, achieving significant compression with minimal performance drop. Scaling and ablation results further highlight the importance of span-level alignment for efficient and deployable agents.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge