Xuyu Wang
Generalizable and Interpretable RF Fingerprinting with Shapelet-Enhanced Large Language Models
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Deep neural networks (DNNs) have achieved remarkable success in radio frequency (RF) fingerprinting for wireless device authentication. However, their practical deployment faces two major limitations: domain shift, where models trained in one environment struggle to generalize to others, and the black-box nature of DNNs, which limits interpretability. To address these issues, we propose a novel framework that integrates a group of variable-length two-dimensional (2D) shapelets with a pre-trained large language model (LLM) to achieve efficient, interpretable, and generalizable RF fingerprinting. The 2D shapelets explicitly capture diverse local temporal patterns across the in-phase and quadrature (I/Q) components, providing compact and interpretable representations. Complementarily, the pre-trained LLM captures more long-range dependencies and global contextual information, enabling strong generalization with minimal training overhead. Moreover, our framework also supports prototype generation for few-shot inference, enhancing cross-domain performance without additional retraining. To evaluate the effectiveness of our proposed method, we conduct extensive experiments on six datasets across various protocols and domains. The results show that our method achieves superior standard and few-shot performance across both source and unseen domains.
An Efficient and Explainable KAN Framework forWireless Radiation Field Prediction
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Modeling wireless channels accurately remains a challenge due to environmental variations and signal uncertainties. Recent neural networks can learn radio frequency~(RF) signal propagation patterns, but they process each voxel on the ray independently, without considering global context or environmental factors. Our paper presents a new approach that learns comprehensive representations of complete rays rather than individual points, capturing more detailed environmental features. We integrate a Kolmogorov-Arnold network (KAN) architecture with transformer modules to achieve better performance across realistic and synthetic scenes while maintaining computational efficiency. Our experimental results show that this approach outperforms existing methods in various scenarios. Ablation studies confirm that each component of our model contributes to its effectiveness. Additional experiments provide clear explanations for our model's performance.
* Accepted in 2025 IEEE 22nd International Conference on Mobile Ad-Hoc and Smart Systems (MASS). See https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=11206262&tag=1
Digital Twin AI: Opportunities and Challenges from Large Language Models to World Models
Jan 04, 2026Abstract:Digital twins, as precise digital representations of physical systems, have evolved from passive simulation tools into intelligent and autonomous entities through the integration of artificial intelligence technologies. This paper presents a unified four-stage framework that systematically characterizes AI integration across the digital twin lifecycle, spanning modeling, mirroring, intervention, and autonomous management. By synthesizing existing technologies and practices, we distill a unified four-stage framework that systematically characterizes how AI methodologies are embedded across the digital twin lifecycle: (1) modeling the physical twin through physics-based and physics-informed AI approaches, (2) mirroring the physical system into a digital twin with real-time synchronization, (3) intervening in the physical twin through predictive modeling, anomaly detection, and optimization strategies, and (4) achieving autonomous management through large language models, foundation models, and intelligent agents. We analyze the synergy between physics-based modeling and data-driven learning, highlighting the shift from traditional numerical solvers to physics-informed and foundation models for physical systems. Furthermore, we examine how generative AI technologies, including large language models and generative world models, transform digital twins into proactive and self-improving cognitive systems capable of reasoning, communication, and creative scenario generation. Through a cross-domain review spanning eleven application domains, including healthcare, aerospace, smart manufacturing, robotics, and smart cities, we identify common challenges related to scalability, explainability, and trustworthiness, and outline directions for responsible AI-driven digital twin systems.
A Survey on Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces in Practical Systems: Security and Privacy Perspectives
Dec 12, 2025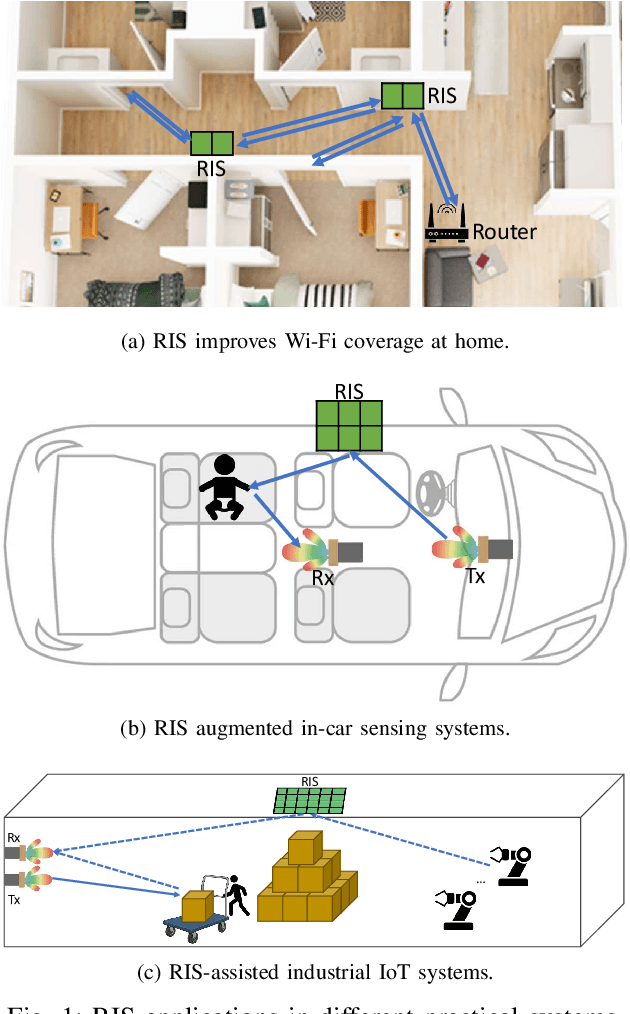
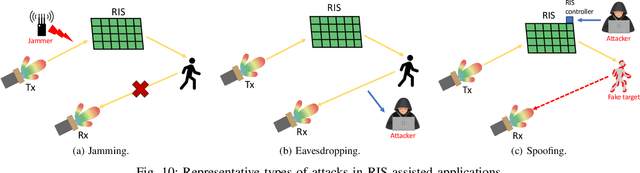
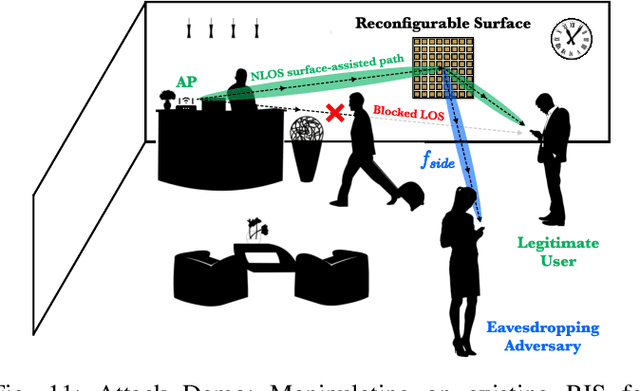
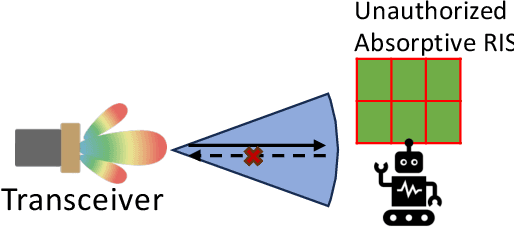
Abstract:Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RIS) have emerged as a transformative technology capable of reshaping wireless environments through dynamic manipulation of electromagnetic waves. While extensive research has explored their theoretical benefits for communication and sensing, practical deployments in smart environments such as homes, vehicles, and industrial settings remain limited and under-examined, particularly from security and privacy perspectives. This survey provides a comprehensive examination of RIS applications in real-world systems, with a focus on the security and privacy threats, vulnerabilities, and defensive strategies relevant to practical use. We analyze scenarios with two types of systems (with and without legitimate RIS) and two types of attackers (with and without malicious RIS), and demonstrate how RIS may introduce new attacks to practical systems, including eavesdropping, jamming, and spoofing attacks. In response, we review defenses against RIS-related attacks in these systems, such as applying additional security algorithms, disrupting attackers, and early detection of unauthorized RIS. We also discuss scenarios in which the legitimate user applies an additional RIS to defend against attacks. To support future research, we also provide a collection of open-source tools, datasets, demos, and papers at: https://awesome-ris-security.github.io/. By highlighting RIS's functionality and its security/privacy challenges and opportunities, this survey aims to guide researchers and engineers toward the development of secure, resilient, and privacy-preserving RIS-enabled practical wireless systems and environments.
Exploring Spatial-Temporal Representation via Star Graph for mmWave Radar-based Human Activity Recognition
Dec 12, 2025



Abstract:Human activity recognition (HAR) requires extracting accurate spatial-temporal features with human movements. A mmWave radar point cloud-based HAR system suffers from sparsity and variable-size problems due to the physical features of the mmWave signal. Existing works usually borrow the preprocessing algorithms for the vision-based systems with dense point clouds, which may not be optimal for mmWave radar systems. In this work, we proposed a graph representation with a discrete dynamic graph neural network (DDGNN) to explore the spatial-temporal representation of human movement-related features. Specifically, we designed a star graph to describe the high-dimensional relative relationship between a manually added static center point and the dynamic mmWave radar points in the same and consecutive frames. We then adopted DDGNN to learn the features residing in the star graph with variable sizes. Experimental results demonstrated that our approach outperformed other baseline methods using real-world HAR datasets. Our system achieved an overall classification accuracy of 94.27\%, which gets the near-optimal performance with a vision-based skeleton data accuracy of 97.25\%. We also conducted an inference test on Raspberry Pi~4 to demonstrate its effectiveness on resource-constraint platforms. \sh{ We provided a comprehensive ablation study for variable DDGNN structures to validate our model design. Our system also outperformed three recent radar-specific methods without requiring resampling or frame aggregators.
Revisiting Pre-trained Language Models for Vulnerability Detection
Jul 22, 2025Abstract:The rapid advancement of pre-trained language models (PLMs) has demonstrated promising results for various code-related tasks. However, their effectiveness in detecting real-world vulnerabilities remains a critical challenge. % for the security community. While existing empirical studies evaluate PLMs for vulnerability detection (VD), their inadequate consideration in data preparation, evaluation setups, and experimental settings undermines the accuracy and comprehensiveness of evaluations. This paper introduces RevisitVD, an extensive evaluation of 17 PLMs spanning smaller code-specific PLMs and large-scale PLMs using newly constructed datasets. Specifically, we compare the performance of PLMs under both fine-tuning and prompt engineering, assess their effectiveness and generalizability across various training and testing settings, and analyze their robustness against code normalization, abstraction, and semantic-preserving transformations. Our findings reveal that, for VD tasks, PLMs incorporating pre-training tasks designed to capture the syntactic and semantic patterns of code outperform both general-purpose PLMs and those solely pre-trained or fine-tuned on large code corpora. However, these models face notable challenges in real-world scenarios, such as difficulties in detecting vulnerabilities with complex dependencies, handling perturbations introduced by code normalization and abstraction, and identifying semantic-preserving vulnerable code transformations. Also, the truncation caused by the limited context windows of PLMs can lead to a non-negligible amount of labeling errors. This study underscores the importance of thorough evaluations of model performance in practical scenarios and outlines future directions to help enhance the effectiveness of PLMs for realistic VD applications.
Protocol-agnostic and Data-free Backdoor Attacks on Pre-trained Models in RF Fingerprinting
May 01, 2025Abstract:While supervised deep neural networks (DNNs) have proven effective for device authentication via radio frequency (RF) fingerprinting, they are hindered by domain shift issues and the scarcity of labeled data. The success of large language models has led to increased interest in unsupervised pre-trained models (PTMs), which offer better generalization and do not require labeled datasets, potentially addressing the issues mentioned above. However, the inherent vulnerabilities of PTMs in RF fingerprinting remain insufficiently explored. In this paper, we thoroughly investigate data-free backdoor attacks on such PTMs in RF fingerprinting, focusing on a practical scenario where attackers lack access to downstream data, label information, and training processes. To realize the backdoor attack, we carefully design a set of triggers and predefined output representations (PORs) for the PTMs. By mapping triggers and PORs through backdoor training, we can implant backdoor behaviors into the PTMs, thereby introducing vulnerabilities across different downstream RF fingerprinting tasks without requiring prior knowledge. Extensive experiments demonstrate the wide applicability of our proposed attack to various input domains, protocols, and PTMs. Furthermore, we explore potential detection and defense methods, demonstrating the difficulty of fully safeguarding against our proposed backdoor attack.
FedCAP: Robust Federated Learning via Customized Aggregation and Personalization
Oct 16, 2024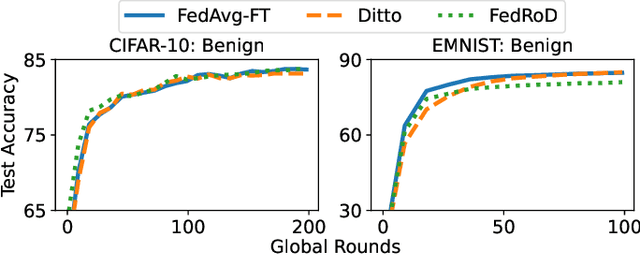
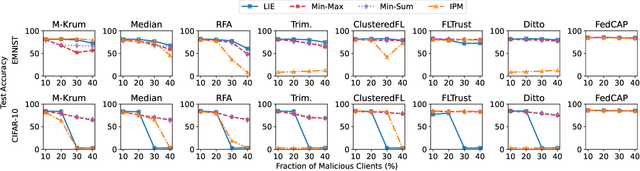
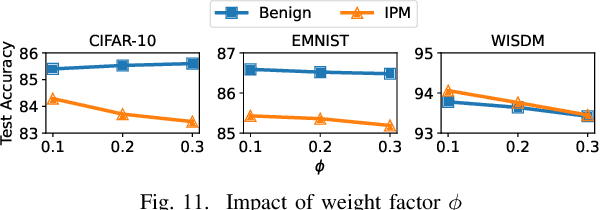
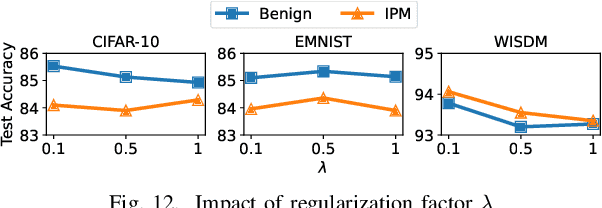
Abstract:Federated learning (FL), an emerging distributed machine learning paradigm, has been applied to various privacy-preserving scenarios. However, due to its distributed nature, FL faces two key issues: the non-independent and identical distribution (non-IID) of user data and vulnerability to Byzantine threats. To address these challenges, in this paper, we propose FedCAP, a robust FL framework against both data heterogeneity and Byzantine attacks. The core of FedCAP is a model update calibration mechanism to help a server capture the differences in the direction and magnitude of model updates among clients. Furthermore, we design a customized model aggregation rule that facilitates collaborative training among similar clients while accelerating the model deterioration of malicious clients. With a Euclidean norm-based anomaly detection mechanism, the server can quickly identify and permanently remove malicious clients. Moreover, the impact of data heterogeneity and Byzantine attacks can be further mitigated through personalization on the client side. We conduct extensive experiments, comparing multiple state-of-the-art baselines, to demonstrate that FedCAP performs well in several non-IID settings and shows strong robustness under a series of poisoning attacks.
On the Efficiency of Privacy Attacks in Federated Learning
Apr 15, 2024
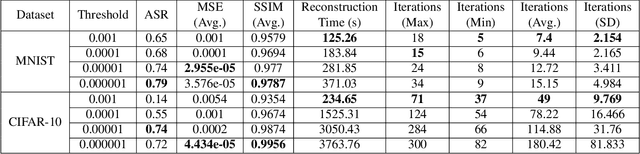
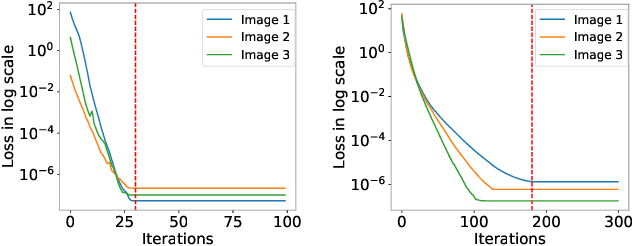
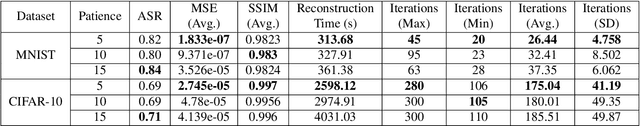
Abstract:Recent studies have revealed severe privacy risks in federated learning, represented by Gradient Leakage Attacks. However, existing studies mainly aim at increasing the privacy attack success rate and overlook the high computation costs for recovering private data, making the privacy attack impractical in real applications. In this study, we examine privacy attacks from the perspective of efficiency and propose a framework for improving the Efficiency of Privacy Attacks in Federated Learning (EPAFL). We make three novel contributions. First, we systematically evaluate the computational costs for representative privacy attacks in federated learning, which exhibits a high potential to optimize efficiency. Second, we propose three early-stopping techniques to effectively reduce the computational costs of these privacy attacks. Third, we perform experiments on benchmark datasets and show that our proposed method can significantly reduce computational costs and maintain comparable attack success rates for state-of-the-art privacy attacks in federated learning. We provide the codes on GitHub at https://github.com/mlsysx/EPAFL.
TrustLLM: Trustworthiness in Large Language Models
Jan 25, 2024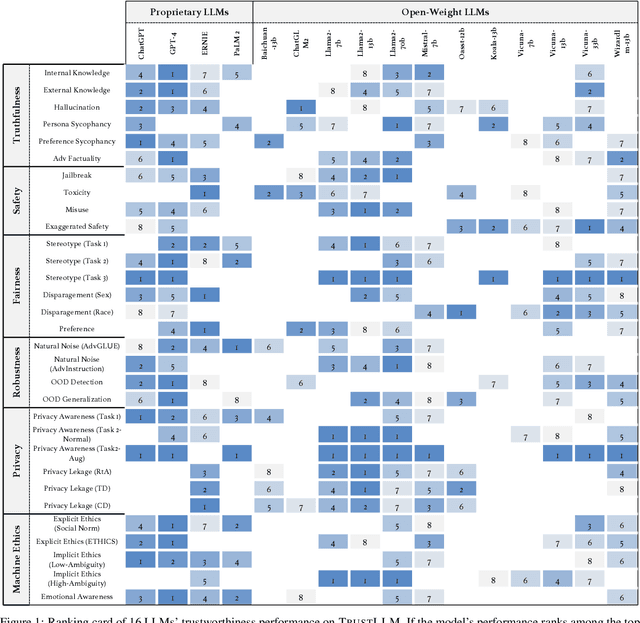

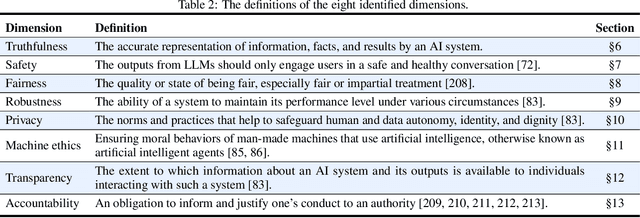
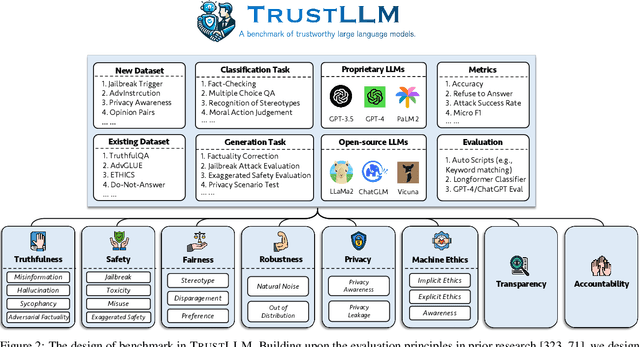
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs), exemplified by ChatGPT, have gained considerable attention for their excellent natural language processing capabilities. Nonetheless, these LLMs present many challenges, particularly in the realm of trustworthiness. Therefore, ensuring the trustworthiness of LLMs emerges as an important topic. This paper introduces TrustLLM, a comprehensive study of trustworthiness in LLMs, including principles for different dimensions of trustworthiness, established benchmark, evaluation, and analysis of trustworthiness for mainstream LLMs, and discussion of open challenges and future directions. Specifically, we first propose a set of principles for trustworthy LLMs that span eight different dimensions. Based on these principles, we further establish a benchmark across six dimensions including truthfulness, safety, fairness, robustness, privacy, and machine ethics. We then present a study evaluating 16 mainstream LLMs in TrustLLM, consisting of over 30 datasets. Our findings firstly show that in general trustworthiness and utility (i.e., functional effectiveness) are positively related. Secondly, our observations reveal that proprietary LLMs generally outperform most open-source counterparts in terms of trustworthiness, raising concerns about the potential risks of widely accessible open-source LLMs. However, a few open-source LLMs come very close to proprietary ones. Thirdly, it is important to note that some LLMs may be overly calibrated towards exhibiting trustworthiness, to the extent that they compromise their utility by mistakenly treating benign prompts as harmful and consequently not responding. Finally, we emphasize the importance of ensuring transparency not only in the models themselves but also in the technologies that underpin trustworthiness. Knowing the specific trustworthy technologies that have been employed is crucial for analyzing their effectiveness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge