Bowen Sun
CamReasoner: Reinforcing Camera Movement Understanding via Structured Spatial Reasoning
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Understanding camera dynamics is a fundamental pillar of video spatial intelligence. However, existing multimodal models predominantly treat this task as a black-box classification, often confusing physically distinct motions by relying on superficial visual patterns rather than geometric cues. We present CamReasoner, a framework that reformulates camera movement understanding as a structured inference process to bridge the gap between perception and cinematic logic. Our approach centers on the Observation-Thinking-Answer (O-T-A) paradigm, which compels the model to decode spatio-temporal cues such as trajectories and view frustums within an explicit reasoning block. To instill this capability, we construct a Large-scale Inference Trajectory Suite comprising 18k SFT reasoning chains and 38k RL feedback samples. Notably, we are the first to employ RL for logical alignment in this domain, ensuring motion inferences are grounded in physical geometry rather than contextual guesswork. By applying Reinforcement Learning to the Observation-Think-Answer (O-T-A) reasoning paradigm, CamReasoner effectively suppresses hallucinations and achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple benchmarks.
PAS: A Training-Free Stabilizer for Temporal Encoding in Video LLMs
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:Video LLMs suffer from temporal inconsistency: small shifts in frame timing can flip attention and suppress relevant frames. We trace this instability to the common extension of Rotary Position Embeddings to video through multimodal RoPE. The induced inverse Fourier time kernel exhibits frame-scale ripples that multiply adjacent frames by different factors, which perturbs attention that should otherwise be governed by the raw query key inner product. We present Phase Aggregated Smoothing (PAS), a simple, training-free mechanism that applies small opposed phase offsets across heads and then aggregates their outputs. PAS preserves the per-head spectrum magnitude, while the aggregation effectively smooths the temporal kernel and reduces phase sensitivity without changing the positional encoding structure. Our analysis shows that the RoPE rotated logit can be approximated as a content dot product scaled by a time kernel; smoothing this kernel yields Lipschitz stability of attention to small temporal shifts; multi phase averaging attenuates high frequency ripples while preserving per-head spectra under Nyquist-valid sampling. Experiments on multiple video understanding benchmarks under matched token budgets show consistent improvements with negligible computational overhead. PAS provides a plug and play upgrade for robust temporal encoding in Video LLMs.
Blockwise SFT for Diffusion Language Models: Reconciling Bidirectional Attention and Autoregressive Decoding
Aug 27, 2025Abstract:Discrete diffusion language models have shown strong potential for text generation, yet standard supervised fine-tuning (SFT) misaligns with their semi-autoregressive inference: training randomly masks tokens across the entire response, while inference generates fixed-size blocks sequentially. This mismatch introduces noisy prefixes and leaky suffixes, biasing gradients away from the desired blockwise likelihood. We propose Blockwise SFT, which partitions responses into fixed-size blocks, selects one active block per step for stochastic masking, freezes all preceding tokens, and fully hides future ones. Loss is computed only over the active block, directly mirroring the blockwise decoding process. Experiments on GSM8K, MATH, and MetaMathQA show consistent gains over classical SFT under equal compute or token budgets. Block size consistency studies and ablations confirm that improvements stem from faithful training-inference alignment rather than incidental masking effects. Our results highlight the importance of matching supervision granularity to the decoding procedure in diffusion-based language models.
Black-box Adversarial Attacks on CNN-based SLAM Algorithms
May 30, 2025Abstract:Continuous advancements in deep learning have led to significant progress in feature detection, resulting in enhanced accuracy in tasks like Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM). Nevertheless, the vulnerability of deep neural networks to adversarial attacks remains a challenge for their reliable deployment in applications, such as navigation of autonomous agents. Even though CNN-based SLAM algorithms are a growing area of research there is a notable absence of a comprehensive presentation and examination of adversarial attacks targeting CNN-based feature detectors, as part of a SLAM system. Our work introduces black-box adversarial perturbations applied to the RGB images fed into the GCN-SLAM algorithm. Our findings on the TUM dataset [30] reveal that even attacks of moderate scale can lead to tracking failure in as many as 76% of the frames. Moreover, our experiments highlight the catastrophic impact of attacking depth instead of RGB input images on the SLAM system.
AIR: A Systematic Analysis of Annotations, Instructions, and Response Pairs in Preference Dataset
Apr 04, 2025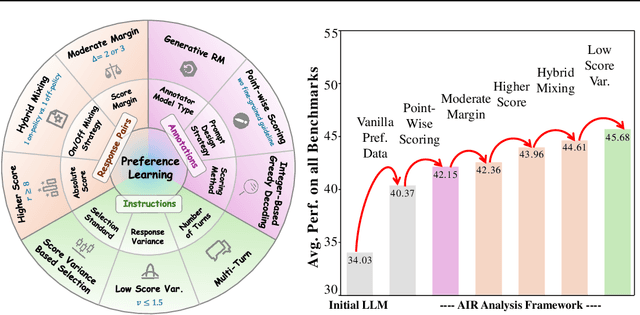
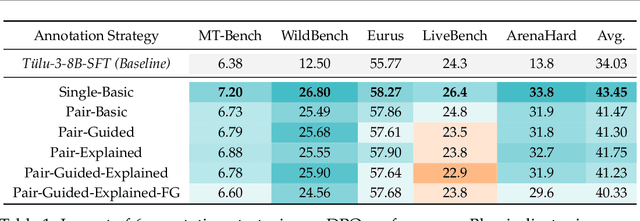
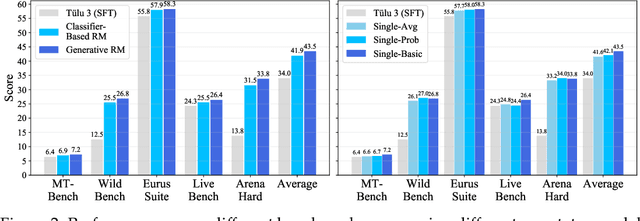
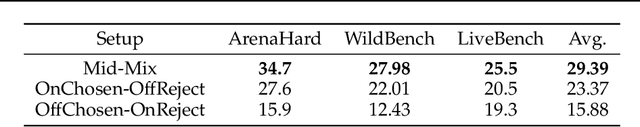
Abstract:Preference learning is critical for aligning large language models (LLMs) with human values, yet its success hinges on high-quality datasets comprising three core components: Preference \textbf{A}nnotations, \textbf{I}nstructions, and \textbf{R}esponse Pairs. Current approaches conflate these components, obscuring their individual impacts and hindering systematic optimization. In this work, we propose \textbf{AIR}, a component-wise analysis framework that systematically isolates and optimizes each component while evaluating their synergistic effects. Through rigorous experimentation, AIR reveals actionable principles: annotation simplicity (point-wise generative scoring), instruction inference stability (variance-based filtering across LLMs), and response pair quality (moderate margins + high absolute scores). When combined, these principles yield +5.3 average gains over baseline method, even with only 14k high-quality pairs. Our work shifts preference dataset design from ad hoc scaling to component-aware optimization, offering a blueprint for efficient, reproducible alignment.
Multi-Style Facial Sketch Synthesis through Masked Generative Modeling
Aug 22, 2024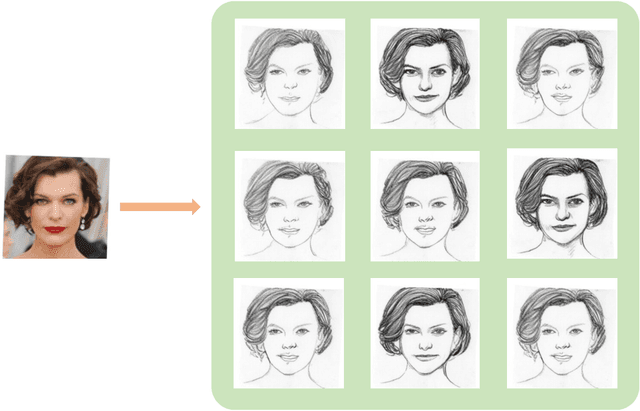
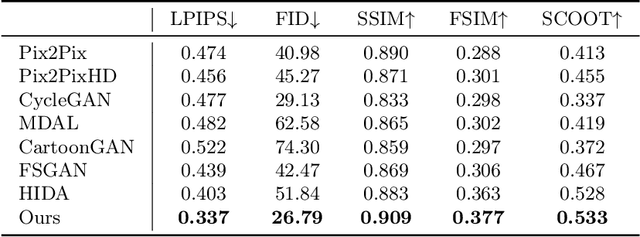
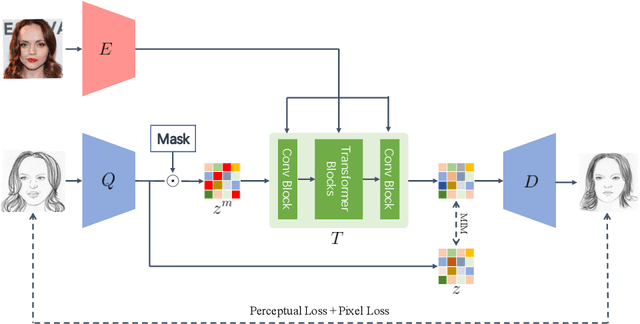

Abstract:The facial sketch synthesis (FSS) model, capable of generating sketch portraits from given facial photographs, holds profound implications across multiple domains, encompassing cross-modal face recognition, entertainment, art, media, among others. However, the production of high-quality sketches remains a formidable task, primarily due to the challenges and flaws associated with three key factors: (1) the scarcity of artist-drawn data, (2) the constraints imposed by limited style types, and (3) the deficiencies of processing input information in existing models. To address these difficulties, we propose a lightweight end-to-end synthesis model that efficiently converts images to corresponding multi-stylized sketches, obviating the necessity for any supplementary inputs (\eg, 3D geometry). In this study, we overcome the issue of data insufficiency by incorporating semi-supervised learning into the training process. Additionally, we employ a feature extraction module and style embeddings to proficiently steer the generative transformer during the iterative prediction of masked image tokens, thus achieving a continuous stylized output that retains facial features accurately in sketches. The extensive experiments demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms previous algorithms across multiple benchmarks, exhibiting a discernible disparity.
Large Language Models as Evaluators for Recommendation Explanations
Jun 06, 2024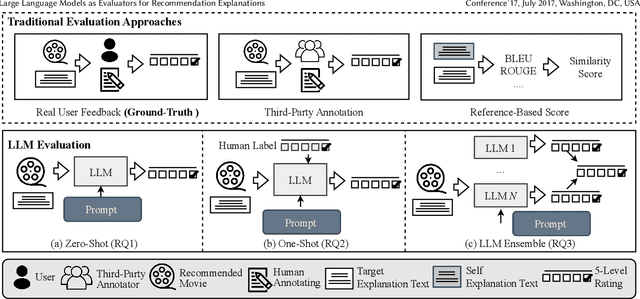
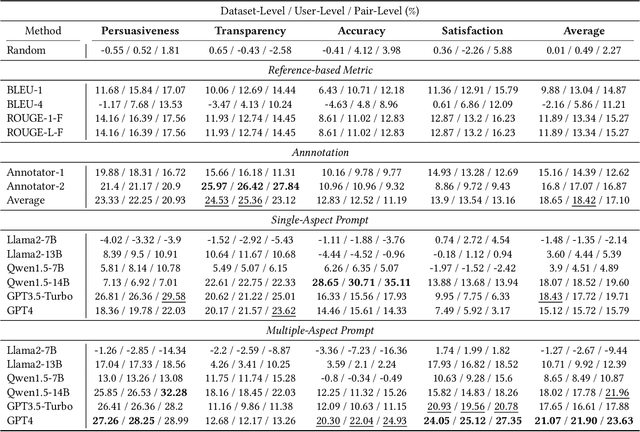


Abstract:The explainability of recommender systems has attracted significant attention in academia and industry. Many efforts have been made for explainable recommendations, yet evaluating the quality of the explanations remains a challenging and unresolved issue. In recent years, leveraging LLMs as evaluators presents a promising avenue in Natural Language Processing tasks (e.g., sentiment classification, information extraction), as they perform strong capabilities in instruction following and common-sense reasoning. However, evaluating recommendation explanatory texts is different from these NLG tasks, as its criteria are related to human perceptions and are usually subjective. In this paper, we investigate whether LLMs can serve as evaluators of recommendation explanations. To answer the question, we utilize real user feedback on explanations given from previous work and additionally collect third-party annotations and LLM evaluations. We design and apply a 3-level meta evaluation strategy to measure the correlation between evaluator labels and the ground truth provided by users. Our experiments reveal that LLMs, such as GPT4, can provide comparable evaluations with appropriate prompts and settings. We also provide further insights into combining human labels with the LLM evaluation process and utilizing ensembles of multiple heterogeneous LLM evaluators to enhance the accuracy and stability of evaluations. Our study verifies that utilizing LLMs as evaluators can be an accurate, reproducible and cost-effective solution for evaluating recommendation explanation texts. Our code is available at https://github.com/Xiaoyu-SZ/LLMasEvaluator.
Oxygen vacancies modulated VO2 for neurons and Spiking Neural Network construction
Apr 16, 2024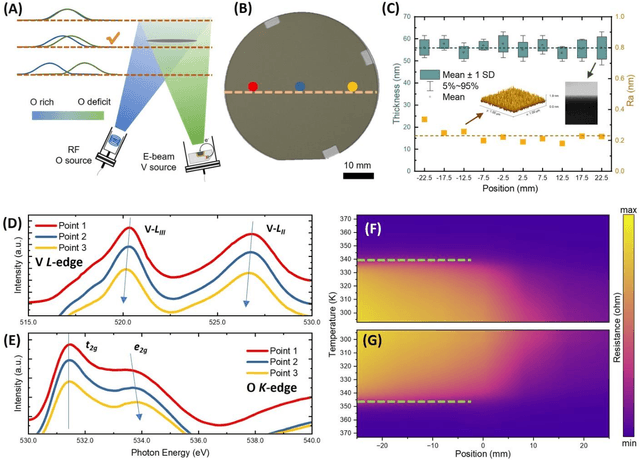
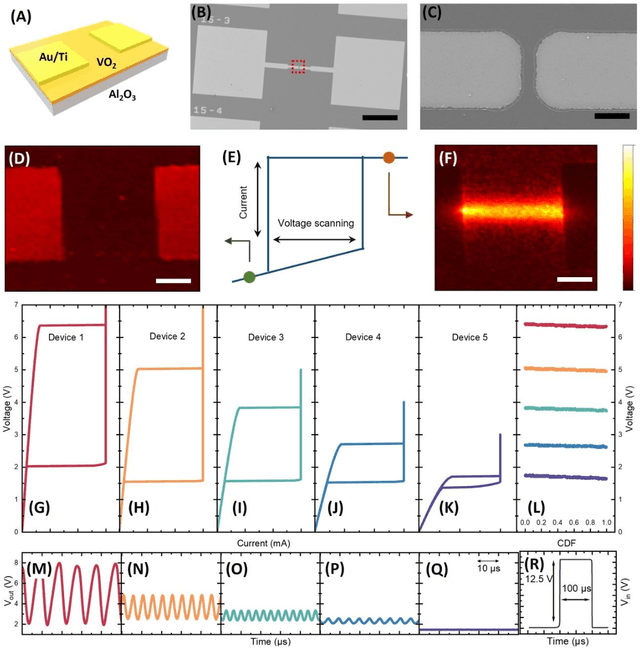
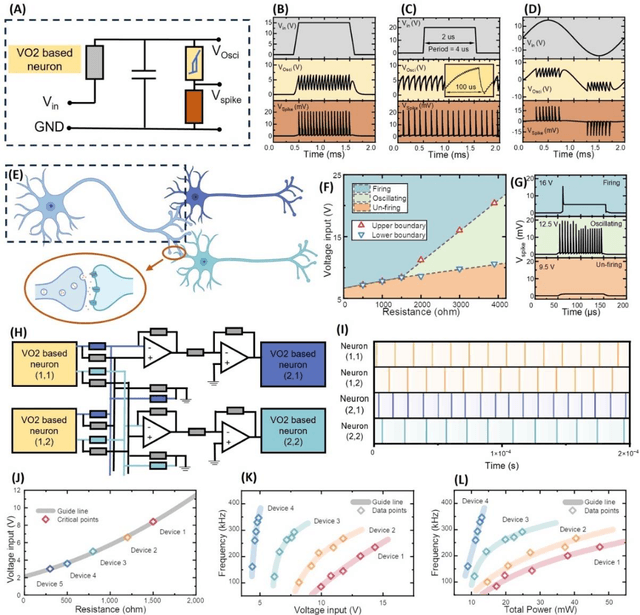
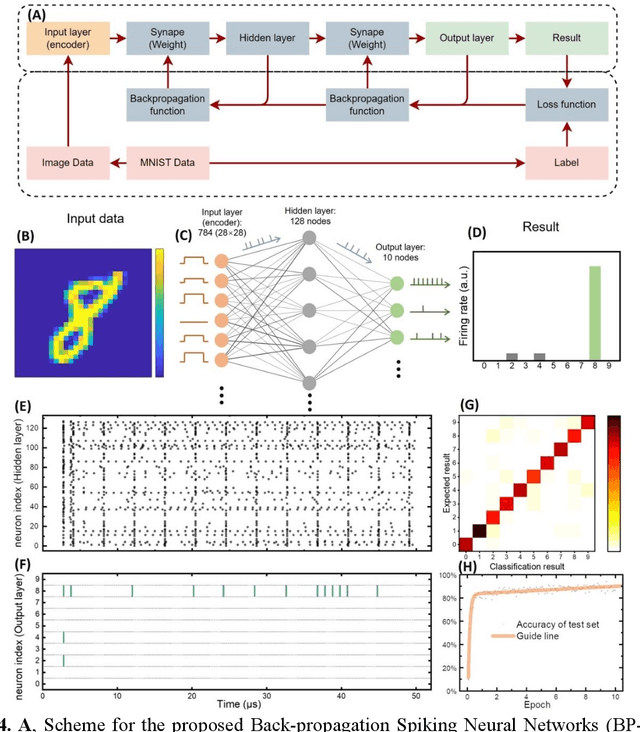
Abstract:Artificial neuronal devices are the basic building blocks for neuromorphic computing systems, which have been motivated by realistic brain emulation. Aiming for these applications, various device concepts have been proposed to mimic the neuronal dynamics and functions. While till now, the artificial neuron devices with high efficiency, high stability and low power consumption are still far from practical application. Due to the special insulator-metal phase transition, Vanadium Dioxide (VO2) has been considered as an idea candidate for neuronal device fabrication. However, its intrinsic insulating state requires the VO2 neuronal device to be driven under large bias voltage, resulting in high power consumption and low frequency. Thus in the current study, we have addressed this challenge by preparing oxygen vacancies modulated VO2 film(VO2-x) and fabricating the VO2-x neuronal devices for Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) construction. Results indicate the neuron devices can be operated under lower voltage with improved processing speed. The proposed VO2-x based back-propagation SNNs (BP-SNNs) system, trained with the MNIST dataset, demonstrates excellent accuracy in image recognition. Our study not only demonstrates the VO2-x based neurons and SNN system for practical application, but also offers an effective way to optimize the future neuromorphic computing systems by defect engineering strategy.
Controllable Preference Optimization: Toward Controllable Multi-Objective Alignment
Feb 29, 2024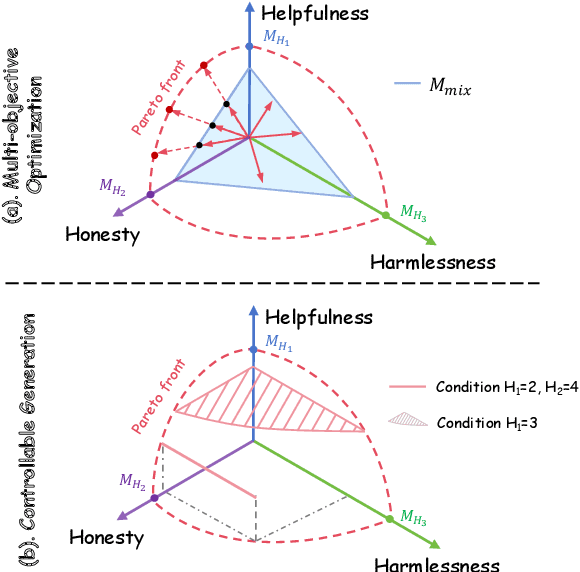
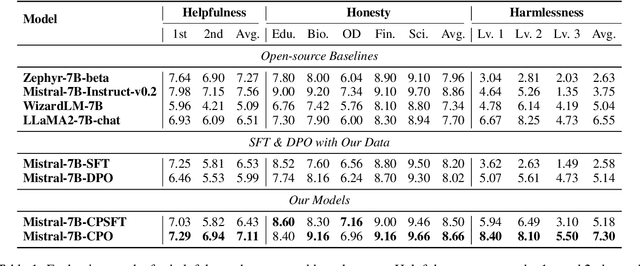
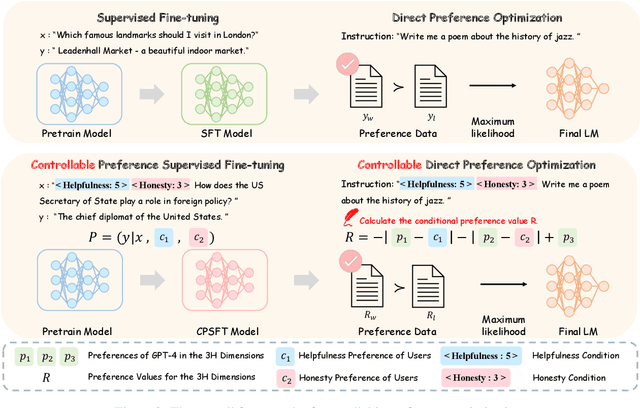
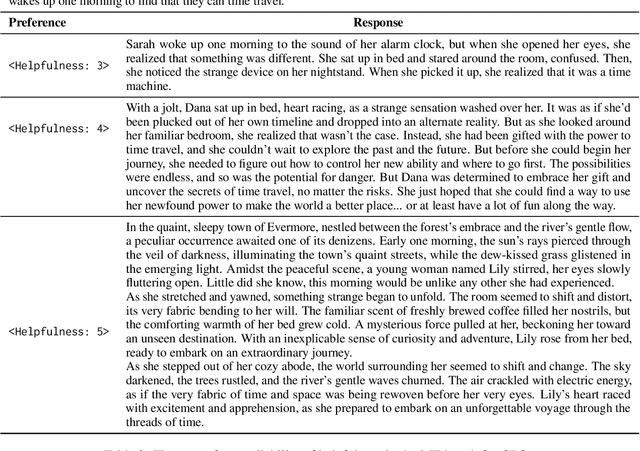
Abstract:Alignment in artificial intelligence pursues the consistency between model responses and human preferences as well as values. In practice, the multifaceted nature of human preferences inadvertently introduces what is known as the "alignment tax" -a compromise where enhancements in alignment within one objective (e.g.,harmlessness) can diminish performance in others (e.g.,helpfulness). However, existing alignment techniques are mostly unidirectional, leading to suboptimal trade-offs and poor flexibility over various objectives. To navigate this challenge, we argue the prominence of grounding LLMs with evident preferences. We introduce controllable preference optimization (CPO), which explicitly specifies preference scores for different objectives, thereby guiding the model to generate responses that meet the requirements. Our experimental analysis reveals that the aligned models can provide responses that match various preferences among the "3H" (helpfulness, honesty, harmlessness) desiderata. Furthermore, by introducing diverse data and alignment goals, we surpass baseline methods in aligning with single objectives, hence mitigating the impact of the alignment tax and achieving Pareto improvements in multi-objective alignment.
FreeFlow: A Comprehensive Understanding on Diffusion Probabilistic Models via Optimal Transport
Dec 09, 2023


Abstract:The blooming diffusion probabilistic models (DPMs) have garnered significant interest due to their impressive performance and the elegant inspiration they draw from physics. While earlier DPMs relied upon the Markovian assumption, recent methods based on differential equations have been rapidly applied to enhance the efficiency and capabilities of these models. However, a theoretical interpretation encapsulating these diverse algorithms is insufficient yet pressingly required to guide further development of DPMs. In response to this need, we present FreeFlow, a framework that provides a thorough explanation of the diffusion formula as time-dependent optimal transport, where the evolutionary pattern of probability density is given by the gradient flows of a functional defined in Wasserstein space. Crucially, our framework necessitates a unified description that not only clarifies the subtle mechanism of DPMs but also indicates the roots of some defects through creative involvement of Lagrangian and Eulerian views to understand the evolution of probability flow. We particularly demonstrate that the core equation of FreeFlow condenses all stochastic and deterministic DPMs into a single case, showcasing the expansibility of our method. Furthermore, the Riemannian geometry employed in our work has the potential to bridge broader subjects in mathematics, which enable the involvement of more profound tools for the establishment of more outstanding and generalized models in the future.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge