Yiwei Wang
University of California, Merced, USA
Accordion-Thinking: Self-Regulated Step Summaries for Efficient and Readable LLM Reasoning
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Scaling test-time compute via long Chain-ofThought unlocks remarkable gains in reasoning capabilities, yet it faces practical limits due to the linear growth of KV cache and quadratic attention complexity. In this paper, we introduce Accordion-Thinking, an end-to-end framework where LLMs learn to self-regulate the granularity of the reasoning steps through dynamic summarization. This mechanism enables a Fold inference mode, where the model periodically summarizes its thought process and discards former thoughts to reduce dependency on historical tokens. We apply reinforcement learning to incentivize this capability further, uncovering a critical insight: the accuracy gap between the highly efficient Fold mode and the exhaustive Unfold mode progressively narrows and eventually vanishes over the course of training. This phenomenon demonstrates that the model learns to encode essential reasoning information into compact summaries, achieving effective compression of the reasoning context. Our Accordion-Thinker demonstrates that with learned self-compression, LLMs can tackle complex reasoning tasks with minimal dependency token overhead without compromising solution quality, and it achieves a 3x throughput while maintaining accuracy on a 48GB GPU memory configuration, while the structured step summaries provide a human-readable account of the reasoning process.
ProjDevBench: Benchmarking AI Coding Agents on End-to-End Project Development
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Recent coding agents can generate complete codebases from simple prompts, yet existing evaluations focus on issue-level bug fixing and lag behind end-to-end development. We introduce ProjDevBench, an end-to-end benchmark that provides project requirements to coding agents and evaluates the resulting repositories. Combining Online Judge (OJ) testing with LLM-assisted code review, the benchmark evaluates agents on (1) system architecture design, (2) functional correctness, and (3) iterative solution refinement. We curate 20 programming problems across 8 categories, covering both concept-oriented tasks and real-world application scenarios, and evaluate six coding agents built on different LLM backends. Our evaluation reports an overall acceptance rate of 27.38%: agents handle basic functionality and data structures but struggle with complex system design, time complexity optimization, and resource management. Our benchmark is available at https://github.com/zsworld6/projdevbench.
CamReasoner: Reinforcing Camera Movement Understanding via Structured Spatial Reasoning
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Understanding camera dynamics is a fundamental pillar of video spatial intelligence. However, existing multimodal models predominantly treat this task as a black-box classification, often confusing physically distinct motions by relying on superficial visual patterns rather than geometric cues. We present CamReasoner, a framework that reformulates camera movement understanding as a structured inference process to bridge the gap between perception and cinematic logic. Our approach centers on the Observation-Thinking-Answer (O-T-A) paradigm, which compels the model to decode spatio-temporal cues such as trajectories and view frustums within an explicit reasoning block. To instill this capability, we construct a Large-scale Inference Trajectory Suite comprising 18k SFT reasoning chains and 38k RL feedback samples. Notably, we are the first to employ RL for logical alignment in this domain, ensuring motion inferences are grounded in physical geometry rather than contextual guesswork. By applying Reinforcement Learning to the Observation-Think-Answer (O-T-A) reasoning paradigm, CamReasoner effectively suppresses hallucinations and achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple benchmarks.
Self-Manager: Parallel Agent Loop for Long-form Deep Research
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:Long-form deep research requires multi-faceted investigations over extended horizons to get a comprehensive report. When handling such complex tasks, existing agents manage context at the subtask level to overcome linear context accumulation and information loss. However, they still adhere to a single context window and sequential execution paradigm, which results in mutual interference and blocking behavior, restricting scalability and adaptability. To address this issue, this paper introduces Self-Manager, a parallel agent loop that enables asynchronous and concurrent execution. The main thread can create multiple subthreads, each with its own isolated context, and manage them iteratively through Thread Control Blocks, allowing for more focused and flexible parallel agent execution. To assess its effectiveness, we benchmark Self-Manager on DeepResearch Bench, where it consistently outperforms existing single-agent loop baselines across all metrics. Furthermore, we conduct extensive analytical experiments to demonstrate the necessity of Self-Manager's design choices, as well as its advantages in contextual capacity, efficiency, and generalization.
OptiSQL: Executable SQL Generation from Optical Tokens
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Executable SQL generation is typically studied in text-to-SQL settings, where tables are provided as fully linearized textual schemas and contents. While effective, this formulation assumes access to structured text and incurs substantial token overhead, which is misaligned with many real-world scenarios where tables appear as visual artifacts in documents or webpages. We investigate whether compact optical representations can serve as an efficient interface for executable semantic parsing. We present OptiSQL, a vision-driven framework that generates executable SQL directly from table images and natural language questions using compact optical tokens. OptiSQL leverages an OCR-oriented visual encoder to compress table structure and content into a small set of optical tokens and fine-tunes a pretrained decoder for SQL generation while freezing the encoder to isolate representation sufficiency. Experiments on a visualized version of Spider 2.0-Snow show that OptiSQL retains strong execution accuracy while reducing table input tokens by an order of magnitude. Robustness analyses further demonstrate that optical tokens preserve essential structural information under visual perturbations.
Locate, Steer, and Improve: A Practical Survey of Actionable Mechanistic Interpretability in Large Language Models
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Mechanistic Interpretability (MI) has emerged as a vital approach to demystify the opaque decision-making of Large Language Models (LLMs). However, existing reviews primarily treat MI as an observational science, summarizing analytical insights while lacking a systematic framework for actionable intervention. To bridge this gap, we present a practical survey structured around the pipeline: "Locate, Steer, and Improve." We formally categorize Localizing (diagnosis) and Steering (intervention) methods based on specific Interpretable Objects to establish a rigorous intervention protocol. Furthermore, we demonstrate how this framework enables tangible improvements in Alignment, Capability, and Efficiency, effectively operationalizing MI as an actionable methodology for model optimization. The curated paper list of this work is available at https://github.com/rattlesnakey/Awesome-Actionable-MI-Survey.
Gated Differentiable Working Memory for Long-Context Language Modeling
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Long contexts challenge transformers: attention scores dilute across thousands of tokens, critical information is often lost in the middle, and models struggle to adapt to novel patterns at inference time. Recent work on test-time adaptation addresses this by maintaining a form of working memory -- transient parameters updated on the current context -- but existing approaches rely on uniform write policies that waste computation on low-utility regions and suffer from high gradient variance across semantically heterogeneous contexts. In this work, we reframe test-time adaptation as a budget-constrained memory consolidation problem, focusing on which parts of the context should be consolidated into working memory under limited computation. We propose Gdwm (Gated Differentiable Working Memory), a framework that introduces a write controller to gate the consolidation process. The controller estimates Contextual Utility, an information-theoretic measure of long-range contextual dependence, and allocates gradient steps accordingly while maintaining global coverage. Experiments on ZeroSCROLLS and LongBench v2 demonstrate that Gdwm achieves comparable or superior performance with 4$\times$ fewer gradient steps than uniform baselines, establishing a new efficiency-performance Pareto frontier for test-time adaptation.
EchoFoley: Event-Centric Hierarchical Control for Video Grounded Creative Sound Generation
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:Sound effects build an essential layer of multimodal storytelling, shaping the emotional atmosphere and the narrative semantics of videos. Despite recent advancement in video-text-to-audio (VT2A), the current formulation faces three key limitations: First, an imbalance between visual and textual conditioning that leads to visual dominance; Second, the absence of a concrete definition for fine-grained controllable generation; Third, weak instruction understanding and following, as existing datasets rely on brief categorical tags. To address these limitations, we introduce EchoFoley, a new task designed for video-grounded sound generation with both event level local control and hierarchical semantic control. Our symbolic representation for sounding events specifies when, what, and how each sound is produced within a video or instruction, enabling fine-grained controls like sound generation, insertion, and editing. To support this task, we construct EchoFoley-6k, a large-scale, expert-curated benchmark containing over 6,000 video-instruction-annotation triplets. Building upon this foundation, we propose EchoVidia a sounding-event-centric agentic generation framework with slow-fast thinking strategy. Experiments show that EchoVidia surpasses recent VT2A models by 40.7% in controllability and 12.5% in perceptual quality.
Bi-Erasing: A Bidirectional Framework for Concept Removal in Diffusion Models
Dec 16, 2025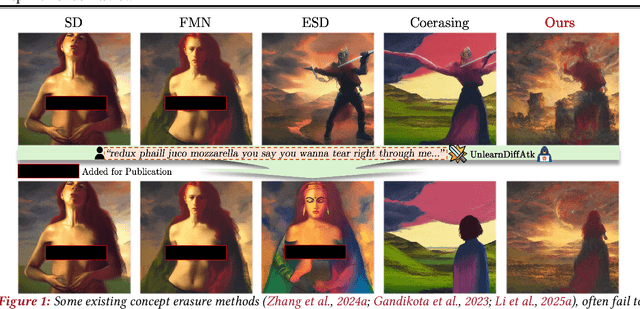
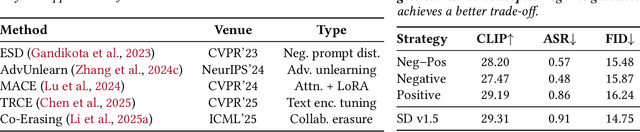
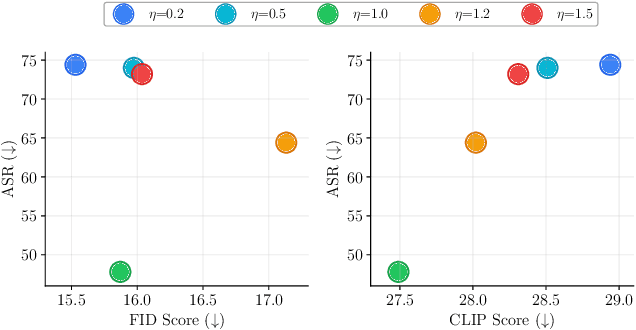
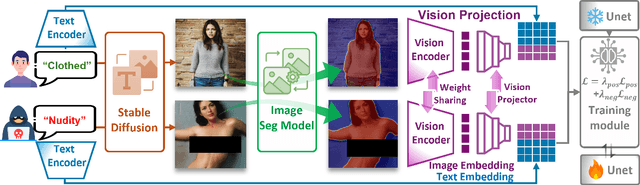
Abstract:Concept erasure, which fine-tunes diffusion models to remove undesired or harmful visual concepts, has become a mainstream approach to mitigating unsafe or illegal image generation in text-to-image models.However, existing removal methods typically adopt a unidirectional erasure strategy by either suppressing the target concept or reinforcing safe alternatives, making it difficult to achieve a balanced trade-off between concept removal and generation quality. To address this limitation, we propose a novel Bidirectional Image-Guided Concept Erasure (Bi-Erasing) framework that performs concept suppression and safety enhancement simultaneously. Specifically, based on the joint representation of text prompts and corresponding images, Bi-Erasing introduces two decoupled image branches: a negative branch responsible for suppressing harmful semantics and a positive branch providing visual guidance for safe alternatives. By jointly optimizing these complementary directions, our approach achieves a balance between erasure efficacy and generation usability. In addition, we apply mask-based filtering to the image branches to prevent interference from irrelevant content during the erasure process. Across extensive experiment evaluations, the proposed Bi-Erasing outperforms baseline methods in balancing concept removal effectiveness and visual fidelity.
Reward and Guidance through Rubrics: Promoting Exploration to Improve Multi-Domain Reasoning
Nov 18, 2025



Abstract:Recent advances in reinforcement learning (RL) have significantly improved the complex reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs). Despite these successes, existing methods mainly focus on single-domain RL (e.g., mathematics) with verifiable rewards (RLVR), and their reliance on purely online RL frameworks restricts the exploration space, thereby limiting reasoning performance. In this paper, we address these limitations by leveraging rubrics to provide both fine-grained reward signals and offline guidance. We propose $\textbf{RGR-GRPO}$ (Reward and Guidance through Rubrics), a rubric-driven RL framework for multi-domain reasoning. RGR-GRPO enables LLMs to receive dense and informative rewards while exploring a larger solution space during GRPO training. Extensive experiments across 14 benchmarks spanning multiple domains demonstrate that RGR-GRPO consistently outperforms RL methods that rely solely on alternative reward schemes or offline guidance. Compared with verifiable online RL baseline, RGR-GRPO achieves average improvements of +7.0%, +5.4%, +8.4%, and +6.6% on mathematics, physics, chemistry, and general reasoning tasks, respectively. Notably, RGR-GRPO maintains stable entropy fluctuations during off-policy training and achieves superior pass@k performance, reflecting sustained exploration and effective breakthrough beyond existing performance bottlenecks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge