Zhong-Zhi Li
Training LLMs for Divide-and-Conquer Reasoning Elevates Test-Time Scalability
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated strong reasoning capabilities through step-by-step chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning. Nevertheless, at the limits of model capability, CoT often proves insufficient, and its strictly sequential nature constrains test-time scalability. A potential alternative is divide-and-conquer (DAC) reasoning, which decomposes a complex problem into subproblems to facilitate more effective exploration of the solution. Although promising, our analysis reveals a fundamental misalignment between general-purpose post-training and DAC-style inference, which limits the model's capacity to fully leverage this potential. To bridge this gap and fully unlock LLMs' reasoning capabilities on the most challenging tasks, we propose an end-to-end reinforcement learning (RL) framework to enhance their DAC-style reasoning capacity. At each step, the policy decomposes a problem into a group of subproblems, solves them sequentially, and addresses the original one conditioned on the subproblem solutions, with both decomposition and solution integrated into RL training. Under comparable training, our DAC-style framework endows the model with a higher performance ceiling and stronger test-time scalability, surpassing CoT by 8.6% in Pass@1 and 6.3% in Pass@32 on competition-level benchmarks.
MedKGent: A Large Language Model Agent Framework for Constructing Temporally Evolving Medical Knowledge Graph
Aug 17, 2025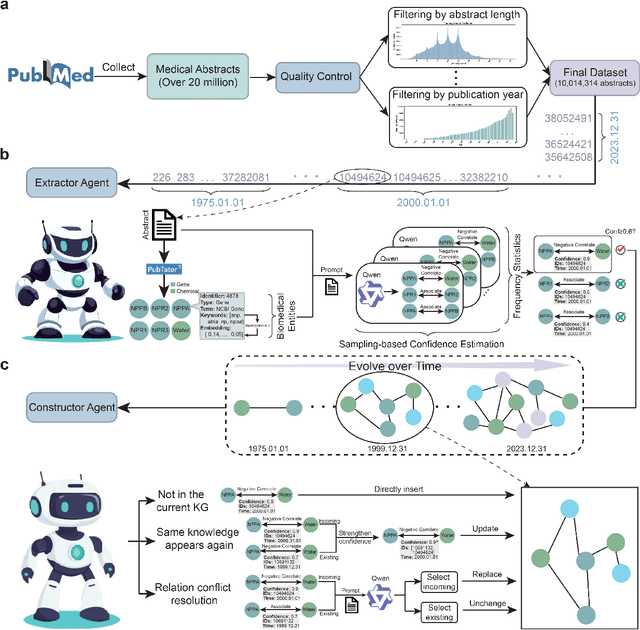
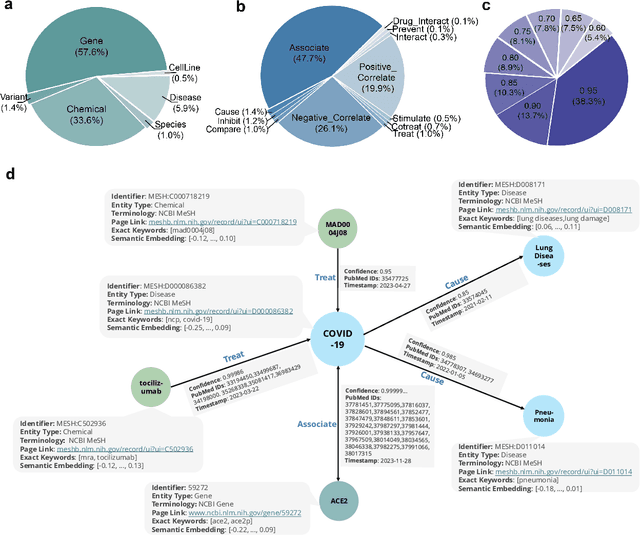
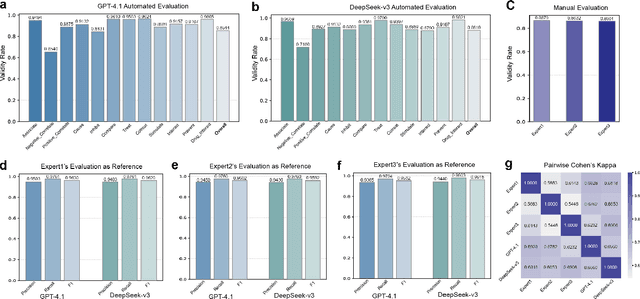
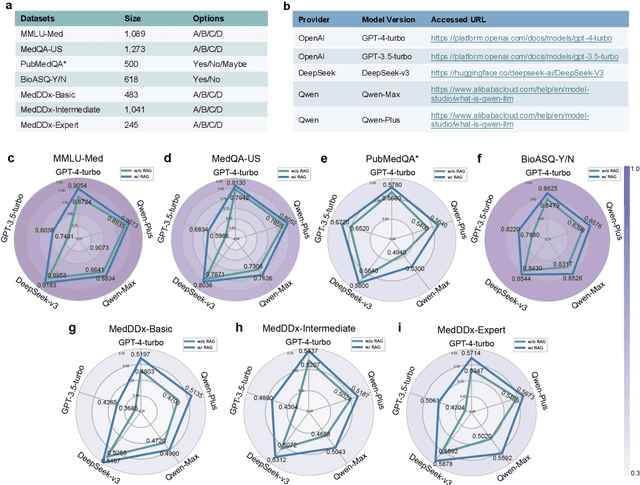
Abstract:The rapid expansion of medical literature presents growing challenges for structuring and integrating domain knowledge at scale. Knowledge Graphs (KGs) offer a promising solution by enabling efficient retrieval, automated reasoning, and knowledge discovery. However, current KG construction methods often rely on supervised pipelines with limited generalizability or naively aggregate outputs from Large Language Models (LLMs), treating biomedical corpora as static and ignoring the temporal dynamics and contextual uncertainty of evolving knowledge. To address these limitations, we introduce MedKGent, a LLM agent framework for constructing temporally evolving medical KGs. Leveraging over 10 million PubMed abstracts published between 1975 and 2023, we simulate the emergence of biomedical knowledge via a fine-grained daily time series. MedKGent incrementally builds the KG in a day-by-day manner using two specialized agents powered by the Qwen2.5-32B-Instruct model. The Extractor Agent identifies knowledge triples and assigns confidence scores via sampling-based estimation, which are used to filter low-confidence extractions and inform downstream processing. The Constructor Agent incrementally integrates the retained triples into a temporally evolving graph, guided by confidence scores and timestamps to reinforce recurring knowledge and resolve conflicts. The resulting KG contains 156,275 entities and 2,971,384 relational triples. Quality assessments by two SOTA LLMs and three domain experts demonstrate an accuracy approaching 90\%, with strong inter-rater agreement. To evaluate downstream utility, we conduct RAG across seven medical question answering benchmarks using five leading LLMs, consistently observing significant improvements over non-augmented baselines. Case studies further demonstrate the KG's value in literature-based drug repurposing via confidence-aware causal inference.
A Survey of Context Engineering for Large Language Models
Jul 17, 2025Abstract:The performance of Large Language Models (LLMs) is fundamentally determined by the contextual information provided during inference. This survey introduces Context Engineering, a formal discipline that transcends simple prompt design to encompass the systematic optimization of information payloads for LLMs. We present a comprehensive taxonomy decomposing Context Engineering into its foundational components and the sophisticated implementations that integrate them into intelligent systems. We first examine the foundational components: context retrieval and generation, context processing and context management. We then explore how these components are architecturally integrated to create sophisticated system implementations: retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), memory systems and tool-integrated reasoning, and multi-agent systems. Through this systematic analysis of over 1300 research papers, our survey not only establishes a technical roadmap for the field but also reveals a critical research gap: a fundamental asymmetry exists between model capabilities. While current models, augmented by advanced context engineering, demonstrate remarkable proficiency in understanding complex contexts, they exhibit pronounced limitations in generating equally sophisticated, long-form outputs. Addressing this gap is a defining priority for future research. Ultimately, this survey provides a unified framework for both researchers and engineers advancing context-aware AI.
SwS: Self-aware Weakness-driven Problem Synthesis in Reinforcement Learning for LLM Reasoning
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) has proven effective for training large language models (LLMs) on complex reasoning tasks, such as mathematical problem solving. A prerequisite for the scalability of RLVR is a high-quality problem set with precise and verifiable answers. However, the scarcity of well-crafted human-labeled math problems and limited-verification answers in existing distillation-oriented synthetic datasets limit their effectiveness in RL. Additionally, most problem synthesis strategies indiscriminately expand the problem set without considering the model's capabilities, leading to low efficiency in generating useful questions. To mitigate this issue, we introduce a Self-aware Weakness-driven problem Synthesis framework (SwS) that systematically identifies model deficiencies and leverages them for problem augmentation. Specifically, we define weaknesses as questions that the model consistently fails to learn through its iterative sampling during RL training. We then extract the core concepts from these failure cases and synthesize new problems to strengthen the model's weak areas in subsequent augmented training, enabling it to focus on and gradually overcome its weaknesses. Without relying on external knowledge distillation, our framework enables robust generalization byempowering the model to self-identify and address its weaknesses in RL, yielding average performance gains of 10.0% and 7.7% on 7B and 32B models across eight mainstream reasoning benchmarks.
From System 1 to System 2: A Survey of Reasoning Large Language Models
Feb 25, 2025Abstract:Achieving human-level intelligence requires refining the transition from the fast, intuitive System 1 to the slower, more deliberate System 2 reasoning. While System 1 excels in quick, heuristic decisions, System 2 relies on logical reasoning for more accurate judgments and reduced biases. Foundational Large Language Models (LLMs) excel at fast decision-making but lack the depth for complex reasoning, as they have not yet fully embraced the step-by-step analysis characteristic of true System 2 thinking. Recently, reasoning LLMs like OpenAI's o1/o3 and DeepSeek's R1 have demonstrated expert-level performance in fields such as mathematics and coding, closely mimicking the deliberate reasoning of System 2 and showcasing human-like cognitive abilities. This survey begins with a brief overview of the progress in foundational LLMs and the early development of System 2 technologies, exploring how their combination has paved the way for reasoning LLMs. Next, we discuss how to construct reasoning LLMs, analyzing their features, the core methods enabling advanced reasoning, and the evolution of various reasoning LLMs. Additionally, we provide an overview of reasoning benchmarks, offering an in-depth comparison of the performance of representative reasoning LLMs. Finally, we explore promising directions for advancing reasoning LLMs and maintain a real-time \href{https://github.com/zzli2022/Awesome-Slow-Reason-System}{GitHub Repository} to track the latest developments. We hope this survey will serve as a valuable resource to inspire innovation and drive progress in this rapidly evolving field.
LongDocURL: a Comprehensive Multimodal Long Document Benchmark Integrating Understanding, Reasoning, and Locating
Dec 24, 2024Abstract:Large vision language models (LVLMs) have improved the document understanding capabilities remarkably, enabling the handling of complex document elements, longer contexts, and a wider range of tasks. However, existing document understanding benchmarks have been limited to handling only a small number of pages and fail to provide a comprehensive analysis of layout elements locating. In this paper, we first define three primary task categories: Long Document Understanding, numerical Reasoning, and cross-element Locating, and then propose a comprehensive benchmark, LongDocURL, integrating above three primary tasks and comprising 20 sub-tasks categorized based on different primary tasks and answer evidences. Furthermore, we develop a semi-automated construction pipeline and collect 2,325 high-quality question-answering pairs, covering more than 33,000 pages of documents, significantly outperforming existing benchmarks. Subsequently, we conduct comprehensive evaluation experiments on both open-source and closed-source models across 26 different configurations, revealing critical performance gaps in this field.
Fuse, Reason and Verify: Geometry Problem Solving with Parsed Clauses from Diagram
Jul 10, 2024Abstract:Geometry problem solving (GPS) requires capacities of multi-modal understanding, multi-hop reasoning and theorem knowledge application. In this paper, we propose a neural-symbolic model for plane geometry problem solving (PGPS), named PGPSNet-v2, with three key steps: modal fusion, reasoning process and knowledge verification. In modal fusion, we leverage textual clauses to express fine-grained structural and semantic content of geometry diagram, and fuse diagram with textual problem efficiently through structural-semantic pre-training. For reasoning, we design an explicable solution program to describe the geometric reasoning process, and employ a self-limited decoder to generate solution program autoregressively. To reduce solution errors, a multi-level theorem verifier is proposed to eliminate solutions that do not match geometric principles, alleviating the hallucination of the neural model. We also construct a large-scale geometry problem dataset called PGPS9K, containing fine-grained annotations of textual clauses, solution program and involved knowledge tuples. Extensive experiments on datasets Geometry3K and PGPS9K show that our PGPSNet solver outperforms existing symbolic and neural solvers in GPS performance, while maintaining good explainability and reliability, and the solver components (fusion, reasoning, verification) are all justified effective.
LANS: A Layout-Aware Neural Solver for Plane Geometry Problem
Nov 25, 2023Abstract:Geometry problem solving (GPS) is a challenging mathematical reasoning task requiring multi-modal understanding, fusion and reasoning. Existing neural solvers take GPS as a vision-language task but be short in the representation of geometry diagrams which carry rich and complex layout information. In this paper, we propose a layout-aware neural solver named LANS, integrated with two new modules: multimodal layout-aware pre-trained language model (MLA-PLM) and layout-aware fusion attention (LA-FA). MLA-PLM adopts structural and semantic pre-training (SSP) to implement global relationship modeling, and point matching pre-training (PMP) to achieve alignment between visual points and textual points. LA-FA employs a layout-aware attention mask to realize point-guided cross-modal fusion for further boosting layout awareness of LANS. Extensive experiments on datasets Geometry3K and PGPS9K validate the effectiveness of the layout-aware modules and superior problem solving performance of our LANS solver, over existing symbolic solvers and neural solvers. The code will make public available soon.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge