Jun Song
How Foundational Skills Influence VLM-based Embodied Agents:A Native Perspective
Feb 24, 2026Abstract:Recent advances in vision-language models (VLMs) have shown promise for human-level embodied intelligence. However, existing benchmarks for VLM-driven embodied agents often rely on high-level commands or discretized action spaces, which are non-native settings that differ markedly from real-world control. In addition, current benchmarks focus primarily on high-level tasks and lack joint evaluation and analysis at both low and high levels. To address these limitations, we present NativeEmbodied, a challenging benchmark for VLM-driven embodied agents that uses a unified, native low-level action space. Built on diverse simulated scenes, NativeEmbodied includes three representative high-level tasks in complex scenarios to evaluate overall performance. For more detailed analysis, we further decouple the skills required by complex tasks and construct four types of low-level tasks, each targeting a fundamental embodied skill. This joint evaluation across task and skill granularities enables fine-grained assessment of embodied agents. Experiments with state-of-the-art VLMs reveal clear deficiencies in several fundamental embodied skills, and further analysis shows that these bottlenecks significantly limit performance on high-level tasks. NativeEmbodied highlights key challenges for current VLM-driven embodied agents and provides insights to guide future research.
GeoEyes: On-Demand Visual Focusing for Evidence-Grounded Understanding of Ultra-High-Resolution Remote Sensing Imagery
Feb 15, 2026Abstract:The "thinking-with-images" paradigm enables multimodal large language models (MLLMs) to actively explore visual scenes via zoom-in tools. This is essential for ultra-high-resolution (UHR) remote sensing VQA, where task-relevant cues are sparse and tiny. However, we observe a consistent failure mode in existing zoom-enabled MLLMs: Tool Usage Homogenization, where tool calls collapse into task-agnostic patterns, limiting effective evidence acquisition. To address this, we propose GeoEyes, a staged training framework consisting of (1) a cold-start SFT dataset, UHR Chain-of-Zoom (UHR-CoZ), which covers diverse zooming regimes, and (2) an agentic reinforcement learning method, AdaZoom-GRPO, that explicitly rewards evidence gain and answer improvement during zoom interactions. The resulting model learns on-demand zooming with proper stopping behavior and achieves substantial improvements on UHR remote sensing benchmarks, with 54.23% accuracy on XLRS-Bench.
Text Before Vision: Staged Knowledge Injection Matters for Agentic RLVR in Ultra-High-Resolution Remote Sensing Understanding
Feb 15, 2026Abstract:Multimodal reasoning for ultra-high-resolution (UHR) remote sensing (RS) is usually bottlenecked by visual evidence acquisition: the model necessitates localizing tiny task-relevant regions in massive pixel spaces. While Agentic Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) using zoom-in tools offers a path forward, we find that standard reinforcement learning struggles to navigate these vast visual spaces without structured domain priors. In this paper, we investigate the interplay between post-training paradigms: comparing Cold-start Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT), RLVR, and Agentic RLVR on the UHR RS benchmark.Our controlled studies yield a counter-intuitive finding: high-quality Earth-science text-only QA is a primary driver of UHR visual reasoning gains. Despite lacking images, domain-specific text injects the concepts, mechanistic explanations, and decision rules necessary to guide visual evidence retrieval.Based on this, we propose a staged knowledge injection recipe: (1) cold-starting with scalable, knowledge-graph-verified Earth-science text QA to instill reasoning structures;and (2) "pre-warming" on the same hard UHR image-text examples during SFT to stabilize and amplify subsequent tool-based RL. This approach achieves a 60.40% Pass@1 on XLRS-Bench, significantly outperforming larger general purpose models (e.g., GPT-5.2, Gemini 3.0 Pro, Intern-S1) and establishing a new state-of-the-art.
Contribution-aware Token Compression for Efficient Video Understanding via Reinforcement Learning
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Video large language models have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in video understanding tasks. However, the redundancy of video tokens introduces significant computational overhead during inference, limiting their practical deployment. Many compression algorithms are proposed to prioritize retaining features with the highest attention scores to minimize perturbations in attention computations. However, the correlation between attention scores and their actual contribution to correct answers remains ambiguous. To address the above limitation, we propose a novel \textbf{C}ontribution-\textbf{a}ware token \textbf{Co}mpression algorithm for \textbf{VID}eo understanding (\textbf{CaCoVID}) that explicitly optimizes the token selection policy based on the contribution of tokens to correct predictions. First, we introduce a reinforcement learning-based framework that optimizes a policy network to select video token combinations with the greatest contribution to correct predictions. This paradigm shifts the focus from passive token preservation to active discovery of optimal compressed token combinations. Secondly, we propose a combinatorial policy optimization algorithm with online combination space sampling, which dramatically reduces the exploration space for video token combinations and accelerates the convergence speed of policy optimization. Extensive experiments on diverse video understanding benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of CaCoVID. Codes will be released.
The Flexibility Trap: Why Arbitrary Order Limits Reasoning Potential in Diffusion Language Models
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Diffusion Large Language Models (dLLMs) break the rigid left-to-right constraint of traditional LLMs, enabling token generation in arbitrary orders. Intuitively, this flexibility implies a solution space that strictly supersets the fixed autoregressive trajectory, theoretically unlocking superior reasoning potential for general tasks like mathematics and coding. Consequently, numerous works have leveraged reinforcement learning (RL) to elicit the reasoning capability of dLLMs. In this paper, we reveal a counter-intuitive reality: arbitrary order generation, in its current form, narrows rather than expands the reasoning boundary of dLLMs. We find that dLLMs tend to exploit this order flexibility to bypass high-uncertainty tokens that are crucial for exploration, leading to a premature collapse of the solution space. This observation challenges the premise of existing RL approaches for dLLMs, where considerable complexities, such as handling combinatorial trajectories and intractable likelihoods, are often devoted to preserving this flexibility. We demonstrate that effective reasoning is better elicited by intentionally forgoing arbitrary order and applying standard Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) instead. Our approach, JustGRPO, is minimalist yet surprisingly effective (e.g., 89.1% accuracy on GSM8K) while fully retaining the parallel decoding ability of dLLMs. Project page: https://nzl-thu.github.io/the-flexibility-trap
Unified Thinker: A General Reasoning Modular Core for Image Generation
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Despite impressive progress in high-fidelity image synthesis, generative models still struggle with logic-intensive instruction following, exposing a persistent reasoning--execution gap. Meanwhile, closed-source systems (e.g., Nano Banana) have demonstrated strong reasoning-driven image generation, highlighting a substantial gap to current open-source models. We argue that closing this gap requires not merely better visual generators, but executable reasoning: decomposing high-level intents into grounded, verifiable plans that directly steer the generative process. To this end, we propose Unified Thinker, a task-agnostic reasoning architecture for general image generation, designed as a unified planning core that can plug into diverse generators and workflows. Unified Thinker decouples a dedicated Thinker from the image Generator, enabling modular upgrades of reasoning without retraining the entire generative model. We further introduce a two-stage training paradigm: we first build a structured planning interface for the Thinker, then apply reinforcement learning to ground its policy in pixel-level feedback, encouraging plans that optimize visual correctness over textual plausibility. Extensive experiments on text-to-image generation and image editing show that Unified Thinker substantially improves image reasoning and generation quality.
CaveAgent: Transforming LLMs into Stateful Runtime Operators
Jan 04, 2026Abstract:LLM-based agents are increasingly capable of complex task execution, yet current agentic systems remain constrained by text-centric paradigms. Traditional approaches rely on procedural JSON-based function calling, which often struggles with long-horizon tasks due to fragile multi-turn dependencies and context drift. In this paper, we present CaveAgent, a framework that transforms the paradigm from "LLM-as-Text-Generator" to "LLM-as-Runtime-Operator." We introduce a Dual-stream Context Architecture that decouples state management into a lightweight semantic stream for reasoning and a persistent, deterministic Python Runtime stream for execution. In addition to leveraging code generation to efficiently resolve interdependent sub-tasks (e.g., loops, conditionals) in a single step, we introduce \textit{Stateful Runtime Management} in CaveAgent. Distinct from existing code-based approaches that remain text-bound and lack the support for external object injection and retrieval, CaveAgent injects, manipulates, and retrieves complex Python objects (e.g., DataFrames, database connections) that persist across turns. This persistence mechanism acts as a high-fidelity external memory to eliminate context drift, avoid catastrophic forgetting, while ensuring that processed data flows losslessly to downstream applications. Comprehensive evaluations on Tau$^2$-bench, BFCL and various case studies across representative SOTA LLMs demonstrate CaveAgent's superiority. Specifically, our framework achieves a 10.5\% success rate improvement on retail tasks and reduces total token consumption by 28.4\% in multi-turn scenarios. On data-intensive tasks, direct variable storage and retrieval reduces token consumption by 59\%, allowing CaveAgent to handle large-scale data that causes context overflow failures in both JSON-based and Code-based agents.
AndroidLens: Long-latency Evaluation with Nested Sub-targets for Android GUI Agents
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:Graphical user interface (GUI) agents can substantially improve productivity by automating frequently executed long-latency tasks on mobile devices. However, existing evaluation benchmarks are still constrained to limited applications, simple tasks, and coarse-grained metrics. To address this, we introduce AndroidLens, a challenging evaluation framework for mobile GUI agents, comprising 571 long-latency tasks in both Chinese and English environments, each requiring an average of more than 26 steps to complete. The framework features: (1) tasks derived from real-world user scenarios across 38 domains, covering complex types such as multi-constraint, multi-goal, and domain-specific tasks; (2) static evaluation that preserves real-world anomalies and allows multiple valid paths to reduce bias; and (3) dynamic evaluation that employs a milestone-based scheme for fine-grained progress measurement via Average Task Progress (ATP). Our evaluation indicates that even the best models reach only a 12.7% task success rate and 50.47% ATP. We also underscore key challenges in real-world environments, including environmental anomalies, adaptive exploration, and long-term memory retention.
Time-Layer Adaptive Alignment for Speaker Similarity in Flow-Matching Based Zero-Shot TTS
Nov 13, 2025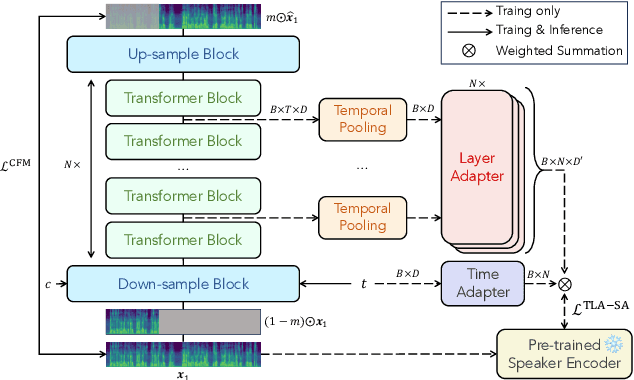
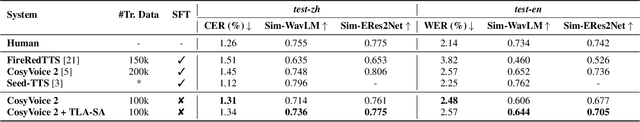
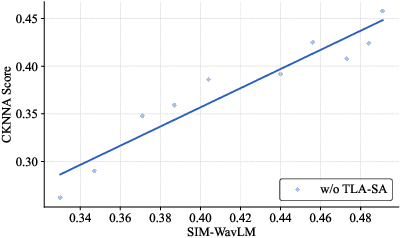
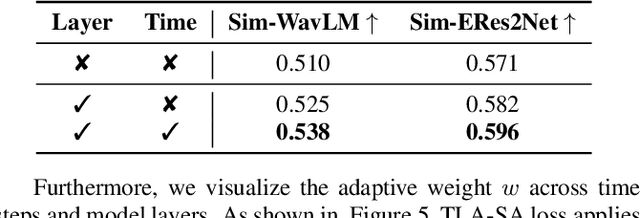
Abstract:Flow-Matching (FM)-based zero-shot text-to-speech (TTS) systems exhibit high-quality speech synthesis and robust generalization capabilities. However, the speaker representation ability of such systems remains underexplored, primarily due to the lack of explicit speaker-specific supervision in the FM framework. To this end, we conduct an empirical analysis of speaker information distribution and reveal its non-uniform allocation across time steps and network layers, underscoring the need for adaptive speaker alignment. Accordingly, we propose Time-Layer Adaptive Speaker Alignment (TLA-SA), a loss that enhances speaker consistency by jointly leveraging temporal and hierarchical variations in speaker information. Experimental results show that TLA-SA significantly improves speaker similarity compared to baseline systems on both research- and industrial-scale datasets and generalizes effectively across diverse model architectures, including decoder-only language models (LM) and FM-based TTS systems free of LM.
MMG-Vid: Maximizing Marginal Gains at Segment-level and Token-level for Efficient Video LLMs
Aug 28, 2025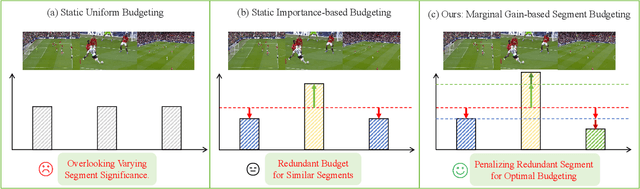
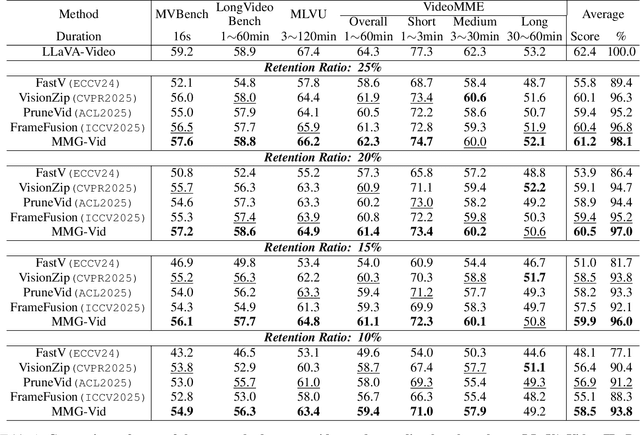
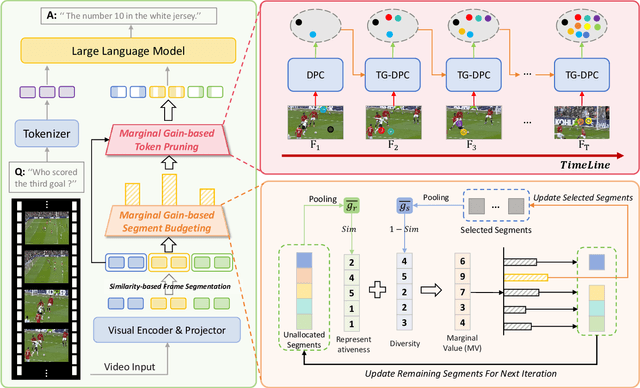
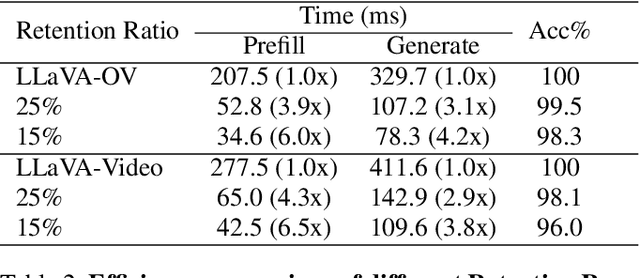
Abstract:Video Large Language Models (VLLMs) excel in video understanding, but their excessive visual tokens pose a significant computational challenge for real-world applications. Current methods aim to enhance inference efficiency by visual token pruning. However, they do not consider the dynamic characteristics and temporal dependencies of video frames, as they perceive video understanding as a multi-frame task. To address these challenges, we propose MMG-Vid, a novel training-free visual token pruning framework that removes redundancy by Maximizing Marginal Gains at both segment-level and token-level. Specifically, we first divide the video into segments based on frame similarity, and then dynamically allocate the token budget for each segment to maximize the marginal gain of each segment. Subsequently, we propose a temporal-guided DPC algorithm that jointly models inter-frame uniqueness and intra-frame diversity, thereby maximizing the marginal gain of each token. By combining both stages, MMG-Vid can maximize the utilization of the limited token budget, significantly improving efficiency while maintaining strong performance. Extensive experiments demonstrate that MMG-Vid can maintain over 99.5% of the original performance, while effectively reducing 75% visual tokens and accelerating the prefilling stage by 3.9x on LLaVA-OneVision-7B. Code will be released soon.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge