Yingbo Wang
FiLA-Video: Spatio-Temporal Compression for Fine-Grained Long Video Understanding
Apr 29, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in video understanding within visual large language models (VLLMs) have led to notable progress. However, the complexity of video data and contextual processing limitations still hinder long-video comprehension. A common approach is video feature compression to reduce token input to large language models, yet many methods either fail to prioritize essential features, leading to redundant inter-frame information, or introduce computationally expensive modules.To address these issues, we propose FiLA(Fine-grained Vision Language Model)-Video, a novel framework that leverages a lightweight dynamic-weight multi-frame fusion strategy, which adaptively integrates multiple frames into a single representation while preserving key video information and reducing computational costs. To enhance frame selection for fusion, we introduce a keyframe selection strategy, effectively identifying informative frames from a larger pool for improved summarization. Additionally, we present a simple yet effective long-video training data generation strategy, boosting model performance without extensive manual annotation. Experimental results demonstrate that FiLA-Video achieves superior efficiency and accuracy in long-video comprehension compared to existing methods.
Graph2text or Graph2token: A Perspective of Large Language Models for Graph Learning
Jan 02, 2025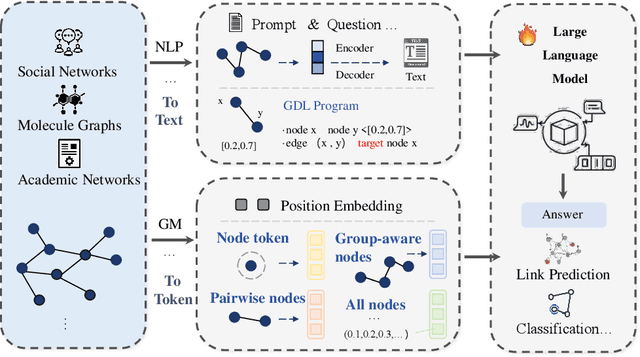
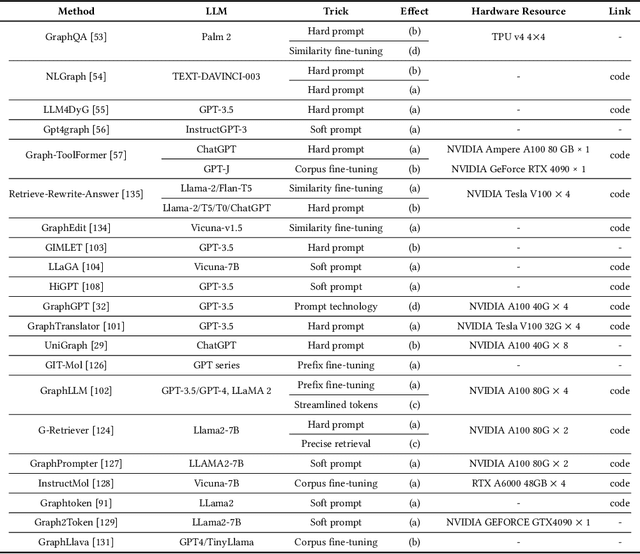
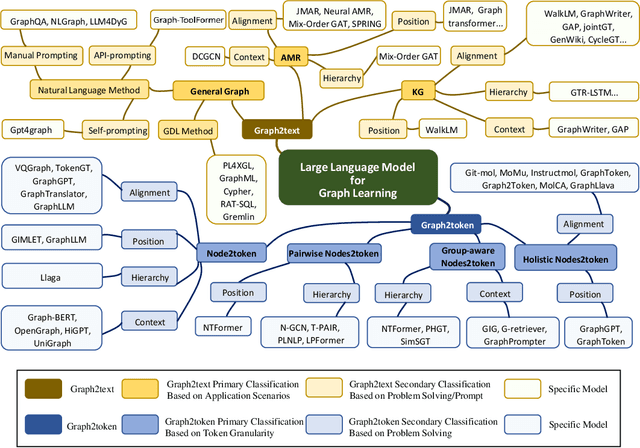
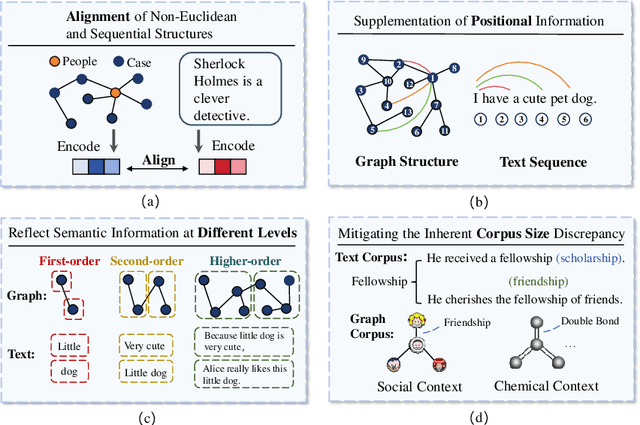
Abstract:Graphs are data structures used to represent irregular networks and are prevalent in numerous real-world applications. Previous methods directly model graph structures and achieve significant success. However, these methods encounter bottlenecks due to the inherent irregularity of graphs. An innovative solution is converting graphs into textual representations, thereby harnessing the powerful capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) to process and comprehend graphs. In this paper, we present a comprehensive review of methodologies for applying LLMs to graphs, termed LLM4graph. The core of LLM4graph lies in transforming graphs into texts for LLMs to understand and analyze. Thus, we propose a novel taxonomy of LLM4graph methods in the view of the transformation. Specifically, existing methods can be divided into two paradigms: Graph2text and Graph2token, which transform graphs into texts or tokens as the input of LLMs, respectively. We point out four challenges during the transformation to systematically present existing methods in a problem-oriented perspective. For practical concerns, we provide a guideline for researchers on selecting appropriate models and LLMs for different graphs and hardware constraints. We also identify five future research directions for LLM4graph.
Panoramic single-pixel imaging with megapixel resolution based on rotational subdivision
Jul 27, 2024Abstract:Single-pixel imaging (SPI) using a single-pixel detector is an unconventional imaging method, which has great application prospects in many fields to realize high-performance imaging. In especial, the recent proposed catadioptric panoramic ghost imaging (CPGI) extends the application potential of SPI to high-performance imaging at a wide field of view (FOV) with recent growing demands. However, the resolution of CPGI is limited by hardware parameters of the digital micromirror device (DMD), which may not meet ultrahigh-resolution panoramic imaging needs that require detailed information. Therefore, to overcome the resolution limitation of CPGI, we propose a panoramic SPI based on rotational subdivision (RSPSI). The key of the proposed RSPSI is to obtain the entire panoramic scene by the rotation-scanning with a rotating mirror tilted 45{\deg}, so that one single pattern that only covers one sub-Fov with a small FOV can complete a uninterrupted modulation on the entire panoramic FOV during a once-through pattern projection. Then, based on temporal resolution subdivision, images sequence of sub-Fovs subdivided from the entire panoramic FOV can be reconstructed with pixels-level or even subpixels-level horizontal shifting adjacently. Experimental results using a proof-of-concept setup show that the panoramic image can be obtained with 10428*543 of 5,662,404 pixels, which is more than 9.6 times higher than the resolution limit of the CPGI using the same DMD. To our best knowledge, the RSPSI is the first to achieve a megapixel resolution via SPI, which can provide potential applications in fields requiring the imaging with ultrahigh-resolution and wide FOV.
RJUA-MedDQA: A Multimodal Benchmark for Medical Document Question Answering and Clinical Reasoning
Feb 19, 2024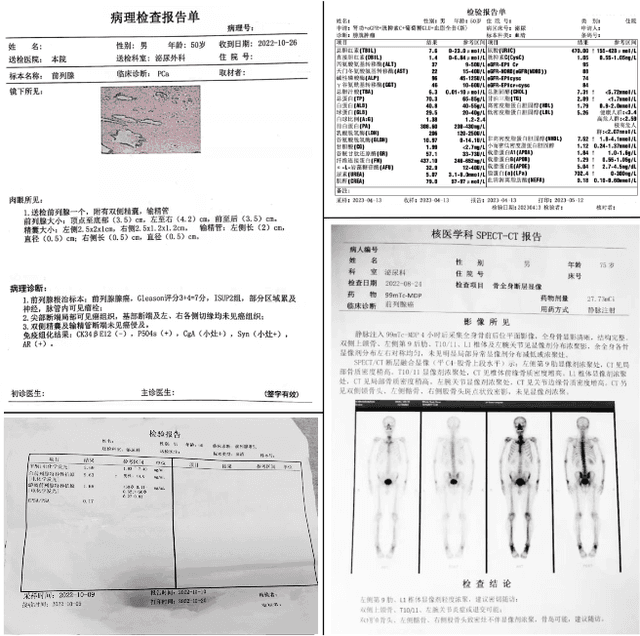
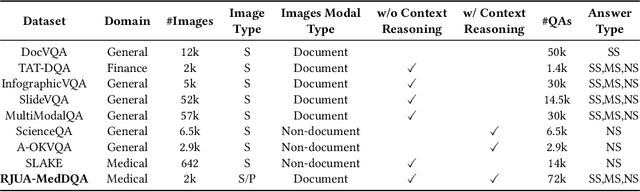
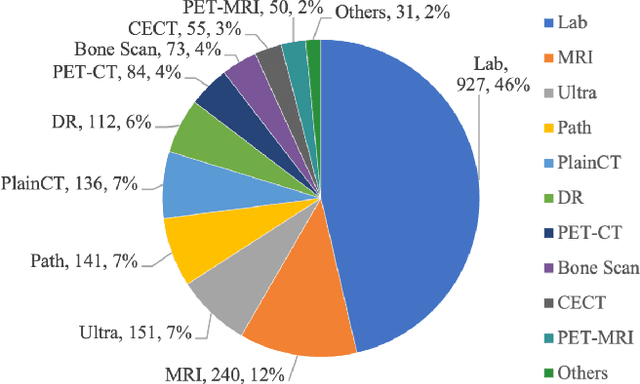
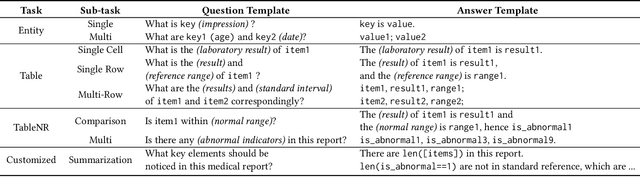
Abstract:Recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) and Large Multi-modal Models (LMMs) have shown potential in various medical applications, such as Intelligent Medical Diagnosis. Although impressive results have been achieved, we find that existing benchmarks do not reflect the complexity of real medical reports and specialized in-depth reasoning capabilities. In this work, we introduced RJUA-MedDQA, a comprehensive benchmark in the field of medical specialization, which poses several challenges: comprehensively interpreting imgage content across diverse challenging layouts, possessing numerical reasoning ability to identify abnormal indicators and demonstrating clinical reasoning ability to provide statements of disease diagnosis, status and advice based on medical contexts. We carefully design the data generation pipeline and proposed the Efficient Structural Restoration Annotation (ESRA) Method, aimed at restoring textual and tabular content in medical report images. This method substantially enhances annotation efficiency, doubling the productivity of each annotator, and yields a 26.8% improvement in accuracy. We conduct extensive evaluations, including few-shot assessments of 5 LMMs which are capable of solving Chinese medical QA tasks. To further investigate the limitations and potential of current LMMs, we conduct comparative experiments on a set of strong LLMs by using image-text generated by ESRA method. We report the performance of baselines and offer several observations: (1) The overall performance of existing LMMs is still limited; however LMMs more robust to low-quality and diverse-structured images compared to LLMs. (3) Reasoning across context and image content present significant challenges. We hope this benchmark helps the community make progress on these challenging tasks in multi-modal medical document understanding and facilitate its application in healthcare.
GACE: Learning Graph-Based Cross-Page Ads Embedding For Click-Through Rate Prediction
Jan 15, 2024Abstract:Predicting click-through rate (CTR) is the core task of many ads online recommendation systems, which helps improve user experience and increase platform revenue. In this type of recommendation system, we often encounter two main problems: the joint usage of multi-page historical advertising data and the cold start of new ads. In this paper, we proposed GACE, a graph-based cross-page ads embedding generation method. It can warm up and generate the representation embedding of cold-start and existing ads across various pages. Specifically, we carefully build linkages and a weighted undirected graph model considering semantic and page-type attributes to guide the direction of feature fusion and generation. We designed a variational auto-encoding task as pre-training module and generated embedding representations for new and old ads based on this task. The results evaluated in the public dataset AliEC from RecBole and the real-world industry dataset from Alipay show that our GACE method is significantly superior to the SOTA method. In the online A/B test, the click-through rate on three real-world pages from Alipay has increased by 3.6%, 2.13%, and 3.02%, respectively. Especially in the cold-start task, the CTR increased by 9.96%, 7.51%, and 8.97%, respectively.
CiT-Net: Convolutional Neural Networks Hand in Hand with Vision Transformers for Medical Image Segmentation
Jun 06, 2023



Abstract:The hybrid architecture of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and Transformer are very popular for medical image segmentation. However, it suffers from two challenges. First, although a CNNs branch can capture the local image features using vanilla convolution, it cannot achieve adaptive feature learning. Second, although a Transformer branch can capture the global features, it ignores the channel and cross-dimensional self-attention, resulting in a low segmentation accuracy on complex-content images. To address these challenges, we propose a novel hybrid architecture of convolutional neural networks hand in hand with vision Transformers (CiT-Net) for medical image segmentation. Our network has two advantages. First, we design a dynamic deformable convolution and apply it to the CNNs branch, which overcomes the weak feature extraction ability due to fixed-size convolution kernels and the stiff design of sharing kernel parameters among different inputs. Second, we design a shifted-window adaptive complementary attention module and a compact convolutional projection. We apply them to the Transformer branch to learn the cross-dimensional long-term dependency for medical images. Experimental results show that our CiT-Net provides better medical image segmentation results than popular SOTA methods. Besides, our CiT-Net requires lower parameters and less computational costs and does not rely on pre-training. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/SR0920/CiT-Net.
Quantum Graph Learning: Frontiers and Outlook
Feb 02, 2023Abstract:Quantum theory has shown its superiority in enhancing machine learning. However, facilitating quantum theory to enhance graph learning is in its infancy. This survey investigates the current advances in quantum graph learning (QGL) from three perspectives, i.e., underlying theories, methods, and prospects. We first look at QGL and discuss the mutualism of quantum theory and graph learning, the specificity of graph-structured data, and the bottleneck of graph learning, respectively. A new taxonomy of QGL is presented, i.e., quantum computing on graphs, quantum graph representation, and quantum circuits for graph neural networks. Pitfall traps are then highlighted and explained. This survey aims to provide a brief but insightful introduction to this emerging field, along with a detailed discussion of frontiers and outlook yet to be investigated.
A Scalable AI Approach for Clinical Trial Cohort Optimization
Sep 07, 2021



Abstract:FDA has been promoting enrollment practices that could enhance the diversity of clinical trial populations, through broadening eligibility criteria. However, how to broaden eligibility remains a significant challenge. We propose an AI approach to Cohort Optimization (AICO) through transformer-based natural language processing of the eligibility criteria and evaluation of the criteria using real-world data. The method can extract common eligibility criteria variables from a large set of relevant trials and measure the generalizability of trial designs to real-world patients. It overcomes the scalability limits of existing manual methods and enables rapid simulation of eligibility criteria design for a disease of interest. A case study on breast cancer trial design demonstrates the utility of the method in improving trial generalizability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge