Bowen Li
Deep GraphRAG: A Balanced Approach to Hierarchical Retrieval and Adaptive Integration
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Graph-based Retrieval-Augmented Generation (GraphRAG) frameworks face a trade-off between the comprehensiveness of global search and the efficiency of local search. Existing methods are often challenged by navigating large-scale hierarchical graphs, optimizing retrieval paths, and balancing exploration-exploitation dynamics, frequently lacking robust multi-stage re-ranking. To overcome these deficits, we propose Deep GraphRAG, a framework designed for a balanced approach to hierarchical retrieval and adaptive integration. It introduces a hierarchical global-to-local retrieval strategy that integrates macroscopic inter-community and microscopic intra-community contextual relations. This strategy employs a three-stage process: (1) inter-community filtering, which prunes the search space using local context; (2) community-level refinement, which prioritizes relevant subgraphs via entity-interaction analysis; and (3) entity-level fine-grained search within target communities. A beam search-optimized dynamic re-ranking module guides this process, continuously filtering candidates to balance efficiency and global comprehensiveness. Deep GraphRAG also features a Knowledge Integration Module leveraging a compact LLM, trained with Dynamic Weighting Reward GRPO (DW-GRPO). This novel reinforcement learning approach dynamically adjusts reward weights to balance three key objectives: relevance, faithfulness, and conciseness. This training enables compact models (1.5B) to approach the performance of large models (70B) in the integration task. Evaluations on Natural Questions and HotpotQA demonstrate that Deep GraphRAG significantly outperforms baseline graph retrieval methods in both accuracy and efficiency.
When to Trust: A Causality-Aware Calibration Framework for Accurate Knowledge Graph Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Knowledge Graph Retrieval-Augmented Generation (KG-RAG) extends the RAG paradigm by incorporating structured knowledge from knowledge graphs, enabling Large Language Models (LLMs) to perform more precise and explainable reasoning. While KG-RAG improves factual accuracy in complex tasks, existing KG-RAG models are often severely overconfident, producing high-confidence predictions even when retrieved sub-graphs are incomplete or unreliable, which raises concerns for deployment in high-stakes domains. To address this issue, we propose Ca2KG, a Causality-aware Calibration framework for KG-RAG. Ca2KG integrates counterfactual prompting, which exposes retrieval-dependent uncertainties in knowledge quality and reasoning reliability, with a panel-based re-scoring mechanism that stabilises predictions across interventions. Extensive experiments on two complex QA datasets demonstrate that Ca2KG consistently improves calibration while maintaining or even enhancing predictive accuracy.
When to Invoke: Refining LLM Fairness with Toxicity Assessment
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly used for toxicity assessment in online moderation systems, where fairness across demographic groups is essential for equitable treatment. However, LLMs often produce inconsistent toxicity judgements for subtle expressions, particularly those involving implicit hate speech, revealing underlying biases that are difficult to correct through standard training. This raises a key question that existing approaches often overlook: when should corrective mechanisms be invoked to ensure fair and reliable assessments? To address this, we propose FairToT, an inference-time framework that enhances LLM fairness through prompt-guided toxicity assessment. FairToT identifies cases where demographic-related variation is likely to occur and determines when additional assessment should be applied. In addition, we introduce two interpretable fairness indicators that detect such cases and improve inference consistency without modifying model parameters. Experiments on benchmark datasets show that FairToT reduces group-level disparities while maintaining stable and reliable toxicity predictions, demonstrating that inference-time refinement offers an effective and practical approach for fairness improvement in LLM-based toxicity assessment systems. The source code can be found at https://aisuko.github.io/fair-tot/.
Debiasing Large Language Models via Adaptive Causal Prompting with Sketch-of-Thought
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Despite notable advancements in prompting methods for Large Language Models (LLMs), such as Chain-of-Thought (CoT), existing strategies still suffer from excessive token usage and limited generalisability across diverse reasoning tasks. To address these limitations, we propose an Adaptive Causal Prompting with Sketch-of-Thought (ACPS) framework, which leverages structural causal models to infer the causal effect of a query on its answer and adaptively select an appropriate intervention (i.e., standard front-door and conditional front-door adjustments). This design enables generalisable causal reasoning across heterogeneous tasks without task-specific retraining. By replacing verbose CoT with concise Sketch-of-Thought, ACPS enables efficient reasoning that significantly reduces token usage and inference cost. Extensive experiments on multiple reasoning benchmarks and LLMs demonstrate that ACPS consistently outperforms existing prompting baselines in terms of accuracy, robustness, and computational efficiency.
Unifying Deep Predicate Invention with Pre-trained Foundation Models
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:Long-horizon robotic tasks are hard due to continuous state-action spaces and sparse feedback. Symbolic world models help by decomposing tasks into discrete predicates that capture object properties and relations. Existing methods learn predicates either top-down, by prompting foundation models without data grounding, or bottom-up, from demonstrations without high-level priors. We introduce UniPred, a bilevel learning framework that unifies both. UniPred uses large language models (LLMs) to propose predicate effect distributions that supervise neural predicate learning from low-level data, while learned feedback iteratively refines the LLM hypotheses. Leveraging strong visual foundation model features, UniPred learns robust predicate classifiers in cluttered scenes. We further propose a predicate evaluation method that supports symbolic models beyond STRIPS assumptions. Across five simulated and one real-robot domains, UniPred achieves 2-4 times higher success rates than top-down methods and 3-4 times faster learning than bottom-up approaches, advancing scalable and flexible symbolic world modeling for robotics.
Pareto-Optimal Sampling and Resource Allocation for Timely Communication in Shared-Spectrum Low-Altitude Networks
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:Guaranteeing stringent data freshness for low-altitude unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) in shared spectrum forces a critical trade-off between two operational costs: the UAV's own energy consumption and the occupation of terrestrial channel resources. The core challenge is to satisfy the aerial data freshness while finding a Pareto-optimal balance between these costs. Leveraging predictive channel models and predictive UAV trajectories, we formulate a bi-objective Pareto optimization problem over a long-term planning horizon to jointly optimize the sampling timing for aerial traffic and the power and spectrum allocation for fair coexistence. However, the problem's non-convex, mixed-integer nature renders classical methods incapable of fully characterizing the complete Pareto frontier. Notably, we show monotonicity properties of the frontier, building on which we transform the bi-objective problem into several single-objective problems. We then propose a new graph-based algorithm and prove that it can find the complete set of Pareto optima with low complexity, linear in the horizon and near-quadratic in the resource block (RB) budget. Numerical comparisons show that our approach meets the stringent timeliness requirement and achieves a six-fold reduction in RB utilization or a 6 dB energy saving compared to benchmarks.
Revolutionizing Reinforcement Learning Framework for Diffusion Large Language Models
Sep 08, 2025Abstract:We propose TraceRL, a trajectory-aware reinforcement learning framework for diffusion language models (DLMs) that incorporates preferred inference trajectory into post-training, and is applicable across different architectures. Equipped with a diffusion-based value model that enhances training stability, we demonstrate improved reasoning performance on complex math and coding tasks. Besides, it can also be applied to adapt block-specific models to larger blocks, which improves sampling flexibility. Employing TraceRL, we derive a series of state-of-the-art diffusion language models, namely TraDo. Although smaller than 7B-scale AR models, TraDo-4B-Instruct still consistently outperforms them across complex math reasoning tasks. TraDo-8B-Instruct achieves relative accuracy improvements of 6.1% over Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct and 51.3% over Llama3.1-8B-Instruct on mathematical reasoning benchmarks. Through curriculum learning, we also derive the first long-CoT DLM, outperforming Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct on MATH500 with an 18.1% relative accuracy gain. To facilitate reproducible research and practical applications, we release a comprehensive open-source framework for building, training, and deploying diffusion LLMs across diverse architectures. The framework integrates accelerated KV-cache techniques and inference engines for both inference and reinforcement learning, and includes implementations of various supervised fine-tuning and RL methods for mathematics, coding, and general tasks. Code and Models: https://github.com/Gen-Verse/dLLM-RL
Quantize More, Lose Less: Autoregressive Generation from Residually Quantized Speech Representations
Jul 16, 2025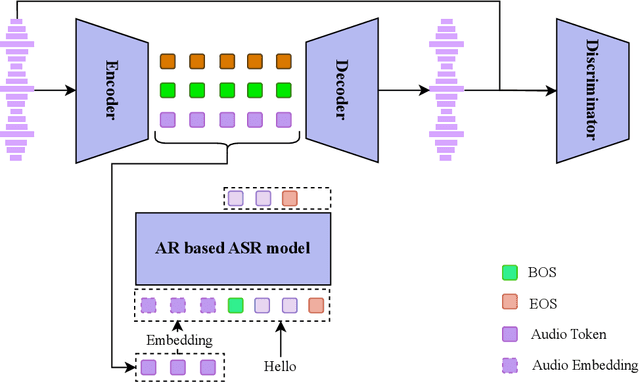
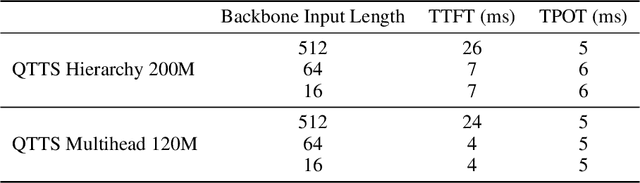
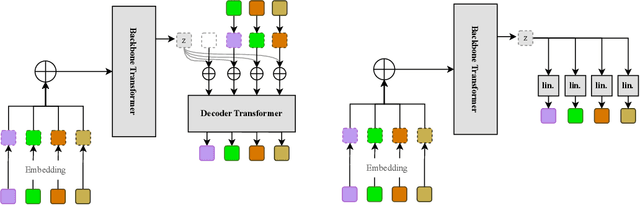
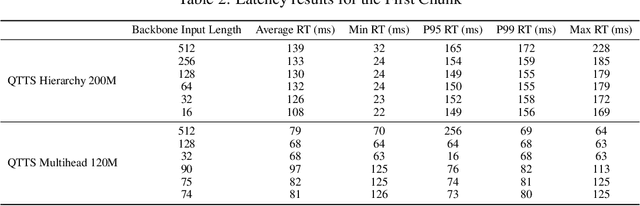
Abstract:Text-to-speech (TTS) synthesis has seen renewed progress under the discrete modeling paradigm. Existing autoregressive approaches often rely on single-codebook representations, which suffer from significant information loss. Even with post-hoc refinement techniques such as flow matching, these methods fail to recover fine-grained details (e.g., prosodic nuances, speaker-specific timbres), especially in challenging scenarios like singing voice or music synthesis. We propose QTTS, a novel TTS framework built upon our new audio codec, QDAC. The core innovation of QDAC lies in its end-to-end training of an ASR-based auto-regressive network with a GAN, which achieves superior semantic feature disentanglement for scalable, near-lossless compression. QTTS models these discrete codes using two innovative strategies: the Hierarchical Parallel architecture, which uses a dual-AR structure to model inter-codebook dependencies for higher-quality synthesis, and the Delay Multihead approach, which employs parallelized prediction with a fixed delay to accelerate inference speed. Our experiments demonstrate that the proposed framework achieves higher synthesis quality and better preserves expressive content compared to baseline. This suggests that scaling up compression via multi-codebook modeling is a promising direction for high-fidelity, general-purpose speech and audio generation.
BrainMAP: Multimodal Graph Learning For Efficient Brain Disease Localization
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Recent years have seen a surge in research focused on leveraging graph learning techniques to detect neurodegenerative diseases. However, existing graph-based approaches typically lack the ability to localize and extract the specific brain regions driving neurodegenerative pathology within the full connectome. Additionally, recent works on multimodal brain graph models often suffer from high computational complexity, limiting their practical use in resource-constrained devices. In this study, we present BrainMAP, a novel multimodal graph learning framework designed for precise and computationally efficient identification of brain regions affected by neurodegenerative diseases. First, BrainMAP utilizes an atlas-driven filtering approach guided by the AAL atlas to pinpoint and extract critical brain subgraphs. Unlike recent state-of-the-art methods, which model the entire brain network, BrainMAP achieves more than 50% reduction in computational overhead by concentrating on disease-relevant subgraphs. Second, we employ an advanced multimodal fusion process comprising cross-node attention to align functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) data, coupled with an adaptive gating mechanism to blend and integrate these modalities dynamically. Experimental results demonstrate that BrainMAP outperforms state-of-the-art methods in computational efficiency, without compromising predictive accuracy.
SWE-bench Goes Live!
May 29, 2025Abstract:The issue-resolving task, where a model generates patches to fix real-world bugs, has emerged as a critical benchmark for evaluating the capabilities of large language models (LLMs). While SWE-bench and its variants have become standard in this domain, they suffer from key limitations: they have not been updated since their initial releases, cover a narrow set of repositories, and depend heavily on manual effort for instance construction and environment setup. These factors hinder scalability and introduce risks of overfitting and data contamination. In this work, we present \textbf{SWE-bench-Live}, a \textit{live-updatable} benchmark designed to overcome these challenges. Our initial release consists of 1,319 tasks derived from real GitHub issues created since 2024, spanning 93 repositories. Each task is accompanied by a dedicated Docker image to ensure reproducible execution. Central to our benchmark is \method, an automated curation pipeline that streamlines the entire process from instance creation to environment setup, removing manual bottlenecks and enabling scalability and continuous updates. We evaluate a range of state-of-the-art agent frameworks and LLMs on SWE-bench-Live, revealing a substantial performance gap compared to static benchmarks like SWE-bench, even under controlled evaluation conditions. To better understand this discrepancy, we perform detailed analyses across repository origin, issue recency, and task difficulty. By providing a fresh, diverse, and executable benchmark grounded in live repository activity, SWE-bench-Live facilitates rigorous, contamination-resistant evaluation of LLMs and agents in dynamic, real-world software development settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge