Yuanjun Laili
GenAI for Simulation Model in Model-Based Systems Engineering
Mar 09, 2025Abstract:Generative AI (GenAI) has demonstrated remarkable capabilities in code generation, and its integration into complex product modeling and simulation code generation can significantly enhance the efficiency of the system design phase in Model-Based Systems Engineering (MBSE). In this study, we introduce a generative system design methodology framework for MBSE, offering a practical approach for the intelligent generation of simulation models for system physical properties. First, we employ inference techniques, generative models, and integrated modeling and simulation languages to construct simulation models for system physical properties based on product design documents. Subsequently, we fine-tune the language model used for simulation model generation on an existing library of simulation models and additional datasets generated through generative modeling. Finally, we introduce evaluation metrics for the generated simulation models for system physical properties. Our proposed approach to simulation model generation presents the innovative concept of scalable templates for simulation models. Using these templates, GenAI generates simulation models for system physical properties through code completion. The experimental results demonstrate that, for mainstream open-source Transformer-based models, the quality of the simulation model is significantly improved using the simulation model generation method proposed in this paper.
Large Language Models Meet Symbolic Provers for Logical Reasoning Evaluation
Feb 10, 2025Abstract:First-order logic (FOL) reasoning, which involves sequential deduction, is pivotal for intelligent systems and serves as a valuable task for evaluating reasoning capabilities, particularly in chain-of-thought (CoT) contexts. Existing benchmarks often rely on extensive human annotation or handcrafted templates, making it difficult to achieve the necessary complexity, scalability, and diversity for robust evaluation. To address these limitations, we propose a novel framework called ProverGen that synergizes the generative strengths of Large Language Models (LLMs) with the rigor and precision of symbolic provers, enabling the creation of a scalable, diverse, and high-quality FOL reasoning dataset, ProverQA. ProverQA is also distinguished by its inclusion of accessible and logically coherent intermediate reasoning steps for each problem. Our evaluation shows that state-of-the-art LLMs struggle to solve ProverQA problems, even with CoT prompting, highlighting the dataset's challenging nature. We also finetune Llama3.1-8B-Instruct on a separate training set generated by our framework. The finetuned model demonstrates consistent improvements on both in-distribution and out-of-distribution test sets, suggesting the value of our proposed data generation framework. Code available at: https://github.com/opendatalab/ProverGen
Diff-MTS: Temporal-Augmented Conditional Diffusion-based AIGC for Industrial Time Series Towards the Large Model Era
Jul 16, 2024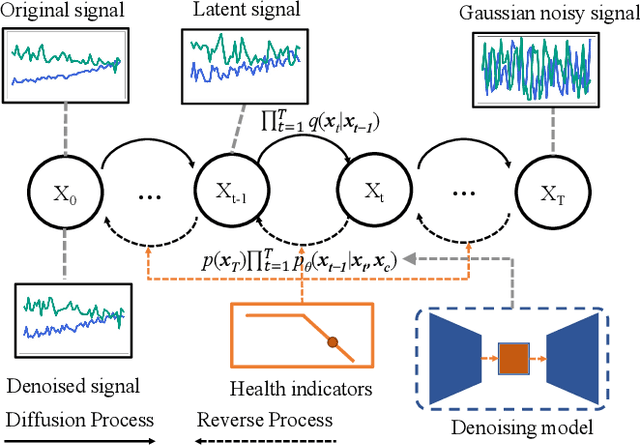
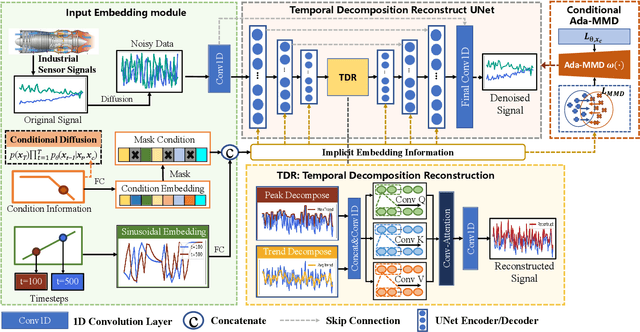
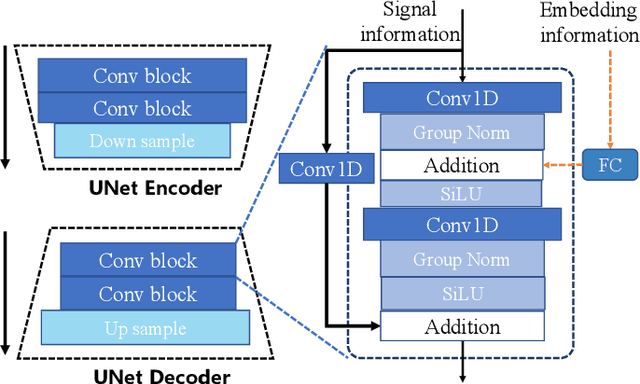
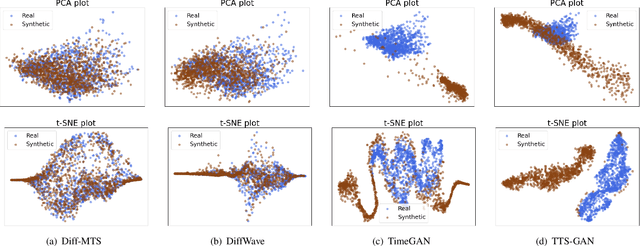
Abstract:Industrial Multivariate Time Series (MTS) is a critical view of the industrial field for people to understand the state of machines. However, due to data collection difficulty and privacy concerns, available data for building industrial intelligence and industrial large models is far from sufficient. Therefore, industrial time series data generation is of great importance. Existing research usually applies Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) to generate MTS. However, GANs suffer from unstable training process due to the joint training of the generator and discriminator. This paper proposes a temporal-augmented conditional adaptive diffusion model, termed Diff-MTS, for MTS generation. It aims to better handle the complex temporal dependencies and dynamics of MTS data. Specifically, a conditional Adaptive Maximum-Mean Discrepancy (Ada-MMD) method has been proposed for the controlled generation of MTS, which does not require a classifier to control the generation. It improves the condition consistency of the diffusion model. Moreover, a Temporal Decomposition Reconstruction UNet (TDR-UNet) is established to capture complex temporal patterns and further improve the quality of the synthetic time series. Comprehensive experiments on the C-MAPSS and FEMTO datasets demonstrate that the proposed Diff-MTS performs substantially better in terms of diversity, fidelity, and utility compared with GAN-based methods. These results show that Diff-MTS facilitates the generation of industrial data, contributing to intelligent maintenance and the construction of industrial large models.
An Investigation of LLMs' Inefficacy in Understanding Converse Relations
Oct 25, 2023



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable success in many formal language oriented tasks, such as structural data-to-text and semantic parsing. However current benchmarks mostly follow the data distribution of the pre-training data of LLMs. Therefore, a natural question rises that do LLMs really understand the structured semantics of formal languages. In this paper, we investigate this problem on a special case, converse binary relation. We introduce a new benchmark ConvRe focusing on converse relations, which contains 17 relations and 1240 triples extracted from popular knowledge graph completion datasets. Our ConvRE features two tasks, Re2Text and Text2Re, which are formulated as multi-choice question answering to evaluate LLMs' ability to determine the matching between relations and associated text. For the evaluation protocol, apart from different prompting methods, we further introduce variants to the test text and few-shot example text. We conduct experiments on three popular LLM families and have observed various scaling trends. The results suggest that LLMs often resort to shortcut learning and still face challenges on our proposed benchmark.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge