Yanan Guo
Multi-view Normal and Distance Guidance Gaussian Splatting for Surface Reconstruction
Aug 13, 2025Abstract:3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) achieves remarkable results in the field of surface reconstruction. However, when Gaussian normal vectors are aligned within the single-view projection plane, while the geometry appears reasonable in the current view, biases may emerge upon switching to nearby views. To address the distance and global matching challenges in multi-view scenes, we design multi-view normal and distance-guided Gaussian splatting. This method achieves geometric depth unification and high-accuracy reconstruction by constraining nearby depth maps and aligning 3D normals. Specifically, for the reconstruction of small indoor and outdoor scenes, we propose a multi-view distance reprojection regularization module that achieves multi-view Gaussian alignment by computing the distance loss between two nearby views and the same Gaussian surface. Additionally, we develop a multi-view normal enhancement module, which ensures consistency across views by matching the normals of pixel points in nearby views and calculating the loss. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that our method outperforms the baseline in both quantitative and qualitative evaluations, significantly enhancing the surface reconstruction capability of 3DGS. Our code will be made publicly available at (https://github.com/Bistu3DV/MND-GS/).
FiLA-Video: Spatio-Temporal Compression for Fine-Grained Long Video Understanding
Apr 29, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in video understanding within visual large language models (VLLMs) have led to notable progress. However, the complexity of video data and contextual processing limitations still hinder long-video comprehension. A common approach is video feature compression to reduce token input to large language models, yet many methods either fail to prioritize essential features, leading to redundant inter-frame information, or introduce computationally expensive modules.To address these issues, we propose FiLA(Fine-grained Vision Language Model)-Video, a novel framework that leverages a lightweight dynamic-weight multi-frame fusion strategy, which adaptively integrates multiple frames into a single representation while preserving key video information and reducing computational costs. To enhance frame selection for fusion, we introduce a keyframe selection strategy, effectively identifying informative frames from a larger pool for improved summarization. Additionally, we present a simple yet effective long-video training data generation strategy, boosting model performance without extensive manual annotation. Experimental results demonstrate that FiLA-Video achieves superior efficiency and accuracy in long-video comprehension compared to existing methods.
HyViLM: Enhancing Fine-Grained Recognition with a Hybrid Encoder for Vision-Language Models
Dec 11, 2024



Abstract:Recently, there has been growing interest in the capability of multimodal large language models (MLLMs) to process high-resolution images. A common approach currently involves dynamically cropping the original high-resolution image into smaller sub-images, which are then fed into a vision encoder that was pre-trained on lower-resolution images. However, this cropping approach often truncates objects and connected areas in the original image, causing semantic breaks. To address this limitation, we introduce HyViLM, designed to process images of any resolution while retaining the overall context during encoding. Specifically, we: (i) Design a new visual encoder called Hybrid Encoder that not only encodes individual sub-images but also interacts with detailed global visual features, significantly improving the model's ability to encode high-resolution images. (ii) Propose an optimal feature fusion strategy for the dynamic cropping approach, effectively leveraging information from different layers of the vision encoder. Compared with the state-of-the-art MLLMs under the same setting, our HyViLM outperforms existing MLLMs in nine out of ten tasks. Specifically, HyViLM achieves a 9.6% improvement in performance on the TextVQA task and a 6.9% enhancement on the DocVQA task.
Hybrid bundle-adjusting 3D Gaussians for view consistent rendering with pose optimization
Oct 17, 2024Abstract:Novel view synthesis has made significant progress in the field of 3D computer vision. However, the rendering of view-consistent novel views from imperfect camera poses remains challenging. In this paper, we introduce a hybrid bundle-adjusting 3D Gaussians model that enables view-consistent rendering with pose optimization. This model jointly extract image-based and neural 3D representations to simultaneously generate view-consistent images and camera poses within forward-facing scenes. The effective of our model is demonstrated through extensive experiments conducted on both real and synthetic datasets. These experiments clearly illustrate that our model can effectively optimize neural scene representations while simultaneously resolving significant camera pose misalignments. The source code is available at https://github.com/Bistu3DV/hybridBA.
Snore-GANs: Improving Automatic Snore Sound Classification with Synthesized Data
Mar 29, 2019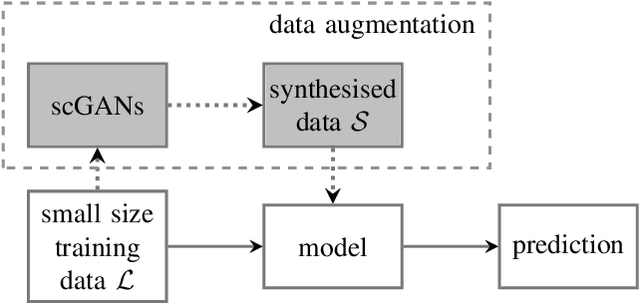
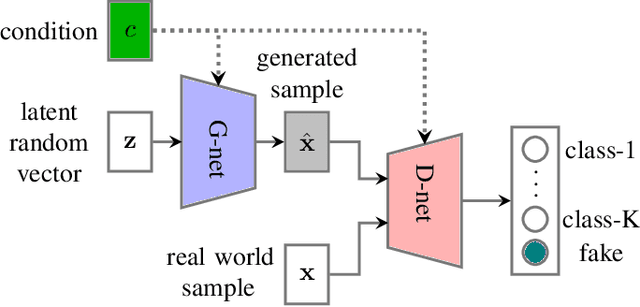
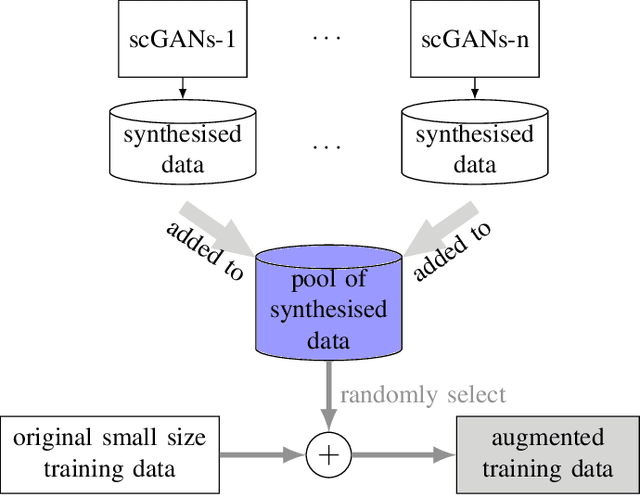
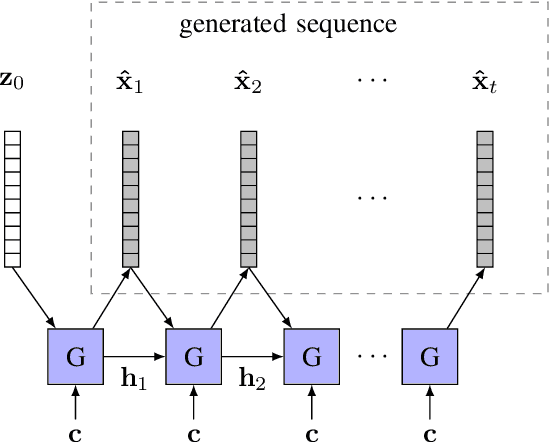
Abstract:One of the frontier issues that severely hamper the development of automatic snore sound classification (ASSC) associates to the lack of sufficient supervised training data. To cope with this problem, we propose a novel data augmentation approach based on semi-supervised conditional Generative Adversarial Networks (scGANs), which aims to automatically learn a mapping strategy from a random noise space to original data distribution. The proposed approach has the capability of well synthesizing 'realistic' high-dimensional data, while requiring no additional annotation process. To handle the mode collapse problem of GANs, we further introduce an ensemble strategy to enhance the diversity of the generated data. The systematic experiments conducted on a widely used Munich-Passau snore sound corpus demonstrate that the scGANs-based systems can remarkably outperform other classic data augmentation systems, and are also competitive to other recently reported systems for ASSC.
Multiview Cauchy Estimator Feature Embedding for Depth and Inertial Sensor-Based Human Action Recognition
Sep 04, 2016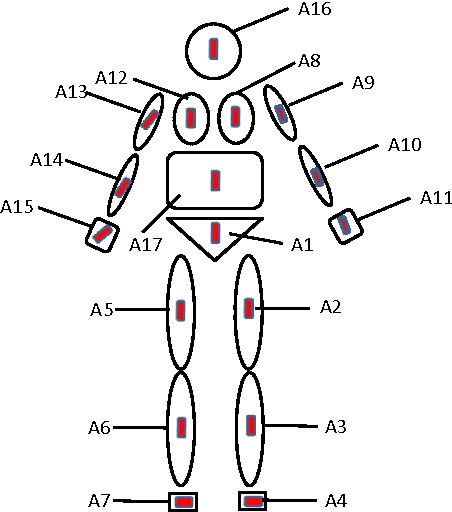
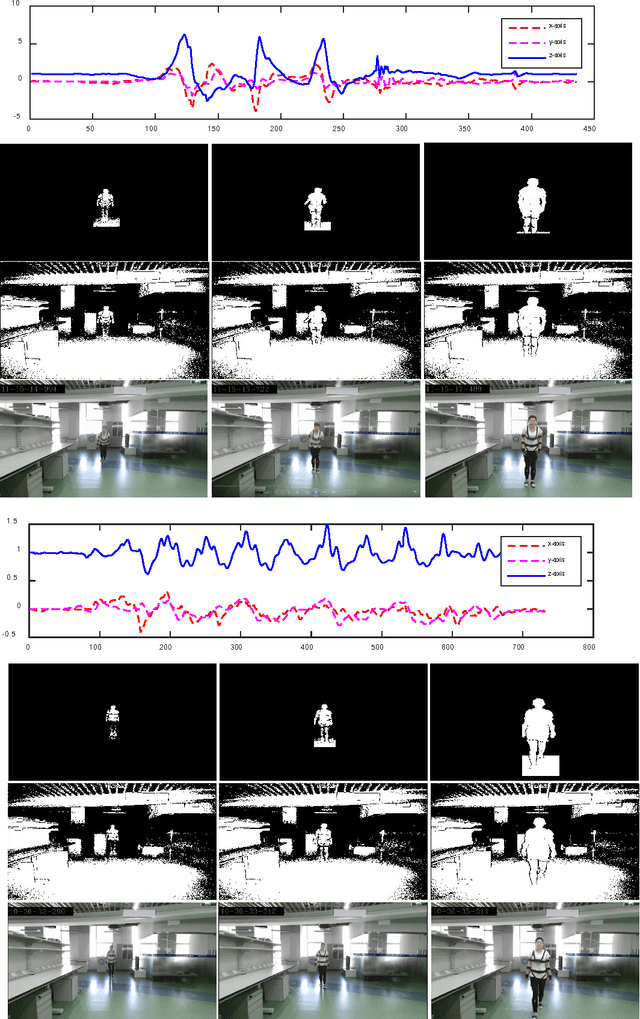
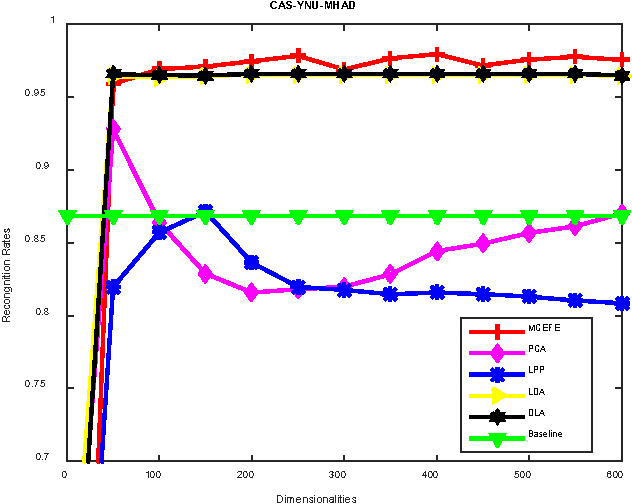
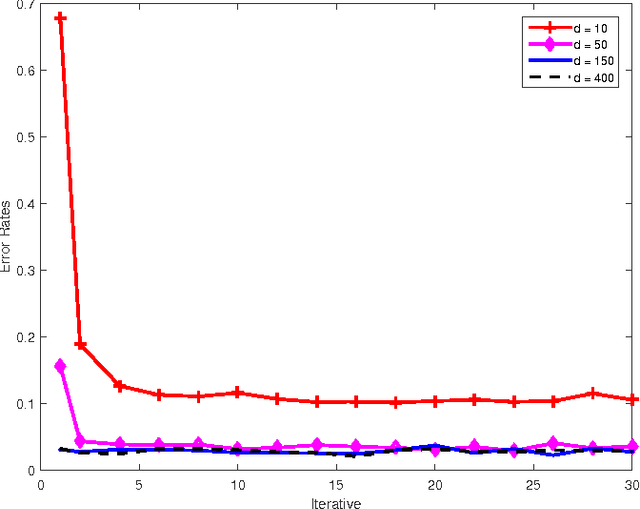
Abstract:The ever-growing popularity of Kinect and inertial sensors has prompted intensive research efforts on human action recognition. Since human actions can be characterized by multiple feature representations extracted from Kinect and inertial sensors, multiview features must be encoded into a unified space optimal for human action recognition. In this paper, we propose a new unsupervised feature fusion method termed Multiview Cauchy Estimator Feature Embedding (MCEFE) for human action recognition. By minimizing empirical risk, MCEFE integrates the encoded complementary information in multiple views to find the unified data representation and the projection matrices. To enhance robustness to outliers, the Cauchy estimator is imposed on the reconstruction error. Furthermore, ensemble manifold regularization is enforced on the projection matrices to encode the correlations between different views and avoid overfitting. Experiments are conducted on the new Chinese Academy of Sciences - Yunnan University - Multimodal Human Action Database (CAS-YNU-MHAD) to demonstrate the effectiveness and robustness of MCEFE for human action recognition.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge