Xiaoyu Gu
Masked Self-distilled Transducer-based Keyword Spotting with Semi-autoregressive Decoding
May 30, 2025Abstract:RNN-T-based keyword spotting (KWS) with autoregressive decoding~(AR) has gained attention due to its streaming architecture and superior performance. However, the simplicity of the prediction network in RNN-T poses an overfitting issue, especially under challenging scenarios, resulting in degraded performance. In this paper, we propose a masked self-distillation (MSD) training strategy that avoids RNN-Ts overly relying on prediction networks to alleviate overfitting. Such training enables masked non-autoregressive (NAR) decoding, which fully masks the RNN-T predictor output during KWS decoding. In addition, we propose a semi-autoregressive (SAR) decoding approach to integrate the advantages of AR and NAR decoding. Our experiments across multiple KWS datasets demonstrate that MSD training effectively alleviates overfitting. The SAR decoding method preserves the superior performance of AR decoding while benefits from the overfitting suppression of NAR decoding, achieving excellent results.
MFA-KWS: Effective Keyword Spotting with Multi-head Frame-asynchronous Decoding
May 26, 2025Abstract:Keyword spotting (KWS) is essential for voice-driven applications, demanding both accuracy and efficiency. Traditional ASR-based KWS methods, such as greedy and beam search, explore the entire search space without explicitly prioritizing keyword detection, often leading to suboptimal performance. In this paper, we propose an effective keyword-specific KWS framework by introducing a streaming-oriented CTC-Transducer-combined frame-asynchronous system with multi-head frame-asynchronous decoding (MFA-KWS). Specifically, MFA-KWS employs keyword-specific phone-synchronous decoding for CTC and replaces conventional RNN-T with Token-and-Duration Transducer to enhance both performance and efficiency. Furthermore, we explore various score fusion strategies, including single-frame-based and consistency-based methods. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superior performance of MFA-KWS, which achieves state-of-the-art results on both fixed keyword and arbitrary keywords datasets, such as Snips, MobvoiHotwords, and LibriKWS-20, while exhibiting strong robustness in noisy environments. Among fusion strategies, the consistency-based CDC-Last method delivers the best performance. Additionally, MFA-KWS achieves a 47% to 63% speed-up over the frame-synchronous baselines across various datasets. Extensive experimental results confirm that MFA-KWS is an effective and efficient KWS framework, making it well-suited for on-device deployment.
Streaming Keyword Spotting Boosted by Cross-layer Discrimination Consistency
Dec 17, 2024



Abstract:Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC), a non-autoregressive training criterion, is widely used in online keyword spotting (KWS). However, existing CTC-based KWS decoding strategies either rely on Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR), which performs suboptimally due to its broad search over the acoustic space without keyword-specific optimization, or on KWS-specific decoding graphs, which are complex to implement and maintain. In this work, we propose a streaming decoding algorithm enhanced by Cross-layer Discrimination Consistency (CDC), tailored for CTC-based KWS. Specifically, we introduce a streamlined yet effective decoding algorithm capable of detecting the start of the keyword at any arbitrary position. Furthermore, we leverage discrimination consistency information across layers to better differentiate between positive and false alarm samples. Our experiments on both clean and noisy Hey Snips datasets show that the proposed streaming decoding strategy outperforms ASR-based and graph-based KWS baselines. The CDC-boosted decoding further improves performance, yielding an average absolute recall improvement of 6.8% and a 46.3% relative reduction in the miss rate compared to the graph-based KWS baseline, with a very low false alarm rate of 0.05 per hour.
Color image segmentation based on a convex K-means approach
Mar 17, 2021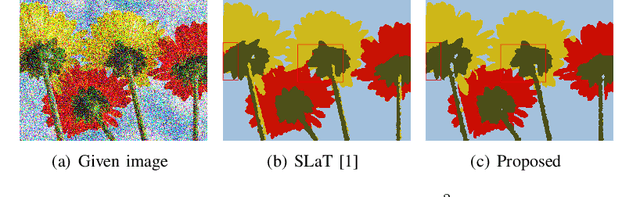
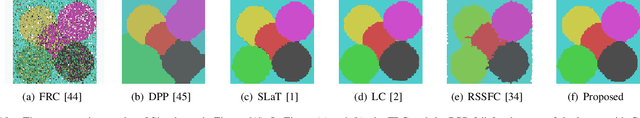

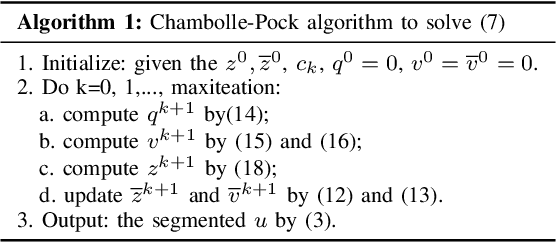
Abstract:Image segmentation is a fundamental and challenging task in image processing and computer vision. The color image segmentation is attracting more attention due to the color image provides more information than the gray image. In this paper, we propose a variational model based on a convex K-means approach to segment color images. The proposed variational method uses a combination of $l_1$ and $l_2$ regularizers to maintain edge information of objects in images while overcoming the staircase effect. Meanwhile, our one-stage strategy is an improved version based on the smoothing and thresholding strategy, which contributes to improving the accuracy of segmentation. The proposed method performs the following steps. First, we specify the color set which can be determined by human or the K-means method. Second, we use a variational model to obtain the most appropriate color for each pixel from the color set via convex relaxation and lifting. The Chambolle-Pock algorithm and simplex projection are applied to solve the variational model effectively. Experimental results and comparison analysis demonstrate the effectiveness and robustness of our method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge