Meng Cao
Multi-Agent Teams Hold Experts Back
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Multi-agent LLM systems are increasingly deployed as autonomous collaborators, where agents interact freely rather than execute fixed, pre-specified workflows. In such settings, effective coordination cannot be fully designed in advance and must instead emerge through interaction. However, most prior work enforces coordination through fixed roles, workflows, or aggregation rules, leaving open the question of how well self-organizing teams perform when coordination is unconstrained. Drawing on organizational psychology, we study whether self-organizing LLM teams achieve strong synergy, where team performance matches or exceeds the best individual member. Across human-inspired and frontier ML benchmarks, we find that -- unlike human teams -- LLM teams consistently fail to match their expert agent's performance, even when explicitly told who the expert is, incurring performance losses of up to 37.6%. Decomposing this failure, we show that expert leveraging, rather than identification, is the primary bottleneck. Conversational analysis reveals a tendency toward integrative compromise -- averaging expert and non-expert views rather than appropriately weighting expertise -- which increases with team size and correlates negatively with performance. Interestingly, this consensus-seeking behavior improves robustness to adversarial agents, suggesting a trade-off between alignment and effective expertise utilization. Our findings reveal a significant gap in the ability of self-organizing multi-agent teams to harness the collective expertise of their members.
DynaWeb: Model-Based Reinforcement Learning of Web Agents
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:The development of autonomous web agents, powered by Large Language Models (LLMs) and reinforcement learning (RL), represents a significant step towards general-purpose AI assistants. However, training these agents is severely hampered by the challenges of interacting with the live internet, which is inefficient, costly, and fraught with risks. Model-based reinforcement learning (MBRL) offers a promising solution by learning a world model of the environment to enable simulated interaction. This paper introduces DynaWeb, a novel MBRL framework that trains web agents through interacting with a web world model trained to predict naturalistic web page representations given agent actions. This model serves as a synthetic web environment where an agent policy can dream by generating vast quantities of rollout action trajectories for efficient online reinforcement learning. Beyond free policy rollouts, DynaWeb incorporates real expert trajectories from training data, which are randomly interleaved with on-policy rollouts during training to improve stability and sample efficiency. Experiments conducted on the challenging WebArena and WebVoyager benchmarks demonstrate that DynaWeb consistently and significantly improves the performance of state-of-the-art open-source web agent models. Our findings establish the viability of training web agents through imagination, offering a scalable and efficient way to scale up online agentic RL.
Negatives-Dominant Contrastive Learning for Generalization in Imbalanced Domains
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Imbalanced Domain Generalization (IDG) focuses on mitigating both domain and label shifts, both of which fundamentally shape the model's decision boundaries, particularly under heterogeneous long-tailed distributions across domains. Despite its practical significance, it remains underexplored, primarily due to the technical complexity of handling their entanglement and the paucity of theoretical foundations. In this paper, we begin by theoretically establishing the generalization bound for IDG, highlighting the role of posterior discrepancy and decision margin. This bound motivates us to focus on directly steering decision boundaries, marking a clear departure from existing methods. Subsequently, we technically propose a novel Negative-Dominant Contrastive Learning (NDCL) for IDG to enhance discriminability while enforce posterior consistency across domains. Specifically, inter-class decision-boundary separation is enhanced by placing greater emphasis on negatives as the primary signal in our contrastive learning, naturally amplifying gradient signals for minority classes to avoid the decision boundary being biased toward majority classes. Meanwhile, intra-class compactness is encouraged through a re-weighted cross-entropy strategy, and posterior consistency across domains is enforced through a prediction-central alignment strategy. Finally, rigorous yet challenging experiments on benchmarks validate the effectiveness of our NDCL. The code is available at https://github.com/Alrash/NDCL.
Order from Chaos: Physical World Understanding from Glitchy Gameplay Videos
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Understanding the physical world, including object dynamics, material properties, and causal interactions, remains a core challenge in artificial intelligence. Although recent multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) have demonstrated impressive general reasoning capabilities, they still fall short of achieving human-level understanding of physical principles. Existing datasets for physical reasoning either rely on real-world videos, which incur high annotation costs, or on synthetic simulations, which suffer from limited realism and diversity. In this paper, we propose a novel paradigm that leverages glitches in gameplay videos, referring to visual anomalies that violate predefined physical laws, as a rich and scalable supervision source for physical world understanding. We introduce PhysGame, an meta information guided instruction-tuning dataset containing 140,057 glitch-centric question-answer pairs across five physical domains and sixteen fine-grained categories. To ensure data accuracy, we design a prompting strategy that utilizes gameplay metadata such as titles and descriptions to guide high-quality QA generation. Complementing PhysGame, we construct GameBench, an expert-annotated benchmark with 880 glitch-identified gameplay videos designed to evaluate physical reasoning capabilities. Extensive experiments show that PhysGame significantly enhances both Game2Real transferability, improving the real world physical reasoning performance of Qwen2.5VL by 2.5% on PhysBench, and Game2General transferability, yielding a 1.9% gain on the MVBench benchmark. Moreover, PhysGame-tuned models achieve a 3.7% absolute improvement on GameBench, demonstrating enhanced robustness in detecting physical implausibilities. These results indicate that learning from gameplay anomalies offers a scalable and effective pathway toward advancing physical world understanding in multimodal intelligence.
CARE What Fails: Contrastive Anchored-REflection for Verifiable Multimodal
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:Group-relative reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards (RLVR) often wastes the most informative data it already has the failures. When all rollouts are wrong, gradients stall; when one happens to be correct, the update usually ignores why the others are close-but-wrong, and credit can be misassigned to spurious chains. We present CARE (Contrastive Anchored REflection), a failure-centric post-training framework for multimodal reasoning that turns errors into supervision. CARE combines: (i) an anchored-contrastive objective that forms a compact subgroup around the best rollout and a set of semantically proximate hard negatives, performs within-subgroup z-score normalization with negative-only scaling, and includes an all-negative rescue to prevent zero-signal batches; and (ii) Reflection-Guided Resampling (RGR), a one-shot structured self-repair that rewrites a representative failure and re-scores it with the same verifier, converting near-misses into usable positives without any test-time reflection. CARE improves accuracy and training smoothness while explicitly increasing the share of learning signal that comes from failures. On Qwen2.5-VL-7B, CARE lifts macro-averaged accuracy by 4.6 points over GRPO across six verifiable visual-reasoning benchmarks; with Qwen3-VL-8B it reaches competitive or state-of-the-art results on MathVista and MMMU-Pro under an identical evaluation protocol.
GLaD: Geometric Latent Distillation for Vision-Language-Action Models
Dec 10, 2025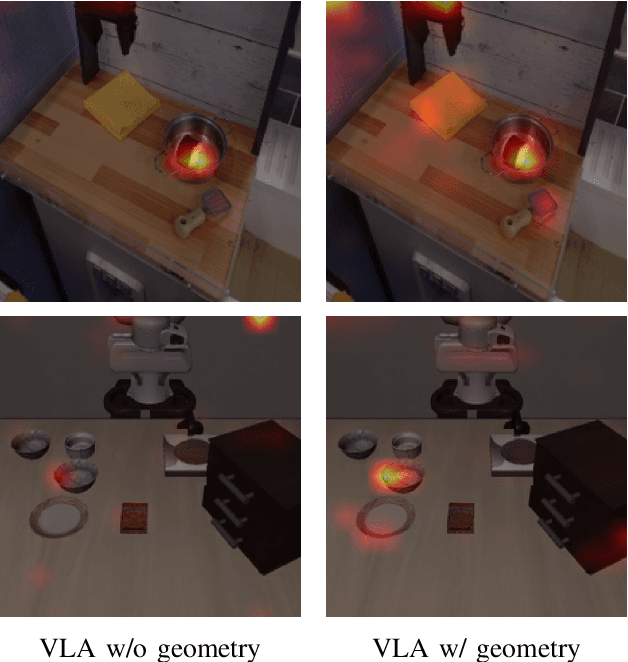
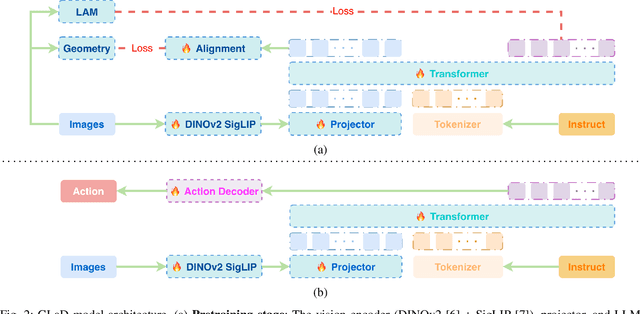
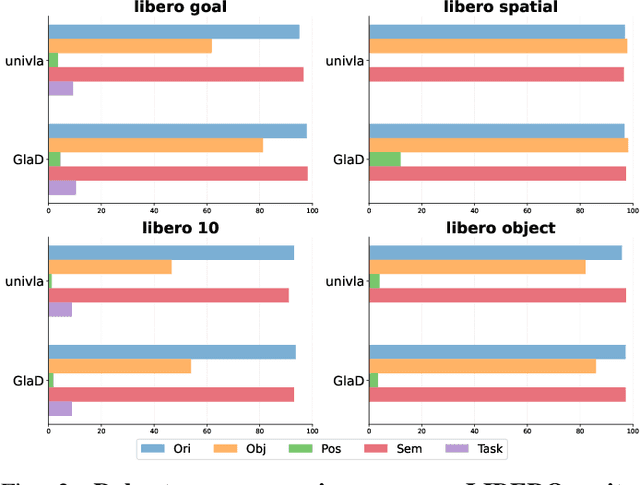
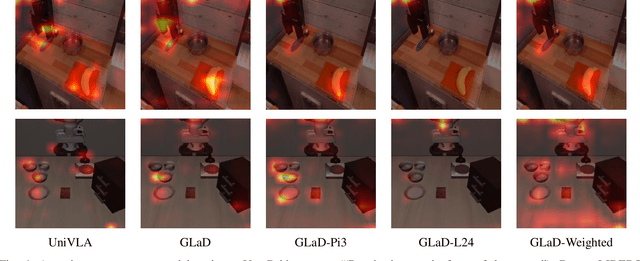
Abstract:Most existing Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models rely primarily on RGB information, while ignoring geometric cues crucial for spatial reasoning and manipulation. In this work, we introduce GLaD, a geometry-aware VLA framework that incorporates 3D geometric priors during pretraining through knowledge distillation. Rather than distilling geometric features solely into the vision encoder, we align the LLM's hidden states corresponding to visual tokens with features from a frozen geometry-aware vision transformer (VGGT), ensuring that geometric understanding is deeply integrated into the multimodal representations that drive action prediction. Pretrained on the Bridge dataset with this geometry distillation mechanism, GLaD achieves 94.1% average success rate across four LIBERO task suites, outperforming UniVLA (92.5%) which uses identical pretraining data. These results validate that geometry-aware pretraining enhances spatial reasoning and policy generalization without requiring explicit depth sensors or 3D annotations.
SpatialDreamer: Incentivizing Spatial Reasoning via Active Mental Imagery
Dec 08, 2025Abstract:Despite advancements in Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) for scene understanding, their performance on complex spatial reasoning tasks requiring mental simulation remains significantly limited. Current methods often rely on passive observation of spatial data, failing to internalize an active mental imagery process. To bridge this gap, we propose SpatialDreamer, a reinforcement learning framework that enables spatial reasoning through a closedloop process of active exploration, visual imagination via a world model, and evidence-grounded reasoning. To address the lack of fine-grained reward supervision in longhorizontal reasoning tasks, we propose Geometric Policy Optimization (GeoPO), which introduces tree-structured sampling and step-level reward estimation with geometric consistency constraints. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SpatialDreamer delivers highly competitive results across multiple challenging benchmarks, signifying a critical advancement in human-like active spatial mental simulation for MLLMs.
Video Spatial Reasoning with Object-Centric 3D Rollout
Nov 17, 2025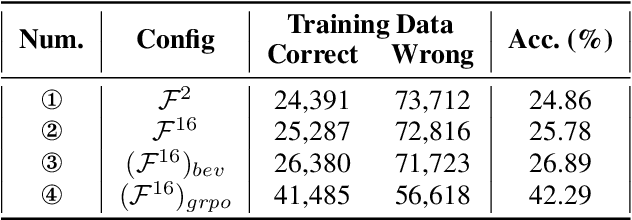
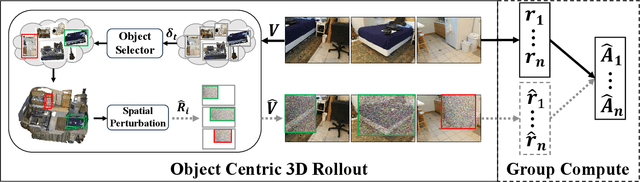
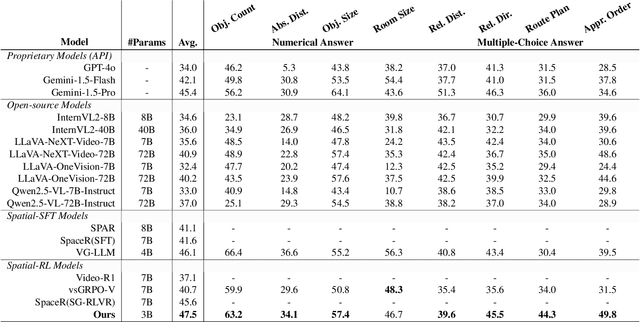
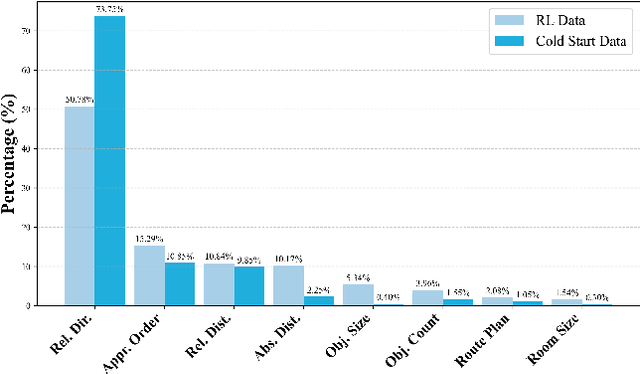
Abstract:Recent advances in Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have showcased remarkable capabilities in vision-language understanding. However, enabling robust video spatial reasoning-the ability to comprehend object locations, orientations, and inter-object relationships in dynamic 3D scenes-remains a key unsolved challenge. Existing approaches primarily rely on spatially grounded supervised fine-tuning or reinforcement learning, yet we observe that such models often exhibit query-locked reasoning, focusing narrowly on objects explicitly mentioned in the prompt while ignoring critical contextual cues. To address this limitation, we propose Object-Centric 3D Rollout (OCR), a novel strategy that introduces structured perturbations to the 3D geometry of selected objects during training. By degrading object-specific visual cues and projecting the altered geometry into 2D space, OCR compels the model to reason holistically across the entire scene. We further design a rollout-based training pipeline that jointly leverages vanilla and region-noisy videos to optimize spatial reasoning trajectories. Experiments demonstrate state-of-the-art performance: our 3B-parameter model achieves 47.5% accuracy on VSI-Bench, outperforming several 7B baselines. Ablations confirm OCR's superiority over prior rollout strategies (e.g., T-GRPO, NoisyRollout).
Beyond Observations: Reconstruction Error-Guided Irregularly Sampled Time Series Representation Learning
Nov 15, 2025Abstract:Irregularly sampled time series (ISTS), characterized by non-uniform time intervals with natural missingness, are prevalent in real-world applications. Existing approaches for ISTS modeling primarily rely on observed values to impute unobserved ones or infer latent dynamics. However, these methods overlook a critical source of learning signal: the reconstruction error inherently produced during model training. Such error implicitly reflects how well a model captures the underlying data structure and can serve as an informative proxy for unobserved values. To exploit this insight, we propose iTimER, a simple yet effective self-supervised pre-training framework for ISTS representation learning. iTimER models the distribution of reconstruction errors over observed values and generates pseudo-observations for unobserved timestamps through a mixup strategy between sampled errors and the last available observations. This transforms unobserved timestamps into noise-aware training targets, enabling meaningful reconstruction signals. A Wasserstein metric aligns reconstruction error distributions between observed and pseudo-observed regions, while a contrastive learning objective enhances the discriminability of learned representations. Extensive experiments on classification, interpolation, and forecasting tasks demonstrate that iTimER consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods under the ISTS setting.
COMPASS: A Multi-Turn Benchmark for Tool-Mediated Planning & Preference Optimization
Oct 08, 2025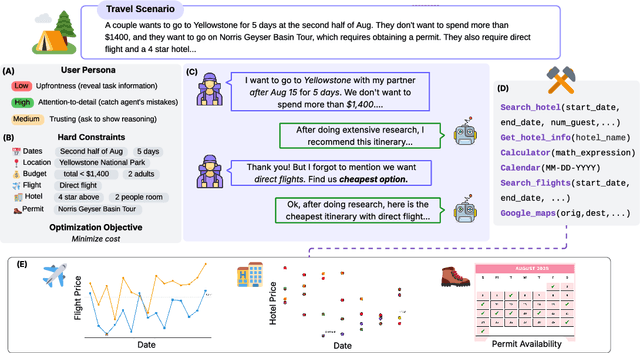
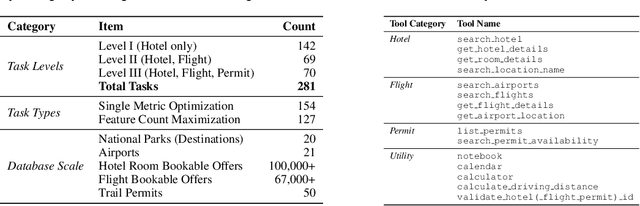
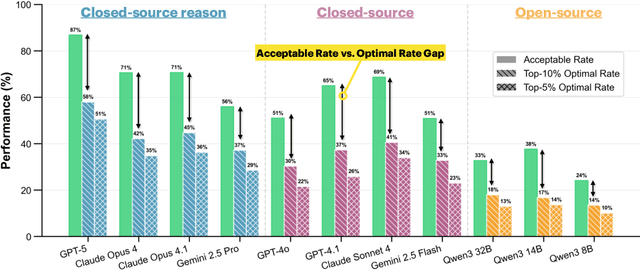
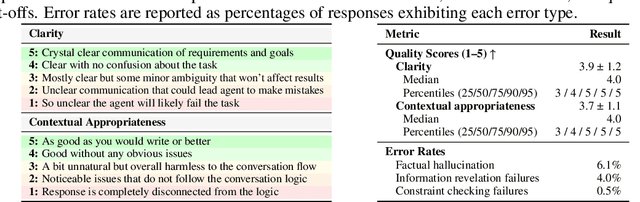
Abstract:Real-world large language model (LLM) agents must master strategic tool use and user preference optimization through multi-turn interactions to assist users with complex planning tasks. We introduce COMPASS (Constrained Optimization through Multi-turn Planning and Strategic Solutions), a benchmark that evaluates agents on realistic travel-planning scenarios. We cast travel planning as a constrained preference optimization problem, where agents must satisfy hard constraints while simultaneously optimizing soft user preferences. To support this, we build a realistic travel database covering transportation, accommodation, and ticketing for 20 U.S. National Parks, along with a comprehensive tool ecosystem that mirrors commercial booking platforms. Evaluating state-of-the-art models, we uncover two critical gaps: (i) an acceptable-optimal gap, where agents reliably meet constraints but fail to optimize preferences, and (ii) a plan-coordination gap, where performance collapses on multi-service (flight and hotel) coordination tasks, especially for open-source models. By grounding reasoning and planning in a practical, user-facing domain, COMPASS provides a benchmark that directly measures an agent's ability to optimize user preferences in realistic tasks, bridging theoretical advances with real-world impact.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge