Liang Ma
ReV, LS2N
Deep Deterministic Nonlinear ICA via Total Correlation Minimization with Matrix-Based Entropy Functional
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:Blind source separation, particularly through independent component analysis (ICA), is widely utilized across various signal processing domains for disentangling underlying components from observed mixed signals, owing to its fully data-driven nature that minimizes reliance on prior assumptions. However, conventional ICA methods rely on an assumption of linear mixing, limiting their ability to capture complex nonlinear relationships and to maintain robustness in noisy environments. In this work, we present deep deterministic nonlinear independent component analysis (DDICA), a novel deep neural network-based framework designed to address these limitations. DDICA leverages a matrix-based entropy function to directly optimize the independence criterion via stochastic gradient descent, bypassing the need for variational approximations or adversarial schemes. This results in a streamlined training process and improved resilience to noise. We validated the effectiveness and generalizability of DDICA across a range of applications, including simulated signal mixtures, hyperspectral image unmixing, modeling of primary visual receptive fields, and resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) data analysis. Experimental results demonstrate that DDICA effectively separates independent components with high accuracy across a range of applications. These findings suggest that DDICA offers a robust and versatile solution for blind source separation in diverse signal processing tasks.
PhyBlock: A Progressive Benchmark for Physical Understanding and Planning via 3D Block Assembly
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:While vision-language models (VLMs) have demonstrated promising capabilities in reasoning and planning for embodied agents, their ability to comprehend physical phenomena, particularly within structured 3D environments, remains severely limited. To close this gap, we introduce PhyBlock, a progressive benchmark designed to assess VLMs on physical understanding and planning through robotic 3D block assembly tasks. PhyBlock integrates a novel four-level cognitive hierarchy assembly task alongside targeted Visual Question Answering (VQA) samples, collectively aimed at evaluating progressive spatial reasoning and fundamental physical comprehension, including object properties, spatial relationships, and holistic scene understanding. PhyBlock includes 2600 block tasks (400 assembly tasks, 2200 VQA tasks) and evaluates models across three key dimensions: partial completion, failure diagnosis, and planning robustness. We benchmark 21 state-of-the-art VLMs, highlighting their strengths and limitations in physically grounded, multi-step planning. Our empirical findings indicate that the performance of VLMs exhibits pronounced limitations in high-level planning and reasoning capabilities, leading to a notable decline in performance for the growing complexity of the tasks. Error analysis reveals persistent difficulties in spatial orientation and dependency reasoning. Surprisingly, chain-of-thought prompting offers minimal improvements, suggesting spatial tasks heavily rely on intuitive model comprehension. We position PhyBlock as a unified testbed to advance embodied reasoning, bridging vision-language understanding and real-world physical problem-solving.
MineAnyBuild: Benchmarking Spatial Planning for Open-world AI Agents
May 26, 2025Abstract:Spatial Planning is a crucial part in the field of spatial intelligence, which requires the understanding and planning about object arrangements in space perspective. AI agents with the spatial planning ability can better adapt to various real-world applications, including robotic manipulation, automatic assembly, urban planning etc. Recent works have attempted to construct benchmarks for evaluating the spatial intelligence of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs). Nevertheless, these benchmarks primarily focus on spatial reasoning based on typical Visual Question-Answering (VQA) forms, which suffers from the gap between abstract spatial understanding and concrete task execution. In this work, we take a step further to build a comprehensive benchmark called MineAnyBuild, aiming to evaluate the spatial planning ability of open-world AI agents in the Minecraft game. Specifically, MineAnyBuild requires an agent to generate executable architecture building plans based on the given multi-modal human instructions. It involves 4,000 curated spatial planning tasks and also provides a paradigm for infinitely expandable data collection by utilizing rich player-generated content. MineAnyBuild evaluates spatial planning through four core supporting dimensions: spatial understanding, spatial reasoning, creativity, and spatial commonsense. Based on MineAnyBuild, we perform a comprehensive evaluation for existing MLLM-based agents, revealing the severe limitations but enormous potential in their spatial planning abilities. We believe our MineAnyBuild will open new avenues for the evaluation of spatial intelligence and help promote further development for open-world AI agents capable of spatial planning.
Unbiased Evaluation of Large Language Models from a Causal Perspective
Feb 10, 2025



Abstract:Benchmark contamination has become a significant concern in the LLM evaluation community. Previous Agents-as-an-Evaluator address this issue by involving agents in the generation of questions. Despite their success, the biases in Agents-as-an-Evaluator methods remain largely unexplored. In this paper, we present a theoretical formulation of evaluation bias, providing valuable insights into designing unbiased evaluation protocols. Furthermore, we identify two type of bias in Agents-as-an-Evaluator through carefully designed probing tasks on a minimal Agents-as-an-Evaluator setup. To address these issues, we propose the Unbiased Evaluator, an evaluation protocol that delivers a more comprehensive, unbiased, and interpretable assessment of LLMs.Extensive experiments reveal significant room for improvement in current LLMs. Additionally, we demonstrate that the Unbiased Evaluator not only offers strong evidence of benchmark contamination but also provides interpretable evaluation results.
RoomTour3D: Geometry-Aware Video-Instruction Tuning for Embodied Navigation
Dec 11, 2024Abstract:Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN) suffers from the limited diversity and scale of training data, primarily constrained by the manual curation of existing simulators. To address this, we introduce RoomTour3D, a video-instruction dataset derived from web-based room tour videos that capture real-world indoor spaces and human walking demonstrations. Unlike existing VLN datasets, RoomTour3D leverages the scale and diversity of online videos to generate open-ended human walking trajectories and open-world navigable instructions. To compensate for the lack of navigation data in online videos, we perform 3D reconstruction and obtain 3D trajectories of walking paths augmented with additional information on the room types, object locations and 3D shape of surrounding scenes. Our dataset includes $\sim$100K open-ended description-enriched trajectories with $\sim$200K instructions, and 17K action-enriched trajectories from 1847 room tour environments. We demonstrate experimentally that RoomTour3D enables significant improvements across multiple VLN tasks including CVDN, SOON, R2R, and REVERIE. Moreover, RoomTour3D facilitates the development of trainable zero-shot VLN agents, showcasing the potential and challenges of advancing towards open-world navigation.
EACO: Enhancing Alignment in Multimodal LLMs via Critical Observation
Dec 06, 2024



Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have achieved remarkable progress on various visual question answering and reasoning tasks leveraging instruction fine-tuning specific datasets. They can also learn from preference data annotated by human to enhance their reasoning ability and mitigate hallucinations. Most of preference data is generated from the model itself. However, existing methods require high-quality critical labels, which are costly and rely on human or proprietary models like GPT-4V. In this work, we propose Enhancing Alignment in MLLMs via Critical Observation (EACO), which aligns MLLMs by self-generated preference data using only 5k images economically. Our approach begins with collecting and refining a Scoring Evaluation Instruction-tuning dataset to train a critical evaluation model, termed the Critic. This Critic observes model responses across multiple dimensions, selecting preferred and non-preferred outputs for refined Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) tuning. To further enhance model performance, we employ an additional supervised fine-tuning stage after preference tuning. EACO reduces the overall hallucinations by 65.6% on HallusionBench and improves the reasoning ability by 21.8% on MME-Cognition. EACO achieves an 8.5% improvement over LLaVA-v1.6-Mistral-7B across multiple benchmarks. Remarkably, EACO also shows the potential critical ability in open-source MLLMs, demonstrating that EACO is a viable path to boost the competence of MLLMs.
An Outline of Prognostics and Health Management Large Model: Concepts, Paradigms, and Challenges
Jul 01, 2024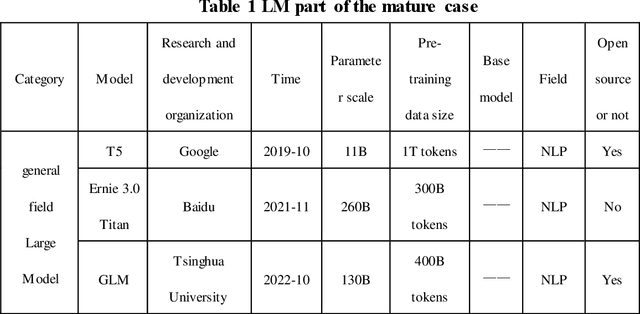
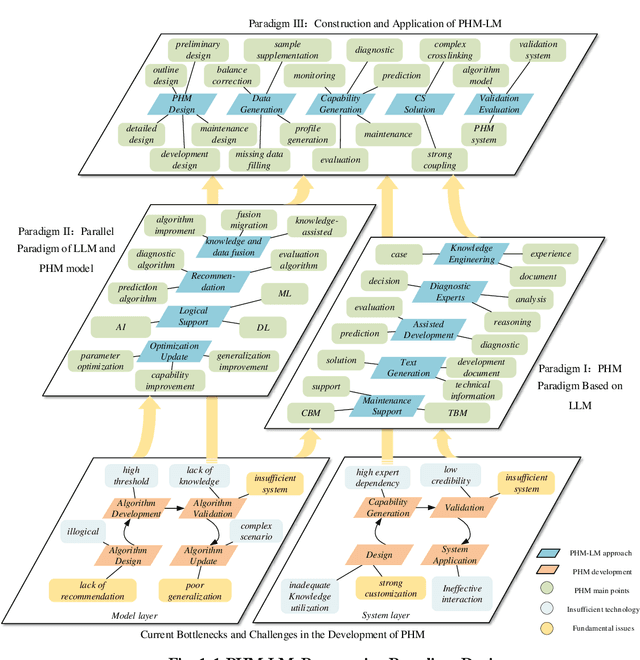
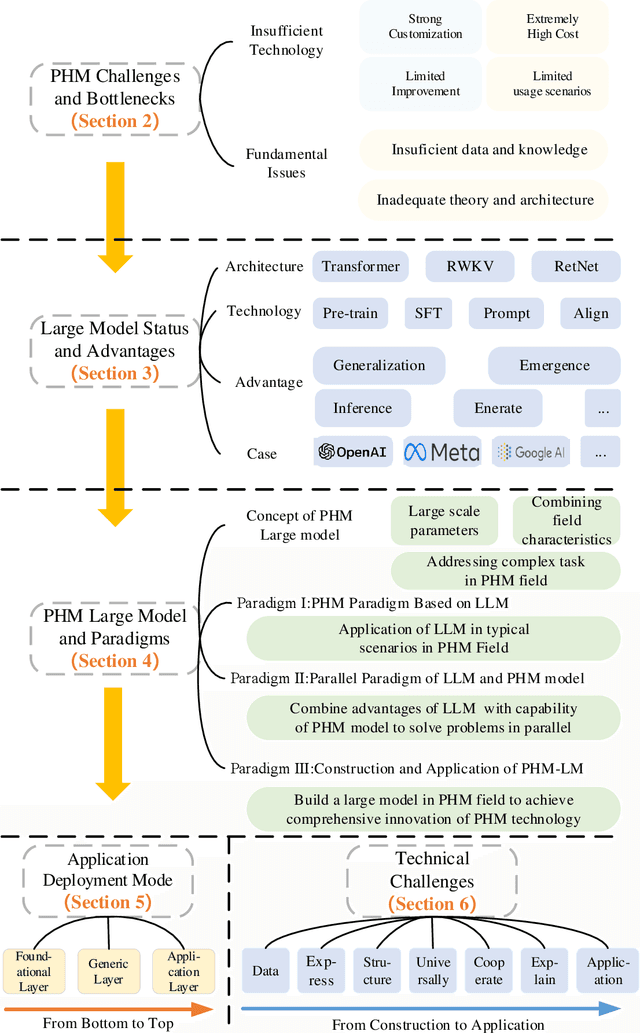
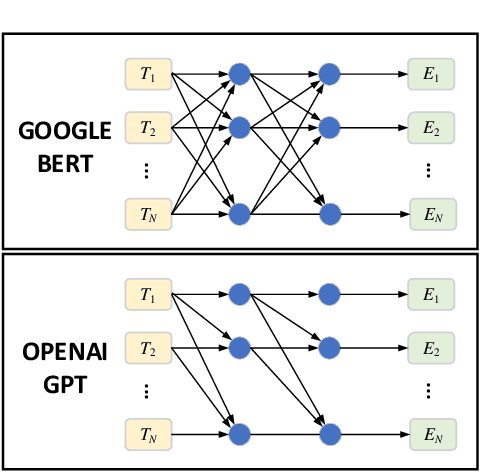
Abstract:Prognosis and Health Management (PHM), critical for ensuring task completion by complex systems and preventing unexpected failures, is widely adopted in aerospace, manufacturing, maritime, rail, energy, etc. However, PHM's development is constrained by bottlenecks like generalization, interpretation and verification abilities. Presently, generative artificial intelligence (AI), represented by Large Model, heralds a technological revolution with the potential to fundamentally reshape traditional technological fields and human production methods. Its capabilities, including strong generalization, reasoning, and generative attributes, present opportunities to address PHM's bottlenecks. To this end, based on a systematic analysis of the current challenges and bottlenecks in PHM, as well as the research status and advantages of Large Model, we propose a novel concept and three progressive paradigms of Prognosis and Health Management Large Model (PHM-LM) through the integration of the Large Model with PHM. Subsequently, we provide feasible technical approaches for PHM-LM to bolster PHM's core capabilities within the framework of the three paradigms. Moreover, to address core issues confronting PHM, we discuss a series of technical challenges of PHM-LM throughout the entire process of construction and application. This comprehensive effort offers a holistic PHM-LM technical framework, and provides avenues for new PHM technologies, methodologies, tools, platforms and applications, which also potentially innovates design, research & development, verification and application mode of PHM. And furthermore, a new generation of PHM with AI will also capably be realized, i.e., from custom to generalized, from discriminative to generative, and from theoretical conditions to practical applications.
MIPI 2024 Challenge on Demosaic for HybridEVS Camera: Methods and Results
May 08, 2024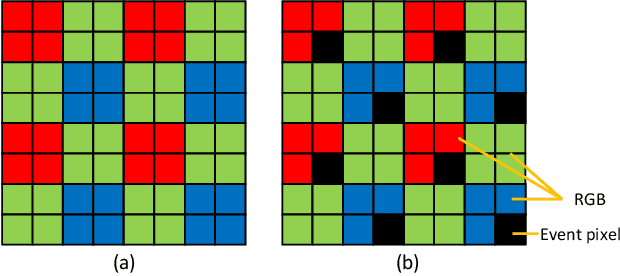
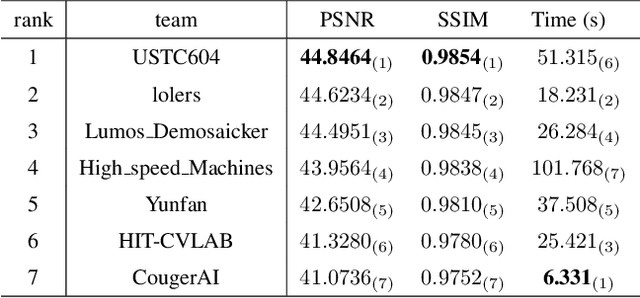
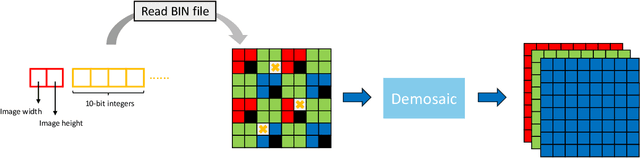

Abstract:The increasing demand for computational photography and imaging on mobile platforms has led to the widespread development and integration of advanced image sensors with novel algorithms in camera systems. However, the scarcity of high-quality data for research and the rare opportunity for in-depth exchange of views from industry and academia constrain the development of mobile intelligent photography and imaging (MIPI). Building on the achievements of the previous MIPI Workshops held at ECCV 2022 and CVPR 2023, we introduce our third MIPI challenge including three tracks focusing on novel image sensors and imaging algorithms. In this paper, we summarize and review the Nighttime Flare Removal track on MIPI 2024. In total, 170 participants were successfully registered, and 14 teams submitted results in the final testing phase. The developed solutions in this challenge achieved state-of-the-art performance on Nighttime Flare Removal. More details of this challenge and the link to the dataset can be found at https://mipi-challenge.org/MIPI2024/.
GarchingSim: An Autonomous Driving Simulator with Photorealistic Scenes and Minimalist Workflow
Jan 30, 2024



Abstract:Conducting real road testing for autonomous driving algorithms can be expensive and sometimes impractical, particularly for small startups and research institutes. Thus, simulation becomes an important method for evaluating these algorithms. However, the availability of free and open-source simulators is limited, and the installation and configuration process can be daunting for beginners and interdisciplinary researchers. We introduce an autonomous driving simulator with photorealistic scenes, meanwhile keeping a user-friendly workflow. The simulator is able to communicate with external algorithms through ROS2 or Socket.IO, making it compatible with existing software stacks. Furthermore, we implement a highly accurate vehicle dynamics model within the simulator to enhance the realism of the vehicle's physical effects. The simulator is able to serve various functions, including generating synthetic data and driving with machine learning-based algorithms. Moreover, we prioritize simplicity in the deployment process, ensuring that beginners find it approachable and user-friendly.
Versatile Medical Image Segmentation Learned from Multi-Source Datasets via Model Self-Disambiguation
Nov 17, 2023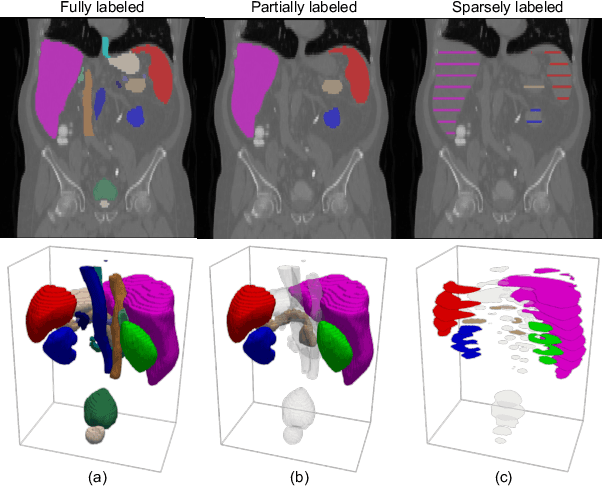
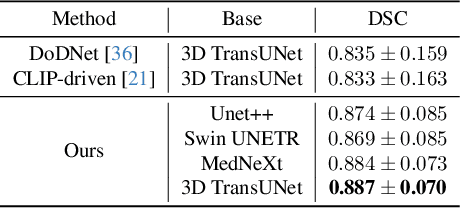
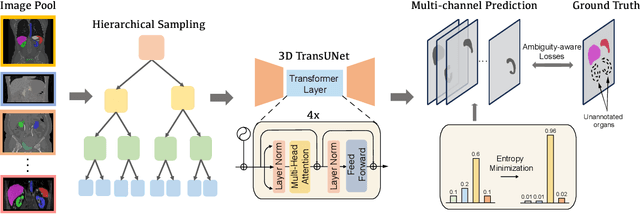

Abstract:A versatile medical image segmentation model applicable to imaging data collected with diverse equipment and protocols can facilitate model deployment and maintenance. However, building such a model typically requires a large, diverse, and fully annotated dataset, which is rarely available due to the labor-intensive and costly data curation. In this study, we develop a cost-efficient method by harnessing readily available data with partially or even sparsely annotated segmentation labels. We devise strategies for model self-disambiguation, prior knowledge incorporation, and imbalance mitigation to address challenges associated with inconsistently labeled data from various sources, including label ambiguity and imbalances across modalities, datasets, and segmentation labels. Experimental results on a multi-modal dataset compiled from eight different sources for abdominal organ segmentation have demonstrated our method's effectiveness and superior performance over alternative state-of-the-art methods, highlighting its potential for optimizing the use of existing annotated data and reducing the annotation efforts for new data to further enhance model capability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge