Min Lin
Rethinking the Trust Region in LLM Reinforcement Learning
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) has become a cornerstone for fine-tuning Large Language Models (LLMs), with Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) serving as the de facto standard algorithm. Despite its ubiquity, we argue that the core ratio clipping mechanism in PPO is structurally ill-suited for the large vocabularies inherent to LLMs. PPO constrains policy updates based on the probability ratio of sampled tokens, which serves as a noisy single-sample Monte Carlo estimate of the true policy divergence. This creates a sub-optimal learning dynamic: updates to low-probability tokens are aggressively over-penalized, while potentially catastrophic shifts in high-probability tokens are under-constrained, leading to training inefficiency and instability. To address this, we propose Divergence Proximal Policy Optimization (DPPO), which substitutes heuristic clipping with a more principled constraint based on a direct estimate of policy divergence (e.g., Total Variation or KL). To avoid huge memory footprint, we introduce the efficient Binary and Top-K approximations to capture the essential divergence with negligible overhead. Extensive empirical evaluations demonstrate that DPPO achieves superior training stability and efficiency compared to existing methods, offering a more robust foundation for RL-based LLM fine-tuning.
Revisiting Parameter Server in LLM Post-Training
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Modern data parallel (DP) training favors collective communication over parameter servers (PS) for its simplicity and efficiency under balanced workloads. However, the balanced workload assumption no longer holds in large language model (LLM) post-training due to the high variance in sequence lengths. Under imbalanced workloads, collective communication creates synchronization barriers, leading to under-utilization of devices with smaller workloads. This change in training dynamics calls for a revisit of the PS paradigm for its robustness to such imbalance. We propose \textbf{On-Demand Communication (ODC)}, which adapts PS into Fully Sharded Data Parallel (FSDP) by replacing collective all-gather and reduce-scatter with direct point-to-point communication. Compared to FSDP, ODC reduces the synchronization barrier from once per layer to once per minibatch and decouples the workload on each device so that faster workers are not stalled. It also enables simpler and more effective load balancing at the minibatch level. Across diverse LLM post-training tasks, ODC consistently improves device utilization and training throughput, achieving up to a 36\% speedup over standard FSDP. These results demonstrate that ODC is a superior fit for the prevalent imbalanced workloads in LLM post-training. Our implementation of ODC and integration with FSDP is open-sourced at https://github.com/sail-sg/odc.
Defeating the Training-Inference Mismatch via FP16
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) fine-tuning of large language models (LLMs) often suffers from instability due to the numerical mismatch between the training and inference policies. While prior work has attempted to mitigate this issue through algorithmic corrections or engineering alignments, we show that its root cause lies in the floating point precision itself. The widely adopted BF16, despite its large dynamic range, introduces large rounding errors that breaks the consistency between training and inference. In this work, we demonstrate that simply reverting to \textbf{FP16} effectively eliminates this mismatch. The change is simple, fully supported by modern frameworks with only a few lines of code change, and requires no modification to the model architecture or learning algorithm. Our results suggest that using FP16 uniformly yields more stable optimization, faster convergence, and stronger performance across diverse tasks, algorithms and frameworks. We hope these findings motivate a broader reconsideration of precision trade-offs in RL fine-tuning.
Nonparametric Data Attribution for Diffusion Models
Oct 16, 2025Abstract:Data attribution for generative models seeks to quantify the influence of individual training examples on model outputs. Existing methods for diffusion models typically require access to model gradients or retraining, limiting their applicability in proprietary or large-scale settings. We propose a nonparametric attribution method that operates entirely on data, measuring influence via patch-level similarity between generated and training images. Our approach is grounded in the analytical form of the optimal score function and naturally extends to multiscale representations, while remaining computationally efficient through convolution-based acceleration. In addition to producing spatially interpretable attributions, our framework uncovers patterns that reflect intrinsic relationships between training data and outputs, independent of any specific model. Experiments demonstrate that our method achieves strong attribution performance, closely matching gradient-based approaches and substantially outperforming existing nonparametric baselines. Code is available at https://github.com/sail-sg/NDA.
DEPTHOR++: Robust Depth Enhancement from a Real-World Lightweight dToF and RGB Guidance
Sep 30, 2025Abstract:Depth enhancement, which converts raw dToF signals into dense depth maps using RGB guidance, is crucial for improving depth perception in high-precision tasks such as 3D reconstruction and SLAM. However, existing methods often assume ideal dToF inputs and perfect dToF-RGB alignment, overlooking calibration errors and anomalies, thus limiting real-world applicability. This work systematically analyzes the noise characteristics of real-world lightweight dToF sensors and proposes a practical and novel depth completion framework, DEPTHOR++, which enhances robustness to noisy dToF inputs from three key aspects. First, we introduce a simulation method based on synthetic datasets to generate realistic training samples for robust model training. Second, we propose a learnable-parameter-free anomaly detection mechanism to identify and remove erroneous dToF measurements, preventing misleading propagation during completion. Third, we design a depth completion network tailored to noisy dToF inputs, which integrates RGB images and pre-trained monocular depth estimation priors to improve depth recovery in challenging regions. On the ZJU-L5 dataset and real-world samples, our training strategy significantly boosts existing depth completion models, with our model achieving state-of-the-art performance, improving RMSE and Rel by 22% and 11% on average. On the Mirror3D-NYU dataset, by incorporating the anomaly detection method, our model improves upon the previous SOTA by 37% in mirror regions. On the Hammer dataset, using simulated low-cost dToF data from RealSense L515, our method surpasses the L515 measurements with an average gain of 22%, demonstrating its potential to enable low-cost sensors to outperform higher-end devices. Qualitative results across diverse real-world datasets further validate the effectiveness and generalizability of our approach.
Language Models Can Learn from Verbal Feedback Without Scalar Rewards
Sep 26, 2025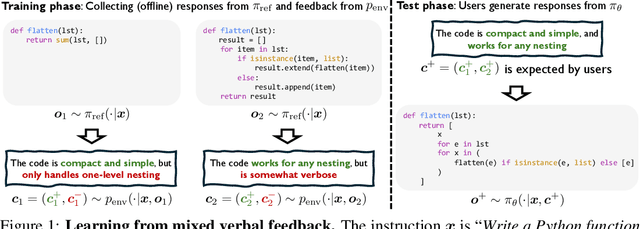
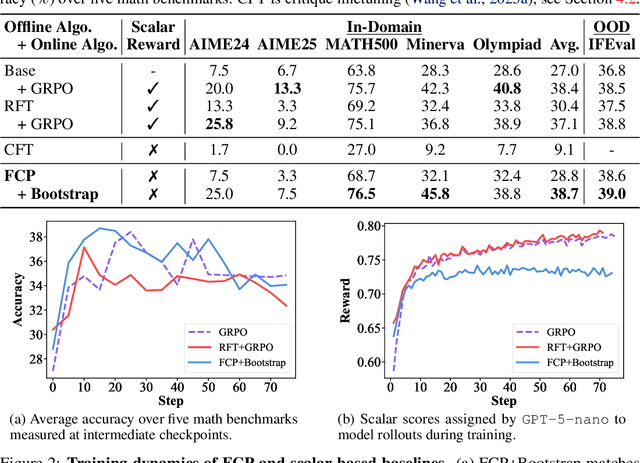
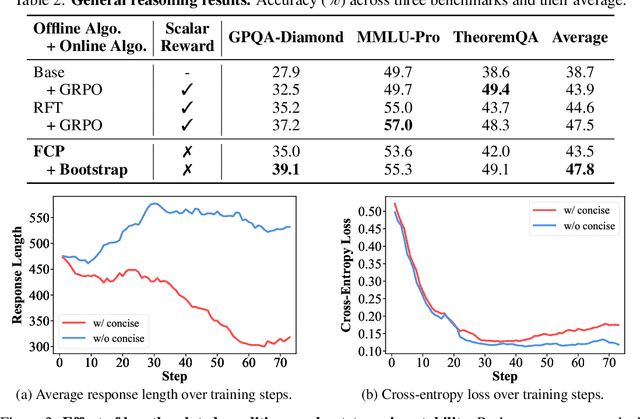
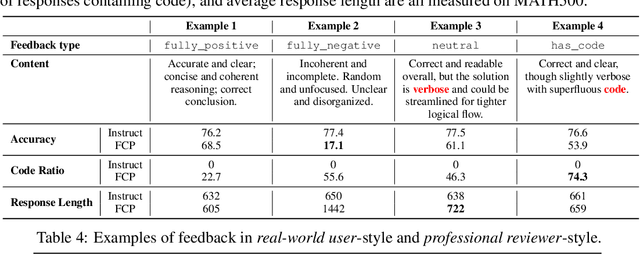
Abstract:LLMs are often trained with RL from human or AI feedback, yet such methods typically compress nuanced feedback into scalar rewards, discarding much of their richness and inducing scale imbalance. We propose treating verbal feedback as a conditioning signal. Inspired by language priors in text-to-image generation, which enable novel outputs from unseen prompts, we introduce the feedback-conditional policy (FCP). FCP learns directly from response-feedback pairs, approximating the feedback-conditional posterior through maximum likelihood training on offline data. We further develop an online bootstrapping stage where the policy generates under positive conditions and receives fresh feedback to refine itself. This reframes feedback-driven learning as conditional generation rather than reward optimization, offering a more expressive way for LLMs to directly learn from verbal feedback. Our code is available at https://github.com/sail-sg/feedback-conditional-policy.
Variational Reasoning for Language Models
Sep 26, 2025



Abstract:We introduce a variational reasoning framework for language models that treats thinking traces as latent variables and optimizes them through variational inference. Starting from the evidence lower bound (ELBO), we extend it to a multi-trace objective for tighter bounds and propose a forward-KL formulation that stabilizes the training of the variational posterior. We further show that rejection sampling finetuning and binary-reward RL, including GRPO, can be interpreted as local forward-KL objectives, where an implicit weighting by model accuracy naturally arises from the derivation and reveals a previously unnoticed bias toward easier questions. We empirically validate our method on the Qwen 2.5 and Qwen 3 model families across a wide range of reasoning tasks. Overall, our work provides a principled probabilistic perspective that unifies variational inference with RL-style methods and yields stable objectives for improving the reasoning ability of language models. Our code is available at https://github.com/sail-sg/variational-reasoning.
PhyBlock: A Progressive Benchmark for Physical Understanding and Planning via 3D Block Assembly
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:While vision-language models (VLMs) have demonstrated promising capabilities in reasoning and planning for embodied agents, their ability to comprehend physical phenomena, particularly within structured 3D environments, remains severely limited. To close this gap, we introduce PhyBlock, a progressive benchmark designed to assess VLMs on physical understanding and planning through robotic 3D block assembly tasks. PhyBlock integrates a novel four-level cognitive hierarchy assembly task alongside targeted Visual Question Answering (VQA) samples, collectively aimed at evaluating progressive spatial reasoning and fundamental physical comprehension, including object properties, spatial relationships, and holistic scene understanding. PhyBlock includes 2600 block tasks (400 assembly tasks, 2200 VQA tasks) and evaluates models across three key dimensions: partial completion, failure diagnosis, and planning robustness. We benchmark 21 state-of-the-art VLMs, highlighting their strengths and limitations in physically grounded, multi-step planning. Our empirical findings indicate that the performance of VLMs exhibits pronounced limitations in high-level planning and reasoning capabilities, leading to a notable decline in performance for the growing complexity of the tasks. Error analysis reveals persistent difficulties in spatial orientation and dependency reasoning. Surprisingly, chain-of-thought prompting offers minimal improvements, suggesting spatial tasks heavily rely on intuitive model comprehension. We position PhyBlock as a unified testbed to advance embodied reasoning, bridging vision-language understanding and real-world physical problem-solving.
Reinforcing General Reasoning without Verifiers
May 27, 2025Abstract:The recent paradigm shift towards training large language models (LLMs) using DeepSeek-R1-Zero-style reinforcement learning (RL) on verifiable rewards has led to impressive advancements in code and mathematical reasoning. However, this methodology is limited to tasks where rule-based answer verification is possible and does not naturally extend to real-world domains such as chemistry, healthcare, engineering, law, biology, business, and economics. Current practical workarounds use an additional LLM as a model-based verifier; however, this introduces issues such as reliance on a strong verifier LLM, susceptibility to reward hacking, and the practical burden of maintaining the verifier model in memory during training. To address this and extend DeepSeek-R1-Zero-style training to general reasoning domains, we propose a verifier-free method (VeriFree) that bypasses answer verification and instead uses RL to directly maximize the probability of generating the reference answer. We compare VeriFree with verifier-based methods and demonstrate that, in addition to its significant practical benefits and reduced compute requirements, VeriFree matches and even surpasses verifier-based methods on extensive evaluations across MMLU-Pro, GPQA, SuperGPQA, and math-related benchmarks. Moreover, we provide insights into this method from multiple perspectives: as an elegant integration of training both the policy and implicit verifier in a unified model, and as a variational optimization approach. Code is available at https://github.com/sail-sg/VeriFree.
Lifelong Safety Alignment for Language Models
May 26, 2025



Abstract:LLMs have made impressive progress, but their growing capabilities also expose them to highly flexible jailbreaking attacks designed to bypass safety alignment. While many existing defenses focus on known types of attacks, it is more critical to prepare LLMs for unseen attacks that may arise during deployment. To address this, we propose a lifelong safety alignment framework that enables LLMs to continuously adapt to new and evolving jailbreaking strategies. Our framework introduces a competitive setup between two components: a Meta-Attacker, trained to actively discover novel jailbreaking strategies, and a Defender, trained to resist them. To effectively warm up the Meta-Attacker, we first leverage the GPT-4o API to extract key insights from a large collection of jailbreak-related research papers. Through iterative training, the first iteration Meta-Attacker achieves a 73% attack success rate (ASR) on RR and a 57% transfer ASR on LAT using only single-turn attacks. Meanwhile, the Defender progressively improves its robustness and ultimately reduces the Meta-Attacker's success rate to just 7%, enabling safer and more reliable deployment of LLMs in open-ended environments. The code is available at https://github.com/sail-sg/LifelongSafetyAlignment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge