Yong Fan
from the iSTAGING consortium, for the ADNI
DeltaDiff: A Residual-Guided Diffusion Model for Enhanced Image Super-Resolution
Feb 18, 2025Abstract:Recently, the application of diffusion models in super-resolution tasks has become a popular research direction. Existing work is focused on fully migrating diffusion models to SR tasks. The diffusion model is proposed in the field of image generation, so in order to make the generated results diverse, the diffusion model combines random Gaussian noise and distributed sampling to increase the randomness of the model. However, the essence of super-resolution tasks requires the model to generate high-resolution images with fidelity. Excessive addition of random factors can result in the model generating detailed information that does not belong to the HR image. To address this issue, we propose a new diffusion model called Deltadiff, which uses only residuals between images for diffusion, making the entire diffusion process more stable. The experimental results show that our method surpasses state-of-the-art models and generates results with better fidelity. Our code and model are publicly available at https://github.com/continueyang/DeltaDiff
GVTNet: Graph Vision Transformer For Face Super-Resolution
Feb 18, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in face super-resolution research have utilized the Transformer architecture. This method processes the input image into a series of small patches. However, because of the strong correlation between different facial components in facial images. When it comes to super-resolution of low-resolution images, existing algorithms cannot handle the relationships between patches well, resulting in distorted facial components in the super-resolution results. To solve the problem, we propose a transformer architecture based on graph neural networks called graph vision transformer network. We treat each patch as a graph node and establish an adjacency matrix based on the information between patches. In this way, the patch only interacts between neighboring patches, further processing the relationship of facial components. Quantitative and visualization experiments have underscored the superiority of our algorithm over state-of-the-art techniques. Through detailed comparisons, we have demonstrated that our algorithm possesses more advanced super-resolution capabilities, particularly in enhancing facial components. The PyTorch code is available at https://github.com/continueyang/GVTNet
CopilotCAD: Empowering Radiologists with Report Completion Models and Quantitative Evidence from Medical Image Foundation Models
Apr 11, 2024



Abstract:Computer-aided diagnosis systems hold great promise to aid radiologists and clinicians in radiological clinical practice and enhance diagnostic accuracy and efficiency. However, the conventional systems primarily focus on delivering diagnostic results through text report generation or medical image classification, positioning them as standalone decision-makers rather than helpers and ignoring radiologists' expertise. This study introduces an innovative paradigm to create an assistive co-pilot system for empowering radiologists by leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) and medical image analysis tools. Specifically, we develop a collaborative framework to integrate LLMs and quantitative medical image analysis results generated by foundation models with radiologists in the loop, achieving efficient and safe generation of radiology reports and effective utilization of computational power of AI and the expertise of medical professionals. This approach empowers radiologists to generate more precise and detailed diagnostic reports, enhancing patient outcomes while reducing the burnout of clinicians. Our methodology underscores the potential of AI as a supportive tool in medical diagnostics, promoting a harmonious integration of technology and human expertise to advance the field of radiology.
Versatile Medical Image Segmentation Learned from Multi-Source Datasets via Model Self-Disambiguation
Nov 17, 2023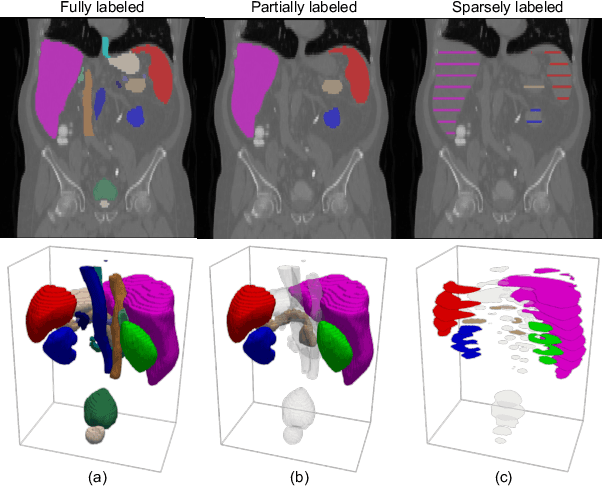
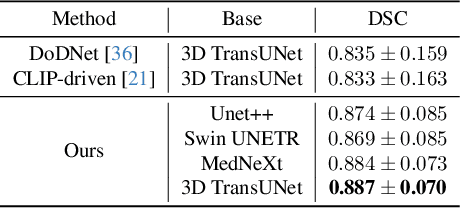
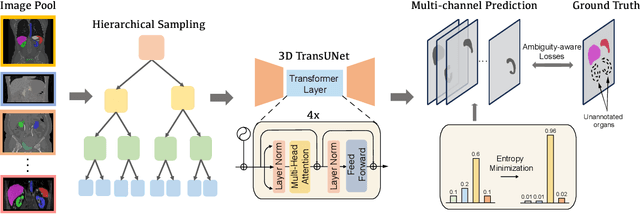

Abstract:A versatile medical image segmentation model applicable to imaging data collected with diverse equipment and protocols can facilitate model deployment and maintenance. However, building such a model typically requires a large, diverse, and fully annotated dataset, which is rarely available due to the labor-intensive and costly data curation. In this study, we develop a cost-efficient method by harnessing readily available data with partially or even sparsely annotated segmentation labels. We devise strategies for model self-disambiguation, prior knowledge incorporation, and imbalance mitigation to address challenges associated with inconsistently labeled data from various sources, including label ambiguity and imbalances across modalities, datasets, and segmentation labels. Experimental results on a multi-modal dataset compiled from eight different sources for abdominal organ segmentation have demonstrated our method's effectiveness and superior performance over alternative state-of-the-art methods, highlighting its potential for optimizing the use of existing annotated data and reducing the annotation efforts for new data to further enhance model capability.
Medical Image Segmentation with Domain Adaptation: A Survey
Nov 03, 2023



Abstract:Deep learning (DL) has shown remarkable success in various medical imaging data analysis applications. However, it remains challenging for DL models to achieve good generalization, especially when the training and testing datasets are collected at sites with different scanners, due to domain shift caused by differences in data distributions. Domain adaptation has emerged as an effective means to address this challenge by mitigating domain gaps in medical imaging applications. In this review, we specifically focus on domain adaptation approaches for DL-based medical image segmentation. We first present the motivation and background knowledge underlying domain adaptations, then provide a comprehensive review of domain adaptation applications in medical image segmentations, and finally discuss the challenges, limitations, and future research trends in the field to promote the methodology development of domain adaptation in the context of medical image segmentation. Our goal was to provide researchers with up-to-date references on the applications of domain adaptation in medical image segmentation studies.
HNAS-reg: hierarchical neural architecture search for deformable medical image registration
Aug 23, 2023Abstract:Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have been widely used to build deep learning models for medical image registration, but manually designed network architectures are not necessarily optimal. This paper presents a hierarchical NAS framework (HNAS-Reg), consisting of both convolutional operation search and network topology search, to identify the optimal network architecture for deformable medical image registration. To mitigate the computational overhead and memory constraints, a partial channel strategy is utilized without losing optimization quality. Experiments on three datasets, consisting of 636 T1-weighted magnetic resonance images (MRIs), have demonstrated that the proposal method can build a deep learning model with improved image registration accuracy and reduced model size, compared with state-of-the-art image registration approaches, including one representative traditional approach and two unsupervised learning-based approaches.
SurfNN: Joint Reconstruction of Multiple Cortical Surfaces from Magnetic Resonance Images
Mar 06, 2023Abstract:To achieve fast, robust, and accurate reconstruction of the human cortical surfaces from 3D magnetic resonance images (MRIs), we develop a novel deep learning-based framework, referred to as SurfNN, to reconstruct simultaneously both inner (between white matter and gray matter) and outer (pial) surfaces from MRIs. Different from existing deep learning-based cortical surface reconstruction methods that either reconstruct the cortical surfaces separately or neglect the interdependence between the inner and outer surfaces, SurfNN reconstructs both the inner and outer cortical surfaces jointly by training a single network to predict a midthickness surface that lies at the center of the inner and outer cortical surfaces. The input of SurfNN consists of a 3D MRI and an initialization of the midthickness surface that is represented both implicitly as a 3D distance map and explicitly as a triangular mesh with spherical topology, and its output includes both the inner and outer cortical surfaces, as well as the midthickness surface. The method has been evaluated on a large-scale MRI dataset and demonstrated competitive cortical surface reconstruction performance.
Deep Clustering Survival Machines with Interpretable Expert Distributions
Jan 27, 2023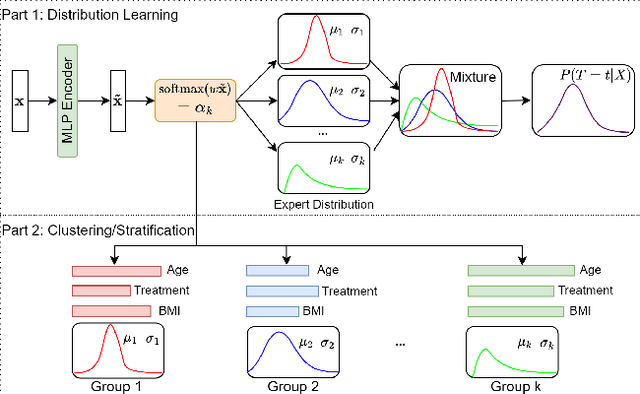
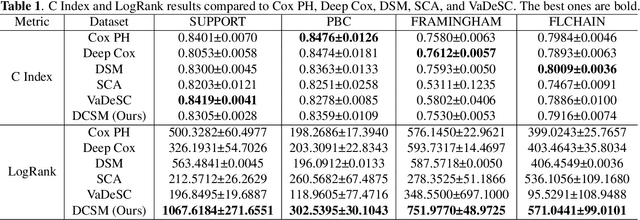
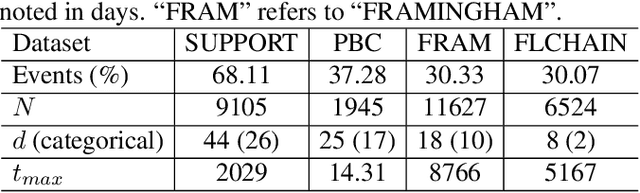
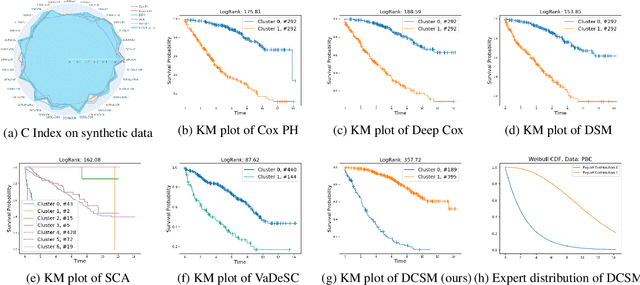
Abstract:Conventional survival analysis methods are typically ineffective to characterize heterogeneity in the population while such information can be used to assist predictive modeling. In this study, we propose a hybrid survival analysis method, referred to as deep clustering survival machines, that combines the discriminative and generative mechanisms. Similar to the mixture models, we assume that the timing information of survival data is generatively described by a mixture of certain numbers of parametric distributions, i.e., expert distributions. We learn weights of the expert distributions for individual instances according to their features discriminatively such that each instance's survival information can be characterized by a weighted combination of the learned constant expert distributions. This method also facilitates interpretable subgrouping/clustering of all instances according to their associated expert distributions. Extensive experiments on both real and synthetic datasets have demonstrated that the method is capable of obtaining promising clustering results and competitive time-to-event predicting performance.
Learning Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Maps from Undersampled Radial k-Space Diffusion-Weighted MRI in Mice using a Deep CNN-Transformer Model in Conjunction with a Monoexponential Model
Jul 06, 2022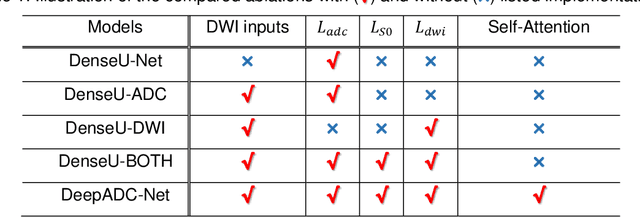
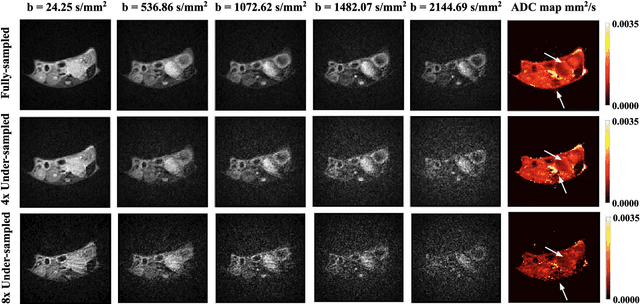
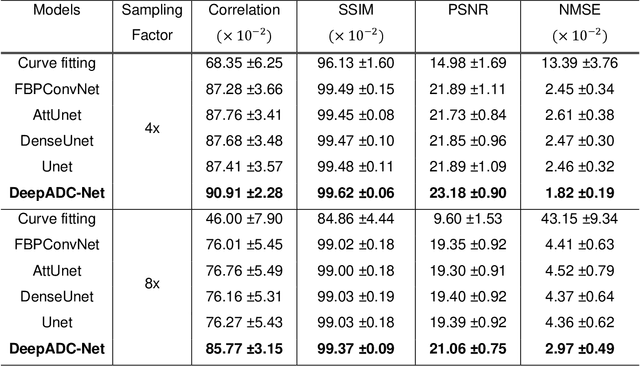
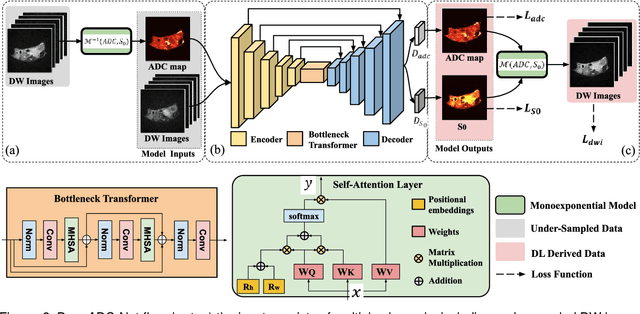
Abstract:Purpose: To accelerate radially sampled diffusion weighted spin-echo (Rad-DW-SE) acquisition method for generating high quality of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) maps. Methods: A deep learning method was developed to generate accurate ADC map reconstruction from undersampled DWI data acquired with the Rad-DW-SE method. The deep learning method integrates convolutional neural networks (CNNs) with vison transformers to generate high quality ADC maps from undersampled DWI data, regularized by a monoexponential ADC model fitting term. A model was trained on DWI data of 147 mice and evaluated on DWI data of 36 mice, with undersampling rates of 4x and 8x. Results: Ablation studies and experimental results have demonstrated that the proposed deep learning model can generate high quality ADC maps from undersampled DWI data, better than alternative deep learning methods under comparison, with their performance quantified on different levels of images, tumors, kidneys, and muscles. Conclusions: The deep learning method with integrated CNNs and transformers provides an effective means to accurately compute ADC maps from undersampled DWI data acquired with the Rad-DW-SE method.
Multidimensional representations in late-life depression: convergence in neuroimaging, cognition, clinical symptomatology and genetics
Oct 25, 2021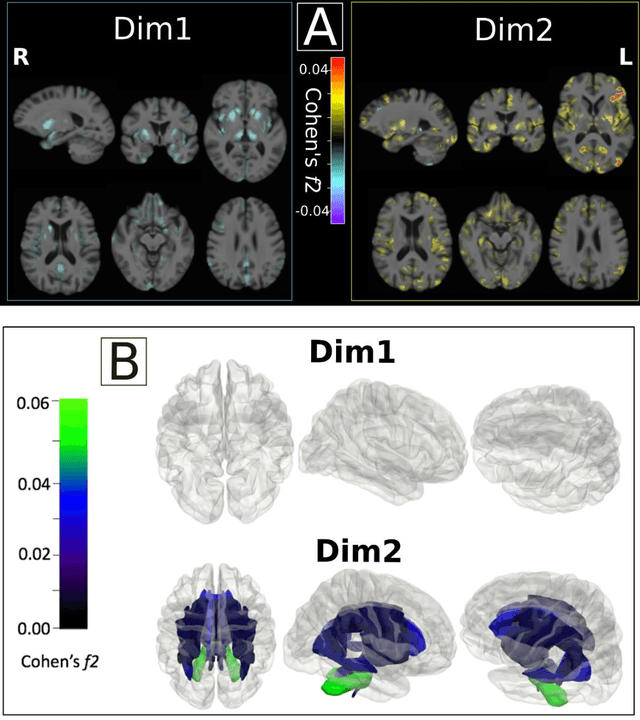
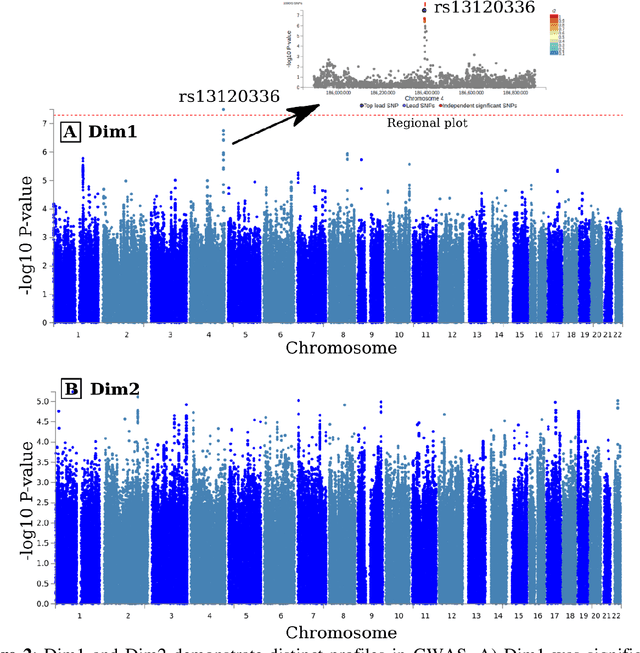
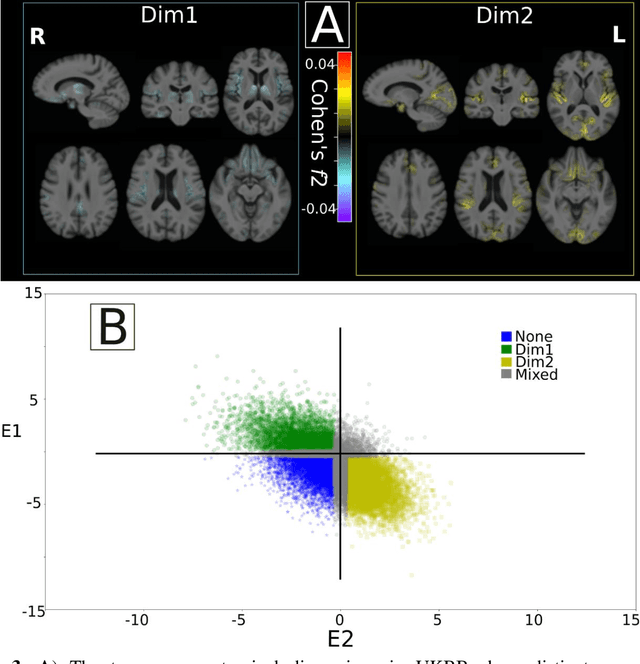
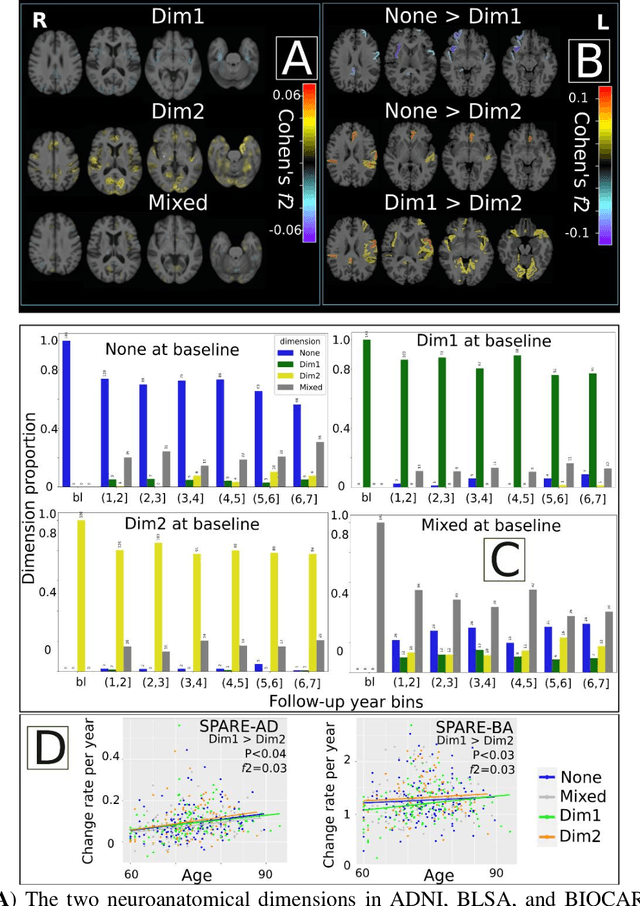
Abstract:Late-life depression (LLD) is characterized by considerable heterogeneity in clinical manifestation. Unraveling such heterogeneity would aid in elucidating etiological mechanisms and pave the road to precision and individualized medicine. We sought to delineate, cross-sectionally and longitudinally, disease-related heterogeneity in LLD linked to neuroanatomy, cognitive functioning, clinical symptomatology, and genetic profiles. Multimodal data from a multicentre sample (N=996) were analyzed. A semi-supervised clustering method (HYDRA) was applied to regional grey matter (GM) brain volumes to derive dimensional representations. Two dimensions were identified, which accounted for the LLD-related heterogeneity in voxel-wise GM maps, white matter (WM) fractional anisotropy (FA), neurocognitive functioning, clinical phenotype, and genetics. Dimension one (Dim1) demonstrated relatively preserved brain anatomy without WM disruptions relative to healthy controls. In contrast, dimension two (Dim2) showed widespread brain atrophy and WM integrity disruptions, along with cognitive impairment and higher depression severity. Moreover, one de novo independent genetic variant (rs13120336) was significantly associated with Dim 1 but not with Dim 2. Notably, the two dimensions demonstrated significant SNP-based heritability of 18-27% within the general population (N=12,518 in UKBB). Lastly, in a subset of individuals having longitudinal measurements, Dim2 demonstrated a more rapid longitudinal decrease in GM and brain age, and was more likely to progress to Alzheimers disease, compared to Dim1 (N=1,413 participants and 7,225 scans from ADNI, BLSA, and BIOCARD datasets).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge