Duygu Tosun
7T MRI Synthesization from 3T Acquisitions
Mar 13, 2024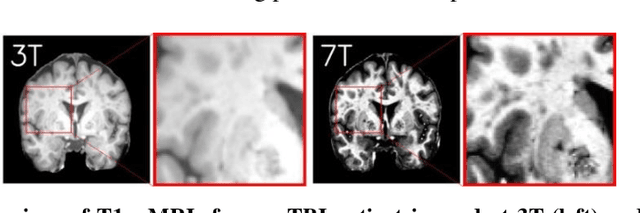
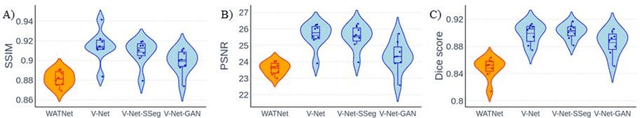
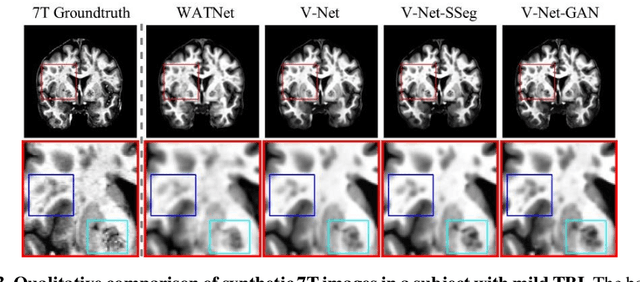
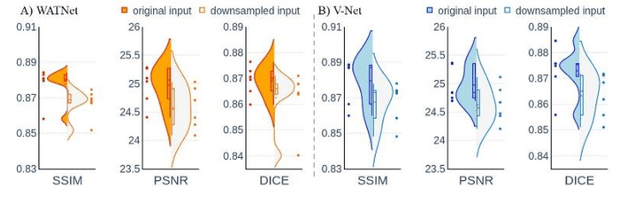
Abstract:Supervised deep learning techniques can be used to generate synthetic 7T MRIs from 3T MRI inputs. This image enhancement process leverages the advantages of ultra-high-field MRI to improve the signal-to-noise and contrast-to-noise ratios of 3T acquisitions. In this paper, we introduce multiple novel 7T synthesization algorithms based on custom-designed variants of the V-Net convolutional neural network. We demonstrate that the V-Net based model has superior performance in enhancing both single-site and multi-site MRI datasets compared to the existing benchmark model. When trained on 3T-7T MRI pairs from 8 subjects with mild Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI), our model achieves state-of-the-art 7T synthesization performance. Compared to previous works, synthetic 7T images generated from our pipeline also display superior enhancement of pathological tissue. Additionally, we implement and test a data augmentation scheme for training models that are robust to variations in the input distribution. This allows synthetic 7T models to accommodate intra-scanner and inter-scanner variability in multisite datasets. On a harmonized dataset consisting of 18 3T-7T MRI pairs from two institutions, including both healthy subjects and those with mild TBI, our model maintains its performance and can generalize to 3T MRI inputs with lower resolution. Our findings demonstrate the promise of V-Net based models for MRI enhancement and offer a preliminary probe into improving the generalizability of synthetic 7T models with data augmentation.
Multidimensional representations in late-life depression: convergence in neuroimaging, cognition, clinical symptomatology and genetics
Oct 25, 2021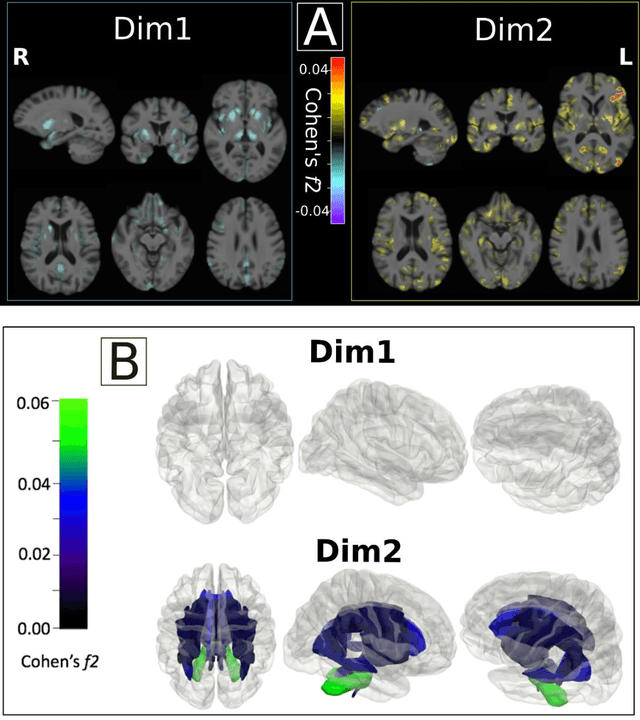
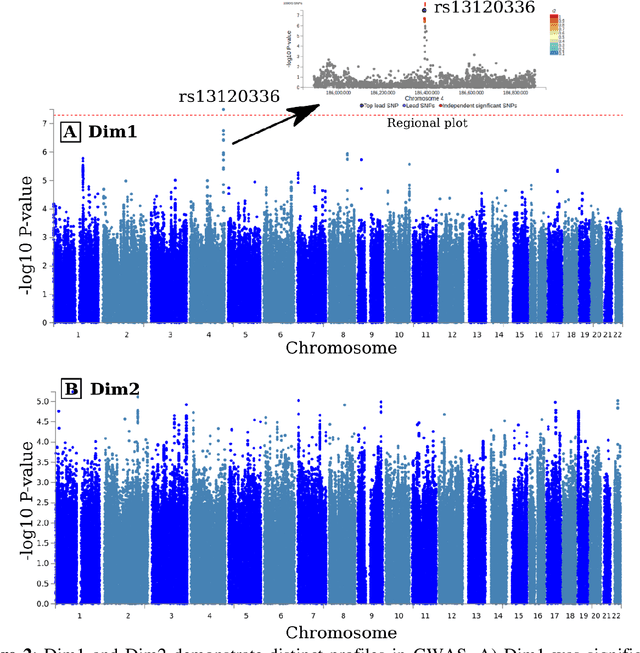
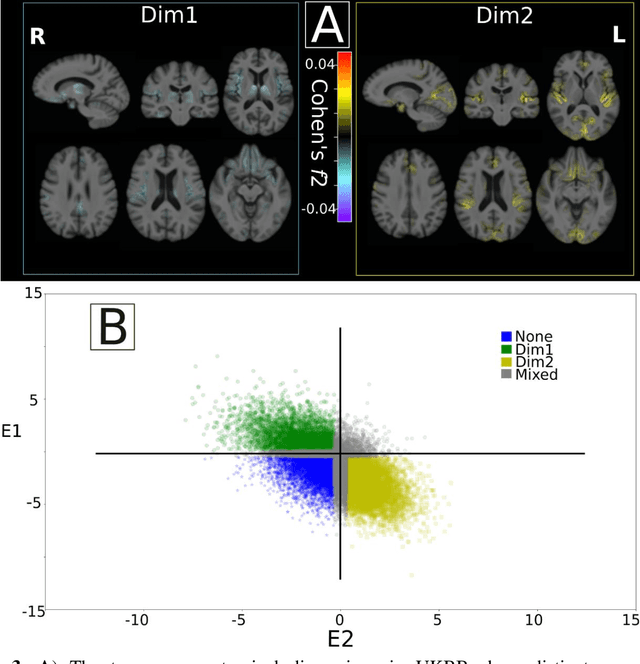
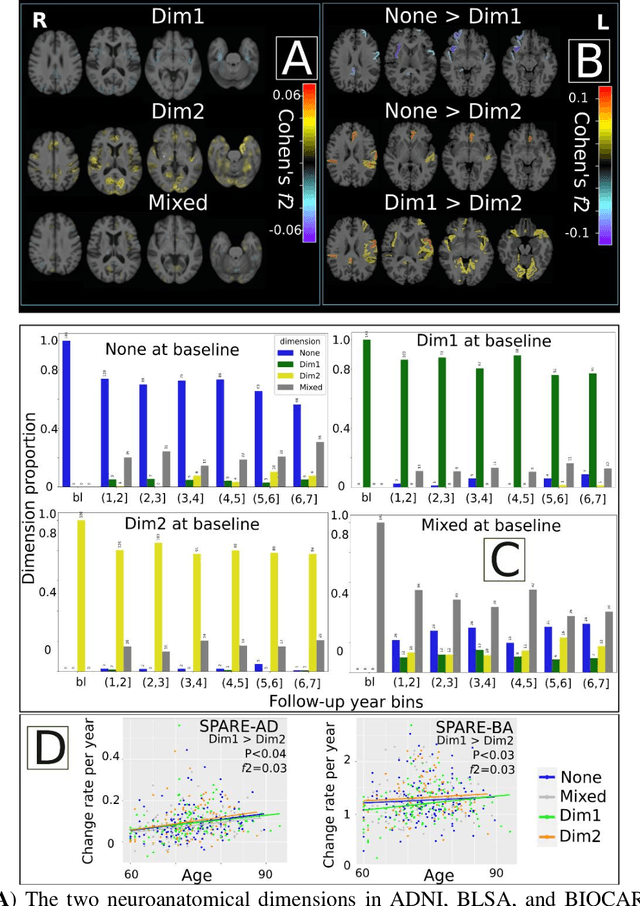
Abstract:Late-life depression (LLD) is characterized by considerable heterogeneity in clinical manifestation. Unraveling such heterogeneity would aid in elucidating etiological mechanisms and pave the road to precision and individualized medicine. We sought to delineate, cross-sectionally and longitudinally, disease-related heterogeneity in LLD linked to neuroanatomy, cognitive functioning, clinical symptomatology, and genetic profiles. Multimodal data from a multicentre sample (N=996) were analyzed. A semi-supervised clustering method (HYDRA) was applied to regional grey matter (GM) brain volumes to derive dimensional representations. Two dimensions were identified, which accounted for the LLD-related heterogeneity in voxel-wise GM maps, white matter (WM) fractional anisotropy (FA), neurocognitive functioning, clinical phenotype, and genetics. Dimension one (Dim1) demonstrated relatively preserved brain anatomy without WM disruptions relative to healthy controls. In contrast, dimension two (Dim2) showed widespread brain atrophy and WM integrity disruptions, along with cognitive impairment and higher depression severity. Moreover, one de novo independent genetic variant (rs13120336) was significantly associated with Dim 1 but not with Dim 2. Notably, the two dimensions demonstrated significant SNP-based heritability of 18-27% within the general population (N=12,518 in UKBB). Lastly, in a subset of individuals having longitudinal measurements, Dim2 demonstrated a more rapid longitudinal decrease in GM and brain age, and was more likely to progress to Alzheimers disease, compared to Dim1 (N=1,413 participants and 7,225 scans from ADNI, BLSA, and BIOCARD datasets).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge