Zhou Yu
University of California, Davis
Reinforcement World Model Learning for LLM-based Agents
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have achieved strong performance in language-centric tasks. However, in agentic settings, LLMs often struggle to anticipate action consequences and adapt to environment dynamics, highlighting the need for world-modeling capabilities in LLM-based agents. We propose Reinforcement World Model Learning (RWML), a self-supervised method that learns action-conditioned world models for LLM-based agents on textual states using sim-to-real gap rewards. Our method aligns simulated next states produced by the model with realized next states observed from the environment, encouraging consistency between internal world simulations and actual environment dynamics in a pre-trained embedding space. Unlike next-state token prediction, which prioritizes token-level fidelity (i.e., reproducing exact wording) over semantic equivalence and can lead to model collapse, our method provides a more robust training signal and is empirically less susceptible to reward hacking than LLM-as-a-judge. We evaluate our method on ALFWorld and $τ^2$ Bench and observe significant gains over the base model, despite being entirely self-supervised. When combined with task-success rewards, our method outperforms direct task-success reward RL by 6.9 and 5.7 points on ALFWorld and $τ^2$ Bench respectively, while matching the performance of expert-data training.
A$^2$-LLM: An End-to-end Conversational Audio Avatar Large Language Model
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Developing expressive and responsive conversational digital humans is a cornerstone of next-generation human-computer interaction. While large language models (LLMs) have significantly enhanced dialogue capabilities, most current systems still rely on cascaded architectures that connect independent modules. These pipelines are often plagued by accumulated errors, high latency, and poor real-time performance. Lacking access to the underlying conversational context, these pipelines inherently prioritize rigid lip-sync over emotional depth. To address these challenges, we propose A$^2$-LLM, an end-to-end conversational audio avatar large language model that jointly reasons about language, audio prosody, and 3D facial motion within a unified framework. To facilitate training, we introduce FLAME-QA, a high-quality multimodal dataset designed to align semantic intent with expressive facial dynamics within a QA format. By leveraging deep semantic understanding, A$^2$-LLM generates emotionally rich facial movements beyond simple lip-synchronization. Experimental results demonstrate that our system achieves superior emotional expressiveness while maintaining real-time efficiency (500 ms latency, 0.7 RTF).
Factuality on Demand: Controlling the Factuality-Informativeness Trade-off in Text Generation
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) encode knowledge with varying degrees of confidence. When responding to queries, models face an inherent trade-off: they can generate responses that are less informative but highly factual, or more informative but potentially less accurate. Different applications demand different balances between informativeness and factuality. We introduce Factuality-Controlled Generation (FCG), a framework that enables users to specify factuality constraints alongside their queries. We propose to evaluate FCG performance on two dimensions: adherence to factuality constraints and response informativeness. We propose to train models on the FCG task using synthetic data, and show that our synthetic training significantly improves models' ability to both respect factuality requirements and maintain informativeness in their outputs.
Business Logic-Driven Text-to-SQL Data Synthesis for Business Intelligence
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Evaluating Text-to-SQL agents in private business intelligence (BI) settings is challenging due to the scarcity of realistic, domain-specific data. While synthetic evaluation data offers a scalable solution, existing generation methods fail to capture business realism--whether questions reflect realistic business logic and workflows. We propose a Business Logic-Driven Data Synthesis framework that generates data grounded in business personas, work scenarios, and workflows. In addition, we improve the data quality by imposing a business reasoning complexity control strategy that diversifies the analytical reasoning steps required to answer the questions. Experiments on a production-scale Salesforce database show that our synthesized data achieves high business realism (98.44%), substantially outperforming OmniSQL (+19.5%) and SQL-Factory (+54.7%), while maintaining strong question-SQL alignment (98.59%). Our synthetic data also reveals that state-of-the-art Text-to-SQL models still have significant performance gaps, achieving only 42.86% execution accuracy on the most complex business queries.
Budget-Aware Anytime Reasoning with LLM-Synthesized Preference Data
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:We study the reasoning behavior of large language models (LLMs) under limited computation budgets. In such settings, producing useful partial solutions quickly is often more practical than exhaustive reasoning, which incurs high inference costs. Many real-world tasks, such as trip planning, require models to deliver the best possible output within a fixed reasoning budget. We introduce an anytime reasoning framework and the Anytime Index, a metric that quantifies how effectively solution quality improves as reasoning tokens increase. To further enhance efficiency, we propose an inference-time self-improvement method using LLM-synthesized preference data, where models learn from their own reasoning comparisons to produce better intermediate solutions. Experiments on NaturalPlan (Trip), AIME, and GPQA datasets show consistent gains across Grok-3, GPT-oss, GPT-4.1/4o, and LLaMA models, improving both reasoning quality and efficiency under budget constraints.
HarmonRank: Ranking-aligned Multi-objective Ensemble for Live-streaming E-commerce Recommendation
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Recommendation for live-streaming e-commerce is gaining increasing attention due to the explosive growth of the live streaming economy. Different from traditional e-commerce, live-streaming e-commerce shifts the focus from products to streamers, which requires ranking mechanism to balance both purchases and user-streamer interactions for long-term ecology. To trade off multiple objectives, a popular solution is to build an ensemble model to integrate multi-objective scores into a unified score. The ensemble model is usually supervised by multiple independent binary classification losses of all objectives. However, this paradigm suffers from two inherent limitations. First, the optimization direction of the binary classification task is misaligned with the ranking task (evaluated by AUC). Second, this paradigm overlooks the alignment between objectives, e.g., comment and buy behaviors are partially dependent which can be revealed in labels correlations. The model can achieve better trade-offs if it learns the aligned parts of ranking abilities among different objectives. To mitigate these limitations, we propose a novel multi-objective ensemble framework HarmonRank to fulfill both alignment to the ranking task and alignment among objectives. For alignment to ranking, we formulate ranking metric AUC as a rank-sum problem and utilize differentiable ranking techniques for ranking-oriented optimization. For inter-objective alignment, we change the original one-step ensemble paradigm to a two-step relation-aware ensemble scheme. Extensive offline experiments results on two industrial datasets and online experiments demonstrate that our approach significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods. The proposed method has been fully deployed in Kuaishou's live-streaming e-commerce recommendation platform with 400 million DAUs, contributing over 2% purchase gain.
On Conditional Stochastic Interpolation for Generative Nonlinear Sufficient Dimension Reduction
Dec 22, 2025
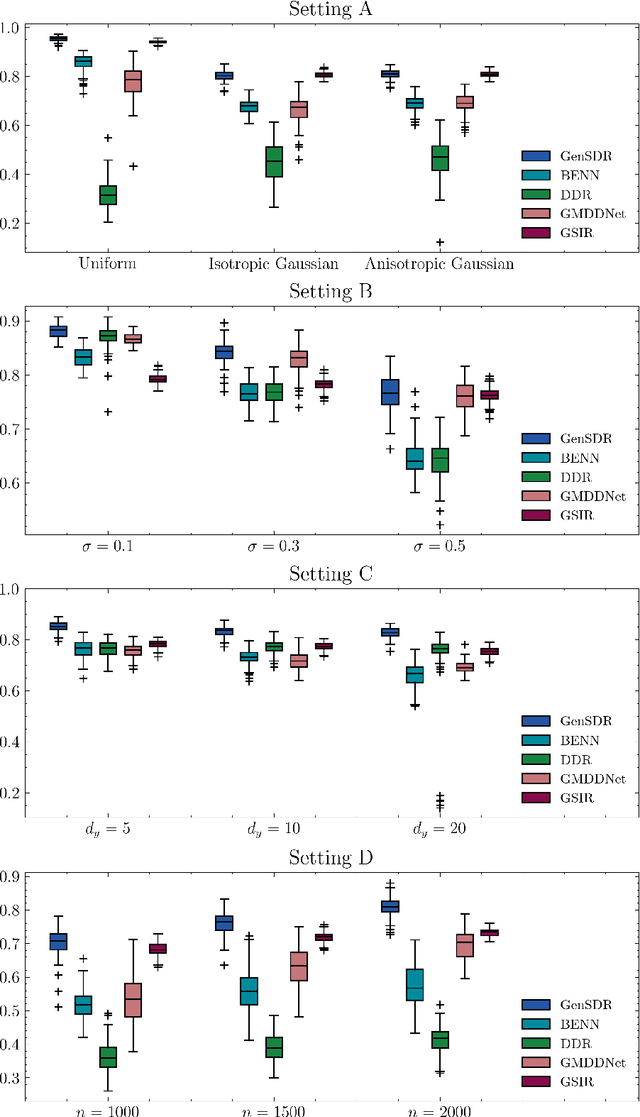
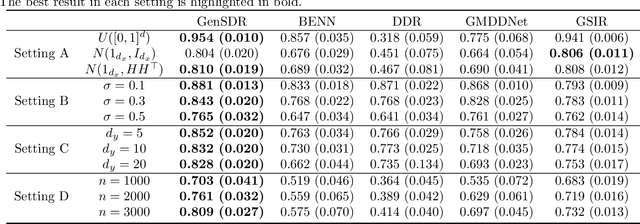
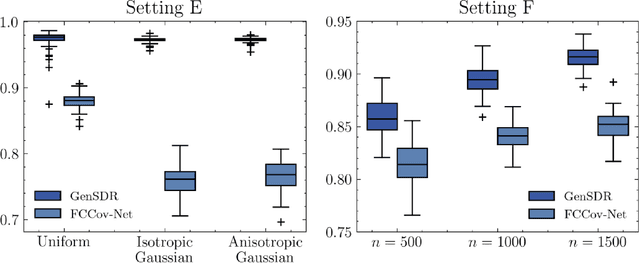
Abstract:Identifying low-dimensional sufficient structures in nonlinear sufficient dimension reduction (SDR) has long been a fundamental yet challenging problem. Most existing methods lack theoretical guarantees of exhaustiveness in identifying lower dimensional structures, either at the population level or at the sample level. We tackle this issue by proposing a new method, generative sufficient dimension reduction (GenSDR), which leverages modern generative models. We show that GenSDR is able to fully recover the information contained in the central $σ$-field at both the population and sample levels. In particular, at the sample level, we establish a consistency property for the GenSDR estimator from the perspective of conditional distributions, capitalizing on the distributional learning capabilities of deep generative models. Moreover, by incorporating an ensemble technique, we extend GenSDR to accommodate scenarios with non-Euclidean responses, thereby substantially broadening its applicability. Extensive numerical results demonstrate the outstanding empirical performance of GenSDR and highlight its strong potential for addressing a wide range of complex, real-world tasks.
VideoARM: Agentic Reasoning over Hierarchical Memory for Long-Form Video Understanding
Dec 13, 2025



Abstract:Long-form video understanding remains challenging due to the extended temporal structure and dense multimodal cues. Despite recent progress, many existing approaches still rely on hand-crafted reasoning pipelines or employ token-consuming video preprocessing to guide MLLMs in autonomous reasoning. To overcome these limitations, we introduce VideoARM, an Agentic Reasoning-over-hierarchical-Memory paradigm for long-form video understanding. Instead of static, exhaustive preprocessing, VideoARM performs adaptive, on-the-fly agentic reasoning and memory construction. Specifically, VideoARM performs an adaptive and continuous loop of observing, thinking, acting, and memorizing, where a controller autonomously invokes tools to interpret the video in a coarse-to-fine manner, thereby substantially reducing token consumption. In parallel, a hierarchical multimodal memory continuously captures and updates multi-level clues throughout the operation of the agent, providing precise contextual information to support the controller in decision-making. Experiments on prevalent benchmarks demonstrate that VideoARM outperforms the state-of-the-art method, DVD, while significantly reducing token consumption for long-form videos.
SRSplat: Feed-Forward Super-Resolution Gaussian Splatting from Sparse Multi-View Images
Nov 15, 2025Abstract:Feed-forward 3D reconstruction from sparse, low-resolution (LR) images is a crucial capability for real-world applications, such as autonomous driving and embodied AI. However, existing methods often fail to recover fine texture details. This limitation stems from the inherent lack of high-frequency information in LR inputs. To address this, we propose \textbf{SRSplat}, a feed-forward framework that reconstructs high-resolution 3D scenes from only a few LR views. Our main insight is to compensate for the deficiency of texture information by jointly leveraging external high-quality reference images and internal texture cues. We first construct a scene-specific reference gallery, generated for each scene using Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) and diffusion models. To integrate this external information, we introduce the \textit{Reference-Guided Feature Enhancement (RGFE)} module, which aligns and fuses features from the LR input images and their reference twin image. Subsequently, we train a decoder to predict the Gaussian primitives using the multi-view fused feature obtained from \textit{RGFE}. To further refine predicted Gaussian primitives, we introduce \textit{Texture-Aware Density Control (TADC)}, which adaptively adjusts Gaussian density based on the internal texture richness of the LR inputs. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our SRSplat outperforms existing methods on various datasets, including RealEstate10K, ACID, and DTU, and exhibits strong cross-dataset and cross-resolution generalization capabilities.
Sparse4DGS: 4D Gaussian Splatting for Sparse-Frame Dynamic Scene Reconstruction
Nov 10, 2025



Abstract:Dynamic Gaussian Splatting approaches have achieved remarkable performance for 4D scene reconstruction. However, these approaches rely on dense-frame video sequences for photorealistic reconstruction. In real-world scenarios, due to equipment constraints, sometimes only sparse frames are accessible. In this paper, we propose Sparse4DGS, the first method for sparse-frame dynamic scene reconstruction. We observe that dynamic reconstruction methods fail in both canonical and deformed spaces under sparse-frame settings, especially in areas with high texture richness. Sparse4DGS tackles this challenge by focusing on texture-rich areas. For the deformation network, we propose Texture-Aware Deformation Regularization, which introduces a texture-based depth alignment loss to regulate Gaussian deformation. For the canonical Gaussian field, we introduce Texture-Aware Canonical Optimization, which incorporates texture-based noise into the gradient descent process of canonical Gaussians. Extensive experiments show that when taking sparse frames as inputs, our method outperforms existing dynamic or few-shot techniques on NeRF-Synthetic, HyperNeRF, NeRF-DS, and our iPhone-4D datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge