Kamila Zhumakhanova
RoomTour3D: Geometry-Aware Video-Instruction Tuning for Embodied Navigation
Dec 11, 2024Abstract:Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN) suffers from the limited diversity and scale of training data, primarily constrained by the manual curation of existing simulators. To address this, we introduce RoomTour3D, a video-instruction dataset derived from web-based room tour videos that capture real-world indoor spaces and human walking demonstrations. Unlike existing VLN datasets, RoomTour3D leverages the scale and diversity of online videos to generate open-ended human walking trajectories and open-world navigable instructions. To compensate for the lack of navigation data in online videos, we perform 3D reconstruction and obtain 3D trajectories of walking paths augmented with additional information on the room types, object locations and 3D shape of surrounding scenes. Our dataset includes $\sim$100K open-ended description-enriched trajectories with $\sim$200K instructions, and 17K action-enriched trajectories from 1847 room tour environments. We demonstrate experimentally that RoomTour3D enables significant improvements across multiple VLN tasks including CVDN, SOON, R2R, and REVERIE. Moreover, RoomTour3D facilitates the development of trainable zero-shot VLN agents, showcasing the potential and challenges of advancing towards open-world navigation.
All Languages Matter: Evaluating LMMs on Culturally Diverse 100 Languages
Nov 25, 2024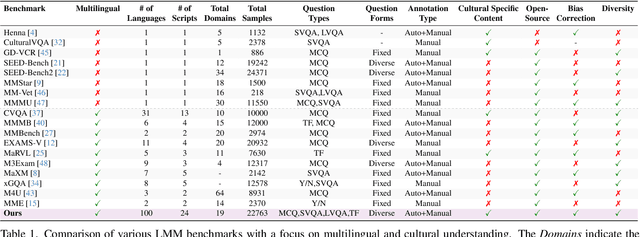
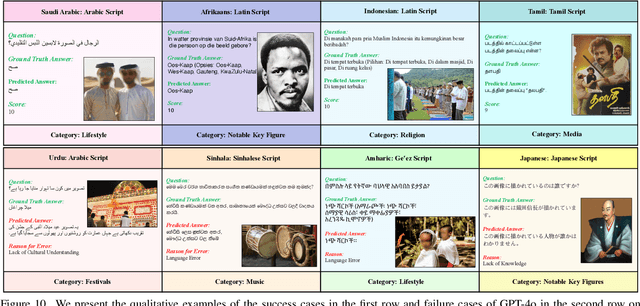
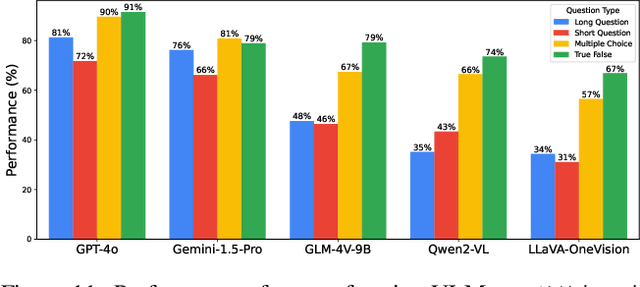
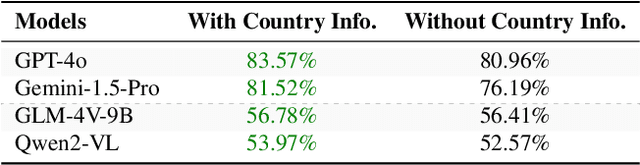
Abstract:Existing Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) generally focus on only a few regions and languages. As LMMs continue to improve, it is increasingly important to ensure they understand cultural contexts, respect local sensitivities, and support low-resource languages, all while effectively integrating corresponding visual cues. In pursuit of culturally diverse global multimodal models, our proposed All Languages Matter Benchmark (ALM-bench) represents the largest and most comprehensive effort to date for evaluating LMMs across 100 languages. ALM-bench challenges existing models by testing their ability to understand and reason about culturally diverse images paired with text in various languages, including many low-resource languages traditionally underrepresented in LMM research. The benchmark offers a robust and nuanced evaluation framework featuring various question formats, including true/false, multiple choice, and open-ended questions, which are further divided into short and long-answer categories. ALM-bench design ensures a comprehensive assessment of a model's ability to handle varied levels of difficulty in visual and linguistic reasoning. To capture the rich tapestry of global cultures, ALM-bench carefully curates content from 13 distinct cultural aspects, ranging from traditions and rituals to famous personalities and celebrations. Through this, ALM-bench not only provides a rigorous testing ground for state-of-the-art open and closed-source LMMs but also highlights the importance of cultural and linguistic inclusivity, encouraging the development of models that can serve diverse global populations effectively. Our benchmark is publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge