Xiao Liang
GPD: Guided Progressive Distillation for Fast and High-Quality Video Generation
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Diffusion models have achieved remarkable success in video generation; however, the high computational cost of the denoising process remains a major bottleneck. Existing approaches have shown promise in reducing the number of diffusion steps, but they often suffer from significant quality degradation when applied to video generation. We propose Guided Progressive Distillation (GPD), a framework that accelerates the diffusion process for fast and high-quality video generation. GPD introduces a novel training strategy in which a teacher model progressively guides a student model to operate with larger step sizes. The framework consists of two key components: (1) an online-generated training target that reduces optimization difficulty while improving computational efficiency, and (2) frequency-domain constraints in the latent space that promote the preservation of fine-grained details and temporal dynamics. Applied to the Wan2.1 model, GPD reduces the number of sampling steps from 48 to 6 while maintaining competitive visual quality on VBench. Compared with existing distillation methods, GPD demonstrates clear advantages in both pipeline simplicity and quality preservation.
Training LLMs for Divide-and-Conquer Reasoning Elevates Test-Time Scalability
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated strong reasoning capabilities through step-by-step chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning. Nevertheless, at the limits of model capability, CoT often proves insufficient, and its strictly sequential nature constrains test-time scalability. A potential alternative is divide-and-conquer (DAC) reasoning, which decomposes a complex problem into subproblems to facilitate more effective exploration of the solution. Although promising, our analysis reveals a fundamental misalignment between general-purpose post-training and DAC-style inference, which limits the model's capacity to fully leverage this potential. To bridge this gap and fully unlock LLMs' reasoning capabilities on the most challenging tasks, we propose an end-to-end reinforcement learning (RL) framework to enhance their DAC-style reasoning capacity. At each step, the policy decomposes a problem into a group of subproblems, solves them sequentially, and addresses the original one conditioned on the subproblem solutions, with both decomposition and solution integrated into RL training. Under comparable training, our DAC-style framework endows the model with a higher performance ceiling and stronger test-time scalability, surpassing CoT by 8.6% in Pass@1 and 6.3% in Pass@32 on competition-level benchmarks.
A General One-Shot Multimodal Active Perception Framework for Robotic Manipulation: Learning to Predict Optimal Viewpoint
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Active perception in vision-based robotic manipulation aims to move the camera toward more informative observation viewpoints, thereby providing high-quality perceptual inputs for downstream tasks. Most existing active perception methods rely on iterative optimization, leading to high time and motion costs, and are tightly coupled with task-specific objectives, which limits their transferability. In this paper, we propose a general one-shot multimodal active perception framework for robotic manipulation. The framework enables direct inference of optimal viewpoints and comprises a data collection pipeline and an optimal viewpoint prediction network. Specifically, the framework decouples viewpoint quality evaluation from the overall architecture, supporting heterogeneous task requirements. Optimal viewpoints are defined through systematic sampling and evaluation of candidate viewpoints, after which large-scale training datasets are constructed via domain randomization. Moreover, a multimodal optimal viewpoint prediction network is developed, leveraging cross-attention to align and fuse multimodal features and directly predict camera pose adjustments. The proposed framework is instantiated in robotic grasping under viewpoint-constrained environments. Experimental results demonstrate that active perception guided by the framework significantly improves grasp success rates. Notably, real-world evaluations achieve nearly double the grasp success rate and enable seamless sim-to-real transfer without additional fine-tuning, demonstrating the effectiveness of the proposed framework.
Locate, Steer, and Improve: A Practical Survey of Actionable Mechanistic Interpretability in Large Language Models
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Mechanistic Interpretability (MI) has emerged as a vital approach to demystify the opaque decision-making of Large Language Models (LLMs). However, existing reviews primarily treat MI as an observational science, summarizing analytical insights while lacking a systematic framework for actionable intervention. To bridge this gap, we present a practical survey structured around the pipeline: "Locate, Steer, and Improve." We formally categorize Localizing (diagnosis) and Steering (intervention) methods based on specific Interpretable Objects to establish a rigorous intervention protocol. Furthermore, we demonstrate how this framework enables tangible improvements in Alignment, Capability, and Efficiency, effectively operationalizing MI as an actionable methodology for model optimization. The curated paper list of this work is available at https://github.com/rattlesnakey/Awesome-Actionable-MI-Survey.
Domain Adaptation in Structural Health Monitoring of Civil Infrastructure: A Systematic Review
Dec 21, 2025Abstract:This study provides a comprehensive review of domain adaptation (DA) techniques in vibration-based structural health monitoring (SHM). As data-driven models increasingly support the assessment of civil structures, the persistent challenge of transferring knowledge across varying geometries, materials, and environmental conditions remains a major obstacle. DA offers a systematic approach to mitigate these discrepancies by aligning feature distributions between simulated, laboratory, and field domains while preserving the sensitivity of damage-related information. Drawing on more than sixty representative studies, this paper analyzes the evolution of DA methods for SHM, including statistical alignment, adversarial and subdomain learning, physics-informed adaptation, and generative modeling for simulation-to-real transfer. The review summarizes their contributions and limitations across bridge and building applications, revealing that while DA has improved generalization significantly, key challenges persist: managing domain discrepancy, addressing data scarcity, enhancing model interpretability, and enabling adaptability to multiple sources and time-varying conditions. Future research directions emphasize integrating physical constraints into learning objectives, developing physics-consistent generative frameworks to enhance data realism, establishing interpretable and certifiable DA systems for engineering practice, and advancing multi-source and lifelong adaptation for scalable monitoring. Overall, this review consolidates the methodological foundation of DA for SHM, identifies existing barriers to generalization and trust, and outlines the technological trajectory toward transparent, physics-aware, and adaptive monitoring systems that support the long-term resilience of civil infrastructure.
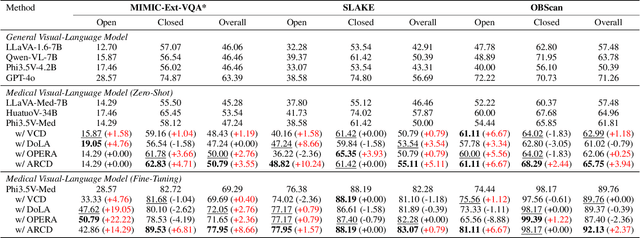
CheXPO-v2: Preference Optimization for Chest X-ray VLMs with Knowledge Graph Consistency
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:Medical Vision-Language Models (VLMs) are prone to hallucinations, compromising clinical reliability. While reinforcement learning methods like Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) offer a low-cost alignment solution, their reliance on sparse, outcome-based rewards inadvertently encourages models to "overthink" -- generating verbose, convoluted, and unverifiable Chain-of-Thought reasoning to justify answers. This focus on outcomes obscures factual errors and poses significant safety risks. To address this, we propose CheXPO-v2, a novel alignment framework that shifts from outcome to process supervision. Our core innovation is a Knowledge Graph Consistency Reward mechanism driven by Entity-Relation Matching. By explicitly parsing reasoning steps into structured "Disease, Relation, Anatomy" triplets, we provide fine-grained supervision that penalizes incoherent logic and hallucinations at the atomic level. Integrating this with a hard-example mining strategy, our approach significantly outperforms GRPO and state-of-the-art models on benchmarks like MIMIC-CXR-VQA. Crucially, CheXPO-v2 achieves new state-of-the-art accuracy using only 5k samples, demonstrating exceptional data efficiency while producing clinically sound and verifiable reasoning. The project source code is publicly available at: https://github.com/ecoxial2007/CheX-Phi4MM.
Anatomical Region-Guided Contrastive Decoding: A Plug-and-Play Strategy for Mitigating Hallucinations in Medical VLMs
Dec 19, 2025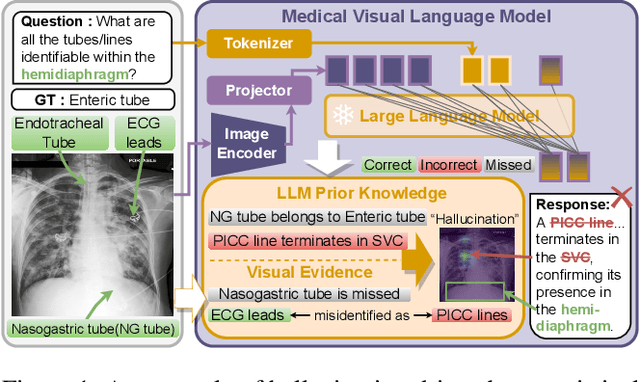
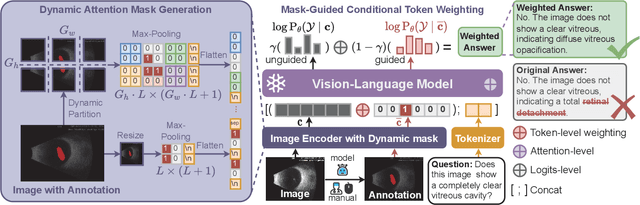

Abstract:Medical Vision-Language Models (MedVLMs) show immense promise in clinical applicability. However, their reliability is hindered by hallucinations, where models often fail to derive answers from visual evidence, instead relying on learned textual priors. Existing mitigation strategies for MedVLMs have distinct limitations: training-based methods rely on costly expert annotations, limiting scalability, while training-free interventions like contrastive decoding, though data-efficient, apply a global, untargeted correction whose effects in complex real-world clinical settings can be unreliable. To address these challenges, we introduce Anatomical Region-Guided Contrastive Decoding (ARCD), a plug-and-play strategy that mitigates hallucinations by providing targeted, region-specific guidance. Our module leverages an anatomical mask to direct a three-tiered contrastive decoding process. By dynamically re-weighting at the token, attention, and logits levels, it verifiably steers the model's focus onto specified regions, reinforcing anatomical understanding and suppressing factually incorrect outputs. Extensive experiments across diverse datasets, including chest X-ray, CT, brain MRI, and ocular ultrasound, demonstrate our method's effectiveness in improving regional understanding, reducing hallucinations, and enhancing overall diagnostic accuracy.
PrediFlow: A Flow-Based Prediction-Refinement Framework for Real-Time Human Motion Prediction in Human-Robot Collaboration
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:Stochastic human motion prediction is critical for safe and effective human-robot collaboration (HRC) in industrial remanufacturing, as it captures human motion uncertainties and multi-modal behaviors that deterministic methods cannot handle. While earlier works emphasize highly diverse predictions, they often generate unrealistic human motions. More recent methods focus on accuracy and real-time performance, yet there remains potential to improve prediction quality further without exceeding time budgets. Additionally, current research on stochastic human motion prediction in HRC typically considers human motion in isolation, neglecting the influence of robot motion on human behavior. To address these research gaps and enable real-time, realistic, and interaction-aware human motion prediction, we propose a novel prediction-refinement framework that integrates both human and robot observed motion to refine the initial predictions produced by a pretrained state-of-the-art predictor. The refinement module employs a Flow Matching structure to account for uncertainty. Experimental studies on the HRC desktop disassembly dataset demonstrate that our method significantly improves prediction accuracy while preserving the uncertainties and multi-modalities of human motion. Moreover, the total inference time of the proposed framework remains within the time budget, highlighting the effectiveness and practicality of our approach.
SAIL-Embedding Technical Report: Omni-modal Embedding Foundation Model
Oct 14, 2025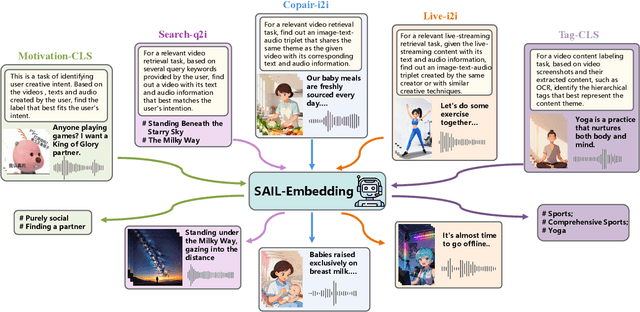
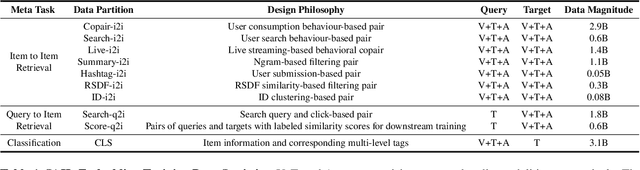
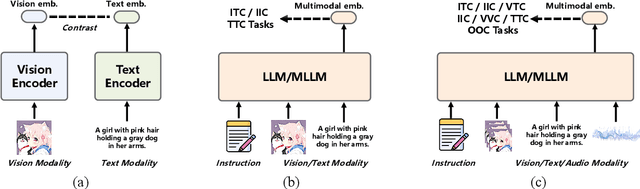
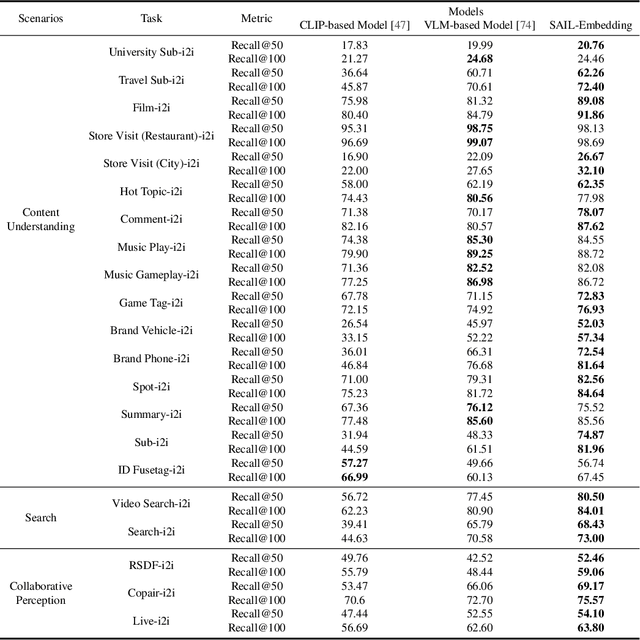
Abstract:Multimodal embedding models aim to yield informative unified representations that empower diverse cross-modal tasks. Despite promising developments in the evolution from CLIP-based dual-tower architectures to large vision-language models, prior works still face unavoidable challenges in real-world applications and business scenarios, such as the limited modality support, unstable training mechanisms, and industrial domain gaps. In this work, we introduce SAIL-Embedding, an omni-modal embedding foundation model that addresses these issues through tailored training strategies and architectural design. In the optimization procedure, we propose a multi-stage training scheme to boost the multifaceted effectiveness of representation learning. Specifically, the content-aware progressive training aims to enhance the model's adaptability to diverse downstream tasks and master enriched cross-modal proficiency. The collaboration-aware recommendation enhancement training further adapts multimodal representations for recommendation scenarios by distilling knowledge from sequence-to-item and ID-to-item embeddings while mining user historical interests. Concurrently, we develop the stochastic specialization and dataset-driven pattern matching to strengthen model training flexibility and generalizability. Experimental results show that SAIL-Embedding achieves SOTA performance compared to other methods in different retrieval tasks. In online experiments across various real-world scenarios integrated with our model, we observe a significant increase in Lifetime (LT), which is a crucial indicator for the recommendation experience. For instance, the model delivers the 7-day LT gain of +0.158% and the 14-day LT gain of +0.144% in the Douyin-Selected scenario. For the Douyin feed rank model, the match features produced by SAIL-Embedding yield a +0.08% AUC gain.
Dynamic Generation of Multi-LLM Agents Communication Topologies with Graph Diffusion Models
Oct 09, 2025Abstract:The efficiency of multi-agent systems driven by large language models (LLMs) largely hinges on their communication topology. However, designing an optimal topology is a non-trivial challenge, as it requires balancing competing objectives such as task performance, communication cost, and robustness. Existing frameworks often rely on static or hand-crafted topologies, which inherently fail to adapt to diverse task requirements, leading to either excessive token consumption for simple problems or performance bottlenecks for complex ones. To address this challenge, we introduce a novel generative framework called \textit{Guided Topology Diffusion (GTD)}. Inspired by conditional discrete graph diffusion models, GTD formulates topology synthesis as an iterative construction process. At each step, the generation is steered by a lightweight proxy model that predicts multi-objective rewards (e.g., accuracy, utility, cost), enabling real-time, gradient-free optimization towards task-adaptive topologies. This iterative, guided synthesis process distinguishes GTD from single-step generative frameworks, enabling it to better navigate complex design trade-offs. We validated GTD across multiple benchmarks, and experiments show that this framework can generate highly task-adaptive, sparse, and efficient communication topologies, significantly outperforming existing methods in LLM agent collaboration.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge