Hongyuan Dong
SAIL-VL2 Technical Report
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:We introduce SAIL-VL2, an open-suite vision-language foundation model (LVM) for comprehensive multimodal understanding and reasoning. As the successor to SAIL-VL, SAIL-VL2 achieves state-of-the-art performance at the 2B and 8B parameter scales across diverse image and video benchmarks, demonstrating strong capabilities from fine-grained perception to complex reasoning. Its effectiveness is driven by three core innovations. First, a large-scale data curation pipeline with scoring and filtering strategies enhances both quality and distribution across captioning, OCR, QA, and video data, improving training efficiency. Second, a progressive training framework begins with a powerful pre-trained vision encoder (SAIL-ViT), advances through multimodal pre-training, and culminates in a thinking-fusion SFT-RL hybrid paradigm that systematically strengthens model capabilities. Third, architectural advances extend beyond dense LLMs to efficient sparse Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) designs. With these contributions, SAIL-VL2 demonstrates competitive performance across 106 datasets and achieves state-of-the-art results on challenging reasoning benchmarks such as MMMU and MathVista. Furthermore, on the OpenCompass leaderboard, SAIL-VL2-2B ranks first among officially released open-source models under the 4B parameter scale, while serving as an efficient and extensible foundation for the open-source multimodal community.
SAILViT: Towards Robust and Generalizable Visual Backbones for MLLMs via Gradual Feature Refinement
Jul 02, 2025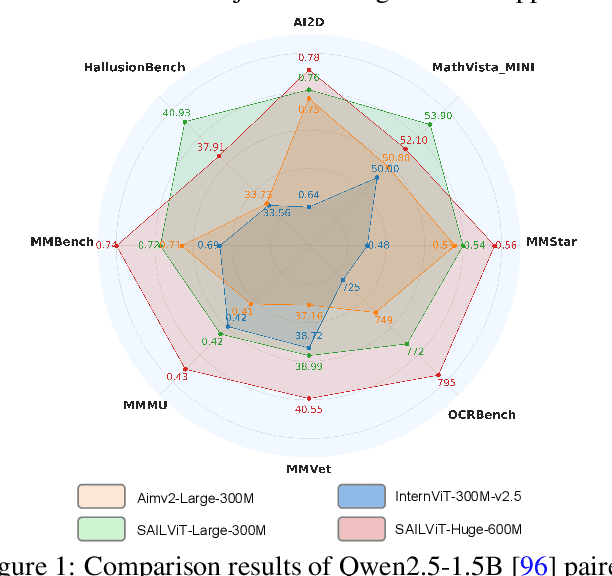
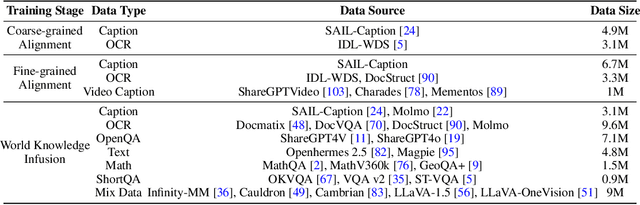
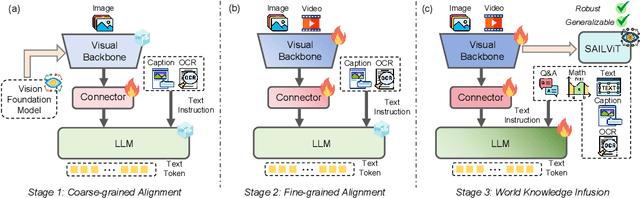
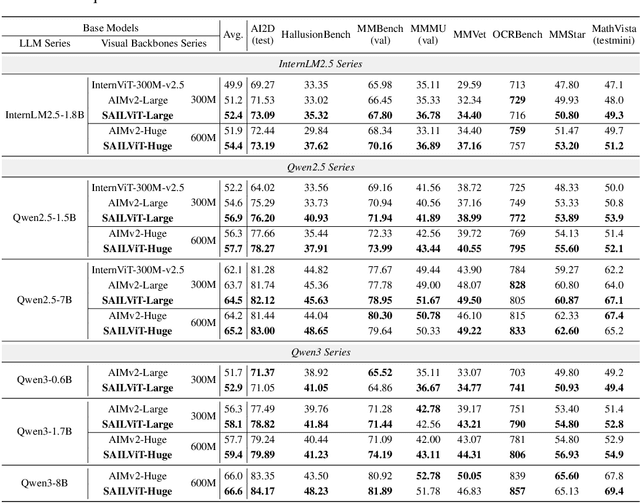
Abstract:Vision Transformers (ViTs) are essential as foundation backbones in establishing the visual comprehension capabilities of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs). Although most ViTs achieve impressive performance through image-text pair-based contrastive learning or self-supervised mechanisms, they struggle to engage in connector-based co-training directly with LLMs due to potential parameter initialization conflicts and modality semantic gaps. To address the above challenges, this paper proposes SAILViT, a gradual feature learning-enhanced ViT for facilitating MLLMs to break through performance bottlenecks in complex multimodal interactions. SAILViT achieves coarse-to-fine-grained feature alignment and world knowledge infusion with gradual feature refinement, which better serves target training demands. We perform thorough empirical analyses to confirm the powerful robustness and generalizability of SAILViT across different dimensions, including parameter sizes, model architectures, training strategies, and data scales. Equipped with SAILViT, existing MLLMs show significant and consistent performance improvements on the OpenCompass benchmark across extensive downstream tasks. SAILViT series models are released at https://huggingface.co/BytedanceDouyinContent.
AdaLRS: Loss-Guided Adaptive Learning Rate Search for Efficient Foundation Model Pretraining
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:Learning rate is widely regarded as crucial for effective foundation model pretraining. Recent research explores and demonstrates the transferability of learning rate configurations across varying model and dataset sizes, etc. Nevertheless, these approaches are constrained to specific training scenarios and typically necessitate extensive hyperparameter tuning on proxy models. In this work, we propose \textbf{AdaLRS}, a plug-in-and-play adaptive learning rate search algorithm that conducts online optimal learning rate search via optimizing loss descent velocities. We provide experiment results to show that the optimization of training loss and loss descent velocity in foundation model pretraining are both convex and share the same optimal learning rate. Relying solely on training loss dynamics, AdaLRS involves few extra computations to guide the search process, and its convergence is guaranteed via theoretical analysis. Experiments on both LLM and VLM pretraining show that AdaLRS adjusts suboptimal learning rates to the neighborhood of optimum with marked efficiency and effectiveness, with model performance improved accordingly. We also show the robust generalizability of AdaLRS across varying training scenarios, such as different model sizes, training paradigms, and base learning rate scheduler choices.
Scalable Vision Language Model Training via High Quality Data Curation
Jan 10, 2025



Abstract:In this paper, we introduce SAIL-VL (ScAlable Vision Language Model TraIning via High QuaLity Data Curation), an open-source vision language model (VLM) of state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance with 2B parameters. We introduce three key improvements that contribute to SAIL-VL's leading performance: (1) Scalable high-quality visual understanding data construction: We implement a visual understanding data construction pipeline, which enables hundred-million-scale high-quality recaption data annotation. Equipped with this pipeline, we curate SAIL-Caption, a large-scale caption dataset with large quantity and the highest data quality compared with opensource caption datasets. (2) Scalable Pretraining with High-Quality Visual Understanding Data: We scale SAIL-VL's pretraining budget up to 131B tokens and show that even a 2B VLM benefits from scaled up training data sizes, exhibiting expected data size scaling laws in visual understanding and instruction following performance. (3) Scalable SFT via quantity and quality scaling: We introduce general guidance for instruction data curation to scale up instruction data continuously, allowing us to construct a large SFT dataset with the highest quality. To further improve SAIL-VL's performance, we propose quality scaling, a multi-stage training recipe with curriculum learning, to improve model performance scaling curves w.r.t. data sizes from logarithmic to be near-linear. SAIL-VL obtains the highest average score in 19 commonly used benchmarks in our evaluation and achieves top1 performance among VLMs of comparable sizes on OpenCompass (https://rank.opencompass.org.cn/leaderboard-multimodal). We release our SAIL-VL-2B model at HuggingFace (https://huggingface.co/BytedanceDouyinContent/SAIL-VL-2B).
Benchmarking and Improving Detail Image Caption
May 29, 2024



Abstract:Image captioning has long been regarded as a fundamental task in visual understanding. Recently, however, few large vision-language model (LVLM) research discusses model's image captioning performance because of the outdated short-caption benchmarks and unreliable evaluation metrics. In this work, we propose to benchmark detail image caption task by curating high-quality evaluation datasets annotated by human experts, GPT-4V and Gemini-1.5-Pro. We also design a more reliable caption evaluation metric called CAPTURE (CAPtion evaluation by exTracting and coUpling coRE information). CAPTURE extracts visual elements, e.g., objects, attributes and relations from captions, and then matches these elements through three stages, achieving the highest consistency with expert judgements over other rule-based or model-based caption metrics. The proposed benchmark and metric provide reliable evaluation for LVLM's detailed image captioning ability. Guided by this evaluation, we further explore to unleash LVLM's detail caption capabilities by synthesizing high-quality data through a five-stage data construction pipeline. Our pipeline only uses a given LVLM itself and other open-source tools, without any human or GPT-4V annotation in the loop. Experiments show that the proposed data construction strategy significantly improves model-generated detail caption data quality for LVLMs with leading performance, and the data quality can be further improved in a self-looping paradigm. All code and dataset will be publicly available at https://github.com/foundation-multimodal-models/CAPTURE.
Unveiling the Tapestry of Consistency in Large Vision-Language Models
May 23, 2024Abstract:Large vision-language models (LVLMs) have recently achieved rapid progress, exhibiting great perception and reasoning abilities concerning visual information. However, when faced with prompts in different sizes of solution spaces, LVLMs fail to always give consistent answers regarding the same knowledge point. This inconsistency of answers between different solution spaces is prevalent in LVLMs and erodes trust. To this end, we provide a multi-modal benchmark ConBench, to intuitively analyze how LVLMs perform when the solution space of a prompt revolves around a knowledge point. Based on the ConBench tool, we are the first to reveal the tapestry and get the following findings: (1) In the discriminate realm, the larger the solution space of the prompt, the lower the accuracy of the answers. (2) Establish the relationship between the discriminative and generative realms: the accuracy of the discriminative question type exhibits a strong positive correlation with its Consistency with the caption. (3) Compared to open-source models, closed-source models exhibit a pronounced bias advantage in terms of Consistency. Eventually, we ameliorate the consistency of LVLMs by trigger-based diagnostic refinement, indirectly improving the performance of their caption. We hope this paper will accelerate the research community in better evaluating their models and encourage future advancements in the consistency domain.
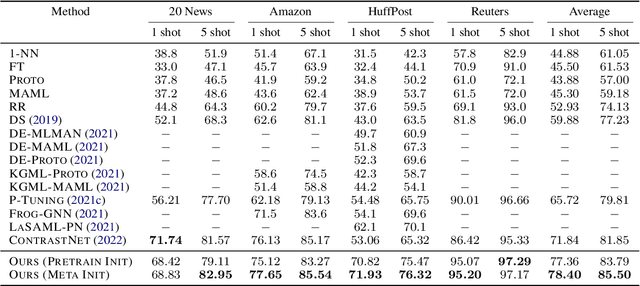
MetricPrompt: Prompting Model as a Relevance Metric for Few-shot Text Classification
Jun 15, 2023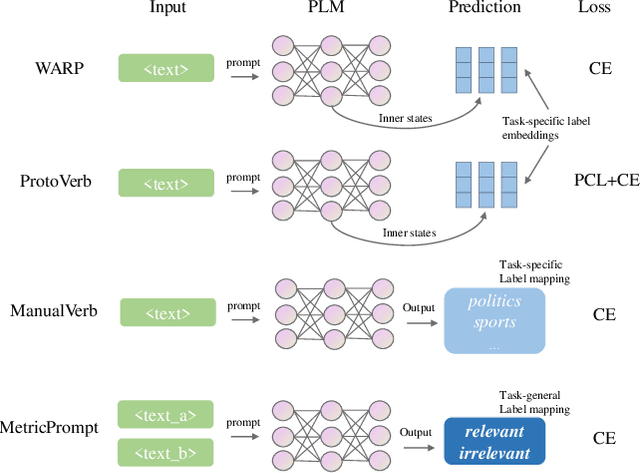
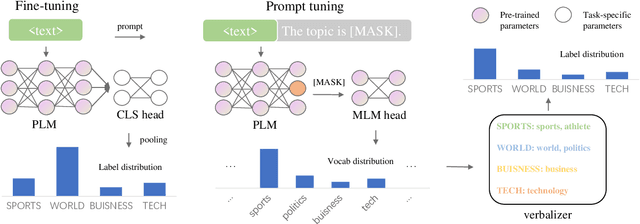
Abstract:Prompting methods have shown impressive performance in a variety of text mining tasks and applications, especially few-shot ones. Despite the promising prospects, the performance of prompting model largely depends on the design of prompt template and verbalizer. In this work, we propose MetricPrompt, which eases verbalizer design difficulty by reformulating few-shot text classification task into text pair relevance estimation task. MetricPrompt adopts prompting model as the relevance metric, further bridging the gap between Pre-trained Language Model's (PLM) pre-training objective and text classification task, making possible PLM's smooth adaption. Taking a training sample and a query one simultaneously, MetricPrompt captures cross-sample relevance information for accurate relevance estimation. We conduct experiments on three widely used text classification datasets across four few-shot settings. Results show that MetricPrompt outperforms manual verbalizer and other automatic verbalizer design methods across all few-shot settings, achieving new state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance.
MetaPrompting: Learning to Learn Better Prompts
Sep 27, 2022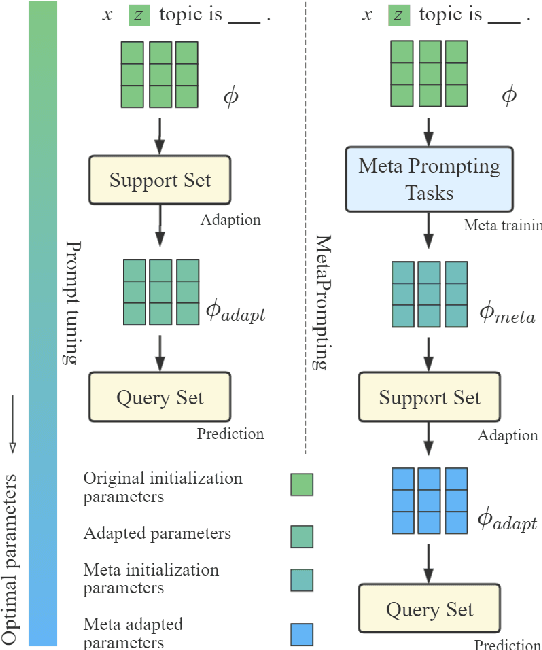
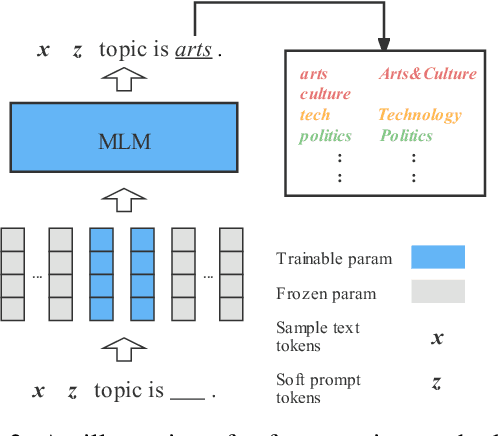

Abstract:Prompting method is regarded as one of the crucial progress for few-shot nature language processing. Recent research on prompting moves from discrete tokens based ``hard prompts'' to continuous ``soft prompts'', which employ learnable vectors as pseudo prompt tokens and achieve better performance. Though showing promising prospects, these soft-prompting methods are observed to rely heavily on good initialization to take effect. Unfortunately, obtaining a perfect initialization for soft prompts requires understanding of inner language models working and elaborate design, which is no easy task and has to restart from scratch for each new task. To remedy this, we propose a generalized soft prompting method called MetaPrompting, which adopts the well-recognized model-agnostic meta-learning algorithm to automatically find better prompt initialization that facilitates fast adaptation to new prompting tasks.Extensive experiments show MetaPrompting tackles soft prompt initialization problem and brings significant improvement on four different datasets (over 6 points improvement in accuracy for 1-shot setting), achieving new state-of-the-art performance.
Variational Autoencoder for Anti-Cancer Drug Response Prediction
Sep 29, 2020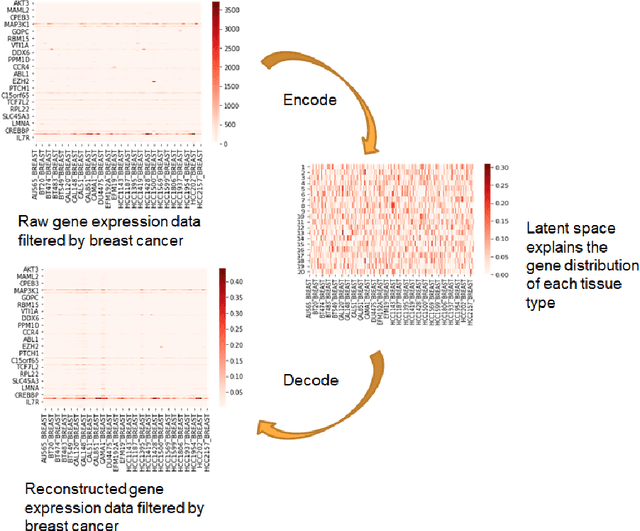

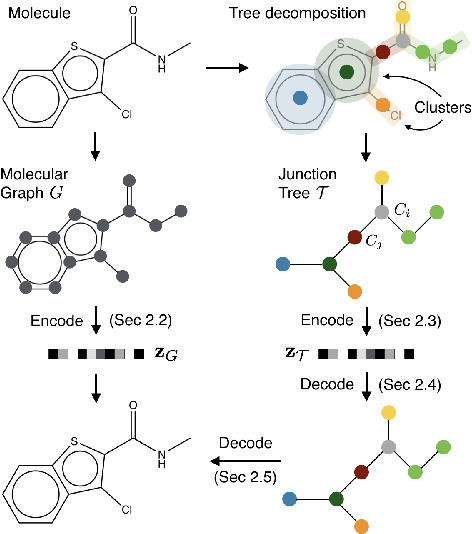
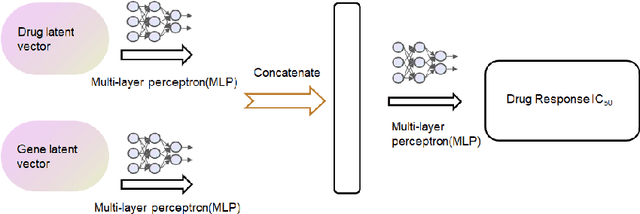
Abstract:Cancer has long been a main cause of human death, and the discovery of new drugs and the customization of cancer therapy have puzzled people for a long time. In order to facilitate the discovery of new anti-cancer drugs and the customization of treatment strategy, we seek to predict the response of different anti-cancer drugs with variational autoencoders (VAE) and multi-layer perceptron (MLP).Our model takes as input gene expression data of cancer cell lines and anti-cancer drug molecular data, and encode these data with {\sc {GeneVae}} model, which is an ordinary VAE, and rectified junction tree variational autoencoder ({\sc JtVae}) (\cite{jin2018junction}) model, respectively. Encoded features are processes by a Multi-layer Perceptron (MLP) model to produce a final prediction. We reach an average coefficient of determination ($R^{2} = 0.83$) in predicting drug response on breast cancer cell lines and an average $R^{2} > 0.84$ on pan-cancer cell lines. Additionally, we show that our model can generate unseen effective drug compounds for specific cancer cell lines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge