Zijian Kang
SAIL-VL2 Technical Report
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:We introduce SAIL-VL2, an open-suite vision-language foundation model (LVM) for comprehensive multimodal understanding and reasoning. As the successor to SAIL-VL, SAIL-VL2 achieves state-of-the-art performance at the 2B and 8B parameter scales across diverse image and video benchmarks, demonstrating strong capabilities from fine-grained perception to complex reasoning. Its effectiveness is driven by three core innovations. First, a large-scale data curation pipeline with scoring and filtering strategies enhances both quality and distribution across captioning, OCR, QA, and video data, improving training efficiency. Second, a progressive training framework begins with a powerful pre-trained vision encoder (SAIL-ViT), advances through multimodal pre-training, and culminates in a thinking-fusion SFT-RL hybrid paradigm that systematically strengthens model capabilities. Third, architectural advances extend beyond dense LLMs to efficient sparse Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) designs. With these contributions, SAIL-VL2 demonstrates competitive performance across 106 datasets and achieves state-of-the-art results on challenging reasoning benchmarks such as MMMU and MathVista. Furthermore, on the OpenCompass leaderboard, SAIL-VL2-2B ranks first among officially released open-source models under the 4B parameter scale, while serving as an efficient and extensible foundation for the open-source multimodal community.
Traceable Evidence Enhanced Visual Grounded Reasoning: Evaluation and Methodology
Jul 10, 2025

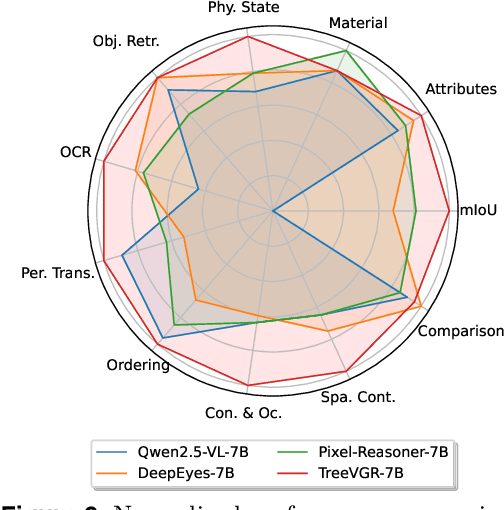
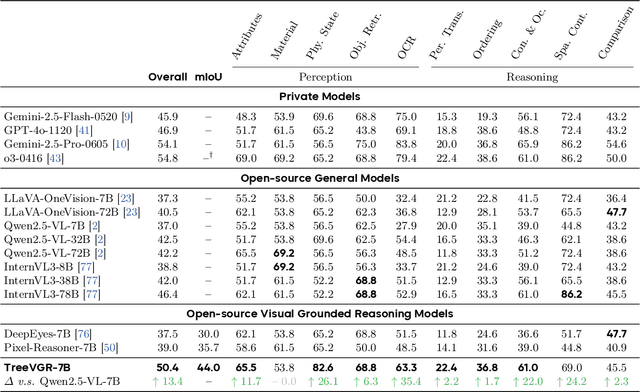
Abstract:Models like OpenAI-o3 pioneer visual grounded reasoning by dynamically referencing visual regions, just like human "thinking with images". However, no benchmark exists to evaluate these capabilities holistically. To bridge this gap, we propose TreeBench (Traceable Evidence Evaluation Benchmark), a diagnostic benchmark built on three principles: (1) focused visual perception of subtle targets in complex scenes, (2) traceable evidence via bounding box evaluation, and (3) second-order reasoning to test object interactions and spatial hierarchies beyond simple object localization. Prioritizing images with dense objects, we initially sample 1K high-quality images from SA-1B, and incorporate eight LMM experts to manually annotate questions, candidate options, and answers for each image. After three stages of quality control, TreeBench consists of 405 challenging visual question-answering pairs, even the most advanced models struggle with this benchmark, where none of them reach 60% accuracy, e.g., OpenAI-o3 scores only 54.87. Furthermore, we introduce TreeVGR (Traceable Evidence Enhanced Visual Grounded Reasoning), a training paradigm to supervise localization and reasoning jointly with reinforcement learning, enabling accurate localizations and explainable reasoning pathways. Initialized from Qwen2.5-VL-7B, it improves V* Bench (+16.8), MME-RealWorld (+12.6), and TreeBench (+13.4), proving traceability is key to advancing vision-grounded reasoning. The code is available at https://github.com/Haochen-Wang409/TreeVGR.
SAILViT: Towards Robust and Generalizable Visual Backbones for MLLMs via Gradual Feature Refinement
Jul 02, 2025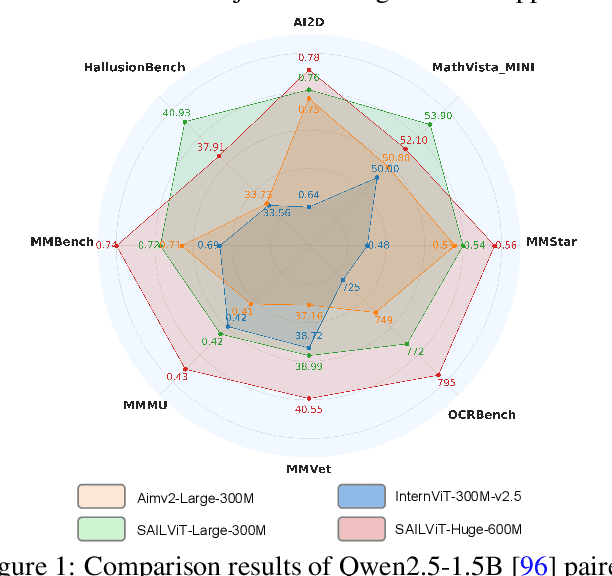
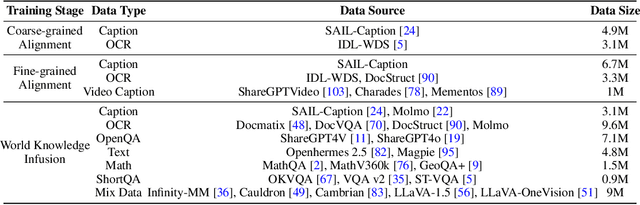
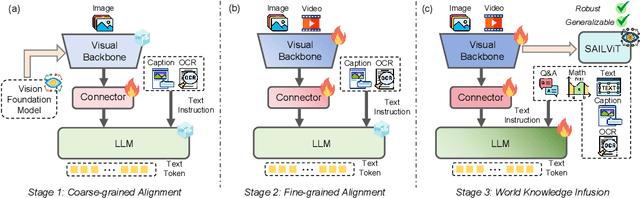
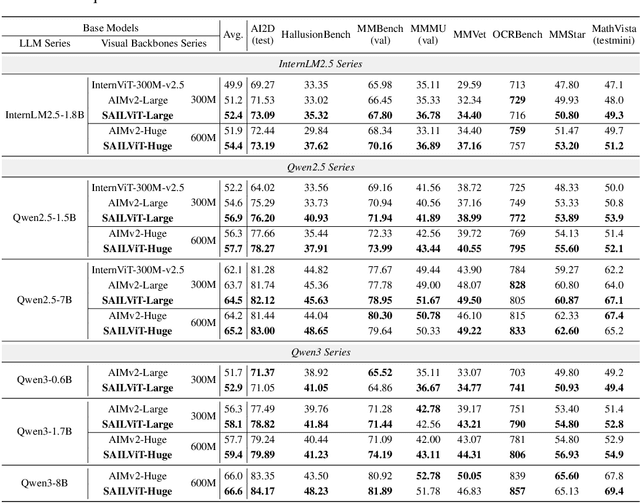
Abstract:Vision Transformers (ViTs) are essential as foundation backbones in establishing the visual comprehension capabilities of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs). Although most ViTs achieve impressive performance through image-text pair-based contrastive learning or self-supervised mechanisms, they struggle to engage in connector-based co-training directly with LLMs due to potential parameter initialization conflicts and modality semantic gaps. To address the above challenges, this paper proposes SAILViT, a gradual feature learning-enhanced ViT for facilitating MLLMs to break through performance bottlenecks in complex multimodal interactions. SAILViT achieves coarse-to-fine-grained feature alignment and world knowledge infusion with gradual feature refinement, which better serves target training demands. We perform thorough empirical analyses to confirm the powerful robustness and generalizability of SAILViT across different dimensions, including parameter sizes, model architectures, training strategies, and data scales. Equipped with SAILViT, existing MLLMs show significant and consistent performance improvements on the OpenCompass benchmark across extensive downstream tasks. SAILViT series models are released at https://huggingface.co/BytedanceDouyinContent.
VGR: Visual Grounded Reasoning
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:In the field of multimodal chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning, existing approaches predominantly rely on reasoning on pure language space, which inherently suffers from language bias and is largely confined to math or science domains. This narrow focus limits their ability to handle complex visual reasoning tasks that demand comprehensive understanding of image details. To address these limitations, this paper introduces VGR, a novel reasoning multimodal large language model (MLLM) with enhanced fine-grained visual perception capabilities. Unlike traditional MLLMs that answer the question or reasoning solely on the language space, our VGR first detects relevant regions that may help to solve problems, and then provides precise answers based on replayed image regions. To achieve this, we conduct a large-scale SFT dataset called VGR -SFT that contains reasoning data with mixed vision grounding and language deduction. The inference pipeline of VGR allows the model to choose bounding boxes for visual reference and a replay stage is introduced to integrates the corresponding regions into the reasoning process, enhancing multimodel comprehension. Experiments on the LLaVA-NeXT-7B baseline show that VGR achieves superior performance on multi-modal benchmarks requiring comprehensive image detail understanding. Compared to the baseline, VGR uses only 30\% of the image token count while delivering scores of +4.1 on MMStar, +7.1 on AI2D, and a +12.9 improvement on ChartQA.
LEREL: Lipschitz Continuity-Constrained Emotion Recognition Ensemble Learning For Electroencephalography
Apr 12, 2025



Abstract:Accurate and efficient perception of emotional states in oneself and others is crucial, as emotion-related disorders are associated with severe psychosocial impairments. While electroencephalography (EEG) offers a powerful tool for emotion detection, current EEG-based emotion recognition (EER) methods face key limitations: insufficient model stability, limited accuracy in processing high-dimensional nonlinear EEG signals, and poor robustness against intra-subject variability and signal noise. To address these challenges, we propose LEREL (Lipschitz continuity-constrained Emotion Recognition Ensemble Learning), a novel framework that significantly enhances both the accuracy and robustness of emotion recognition performance. The LEREL framework employs Lipschitz continuity constraints to enhance model stability and generalization in EEG emotion recognition, reducing signal variability and noise susceptibility while maintaining strong performance on small-sample datasets. The ensemble learning strategy reduces single-model bias and variance through multi-classifier decision fusion, further optimizing overall performance. Experimental results on three public benchmark datasets (EAV, FACED and SEED) demonstrate LEREL's effectiveness, achieving average recognition accuracies of 76.43%, 83.00% and 89.22%, respectively.
Information Bottleneck-Guided Heterogeneous Graph Learning for Interpretable Neurodevelopmental Disorder Diagnosis
Feb 28, 2025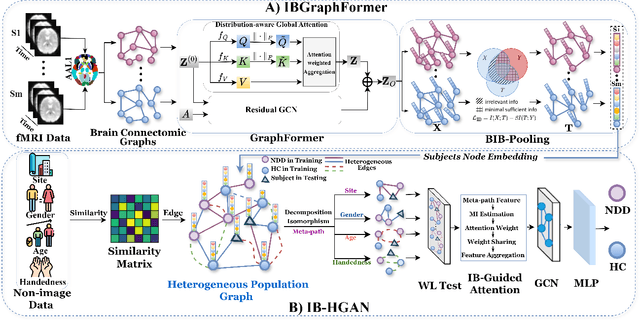
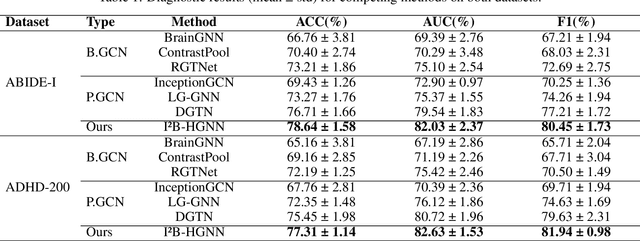
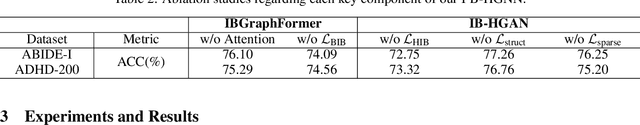
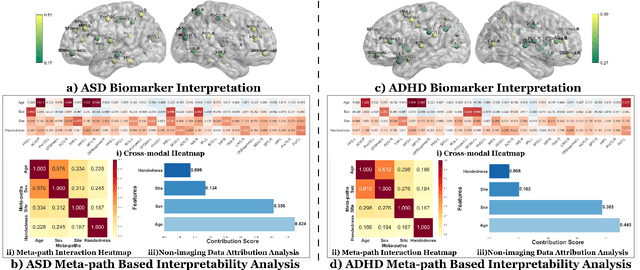
Abstract:Developing interpretable models for diagnosing neurodevelopmental disorders (NDDs) is highly valuable yet challenging, primarily due to the complexity of encoding, decoding and integrating imaging and non-imaging data. Many existing machine learning models struggle to provide comprehensive interpretability, often failing to extract meaningful biomarkers from imaging data, such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), or lacking mechanisms to explain the significance of non-imaging data. In this paper, we propose the Interpretable Information Bottleneck Heterogeneous Graph Neural Network (I2B-HGNN), a novel framework designed to learn from fine-grained local patterns to comprehensive global multi-modal interactions. This framework comprises two key modules. The first module, the Information Bottleneck Graph Transformer (IBGraphFormer) for local patterns, integrates global modeling with brain connectomic-constrained graph neural networks to identify biomarkers through information bottleneck-guided pooling. The second module, the Information Bottleneck Heterogeneous Graph Attention Network (IB-HGAN) for global multi-modal interactions, facilitates interpretable multi-modal fusion of imaging and non-imaging data using heterogeneous graph neural networks. The results of the experiments demonstrate that I2B-HGNN excels in diagnosing NDDs with high accuracy, providing interpretable biomarker identification and effective analysis of non-imaging data.
Scalable Vision Language Model Training via High Quality Data Curation
Jan 10, 2025



Abstract:In this paper, we introduce SAIL-VL (ScAlable Vision Language Model TraIning via High QuaLity Data Curation), an open-source vision language model (VLM) of state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance with 2B parameters. We introduce three key improvements that contribute to SAIL-VL's leading performance: (1) Scalable high-quality visual understanding data construction: We implement a visual understanding data construction pipeline, which enables hundred-million-scale high-quality recaption data annotation. Equipped with this pipeline, we curate SAIL-Caption, a large-scale caption dataset with large quantity and the highest data quality compared with opensource caption datasets. (2) Scalable Pretraining with High-Quality Visual Understanding Data: We scale SAIL-VL's pretraining budget up to 131B tokens and show that even a 2B VLM benefits from scaled up training data sizes, exhibiting expected data size scaling laws in visual understanding and instruction following performance. (3) Scalable SFT via quantity and quality scaling: We introduce general guidance for instruction data curation to scale up instruction data continuously, allowing us to construct a large SFT dataset with the highest quality. To further improve SAIL-VL's performance, we propose quality scaling, a multi-stage training recipe with curriculum learning, to improve model performance scaling curves w.r.t. data sizes from logarithmic to be near-linear. SAIL-VL obtains the highest average score in 19 commonly used benchmarks in our evaluation and achieves top1 performance among VLMs of comparable sizes on OpenCompass (https://rank.opencompass.org.cn/leaderboard-multimodal). We release our SAIL-VL-2B model at HuggingFace (https://huggingface.co/BytedanceDouyinContent/SAIL-VL-2B).
Neural-MCRL: Neural Multimodal Contrastive Representation Learning for EEG-based Visual Decoding
Dec 23, 2024



Abstract:Decoding neural visual representations from electroencephalogram (EEG)-based brain activity is crucial for advancing brain-machine interfaces (BMI) and has transformative potential for neural sensory rehabilitation. While multimodal contrastive representation learning (MCRL) has shown promise in neural decoding, existing methods often overlook semantic consistency and completeness within modalities and lack effective semantic alignment across modalities. This limits their ability to capture the complex representations of visual neural responses. We propose Neural-MCRL, a novel framework that achieves multimodal alignment through semantic bridging and cross-attention mechanisms, while ensuring completeness within modalities and consistency across modalities. Our framework also features the Neural Encoder with Spectral-Temporal Adaptation (NESTA), a EEG encoder that adaptively captures spectral patterns and learns subject-specific transformations. Experimental results demonstrate significant improvements in visual decoding accuracy and model generalization compared to state-of-the-art methods, advancing the field of EEG-based neural visual representation decoding in BMI. Codes will be available at: https://github.com/NZWANG/Neural-MCRL.
Toward Accurate Camera-based 3D Object Detection via Cascade Depth Estimation and Calibration
Feb 07, 2024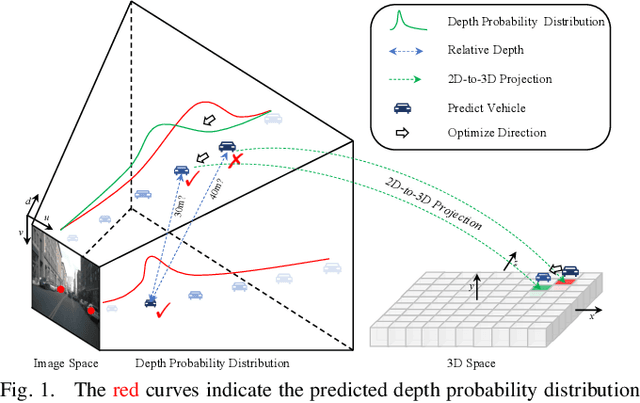
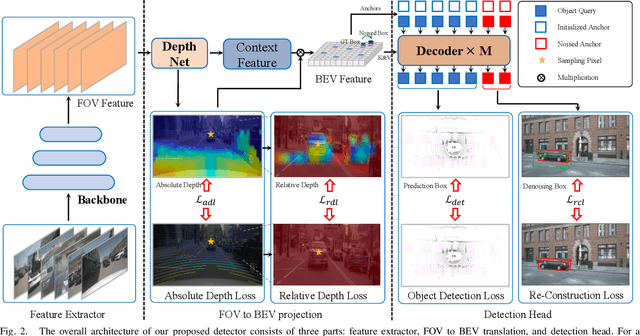
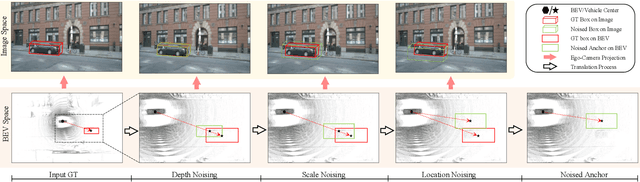
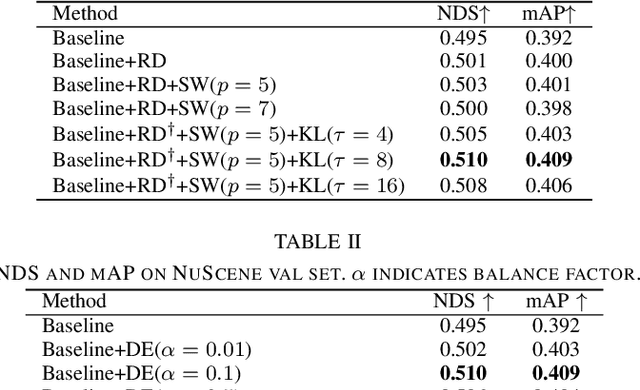
Abstract:Recent camera-based 3D object detection is limited by the precision of transforming from image to 3D feature spaces, as well as the accuracy of object localization within the 3D space. This paper aims to address such a fundamental problem of camera-based 3D object detection: How to effectively learn depth information for accurate feature lifting and object localization. Different from previous methods which directly predict depth distributions by using a supervised estimation model, we propose a cascade framework consisting of two depth-aware learning paradigms. First, a depth estimation (DE) scheme leverages relative depth information to realize the effective feature lifting from 2D to 3D spaces. Furthermore, a depth calibration (DC) scheme introduces depth reconstruction to further adjust the 3D object localization perturbation along the depth axis. In practice, the DE is explicitly realized by using both the absolute and relative depth optimization loss to promote the precision of depth prediction, while the capability of DC is implicitly embedded into the detection Transformer through a depth denoising mechanism in the training phase. The entire model training is accomplished through an end-to-end manner. We propose a baseline detector and evaluate the effectiveness of our proposal with +2.2%/+2.7% NDS/mAP improvements on NuScenes benchmark, and gain a comparable performance with 55.9%/45.7% NDS/mAP. Furthermore, we conduct extensive experiments to demonstrate its generality based on various detectors with about +2% NDS improvements.
SupFusion: Supervised LiDAR-Camera Fusion for 3D Object Detection
Sep 13, 2023



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel training strategy called SupFusion, which provides an auxiliary feature level supervision for effective LiDAR-Camera fusion and significantly boosts detection performance. Our strategy involves a data enhancement method named Polar Sampling, which densifies sparse objects and trains an assistant model to generate high-quality features as the supervision. These features are then used to train the LiDAR-Camera fusion model, where the fusion feature is optimized to simulate the generated high-quality features. Furthermore, we propose a simple yet effective deep fusion module, which contiguously gains superior performance compared with previous fusion methods with SupFusion strategy. In such a manner, our proposal shares the following advantages. Firstly, SupFusion introduces auxiliary feature-level supervision which could boost LiDAR-Camera detection performance without introducing extra inference costs. Secondly, the proposed deep fusion could continuously improve the detector's abilities. Our proposed SupFusion and deep fusion module is plug-and-play, we make extensive experiments to demonstrate its effectiveness. Specifically, we gain around 2% 3D mAP improvements on KITTI benchmark based on multiple LiDAR-Camera 3D detectors.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge