Weiming Zeng
Region-aware Spatiotemporal Modeling with Collaborative Domain Generalization for Cross-Subject EEG Emotion Recognition
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Cross-subject EEG-based emotion recognition (EER) remains challenging due to strong inter-subject variability, which induces substantial distribution shifts in EEG signals, as well as the high complexity of emotion-related neural representations in both spatial organization and temporal evolution. Existing approaches typically improve spatial modeling, temporal modeling, or generalization strategies in isolation, which limits their ability to align representations across subjects while capturing multi-scale dynamics and suppressing subject-specific bias within a unified framework. To address these gaps, we propose a Region-aware Spatiotemporal Modeling framework with Collaborative Domain Generalization (RSM-CoDG) for cross-subject EEG emotion recognition. RSM-CoDG incorporates neuroscience priors derived from functional brain region partitioning to construct region-level spatial representations, thereby improving cross-subject comparability. It also employs multi-scale temporal modeling to characterize the dynamic evolution of emotion-evoked neural activity. In addition, the framework employs a collaborative domain generalization strategy, incorporating multidimensional constraints to reduce subject-specific bias in a fully unseen target subject setting, which enhances the generalization to unknown individuals. Extensive experimental results on SEED series datasets demonstrate that RSM-CoDG consistently outperforms existing competing methods, providing an effective approach for improving robustness. The source code is available at https://github.com/RyanLi-X/RSM-CoDG.
LEREL: Lipschitz Continuity-Constrained Emotion Recognition Ensemble Learning For Electroencephalography
Apr 12, 2025



Abstract:Accurate and efficient perception of emotional states in oneself and others is crucial, as emotion-related disorders are associated with severe psychosocial impairments. While electroencephalography (EEG) offers a powerful tool for emotion detection, current EEG-based emotion recognition (EER) methods face key limitations: insufficient model stability, limited accuracy in processing high-dimensional nonlinear EEG signals, and poor robustness against intra-subject variability and signal noise. To address these challenges, we propose LEREL (Lipschitz continuity-constrained Emotion Recognition Ensemble Learning), a novel framework that significantly enhances both the accuracy and robustness of emotion recognition performance. The LEREL framework employs Lipschitz continuity constraints to enhance model stability and generalization in EEG emotion recognition, reducing signal variability and noise susceptibility while maintaining strong performance on small-sample datasets. The ensemble learning strategy reduces single-model bias and variance through multi-classifier decision fusion, further optimizing overall performance. Experimental results on three public benchmark datasets (EAV, FACED and SEED) demonstrate LEREL's effectiveness, achieving average recognition accuracies of 76.43%, 83.00% and 89.22%, respectively.
Bring Remote Sensing Object Detect Into Nature Language Model: Using SFT Method
Mar 11, 2025



Abstract:Recently, large language models (LLMs) and visionlanguage models (VLMs) have achieved significant success, demonstrating remarkable capabilities in understanding various images and videos, particularly in classification and detection tasks. However, due to the substantial differences between remote sensing images and conventional optical images, these models face considerable challenges in comprehension, especially in detection tasks. Directly prompting VLMs with detection instructions often fails to yield satisfactory results. To address this issue, this letter explores the application of VLMs for object detection in remote sensing images. Specifically, we utilize publicly available remote sensing object detection datasets, including SSDD, HRSID, and NWPU-VHR-10, to convert traditional annotation information into natural language, thereby constructing an instruction-tuning (SFT) dataset for VLM training. We then evaluate the detection performance of different fine-tuning strategies for VLMs and obtain optimized model weights for object detection in remote sensing images. Finally, we assess the model's prior knowledge capabilities through natural language queries.Experimental results demonstrate that, without modifying the model architecture, remote sensing object detection can be effectively achieved using natural language alone. Additionally, the model exhibits the ability to perform certain vision question answering (VQA) tasks. Our dataset and relevant code will be released soon.
Information Bottleneck-Guided Heterogeneous Graph Learning for Interpretable Neurodevelopmental Disorder Diagnosis
Feb 28, 2025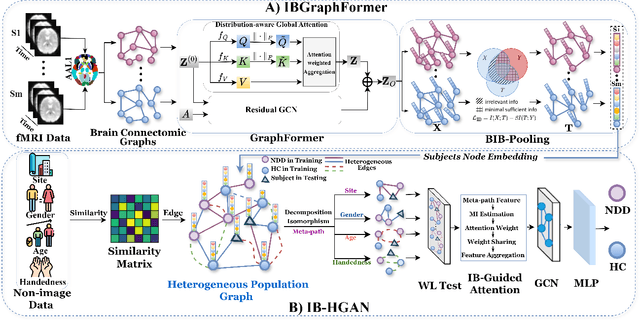
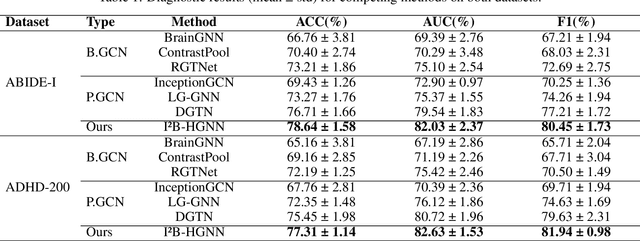
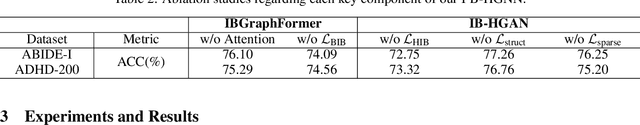
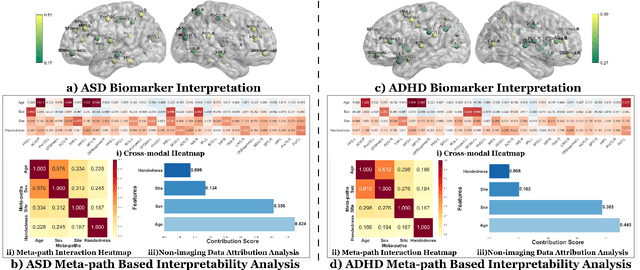
Abstract:Developing interpretable models for diagnosing neurodevelopmental disorders (NDDs) is highly valuable yet challenging, primarily due to the complexity of encoding, decoding and integrating imaging and non-imaging data. Many existing machine learning models struggle to provide comprehensive interpretability, often failing to extract meaningful biomarkers from imaging data, such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), or lacking mechanisms to explain the significance of non-imaging data. In this paper, we propose the Interpretable Information Bottleneck Heterogeneous Graph Neural Network (I2B-HGNN), a novel framework designed to learn from fine-grained local patterns to comprehensive global multi-modal interactions. This framework comprises two key modules. The first module, the Information Bottleneck Graph Transformer (IBGraphFormer) for local patterns, integrates global modeling with brain connectomic-constrained graph neural networks to identify biomarkers through information bottleneck-guided pooling. The second module, the Information Bottleneck Heterogeneous Graph Attention Network (IB-HGAN) for global multi-modal interactions, facilitates interpretable multi-modal fusion of imaging and non-imaging data using heterogeneous graph neural networks. The results of the experiments demonstrate that I2B-HGNN excels in diagnosing NDDs with high accuracy, providing interpretable biomarker identification and effective analysis of non-imaging data.
STARFormer: A Novel Spatio-Temporal Aggregation Reorganization Transformer of FMRI for Brain Disorder Diagnosis
Dec 31, 2024



Abstract:Many existing methods that use functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) classify brain disorders, such as autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), often overlook the integration of spatial and temporal dependencies of the blood oxygen level-dependent (BOLD) signals, which may lead to inaccurate or imprecise classification results. To solve this problem, we propose a Spatio-Temporal Aggregation eorganization ransformer (STARFormer) that effectively captures both spatial and temporal features of BOLD signals by incorporating three key modules. The region of interest (ROI) spatial structure analysis module uses eigenvector centrality (EC) to reorganize brain regions based on effective connectivity, highlighting critical spatial relationships relevant to the brain disorder. The temporal feature reorganization module systematically segments the time series into equal-dimensional window tokens and captures multiscale features through variable window and cross-window attention. The spatio-temporal feature fusion module employs a parallel transformer architecture with dedicated temporal and spatial branches to extract integrated features. The proposed STARFormer has been rigorously evaluated on two publicly available datasets for the classification of ASD and ADHD. The experimental results confirm that the STARFormer achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple evaluation metrics, providing a more accurate and reliable tool for the diagnosis of brain disorders and biomedical research. The codes will be available at: https://github.com/NZWANG/STARFormer.
Neural-MCRL: Neural Multimodal Contrastive Representation Learning for EEG-based Visual Decoding
Dec 23, 2024



Abstract:Decoding neural visual representations from electroencephalogram (EEG)-based brain activity is crucial for advancing brain-machine interfaces (BMI) and has transformative potential for neural sensory rehabilitation. While multimodal contrastive representation learning (MCRL) has shown promise in neural decoding, existing methods often overlook semantic consistency and completeness within modalities and lack effective semantic alignment across modalities. This limits their ability to capture the complex representations of visual neural responses. We propose Neural-MCRL, a novel framework that achieves multimodal alignment through semantic bridging and cross-attention mechanisms, while ensuring completeness within modalities and consistency across modalities. Our framework also features the Neural Encoder with Spectral-Temporal Adaptation (NESTA), a EEG encoder that adaptively captures spectral patterns and learns subject-specific transformations. Experimental results demonstrate significant improvements in visual decoding accuracy and model generalization compared to state-of-the-art methods, advancing the field of EEG-based neural visual representation decoding in BMI. Codes will be available at: https://github.com/NZWANG/Neural-MCRL.
MID: A Comprehensive Shore-Based Dataset for Multi-Scale Dense Ship Occlusion and Interaction Scenarios
Dec 10, 2024



Abstract:This paper introduces the Maritime Ship Navigation Behavior Dataset (MID), designed to address challenges in ship detection within complex maritime environments using Oriented Bounding Boxes (OBB). MID contains 5,673 images with 135,884 finely annotated target instances, supporting both supervised and semi-supervised learning. It features diverse maritime scenarios such as ship encounters under varying weather, docking maneuvers, small target clustering, and partial occlusions, filling critical gaps in datasets like HRSID, SSDD, and NWPU-10. MID's images are sourced from high-definition video clips of real-world navigation across 43 water areas, with varied weather and lighting conditions (e.g., rain, fog). Manually curated annotations enhance the dataset's variety, ensuring its applicability to real-world demands in busy ports and dense maritime regions. This diversity equips models trained on MID to better handle complex, dynamic environments, supporting advancements in maritime situational awareness. To validate MID's utility, we evaluated 10 detection algorithms, providing an in-depth analysis of the dataset, detection results from various models, and a comparative study of baseline algorithms, with a focus on handling occlusions and dense target clusters. The results highlight MID's potential to drive innovation in intelligent maritime traffic monitoring and autonomous navigation systems. The dataset will be made publicly available at https://github.com/VirtualNew/MID_DataSet.
Advances in Photoacoustic Imaging Reconstruction and Quantitative Analysis for Biomedical Applications
Nov 05, 2024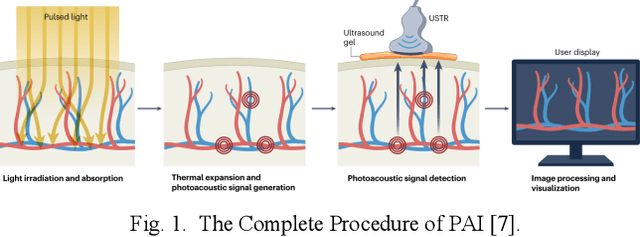
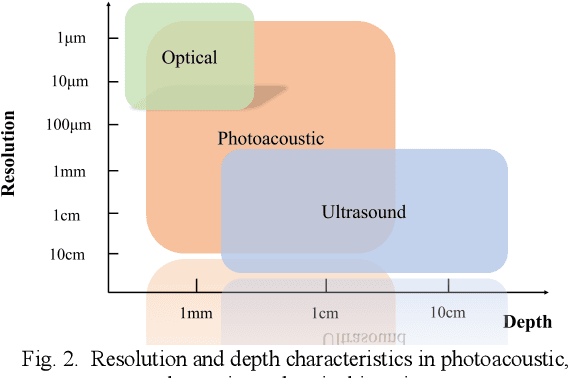
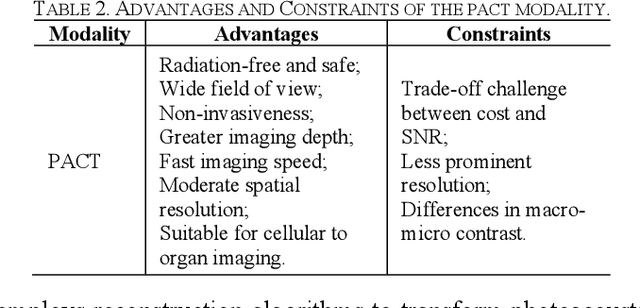
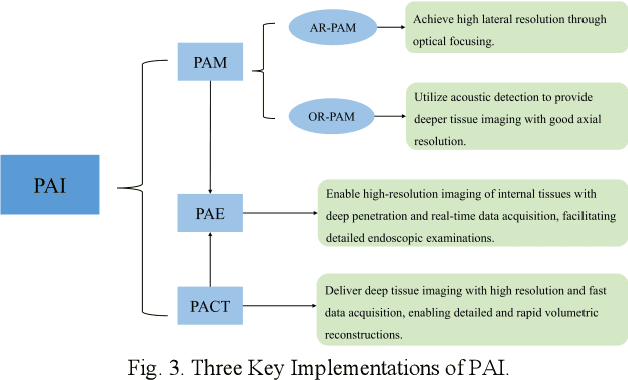
Abstract:Photoacoustic imaging (PAI) represents an innovative biomedical imaging modality that harnesses the advantages of optical resolution and acoustic penetration depth while ensuring enhanced safety. Despite its promising potential across a diverse array of preclinical and clinical applications, the clinical implementation of PAI faces significant challenges, including the trade-off between penetration depth and spatial resolution, as well as the demand for faster imaging speeds. This paper explores the fundamental principles underlying PAI, with a particular emphasis on three primary implementations: photoacoustic computed tomography (PACT), photoacoustic microscopy (PAM), and photoacoustic endoscopy (PAE). We undertake a critical assessment of their respective strengths and practical limitations. Furthermore, recent developments in utilizing conventional or deep learning (DL) methodologies for image reconstruction and artefact mitigation across PACT, PAM, and PAE are outlined, demonstrating considerable potential to enhance image quality and accelerate imaging processes. Furthermore, this paper examines the recent developments in quantitative analysis within PAI, including the quantification of haemoglobin concentration, oxygen saturation, and other physiological parameters within tissues. Finally, our discussion encompasses current trends and future directions in PAI research while emphasizing the transformative impact of deep learning on advancing PAI.
A Visual Question Answering Method for SAR Ship: Breaking the Requirement for Multimodal Dataset Construction and Model Fine-Tuning
Nov 03, 2024



Abstract:Current visual question answering (VQA) tasks often require constructing multimodal datasets and fine-tuning visual language models, which demands significant time and resources. This has greatly hindered the application of VQA to downstream tasks, such as ship information analysis based on Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) imagery. To address this challenge, this letter proposes a novel VQA approach that integrates object detection networks with visual language models, specifically designed for analyzing ships in SAR images. This integration aims to enhance the capabilities of VQA systems, focusing on aspects such as ship location, density, and size analysis, as well as risk behavior detection. Initially, we conducted baseline experiments using YOLO networks on two representative SAR ship detection datasets, SSDD and HRSID, to assess each model's performance in terms of detection accuracy. Based on these results, we selected the optimal model, YOLOv8n, as the most suitable detection network for this task. Subsequently, leveraging the vision-language model Qwen2-VL, we designed and implemented a VQA task specifically for SAR scenes. This task employs the ship location and size information output by the detection network to generate multi-turn dialogues and scene descriptions for SAR imagery. Experimental results indicate that this method not only enables fundamental SAR scene question-answering without the need for additional datasets or fine-tuning but also dynamically adapts to complex, multi-turn dialogue requirements, demonstrating robust semantic understanding and adaptability.
RSNet: A Light Framework for The Detection of Multi-scale Remote Sensing Targets
Oct 30, 2024



Abstract:Recent developments in synthetic aperture radar (SAR) ship detection have seen deep learning techniques achieve remarkable progress in accuracy and speed. However, the detection of small targets against complex backgrounds remains a significant challenge. To tackle these difficulties, this letter presents RSNet, a lightweight framework aimed at enhancing ship detection capabilities in SAR imagery. RSNet features the Waveletpool-ContextGuided (WCG) backbone for enhanced accuracy with fewer parameters, and the Waveletpool-StarFusion (WSF) head for efficient parameter reduction. Additionally, a Lightweight-Shared (LS) module minimizes the detection head's parameter load. Experiments on the SAR Ship Detection Dataset (SSDD) and High-Resolution SAR Image Dataset (HRSID) demonstrate that RSNet achieves a strong balance between lightweight design and detection performance, surpassing many state-of-the-art detectors, reaching 72.5\% and 67.6\% in \textbf{\(\mathbf{mAP_{.50:95}}\) }respectively with 1.49M parameters. Our code will be released soon.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge