Jian Sun
the State Key Lab of Intelligent Control and Decision of Complex Systems and the School of Automation, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, China, Beijing Institute of Technology Chongqing Innovation Center, Chongqing, China
Enhancing Foundation VLM Robustness to Missing Modality: Scalable Diffusion for Bi-directional Feature Restoration
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Vision Language Models (VLMs) typically assume complete modality input during inference. However, their effectiveness drops sharply when certain modalities are unavailable or incomplete. Current research primarily faces two dilemmas: Prompt-based methods struggle to restore missing yet indispensable features and impair generalization of VLMs. Imputation-based approaches, lacking effective guidance, are prone to generating semantically irrelevant noise. Restoring precise semantics while sustaining VLM generalization remains challenging. Therefore, we propose a general missing modality restoration strategy in this paper. We introduce an enhanced diffusion model as a pluggable mid-stage training module to effectively restore missing features. Our strategy introduces two key innovations: (I) Dynamic Modality Gating, which adaptively leverages conditional features to steer the generation of semantically consistent features; (II) Cross-Modal Mutual Learning mechanism, which bridges the semantic spaces of dual encoders to achieve bidirectional alignment. Zero-shot evaluations across benchmark datasets demonstrate that our approach outperforms existing baseline methods. Extensive experiments and ablation studies confirm our model as a robust and scalable extension for VLMs in missing modality scenarios, ensuring reliability across diverse missing rates and environments. Our code and models will be publicly available.
Mixture-of-World Models: Scaling Multi-Task Reinforcement Learning with Modular Latent Dynamics
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:A fundamental challenge in multi-task reinforcement learning (MTRL) is achieving sample efficiency in visual domains where tasks exhibit substantial heterogeneity in both observations and dynamics. Model-based reinforcement learning offers a promising path to improved sample efficiency through world models, but standard monolithic architectures struggle to capture diverse task dynamics, resulting in poor reconstruction and prediction accuracy. We introduce Mixture-of-World Models (MoW), a scalable architecture that combines modular variational autoencoders for task-adaptive visual compression, a hybrid Transformer-based dynamics model with task-conditioned experts and a shared backbone, and a gradient-based task clustering strategy for efficient parameter allocation. On the Atari 100k benchmark, a single MoW agent trained once on 26 Atari games achieves a mean human-normalized score of 110.4%, competitive with the score of 114.2% achieved by STORM, an ensemble of 26 task-specific models, while using 50% fewer parameters. On Meta-World, MoW achieves a 74.5% average success rate within 300 thousand environment steps, establishing a new state of the art. These results demonstrate that MoW provides a scalable and parameter-efficient foundation for generalist world models.
Machine Unlearning in Low-Dimensional Feature Subspace
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Machine Unlearning (MU) aims at removing the influence of specific data from a pretrained model while preserving performance on the remaining data. In this work, a novel perspective for MU is presented upon low-dimensional feature subspaces, which gives rise to the potentials of separating the remaining and forgetting data herein. This separability motivates our LOFT, a method that proceeds unlearning in a LOw-dimensional FeaTure subspace from the pretrained model skithrough principal projections, which are optimized to maximally capture the information of the remaining data and meanwhile diminish that of the forgetting data. In training, LOFT simply optimizes a small-size projection matrix flexibly plugged into the pretrained model, and only requires one-shot feature fetching from the pretrained backbone instead of repetitively accessing the raw data. Hence, LOFT mitigates two critical issues in mainstream MU methods, i.e., the privacy leakage risk from massive data reload and the inefficiency of updates to the entire pretrained model. Extensive experiments validate the significantly lower computational overhead and superior unlearning performance of LOFT across diverse models, datasets, tasks, and applications. Code is anonymously available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/4352/.
VP-AutoTest: A Virtual-Physical Fusion Autonomous Driving Testing Platform
Dec 08, 2025Abstract:The rapid development of autonomous vehicles has led to a surge in testing demand. Traditional testing methods, such as virtual simulation, closed-course, and public road testing, face several challenges, including unrealistic vehicle states, limited testing capabilities, and high costs. These issues have prompted increasing interest in virtual-physical fusion testing. However, despite its potential, virtual-physical fusion testing still faces challenges, such as limited element types, narrow testing scope, and fixed evaluation metrics. To address these challenges, we propose the Virtual-Physical Testing Platform for Autonomous Vehicles (VP-AutoTest), which integrates over ten types of virtual and physical elements, including vehicles, pedestrians, and roadside infrastructure, to replicate the diversity of real-world traffic participants. The platform also supports both single-vehicle interaction and multi-vehicle cooperation testing, employing adversarial testing and parallel deduction to accelerate fault detection and explore algorithmic limits, while OBU and Redis communication enable seamless vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) cooperation across all levels of cooperative automation. Furthermore, VP-AutoTest incorporates a multidimensional evaluation framework and AI-driven expert systems to conduct comprehensive performance assessment and defect diagnosis. Finally, by comparing virtual-physical fusion test results with real-world experiments, the platform performs credibility self-evaluation to ensure both the fidelity and efficiency of autonomous driving testing. Please refer to the website for the full testing functionalities on the autonomous driving public service platform OnSite:https://www.onsite.com.cn.
Cross-View UAV Geo-Localization with Precision-Focused Efficient Design: A Hierarchical Distillation Approach with Multi-view Refinement
Oct 26, 2025Abstract:Cross-view geo-localization (CVGL) enables UAV localization by matching aerial images to geo-tagged satellite databases, which is critical for autonomous navigation in GNSS-denied environments. However, existing methods rely on resource-intensive fine-grained feature extraction and alignment, where multiple branches and modules significantly increase inference costs, limiting their deployment on edge devices. We propose Precision-Focused Efficient Design (PFED), a resource-efficient framework combining hierarchical knowledge transfer and multi-view representation refinement. This innovative method comprises two key components: 1) During training, Hierarchical Distillation paradigm for fast and accurate CVGL (HD-CVGL), coupled with Uncertainty-Aware Prediction Alignment (UAPA) to distill essential information and mitigate the data imbalance without incurring additional inference overhead. 2) During inference, an efficient Multi-view Refinement Module (MRM) leverages mutual information to filter redundant samples and effectively utilize the multi-view data. Extensive experiments show that PFED achieves state-of-the-art performance in both accuracy and efficiency, reaching 97.15\% Recall@1 on University-1652 while being over $5 \times$ more efficient in FLOPs and $3 \times$ faster than previous top methods. Furthermore, PFED runs at 251.5 FPS on the AGX Orin edge device, demonstrating its practical viability for real-time UAV applications. The project is available at https://github.com/SkyEyeLoc/PFED
CoReVLA: A Dual-Stage End-to-End Autonomous Driving Framework for Long-Tail Scenarios via Collect-and-Refine
Sep 19, 2025Abstract:Autonomous Driving (AD) systems have made notable progress, but their performance in long-tail, safety-critical scenarios remains limited. These rare cases contribute a disproportionate number of accidents. Vision-Language Action (VLA) models have strong reasoning abilities and offer a potential solution, but their effectiveness is limited by the lack of high-quality data and inefficient learning in such conditions. To address these challenges, we propose CoReVLA, a continual learning end-to-end autonomous driving framework that improves the performance in long-tail scenarios through a dual-stage process of data Collection and behavior Refinement. First, the model is jointly fine-tuned on a mixture of open-source driving QA datasets, allowing it to acquire a foundational understanding of driving scenarios. Next, CoReVLA is deployed within the Cave Automatic Virtual Environment (CAVE) simulation platform, where driver takeover data is collected from real-time interactions. Each takeover indicates a long-tail scenario that CoReVLA fails to handle reliably. Finally, the model is refined via Direct Preference Optimization (DPO), allowing it to learn directly from human preferences and thereby avoid reward hacking caused by manually designed rewards. Extensive open-loop and closed-loop experiments demonstrate that the proposed CoReVLA model can accurately perceive driving scenarios and make appropriate decisions. On the Bench2Drive benchmark, CoReVLA achieves a Driving Score (DS) of 72.18 and a Success Rate (SR) of 50%, outperforming state-of-the-art methods by 7.96 DS and 15% SR under long-tail, safety-critical scenarios. Furthermore, case studies demonstrate the model's ability to continually improve its performance in similar failure-prone scenarios by leveraging past takeover experiences. All codea and preprocessed datasets are available at: https://github.com/FanGShiYuu/CoReVLA
A Knowledge-Driven Diffusion Policy for End-to-End Autonomous Driving Based on Expert Routing
Sep 05, 2025Abstract:End-to-end autonomous driving remains constrained by the need to generate multi-modal actions, maintain temporal stability, and generalize across diverse scenarios. Existing methods often collapse multi-modality, struggle with long-horizon consistency, or lack modular adaptability. This paper presents KDP, a knowledge-driven diffusion policy that integrates generative diffusion modeling with a sparse mixture-of-experts routing mechanism. The diffusion component generates temporally coherent and multi-modal action sequences, while the expert routing mechanism activates specialized and reusable experts according to context, enabling modular knowledge composition. Extensive experiments across representative driving scenarios demonstrate that KDP achieves consistently higher success rates, reduced collision risk, and smoother control compared to prevailing paradigms. Ablation studies highlight the effectiveness of sparse expert activation and the Transformer backbone, and activation analyses reveal structured specialization and cross-scenario reuse of experts. These results establish diffusion with expert routing as a scalable and interpretable paradigm for knowledge-driven end-to-end autonomous driving.
Interactive Adversarial Testing of Autonomous Vehicles with Adjustable Confrontation Intensity
Jul 29, 2025Abstract:Scientific testing techniques are essential for ensuring the safe operation of autonomous vehicles (AVs), with high-risk, highly interactive scenarios being a primary focus. To address the limitations of existing testing methods, such as their heavy reliance on high-quality test data, weak interaction capabilities, and low adversarial robustness, this paper proposes ExamPPO, an interactive adversarial testing framework that enables scenario-adaptive and intensity-controllable evaluation of autonomous vehicles. The framework models the Surrounding Vehicle (SV) as an intelligent examiner, equipped with a multi-head attention-enhanced policy network, enabling context-sensitive and sustained behavioral interventions. A scalar confrontation factor is introduced to modulate the intensity of adversarial behaviors, allowing continuous, fine-grained adjustment of test difficulty. Coupled with structured evaluation metrics, ExamPPO systematically probes AV's robustness across diverse scenarios and strategies. Extensive experiments across multiple scenarios and AV strategies demonstrate that ExamPPO can effectively modulate adversarial behavior, expose decision-making weaknesses in tested AVs, and generalize across heterogeneous environments, thereby offering a unified and reproducible solution for evaluating the safety and intelligence of autonomous decision-making systems.
MiniMax-M1: Scaling Test-Time Compute Efficiently with Lightning Attention
Jun 16, 2025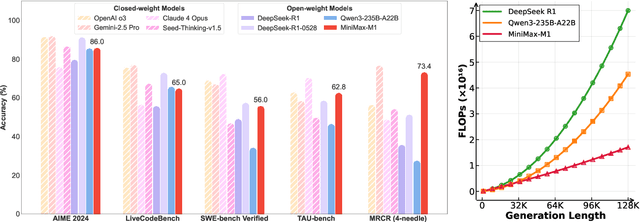
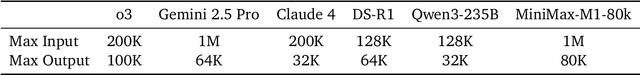
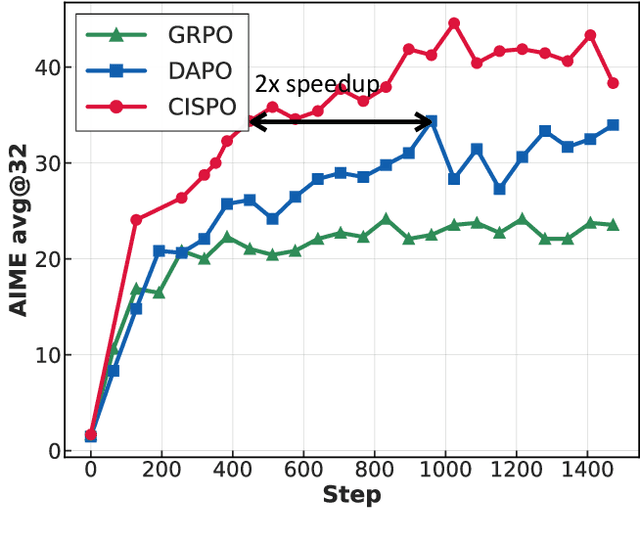
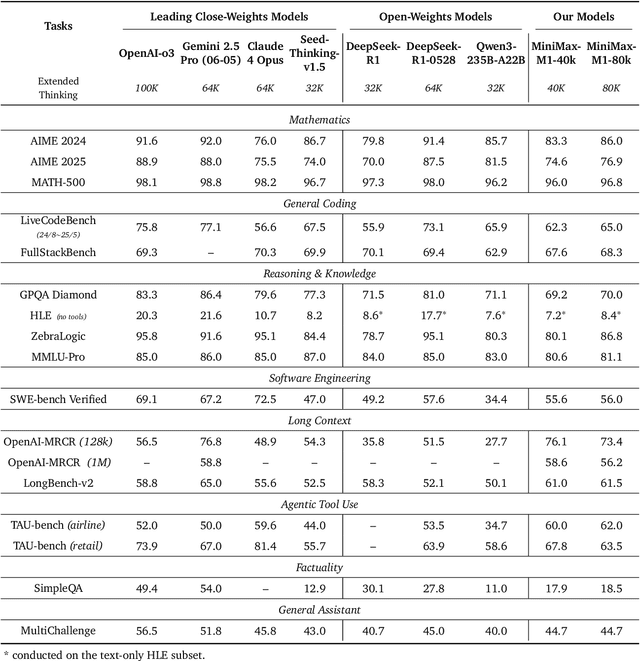
Abstract:We introduce MiniMax-M1, the world's first open-weight, large-scale hybrid-attention reasoning model. MiniMax-M1 is powered by a hybrid Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture combined with a lightning attention mechanism. The model is developed based on our previous MiniMax-Text-01 model, which contains a total of 456 billion parameters with 45.9 billion parameters activated per token. The M1 model natively supports a context length of 1 million tokens, 8x the context size of DeepSeek R1. Furthermore, the lightning attention mechanism in MiniMax-M1 enables efficient scaling of test-time compute. These properties make M1 particularly suitable for complex tasks that require processing long inputs and thinking extensively. MiniMax-M1 is trained using large-scale reinforcement learning (RL) on diverse problems including sandbox-based, real-world software engineering environments. In addition to M1's inherent efficiency advantage for RL training, we propose CISPO, a novel RL algorithm to further enhance RL efficiency. CISPO clips importance sampling weights rather than token updates, outperforming other competitive RL variants. Combining hybrid-attention and CISPO enables MiniMax-M1's full RL training on 512 H800 GPUs to complete in only three weeks, with a rental cost of just $534,700. We release two versions of MiniMax-M1 models with 40K and 80K thinking budgets respectively, where the 40K model represents an intermediate phase of the 80K training. Experiments on standard benchmarks show that our models are comparable or superior to strong open-weight models such as the original DeepSeek-R1 and Qwen3-235B, with particular strengths in complex software engineering, tool utilization, and long-context tasks. We publicly release MiniMax-M1 at https://github.com/MiniMax-AI/MiniMax-M1.
3D Hand Mesh-Guided AI-Generated Malformed Hand Refinement with Hand Pose Transformation via Diffusion Model
Jun 15, 2025Abstract:The malformed hands in the AI-generated images seriously affect the authenticity of the images. To refine malformed hands, existing depth-based approaches use a hand depth estimator to guide the refinement of malformed hands. Due to the performance limitations of the hand depth estimator, many hand details cannot be represented, resulting in errors in the generated hands, such as confusing the palm and the back of the hand. To solve this problem, we propose a 3D mesh-guided refinement framework using a diffusion pipeline. We use a state-of-the-art 3D hand mesh estimator, which provides more details of the hands. For training, we collect and reannotate a dataset consisting of RGB images and 3D hand mesh. Then we design a diffusion inpainting model to generate refined outputs guided by 3D hand meshes. For inference, we propose a double check algorithm to facilitate the 3D hand mesh estimator to obtain robust hand mesh guidance to obtain our refined results. Beyond malformed hand refinement, we propose a novel hand pose transformation method. It increases the flexibility and diversity of the malformed hand refinement task. We made the restored images mimic the hand poses of the reference images. The pose transformation requires no additional training. Extensive experimental results demonstrate the superior performance of our proposed method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge