Gang Wang
the State Key Lab of Intelligent Control and Decision of Complex Systems and the School of Automation, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, China, Beijing Institute of Technology Chongqing Innovation Center, Chongqing, China
HySparse: A Hybrid Sparse Attention Architecture with Oracle Token Selection and KV Cache Sharing
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:This work introduces Hybrid Sparse Attention (HySparse), a new architecture that interleaves each full attention layer with several sparse attention layers. While conceptually simple, HySparse strategically derives each sparse layer's token selection and KV caches directly from the preceding full attention layer. This architecture resolves two fundamental limitations of prior sparse attention methods. First, conventional approaches typically rely on additional proxies to predict token importance, introducing extra complexity and potentially suboptimal performance. In contrast, HySparse uses the full attention layer as a precise oracle to identify important tokens. Second, existing sparse attention designs often reduce computation without saving KV cache. HySparse enables sparse attention layers to reuse the full attention KV cache, thereby reducing both computation and memory. We evaluate HySparse on both 7B dense and 80B MoE models. Across all settings, HySparse consistently outperforms both full attention and hybrid SWA baselines. Notably, in the 80B MoE model with 49 total layers, only 5 layers employ full attention, yet HySparse achieves substantial performance gains while reducing KV cache storage by nearly 10x.
Mixture-of-World Models: Scaling Multi-Task Reinforcement Learning with Modular Latent Dynamics
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:A fundamental challenge in multi-task reinforcement learning (MTRL) is achieving sample efficiency in visual domains where tasks exhibit substantial heterogeneity in both observations and dynamics. Model-based reinforcement learning offers a promising path to improved sample efficiency through world models, but standard monolithic architectures struggle to capture diverse task dynamics, resulting in poor reconstruction and prediction accuracy. We introduce Mixture-of-World Models (MoW), a scalable architecture that combines modular variational autoencoders for task-adaptive visual compression, a hybrid Transformer-based dynamics model with task-conditioned experts and a shared backbone, and a gradient-based task clustering strategy for efficient parameter allocation. On the Atari 100k benchmark, a single MoW agent trained once on 26 Atari games achieves a mean human-normalized score of 110.4%, competitive with the score of 114.2% achieved by STORM, an ensemble of 26 task-specific models, while using 50% fewer parameters. On Meta-World, MoW achieves a 74.5% average success rate within 300 thousand environment steps, establishing a new state of the art. These results demonstrate that MoW provides a scalable and parameter-efficient foundation for generalist world models.
Talos: Optimizing Top-$K$ Accuracy in Recommender Systems
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Recommender systems (RS) aim to retrieve a small set of items that best match individual user preferences. Naturally, RS place primary emphasis on the quality of the Top-$K$ results rather than performance across the entire item set. However, estimating Top-$K$ accuracy (e.g., Precision@$K$, Recall@$K$) requires determining the ranking positions of items, which imposes substantial computational overhead and poses significant challenges for optimization. In addition, RS often suffer from distribution shifts due to evolving user preferences or data biases, further complicating the task. To address these issues, we propose Talos, a loss function that is specifically designed to optimize the Talos recommendation accuracy. Talos leverages a quantile technique that replaces the complex ranking-dependent operations into simpler comparisons between predicted scores and learned score thresholds. We further develop a sampling-based regression algorithm for efficient and accurate threshold estimation, and introduce a constraint term to maintain optimization stability by preventing score inflation. Additionally, we incorporate a tailored surrogate function to address discontinuity and enhance robustness against distribution shifts. Comprehensive theoretical analyzes and empirical experiments are conducted to demonstrate the effectiveness, efficiency, convergence, and distributional robustness of Talos. The code is available at https://github.com/cynthia-shengjia/WWW-2026-Talos.
ChatAD: Reasoning-Enhanced Time-Series Anomaly Detection with Multi-Turn Instruction Evolution
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:LLM-driven Anomaly Detection (AD) helps enhance the understanding and explanatory abilities of anomalous behaviors in Time Series (TS). Existing methods face challenges of inadequate reasoning ability, deficient multi-turn dialogue capability, and narrow generalization. To this end, we 1) propose a multi-agent-based TS Evolution algorithm named TSEvol. On top of it, we 2) introduce the AD reasoning and multi-turn dialogue Dataset TSEData-20K and contribute the Chatbot family for AD, including ChatAD-Llama3-8B, Qwen2.5-7B, and Mistral-7B. Furthermore, 3) we propose the TS Kahneman-Tversky Optimization (TKTO) to enhance ChatAD's cross-task generalization capability. Lastly, 4) we propose a LLM-driven Learning-based AD Benchmark LLADBench to evaluate the performance of ChatAD and nine baselines across seven datasets and tasks. Our three ChatAD models achieve substantial gains, up to 34.50% in accuracy, 34.71% in F1, and a 37.42% reduction in false positives. Besides, via KTKO, our optimized ChatAD achieves competitive performance in reasoning and cross-task generalization on classification, forecasting, and imputation.
AgentGC: Evolutionary Learning-based Lossless Compression for Genomics Data with LLM-driven Multiple Agent
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Lossless compression has made significant advancements in Genomics Data (GD) storage, sharing and management. Current learning-based methods are non-evolvable with problems of low-level compression modeling, limited adaptability, and user-unfriendly interface. To this end, we propose AgentGC, the first evolutionary Agent-based GD Compressor, consisting of 3 layers with multi-agent named Leader and Worker. Specifically, the 1) User layer provides a user-friendly interface via Leader combined with LLM; 2) Cognitive layer, driven by the Leader, integrates LLM to consider joint optimization of algorithm-dataset-system, addressing the issues of low-level modeling and limited adaptability; and 3) Compression layer, headed by Worker, performs compression & decompression via a automated multi-knowledge learning-based compression framework. On top of AgentGC, we design 3 modes to support diverse scenarios: CP for compression-ratio priority, TP for throughput priority, and BM for balanced mode. Compared with 14 baselines on 9 datasets, the average compression ratios gains are 16.66%, 16.11%, and 16.33%, the throughput gains are 4.73x, 9.23x, and 9.15x, respectively.
Beyond BeautifulSoup: Benchmarking LLM-Powered Web Scraping for Everyday Users
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:Web scraping has historically required technical expertise in HTML parsing, session management, and authentication circumvention, which limited large-scale data extraction to skilled developers. We argue that large language models (LLMs) have democratized web scraping, enabling low-skill users to execute sophisticated operations through simple natural language prompts. While extensive benchmarks evaluate these tools under optimal expert conditions, we show that without extensive manual effort, current LLM-based workflows allow novice users to scrape complex websites that would otherwise be inaccessible. We systematically benchmark what everyday users can do with off-the-shelf LLM tools across 35 sites spanning five security tiers, including authentication, anti-bot, and CAPTCHA controls. We devise and evaluate two distinct workflows: (a) LLM-assisted scripting, where users prompt LLMs to generate traditional scraping code but maintain manual execution control, and (b) end-to-end LLM agents, which autonomously navigate and extract data through integrated tool use. Our results demonstrate that end-to-end agents have made complex scraping accessible - requiring as little as a single prompt with minimal refinement (less than 5 changes) to complete workflows. We also highlight scenarios where LLM-assisted scripting may be simpler and faster for static sites. In light of these findings, we provide simple procedures for novices to use these workflows and gauge what adversaries could achieve using these.
MiMo-V2-Flash Technical Report
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:We present MiMo-V2-Flash, a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) model with 309B total parameters and 15B active parameters, designed for fast, strong reasoning and agentic capabilities. MiMo-V2-Flash adopts a hybrid attention architecture that interleaves Sliding Window Attention (SWA) with global attention, with a 128-token sliding window under a 5:1 hybrid ratio. The model is pre-trained on 27 trillion tokens with Multi-Token Prediction (MTP), employing a native 32k context length and subsequently extended to 256k. To efficiently scale post-training compute, MiMo-V2-Flash introduces a novel Multi-Teacher On-Policy Distillation (MOPD) paradigm. In this framework, domain-specialized teachers (e.g., trained via large-scale reinforcement learning) provide dense and token-level reward, enabling the student model to perfectly master teacher expertise. MiMo-V2-Flash rivals top-tier open-weight models such as DeepSeek-V3.2 and Kimi-K2, despite using only 1/2 and 1/3 of their total parameters, respectively. During inference, by repurposing MTP as a draft model for speculative decoding, MiMo-V2-Flash achieves up to 3.6 acceptance length and 2.6x decoding speedup with three MTP layers. We open-source both the model weights and the three-layer MTP weights to foster open research and community collaboration.
MiMo-Audio: Audio Language Models are Few-Shot Learners
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Existing audio language models typically rely on task-specific fine-tuning to accomplish particular audio tasks. In contrast, humans are able to generalize to new audio tasks with only a few examples or simple instructions. GPT-3 has shown that scaling next-token prediction pretraining enables strong generalization capabilities in text, and we believe this paradigm is equally applicable to the audio domain. By scaling MiMo-Audio's pretraining data to over one hundred million of hours, we observe the emergence of few-shot learning capabilities across a diverse set of audio tasks. We develop a systematic evaluation of these capabilities and find that MiMo-Audio-7B-Base achieves SOTA performance on both speech intelligence and audio understanding benchmarks among open-source models. Beyond standard metrics, MiMo-Audio-7B-Base generalizes to tasks absent from its training data, such as voice conversion, style transfer, and speech editing. MiMo-Audio-7B-Base also demonstrates powerful speech continuation capabilities, capable of generating highly realistic talk shows, recitations, livestreaming and debates. At the post-training stage, we curate a diverse instruction-tuning corpus and introduce thinking mechanisms into both audio understanding and generation. MiMo-Audio-7B-Instruct achieves open-source SOTA on audio understanding benchmarks (MMSU, MMAU, MMAR, MMAU-Pro), spoken dialogue benchmarks (Big Bench Audio, MultiChallenge Audio) and instruct-TTS evaluations, approaching or surpassing closed-source models. Model checkpoints and full evaluation suite are available at https://github.com/XiaomiMiMo/MiMo-Audio.
MMDrive: Interactive Scene Understanding Beyond Vision with Multi-representational Fusion
Dec 16, 2025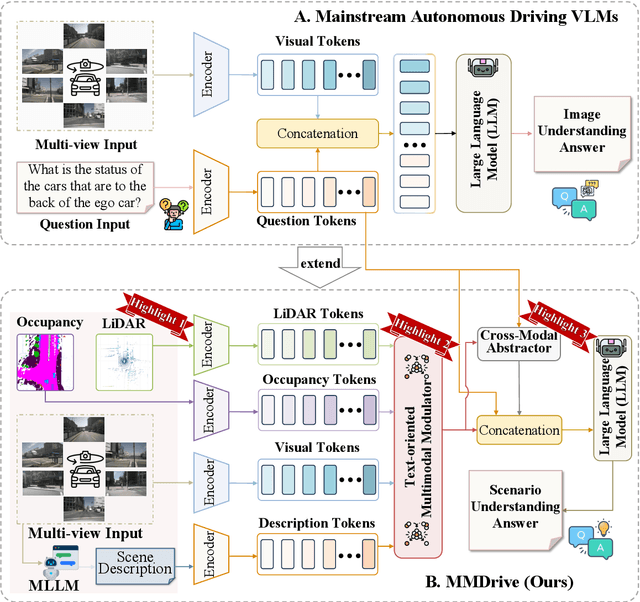
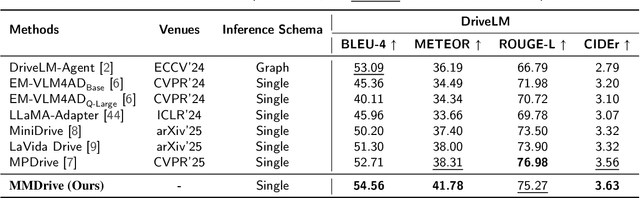

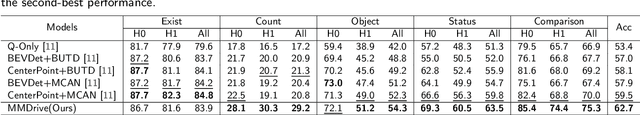
Abstract:Vision-language models enable the understanding and reasoning of complex traffic scenarios through multi-source information fusion, establishing it as a core technology for autonomous driving. However, existing vision-language models are constrained by the image understanding paradigm in 2D plane, which restricts their capability to perceive 3D spatial information and perform deep semantic fusion, resulting in suboptimal performance in complex autonomous driving environments. This study proposes MMDrive, an multimodal vision-language model framework that extends traditional image understanding to a generalized 3D scene understanding framework. MMDrive incorporates three complementary modalities, including occupancy maps, LiDAR point clouds, and textual scene descriptions. To this end, it introduces two novel components for adaptive cross-modal fusion and key information extraction. Specifically, the Text-oriented Multimodal Modulator dynamically weights the contributions of each modality based on the semantic cues in the question, guiding context-aware feature integration. The Cross-Modal Abstractor employs learnable abstract tokens to generate compact, cross-modal summaries that highlight key regions and essential semantics. Comprehensive evaluations on the DriveLM and NuScenes-QA benchmarks demonstrate that MMDrive achieves significant performance gains over existing vision-language models for autonomous driving, with a BLEU-4 score of 54.56 and METEOR of 41.78 on DriveLM, and an accuracy score of 62.7% on NuScenes-QA. MMDrive effectively breaks the traditional image-only understanding barrier, enabling robust multimodal reasoning in complex driving environments and providing a new foundation for interpretable autonomous driving scene understanding.
TCM-Eval: An Expert-Level Dynamic and Extensible Benchmark for Traditional Chinese Medicine
Nov 10, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in modern medicine, yet their application in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) remains severely limited by the absence of standardized benchmarks and the scarcity of high-quality training data. To address these challenges, we introduce TCM-Eval, the first dynamic and extensible benchmark for TCM, meticulously curated from national medical licensing examinations and validated by TCM experts. Furthermore, we construct a large-scale training corpus and propose Self-Iterative Chain-of-Thought Enhancement (SI-CoTE) to autonomously enrich question-answer pairs with validated reasoning chains through rejection sampling, establishing a virtuous cycle of data and model co-evolution. Using this enriched training data, we develop ZhiMingTang (ZMT), a state-of-the-art LLM specifically designed for TCM, which significantly exceeds the passing threshold for human practitioners. To encourage future research and development, we release a public leaderboard, fostering community engagement and continuous improvement.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge