Hailin Zhang
HySparse: A Hybrid Sparse Attention Architecture with Oracle Token Selection and KV Cache Sharing
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:This work introduces Hybrid Sparse Attention (HySparse), a new architecture that interleaves each full attention layer with several sparse attention layers. While conceptually simple, HySparse strategically derives each sparse layer's token selection and KV caches directly from the preceding full attention layer. This architecture resolves two fundamental limitations of prior sparse attention methods. First, conventional approaches typically rely on additional proxies to predict token importance, introducing extra complexity and potentially suboptimal performance. In contrast, HySparse uses the full attention layer as a precise oracle to identify important tokens. Second, existing sparse attention designs often reduce computation without saving KV cache. HySparse enables sparse attention layers to reuse the full attention KV cache, thereby reducing both computation and memory. We evaluate HySparse on both 7B dense and 80B MoE models. Across all settings, HySparse consistently outperforms both full attention and hybrid SWA baselines. Notably, in the 80B MoE model with 49 total layers, only 5 layers employ full attention, yet HySparse achieves substantial performance gains while reducing KV cache storage by nearly 10x.
JudgeRLVR: Judge First, Generate Second for Efficient Reasoning
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) has become a standard paradigm for reasoning in Large Language Models. However, optimizing solely for final-answer correctness often drives models into aimless, verbose exploration, where they rely on exhaustive trial-and-error tactics rather than structured planning to reach solutions. While heuristic constraints like length penalties can reduce verbosity, they often truncate essential reasoning steps, creating a difficult trade-off between efficiency and verification. In this paper, we argue that discriminative capability is a prerequisite for efficient generation: by learning to distinguish valid solutions, a model can internalize a guidance signal that prunes the search space. We propose JudgeRLVR, a two-stage judge-then-generate paradigm. In the first stage, we train the model to judge solution responses with verifiable answers. In the second stage, we fine-tune the same model with vanilla generating RLVR initialized from the judge. Compared to Vanilla RLVR using the same math-domain training data, JudgeRLVR achieves a better quality--efficiency trade-off for Qwen3-30B-A3B: on in-domain math, it delivers about +3.7 points average accuracy gain with -42\% average generation length; on out-of-domain benchmarks, it delivers about +4.5 points average accuracy improvement, demonstrating enhanced generalization.
MiMo-V2-Flash Technical Report
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:We present MiMo-V2-Flash, a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) model with 309B total parameters and 15B active parameters, designed for fast, strong reasoning and agentic capabilities. MiMo-V2-Flash adopts a hybrid attention architecture that interleaves Sliding Window Attention (SWA) with global attention, with a 128-token sliding window under a 5:1 hybrid ratio. The model is pre-trained on 27 trillion tokens with Multi-Token Prediction (MTP), employing a native 32k context length and subsequently extended to 256k. To efficiently scale post-training compute, MiMo-V2-Flash introduces a novel Multi-Teacher On-Policy Distillation (MOPD) paradigm. In this framework, domain-specialized teachers (e.g., trained via large-scale reinforcement learning) provide dense and token-level reward, enabling the student model to perfectly master teacher expertise. MiMo-V2-Flash rivals top-tier open-weight models such as DeepSeek-V3.2 and Kimi-K2, despite using only 1/2 and 1/3 of their total parameters, respectively. During inference, by repurposing MTP as a draft model for speculative decoding, MiMo-V2-Flash achieves up to 3.6 acceptance length and 2.6x decoding speedup with three MTP layers. We open-source both the model weights and the three-layer MTP weights to foster open research and community collaboration.
MiMo-Audio: Audio Language Models are Few-Shot Learners
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Existing audio language models typically rely on task-specific fine-tuning to accomplish particular audio tasks. In contrast, humans are able to generalize to new audio tasks with only a few examples or simple instructions. GPT-3 has shown that scaling next-token prediction pretraining enables strong generalization capabilities in text, and we believe this paradigm is equally applicable to the audio domain. By scaling MiMo-Audio's pretraining data to over one hundred million of hours, we observe the emergence of few-shot learning capabilities across a diverse set of audio tasks. We develop a systematic evaluation of these capabilities and find that MiMo-Audio-7B-Base achieves SOTA performance on both speech intelligence and audio understanding benchmarks among open-source models. Beyond standard metrics, MiMo-Audio-7B-Base generalizes to tasks absent from its training data, such as voice conversion, style transfer, and speech editing. MiMo-Audio-7B-Base also demonstrates powerful speech continuation capabilities, capable of generating highly realistic talk shows, recitations, livestreaming and debates. At the post-training stage, we curate a diverse instruction-tuning corpus and introduce thinking mechanisms into both audio understanding and generation. MiMo-Audio-7B-Instruct achieves open-source SOTA on audio understanding benchmarks (MMSU, MMAU, MMAR, MMAU-Pro), spoken dialogue benchmarks (Big Bench Audio, MultiChallenge Audio) and instruct-TTS evaluations, approaching or surpassing closed-source models. Model checkpoints and full evaluation suite are available at https://github.com/XiaomiMiMo/MiMo-Audio.
SALE : Low-bit Estimation for Efficient Sparse Attention in Long-context LLM Prefilling
May 30, 2025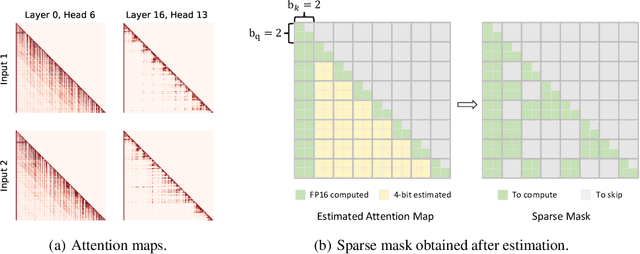
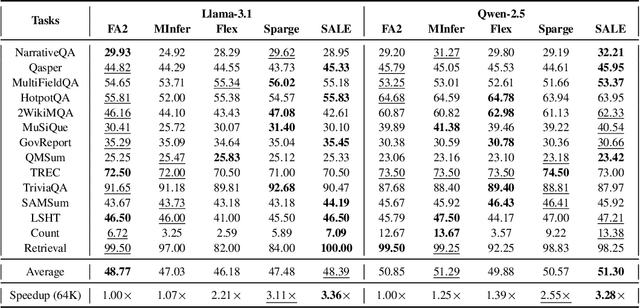
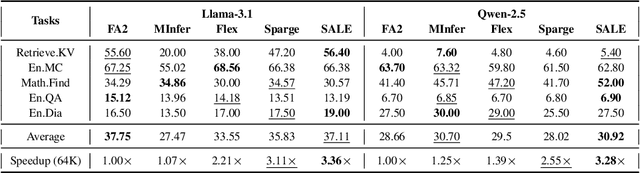
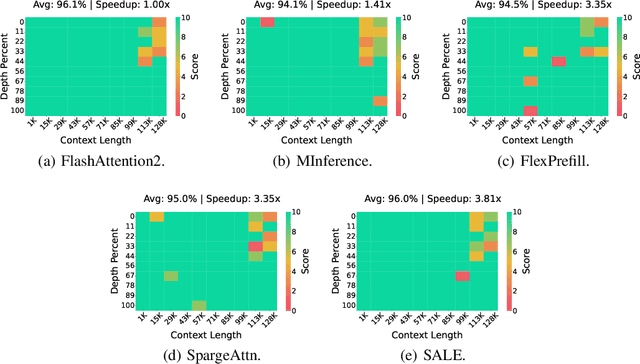
Abstract:Many advanced Large Language Model (LLM) applications require long-context processing, but the self-attention module becomes a bottleneck during the prefilling stage of inference due to its quadratic time complexity with respect to sequence length. Existing sparse attention methods accelerate attention computation by skipping less significant regions of the attention map. However, these approaches typically perform coarse-grained inspection of the attention map, rendering considerable loss in model accuracy. In this paper, we propose SALE, a fine-grained sparse attention method that accelerates the long-context prefilling stage of LLM with negligible loss in model accuracy. SALE achieves fast and accurate fine-grained attention weight estimation through 4-bit quantized query-key products, followed by block-sparse attention to accelerate prefilling computations. For importance evaluation for query-key pairs, we adopt our Relative Attention Score metric, which offers significantly higher efficiency within our framework. We implement a custom CUDA kernel optimized for our approach for hardware efficiency, reducing the additional overhead to approximately 11% of the full attention latency. Notably, SALE requires no parameter training and can be seamlessly integrated into existing systems with trivial code modifications. Experiments on long-context benchmarks demonstrate that our method outperforms existing approaches in accuracy-efficiency trade-offs, achieving at least 3.36x speedups on Llama-3.1-8B for sequences longer than 64K while maintaining model quality.
MiMo: Unlocking the Reasoning Potential of Language Model -- From Pretraining to Posttraining
May 12, 2025Abstract:We present MiMo-7B, a large language model born for reasoning tasks, with optimization across both pre-training and post-training stages. During pre-training, we enhance the data preprocessing pipeline and employ a three-stage data mixing strategy to strengthen the base model's reasoning potential. MiMo-7B-Base is pre-trained on 25 trillion tokens, with additional Multi-Token Prediction objective for enhanced performance and accelerated inference speed. During post-training, we curate a dataset of 130K verifiable mathematics and programming problems for reinforcement learning, integrating a test-difficulty-driven code-reward scheme to alleviate sparse-reward issues and employing strategic data resampling to stabilize training. Extensive evaluations show that MiMo-7B-Base possesses exceptional reasoning potential, outperforming even much larger 32B models. The final RL-tuned model, MiMo-7B-RL, achieves superior performance on mathematics, code and general reasoning tasks, surpassing the performance of OpenAI o1-mini. The model checkpoints are available at https://github.com/xiaomimimo/MiMo.
Orbital-Angular-Momentum Versus MIMO: Orthogonality, Degree of Freedom,and Capacity
Aug 13, 2024



Abstract:The plane wave based wireless communications have becoming more and more matured, along with the well utilization of the traditional resources such as time and frequency. To further increase the capacity for rapidly increasing capacity demand of wireless communications, it is potential to use the twist wave, which has the orbital angular momentum (OAM). In this paper, we discuss the OAM based wireless communications in the aspect of orthogonality, degree of freedom (DoF), and capacity, where both the transmitter and the receiver use uniform circular array (UCA) antennas. In particular, we compare OAM based wireless communications with multiple-input-multiple-output (MIMO) based wireless communications in terms of DoF and capacity. Numerical results are presented to validate and evaluate that the DoF of OAM based wireless communications is greater than or equal to that of correlated MIMO based wireless communications when the transmitter and the receiver antennas are aligned well. The OAM based wireless communications can achieve larger capacity than the correlated MIMO in high signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) region under line-of-sight scenario.
Achieving Practical OAM Based Wireless Communications With Misaligned Transceiver
Aug 13, 2024



Abstract:Orbital angular momentum (OAM) has attracted much attention for radio vortex wireless communications due to the orthogonality among different OAM-modes. To maintain the orthogonality among different OAM modes at the receiver, the strict alignment between transmit and receive antennas is highly demanded. However, it is not practical to guarantee the transceiver alignment in wireless communications. The phase turbulence, resulting from the misaligned transceivers, leads to serious inter-mode interference among different OAM modes and therefore fail for signals detection of multiple OAM modes at the receiver. To achieve practical OAM based wireless communications, in this paper we investigate the radio vortex wireless communications with misaligned transmit and receive antennas. We propose a joint Beamforming and Pre-detection (BePre) scheme, which uses two unitary matrices to convert the channel matrix into the equivalent circulant matrix for keeping the orthogonality among OAM-modes at the receiver. Then, the OAM signals can be detected with the mode-decomposition scheme at the misaligned receiver. Extensive simulations obtained validate and evaluate that our developed joint BePre scheme can efficiently detect the signals of multiple OAM-modes for the misaligned transceiver and can significantly increase the spectrum efficiency.
Orbital-Angular-Momentum Embedded Massive MIMO: Achieving Multiplicative Spectrum-Efficiency for mmWave Communications
Aug 13, 2024



Abstract:By enabling very high bandwidth for radio communications, the millimeter-wave (mmWave), which can easily be integrated with massive-multiple-input-multiple-output (massive-MIMO) due to small antenna size, has been attracting growing attention as a candidate for the fifth-generation (5G) and 5G-beyond wireless communications networks. On the other hand, the communication over the orthogonal states/modes of orbital angular momentum (OAM) is a subset of the solutions offered by massive-MIMO communications. Traditional massive-MIMO based mmWave communications did not concern the potential spectrum-efficiency-gain (SE-gain) offered by orthogonal states of OAM. However, the highly expecting maximum SE-gain for OAM and massive-MIMO communications is the product of SE-gains offered by OAM and multiplexing-MIMO. In this paper, we propose the OAM-embedded-MIMO (OEM) communication framework to obtain the multiplicative SE-gain for joint OAM and massive-MIMO based mmWave wireless communications. We design the parabolic antenna for each uniform circular array antenna to converge OAM signals. Then, we develop the mode-decomposition and multiplexing-detection scheme to obtain the transmit signal on each OAM-mode of each transmit antenna. Also, we develop the OEM-water-filling power allocation policy to achieve the maximum multiplicative SE-gain for OEM communications. The extensive simulations obtained validate and evaluate our developed parabolic antenna based converging method, mode-decomposition and multiplexing-detection scheme, and OEM-water-filling policy, showing that our proposed OEM mmWave communications can significantly increase the spectrum-efficiency as compared with traditional massive-MIMO based mmWave communications.
Quasi-Fractal UCA Based OAM for Highly Efficient Orthogonal Transmission
Aug 10, 2024



Abstract:The development of orbital angular momentum (OAM)-based radio vortex transmission presents a promising opportunity for increasing the capacity of wireless communication in correlated channels due to its inherent orthogonality among different OAM modes. One of the most popular schemes for high-efficient OAM transmission is the digital baseband associated with uniform circular array (UCA) based transceiver. However, the periodicity of complex-exponential feed makes the maximum number of orthogonal signals carried by multiple OAM modes generally restricted to the array-element number of UCA antenna, which poses an open question of how to employ more OAM modes given a fixed number of array elements. Furthermore, signals modulated with high-order OAM modes are difficult to be captured by the receiver due to their serious divergence as propagating in free space, thus severely limiting the capacity of radio vortex communications. To overcome the above challenges, in this paper based on the partly element-overlapped fractal geometry layout and effectively using low-order OAM modes, we propose the quasi-fractal UCA (QF-UCA) antenna based OAM multiplexing transmission. We perform the two-dimension OAM modulation (TOM) and demodulation (TOD) schemes with the orthogonal OAM mode number exceeding the array-element number, which is beyond the traditional concept of multiple antennas based wireless communications. Simulation results show that our proposed scheme can achieve more number of orthogonal multiplexing streams than the maximum number of orthogonal multiplexing corresponding to traditional multiple antenna systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge