Shiyao Wang
ALPBench: A Benchmark for Attribution-level Long-term Personal Behavior Understanding
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Recent advances in large language models have highlighted their potential for personalized recommendation, where accurately capturing user preferences remains a key challenge. Leveraging their strong reasoning and generalization capabilities, LLMs offer new opportunities for modeling long-term user behavior. To systematically evaluate this, we introduce ALPBench, a Benchmark for Attribution-level Long-term Personal Behavior Understanding. Unlike item-focused benchmarks, ALPBench predicts user-interested attribute combinations, enabling ground-truth evaluation even for newly introduced items. It models preferences from long-term historical behaviors rather than users' explicitly expressed requests, better reflecting enduring interests. User histories are represented as natural language sequences, allowing interpretable, reasoning-based personalization. ALPBench enables fine-grained evaluation of personalization by focusing on the prediction of attribute combinations task that remains highly challenging for current LLMs due to the need to capture complex interactions among multiple attributes and reason over long-term user behavior sequences.
OneMall: One Architecture, More Scenarios -- End-to-End Generative Recommender Family at Kuaishou E-Commerce
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:In the wave of generative recommendation, we present OneMall, an end-to-end generative recommendation framework tailored for e-commerce services at Kuaishou. Our OneMall systematically unifies the e-commerce's multiple item distribution scenarios, such as Product-card, short-video and live-streaming. Specifically, it comprises three key components, aligning the entire model training pipeline to the LLM's pre-training/post-training: (1) E-commerce Semantic Tokenizer: we provide a tokenizer solution that captures both real-world semantics and business-specific item relations across different scenarios; (2) Transformer-based Architecture: we largely utilize Transformer as our model backbone, e.g., employing Query-Former for long sequence compression, Cross-Attention for multi-behavior sequence fusion, and Sparse MoE for scalable auto-regressive generation; (3) Reinforcement Learning Pipeline: we further connect retrieval and ranking models via RL, enabling the ranking model to serve as a reward signal for end-to-end policy retrieval model optimization. Extensive experiments demonstrate that OneMall achieves consistent improvements across all e-commerce scenarios: +13.01\% GMV in product-card, +15.32\% Orders in Short-Video, and +2.78\% Orders in Live-Streaming. OneMall has been deployed, serving over 400 million daily active users at Kuaishou.
OneMall: One Model, More Scenarios -- End-to-End Generative Recommender Family at Kuaishou E-Commerce
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:In the wave of generative recommendation, we present OneMall, an end-to-end generative recommendation framework tailored for e-commerce services at Kuaishou. Our OneMall systematically unifies the e-commerce's multiple item distribution scenarios, such as Product-card, short-video and live-streaming. Specifically, it comprises three key components, aligning the entire model training pipeline to the LLM's pre-training/post-training: (1) E-commerce Semantic Tokenizer: we provide a tokenizer solution that captures both real-world semantics and business-specific item relations across different scenarios; (2) Transformer-based Architecture: we largely utilize Transformer as our model backbone, e.g., employing Query-Former for long sequence compression, Cross-Attention for multi-behavior sequence fusion, and Sparse MoE for scalable auto-regressive generation; (3) Reinforcement Learning Pipeline: we further connect retrieval and ranking models via RL, enabling the ranking model to serve as a reward signal for end-to-end policy retrieval model optimization. Extensive experiments demonstrate that OneMall achieves consistent improvements across all e-commerce scenarios: +13.01\% GMV in product-card, +15.32\% Orders in Short-Video, and +2.78\% Orders in Live-Streaming. OneMall has been deployed, serving over 400 million daily active users at Kuaishou.
Unleashing the Native Recommendation Potential: LLM-Based Generative Recommendation via Structured Term Identifiers
Jan 11, 2026Abstract:Leveraging the vast open-world knowledge and understanding capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) to develop general-purpose, semantically-aware recommender systems has emerged as a pivotal research direction in generative recommendation. However, existing methods face bottlenecks in constructing item identifiers. Text-based methods introduce LLMs' vast output space, leading to hallucination, while methods based on Semantic IDs (SIDs) encounter a semantic gap between SIDs and LLMs' native vocabulary, requiring costly vocabulary expansion and alignment training. To address this, this paper introduces Term IDs (TIDs), defined as a set of semantically rich and standardized textual keywords, to serve as robust item identifiers. We propose GRLM, a novel framework centered on TIDs, employs Context-aware Term Generation to convert item's metadata into standardized TIDs and utilizes Integrative Instruction Fine-tuning to collaboratively optimize term internalization and sequential recommendation. Additionally, Elastic Identifier Grounding is designed for robust item mapping. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets demonstrate that GRLM significantly outperforms baselines across multiple scenarios, pointing a promising direction for generalizable and high-performance generative recommendation systems.
OpenOneRec Technical Report
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:While the OneRec series has successfully unified the fragmented recommendation pipeline into an end-to-end generative framework, a significant gap remains between recommendation systems and general intelligence. Constrained by isolated data, they operate as domain specialists-proficient in pattern matching but lacking world knowledge, reasoning capabilities, and instruction following. This limitation is further compounded by the lack of a holistic benchmark to evaluate such integrated capabilities. To address this, our contributions are: 1) RecIF Bench & Open Data: We propose RecIF-Bench, a holistic benchmark covering 8 diverse tasks that thoroughly evaluate capabilities from fundamental prediction to complex reasoning. Concurrently, we release a massive training dataset comprising 96 million interactions from 160,000 users to facilitate reproducible research. 2) Framework & Scaling: To ensure full reproducibility, we open-source our comprehensive training pipeline, encompassing data processing, co-pretraining, and post-training. Leveraging this framework, we demonstrate that recommendation capabilities can scale predictably while mitigating catastrophic forgetting of general knowledge. 3) OneRec-Foundation: We release OneRec Foundation (1.7B and 8B), a family of models establishing new state-of-the-art (SOTA) results across all tasks in RecIF-Bench. Furthermore, when transferred to the Amazon benchmark, our models surpass the strongest baselines with an average 26.8% improvement in Recall@10 across 10 diverse datasets (Figure 1). This work marks a step towards building truly intelligent recommender systems. Nonetheless, realizing this vision presents significant technical and theoretical challenges, highlighting the need for broader research engagement in this promising direction.
OneRec-V2 Technical Report
Aug 28, 2025



Abstract:Recent breakthroughs in generative AI have transformed recommender systems through end-to-end generation. OneRec reformulates recommendation as an autoregressive generation task, achieving high Model FLOPs Utilization. While OneRec-V1 has shown significant empirical success in real-world deployment, two critical challenges hinder its scalability and performance: (1) inefficient computational allocation where 97.66% of resources are consumed by sequence encoding rather than generation, and (2) limitations in reinforcement learning relying solely on reward models. To address these challenges, we propose OneRec-V2, featuring: (1) Lazy Decoder-Only Architecture: Eliminates encoder bottlenecks, reducing total computation by 94% and training resources by 90%, enabling successful scaling to 8B parameters. (2) Preference Alignment with Real-World User Interactions: Incorporates Duration-Aware Reward Shaping and Adaptive Ratio Clipping to better align with user preferences using real-world feedback. Extensive A/B tests on Kuaishou demonstrate OneRec-V2's effectiveness, improving App Stay Time by 0.467%/0.741% while balancing multi-objective recommendations. This work advances generative recommendation scalability and alignment with real-world feedback, representing a step forward in the development of end-to-end recommender systems.
MISS: Multi-Modal Tree Indexing and Searching with Lifelong Sequential Behavior for Retrieval Recommendation
Aug 20, 2025



Abstract:Large-scale industrial recommendation systems typically employ a two-stage paradigm of retrieval and ranking to handle huge amounts of information. Recent research focuses on improving the performance of retrieval model. A promising way is to introduce extensive information about users and items. On one hand, lifelong sequential behavior is valuable. Existing lifelong behavior modeling methods in ranking stage focus on the interaction of lifelong behavior and candidate items from retrieval stage. In retrieval stage, it is difficult to utilize lifelong behavior because of a large corpus of candidate items. On the other hand, existing retrieval methods mostly relay on interaction information, potentially disregarding valuable multi-modal information. To solve these problems, we represent the pioneering exploration of leveraging multi-modal information and lifelong sequence model within the advanced tree-based retrieval model. We propose Multi-modal Indexing and Searching with lifelong Sequence (MISS), which contains a multi-modal index tree and a multi-modal lifelong sequence modeling module. Specifically, for better index structure, we propose multi-modal index tree, which is built using the multi-modal embedding to precisely represent item similarity. To precisely capture diverse user interests in user lifelong sequence, we propose collaborative general search unit (Co-GSU) and multi-modal general search unit (MM-GSU) for multi-perspective interests searching.
Kwai Keye-VL Technical Report
Jul 02, 2025Abstract:While Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) demonstrate remarkable capabilities on static images, they often fall short in comprehending dynamic, information-dense short-form videos, a dominant medium in today's digital landscape. To bridge this gap, we introduce \textbf{Kwai Keye-VL}, an 8-billion-parameter multimodal foundation model engineered for leading-edge performance in short-video understanding while maintaining robust general-purpose vision-language abilities. The development of Keye-VL rests on two core pillars: a massive, high-quality dataset exceeding 600 billion tokens with a strong emphasis on video, and an innovative training recipe. This recipe features a four-stage pre-training process for solid vision-language alignment, followed by a meticulous two-phase post-training process. The first post-training stage enhances foundational capabilities like instruction following, while the second phase focuses on stimulating advanced reasoning. In this second phase, a key innovation is our five-mode ``cold-start'' data mixture, which includes ``thinking'', ``non-thinking'', ``auto-think'', ``think with image'', and high-quality video data. This mixture teaches the model to decide when and how to reason. Subsequent reinforcement learning (RL) and alignment steps further enhance these reasoning capabilities and correct abnormal model behaviors, such as repetitive outputs. To validate our approach, we conduct extensive evaluations, showing that Keye-VL achieves state-of-the-art results on public video benchmarks and remains highly competitive on general image-based tasks (Figure 1). Furthermore, we develop and release the \textbf{KC-MMBench}, a new benchmark tailored for real-world short-video scenarios, where Keye-VL shows a significant advantage.
Kling-Foley: Multimodal Diffusion Transformer for High-Quality Video-to-Audio Generation
Jun 24, 2025
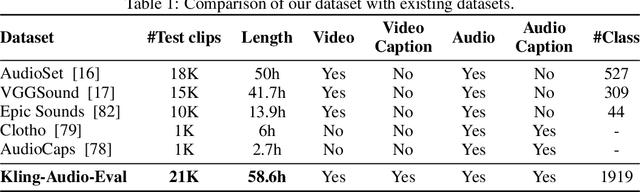
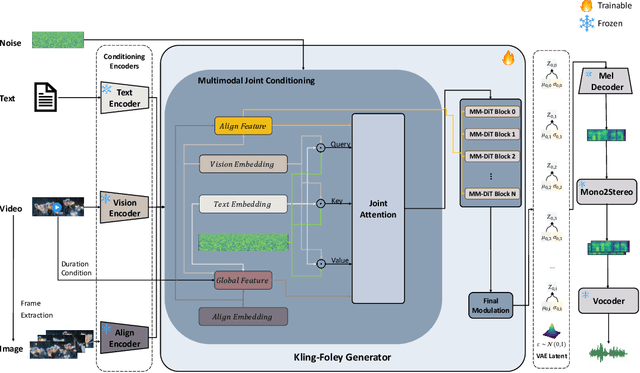
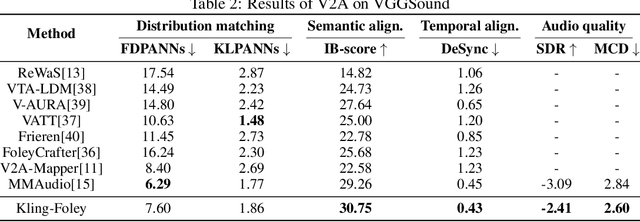
Abstract:We propose Kling-Foley, a large-scale multimodal Video-to-Audio generation model that synthesizes high-quality audio synchronized with video content. In Kling-Foley, we introduce multimodal diffusion transformers to model the interactions between video, audio, and text modalities, and combine it with a visual semantic representation module and an audio-visual synchronization module to enhance alignment capabilities. Specifically, these modules align video conditions with latent audio elements at the frame level, thereby improving semantic alignment and audio-visual synchronization. Together with text conditions, this integrated approach enables precise generation of video-matching sound effects. In addition, we propose a universal latent audio codec that can achieve high-quality modeling in various scenarios such as sound effects, speech, singing, and music. We employ a stereo rendering method that imbues synthesized audio with a spatial presence. At the same time, in order to make up for the incomplete types and annotations of the open-source benchmark, we also open-source an industrial-level benchmark Kling-Audio-Eval. Our experiments show that Kling-Foley trained with the flow matching objective achieves new audio-visual SOTA performance among public models in terms of distribution matching, semantic alignment, temporal alignment and audio quality.
OneRec Technical Report
Jun 16, 2025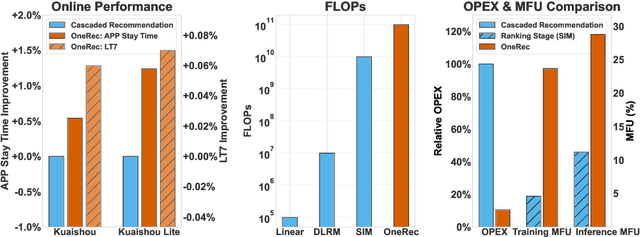

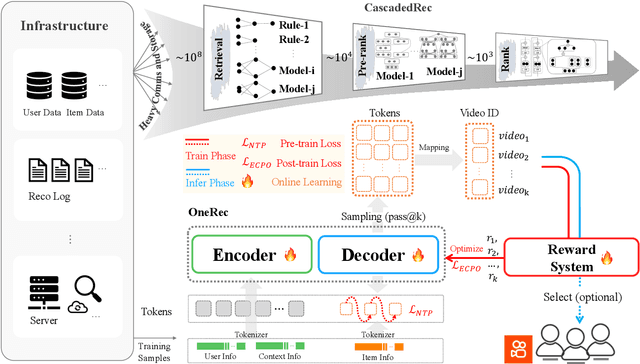

Abstract:Recommender systems have been widely used in various large-scale user-oriented platforms for many years. However, compared to the rapid developments in the AI community, recommendation systems have not achieved a breakthrough in recent years. For instance, they still rely on a multi-stage cascaded architecture rather than an end-to-end approach, leading to computational fragmentation and optimization inconsistencies, and hindering the effective application of key breakthrough technologies from the AI community in recommendation scenarios. To address these issues, we propose OneRec, which reshapes the recommendation system through an end-to-end generative approach and achieves promising results. Firstly, we have enhanced the computational FLOPs of the current recommendation model by 10 $\times$ and have identified the scaling laws for recommendations within certain boundaries. Secondly, reinforcement learning techniques, previously difficult to apply for optimizing recommendations, show significant potential in this framework. Lastly, through infrastructure optimizations, we have achieved 23.7% and 28.8% Model FLOPs Utilization (MFU) on flagship GPUs during training and inference, respectively, aligning closely with the LLM community. This architecture significantly reduces communication and storage overhead, resulting in operating expense that is only 10.6% of traditional recommendation pipelines. Deployed in Kuaishou/Kuaishou Lite APP, it handles 25% of total queries per second, enhancing overall App Stay Time by 0.54% and 1.24%, respectively. Additionally, we have observed significant increases in metrics such as 7-day Lifetime, which is a crucial indicator of recommendation experience. We also provide practical lessons and insights derived from developing, optimizing, and maintaining a production-scale recommendation system with significant real-world impact.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge