Chunyu Qiang
Habibi: Laying the Open-Source Foundation of Unified-Dialectal Arabic Speech Synthesis
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:A notable gap persists in speech synthesis research and development for Arabic dialects, particularly from a unified modeling perspective. Despite its high practical value, the inherent linguistic complexity of Arabic dialects, further compounded by a lack of standardized data, benchmarks, and evaluation guidelines, steers researchers toward safer ground. To bridge this divide, we present Habibi, a suite of specialized and unified text-to-speech models that harnesses existing open-source ASR corpora to support a wide range of high- to low-resource Arabic dialects through linguistically-informed curriculum learning. Our approach outperforms the leading commercial service in generation quality, while maintaining extensibility through effective in-context learning, without requiring text diacritization. We are committed to open-sourcing the model, along with creating the first systematic benchmark for multi-dialect Arabic speech synthesis. Furthermore, by identifying the key challenges in and establishing evaluation standards for the process, we aim to provide a solid groundwork for subsequent research. Resources at https://SWivid.github.io/Habibi/ .
MM-Sonate: Multimodal Controllable Audio-Video Generation with Zero-Shot Voice Cloning
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Joint audio-video generation aims to synthesize synchronized multisensory content, yet current unified models struggle with fine-grained acoustic control, particularly for identity-preserving speech. Existing approaches either suffer from temporal misalignment due to cascaded generation or lack the capability to perform zero-shot voice cloning within a joint synthesis framework. In this work, we present MM-Sonate, a multimodal flow-matching framework that unifies controllable audio-video joint generation with zero-shot voice cloning capabilities. Unlike prior works that rely on coarse semantic descriptions, MM-Sonate utilizes a unified instruction-phoneme input to enforce strict linguistic and temporal alignment. To enable zero-shot voice cloning, we introduce a timbre injection mechanism that effectively decouples speaker identity from linguistic content. Furthermore, addressing the limitations of standard classifier-free guidance in multimodal settings, we propose a noise-based negative conditioning strategy that utilizes natural noise priors to significantly enhance acoustic fidelity. Empirical evaluations demonstrate that MM-Sonate establishes new state-of-the-art performance in joint generation benchmarks, significantly outperforming baselines in lip synchronization and speech intelligibility, while achieving voice cloning fidelity comparable to specialized Text-to-Speech systems.
Klear: Unified Multi-Task Audio-Video Joint Generation
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Audio-video joint generation has progressed rapidly, yet substantial challenges still remain. Non-commercial approaches still suffer audio-visual asynchrony, poor lip-speech alignment, and unimodal degradation, which can be stemmed from weak audio-visual correspondence modeling, limited generalization, and scarce high-quality dense-caption data. To address these issues, we introduce Klear and delve into three axes--model architecture, training strategy, and data curation. Architecturally, we adopt a single-tower design with unified DiT blocks and an Omni-Full Attention mechanism, achieving tight audio-visual alignment and strong scalability. Training-wise, we adopt a progressive multitask regime--random modality masking to joint optimization across tasks, and a multistage curriculum, yielding robust representations, strengthening A-V aligned world knowledge, and preventing unimodal collapse. For datasets, we present the first large-scale audio-video dataset with dense captions, and introduce a novel automated data-construction pipeline which annotates and filters millions of diverse, high-quality, strictly aligned audio-video-caption triplets. Building on this, Klear scales to large datasets, delivering high-fidelity, semantically and temporally aligned, instruction-following generation in both joint and unimodal settings while generalizing robustly to out-of-distribution scenarios. Across tasks, it substantially outperforms prior methods by a large margin and achieves performance comparable to Veo 3, offering a unified, scalable path toward next-generation audio-video synthesis.
Kling-Foley: Multimodal Diffusion Transformer for High-Quality Video-to-Audio Generation
Jun 24, 2025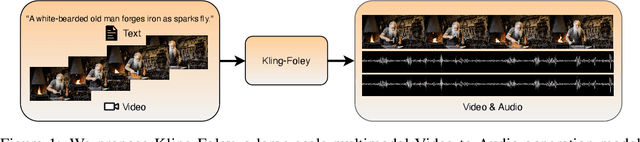
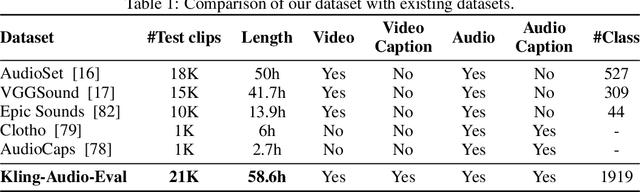
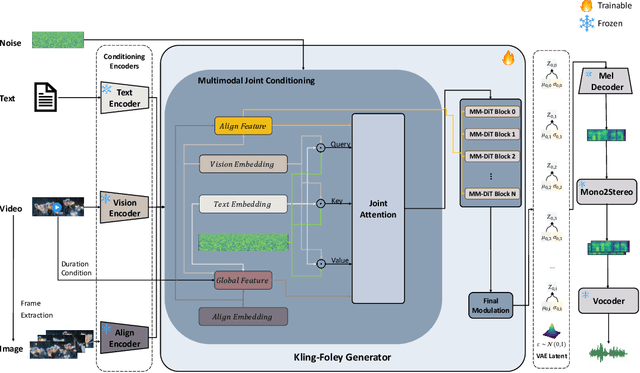
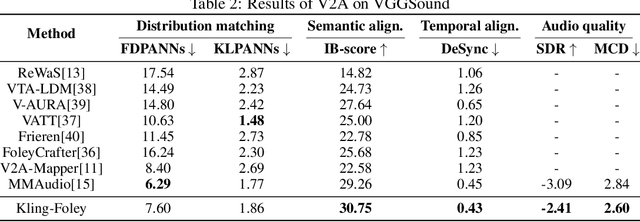
Abstract:We propose Kling-Foley, a large-scale multimodal Video-to-Audio generation model that synthesizes high-quality audio synchronized with video content. In Kling-Foley, we introduce multimodal diffusion transformers to model the interactions between video, audio, and text modalities, and combine it with a visual semantic representation module and an audio-visual synchronization module to enhance alignment capabilities. Specifically, these modules align video conditions with latent audio elements at the frame level, thereby improving semantic alignment and audio-visual synchronization. Together with text conditions, this integrated approach enables precise generation of video-matching sound effects. In addition, we propose a universal latent audio codec that can achieve high-quality modeling in various scenarios such as sound effects, speech, singing, and music. We employ a stereo rendering method that imbues synthesized audio with a spatial presence. At the same time, in order to make up for the incomplete types and annotations of the open-source benchmark, we also open-source an industrial-level benchmark Kling-Audio-Eval. Our experiments show that Kling-Foley trained with the flow matching objective achieves new audio-visual SOTA performance among public models in terms of distribution matching, semantic alignment, temporal alignment and audio quality.
Towards Flow-Matching-based TTS without Classifier-Free Guidance
Apr 29, 2025Abstract:Flow matching has demonstrated strong generative capabilities and has become a core component in modern Text-to-Speech (TTS) systems. To ensure high-quality speech synthesis, Classifier-Free Guidance (CFG) is widely used during the inference of flow-matching-based TTS models. However, CFG incurs substantial computational cost as it requires two forward passes, which hinders its applicability in real-time scenarios. In this paper, we explore removing CFG from flow-matching-based TTS models to improve inference efficiency, while maintaining performance. Specifically, we reformulated the flow matching training target to directly approximate the CFG optimization trajectory. This training method eliminates the need for unconditional model evaluation and guided tuning during inference, effectively cutting the computational overhead in half. Furthermore, It can be seamlessly integrated with existing optimized sampling strategies. We validate our approach using the F5-TTS model on the LibriTTS dataset. Experimental results show that our method achieves a 9$\times$ inference speed-up compared to the baseline F5-TTS, while preserving comparable speech quality. We will release the code and models to support reproducibility and foster further research in this area.
Characteristic-Specific Partial Fine-Tuning for Efficient Emotion and Speaker Adaptation in Codec Language Text-to-Speech Models
Jan 24, 2025



Abstract:Recently, emotional speech generation and speaker cloning have garnered significant interest in text-to-speech (TTS). With the open-sourcing of codec language TTS models trained on massive datasets with large-scale parameters, adapting these general pre-trained TTS models to generate speech with specific emotional expressions and target speaker characteristics has become a topic of great attention. Common approaches, such as full and adapter-based fine-tuning, often overlook the specific contributions of model parameters to emotion and speaker control. Treating all parameters uniformly during fine-tuning, especially when the target data has limited content diversity compared to the pre-training corpus, results in slow training speed and an increased risk of catastrophic forgetting. To address these challenges, we propose a characteristic-specific partial fine-tuning strategy, short as CSP-FT. First, we use a weighted-sum approach to analyze the contributions of different Transformer layers in a pre-trained codec language TTS model for emotion and speaker control in the generated speech. We then selectively fine-tune the layers with the highest and lowest characteristic-specific contributions to generate speech with target emotional expression and speaker identity. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves performance comparable to, or even surpassing, full fine-tuning in generating speech with specific emotional expressions and speaker identities. Additionally, CSP-FT delivers approximately 2x faster training speeds, fine-tunes only around 8% of parameters, and significantly reduces catastrophic forgetting. Furthermore, we show that codec language TTS models perform competitively with self-supervised models in speaker identification and emotion classification tasks, offering valuable insights for developing universal speech processing models.
Mel-Refine: A Plug-and-Play Approach to Refine Mel-Spectrogram in Audio Generation
Dec 11, 2024Abstract:Text-to-audio (TTA) model is capable of generating diverse audio from textual prompts. However, most mainstream TTA models, which predominantly rely on Mel-spectrograms, still face challenges in producing audio with rich content. The intricate details and texture required in Mel-spectrograms for such audio often surpass the models' capacity, leading to outputs that are blurred or lack coherence. In this paper, we begin by investigating the critical role of U-Net in Mel-spectrogram generation. Our analysis shows that in U-Net structure, high-frequency components in skip-connections and the backbone influence texture and detail, while low-frequency components in the backbone are critical for the diffusion denoising process. We further propose ``Mel-Refine'', a plug-and-play approach that enhances Mel-spectrogram texture and detail by adjusting different component weights during inference. Our method requires no additional training or fine-tuning and is fully compatible with any diffusion-based TTA architecture. Experimental results show that our approach boosts performance metrics of the latest TTA model Tango2 by 25\%, demonstrating its effectiveness.
EmoPro: A Prompt Selection Strategy for Emotional Expression in LM-based Speech Synthesis
Sep 27, 2024



Abstract:Recent advancements in speech synthesis models, trained on extensive datasets, have demonstrated remarkable zero-shot capabilities. These models can control content, timbre, and emotion in generated speech based on prompt inputs. Despite these advancements, the choice of prompts significantly impacts the output quality, yet most existing selection schemes do not adequately address the control of emotional intensity. To address this question, this paper proposes a two-stage prompt selection strategy EmoPro, which is specifically designed for emotionally controllable speech synthesis. This strategy focuses on selecting highly expressive and high-quality prompts by evaluating them from four perspectives: emotional expression strength, speech quality, text-emotion consistency, and model generation performance. Experimental results show that prompts selected using the proposed method result in more emotionally expressive and engaging synthesized speech compared to those obtained through baseline. Audio samples and codes will be available at https://whyrrrrun.github.io/EmoPro/.
DPI-TTS: Directional Patch Interaction for Fast-Converging and Style Temporal Modeling in Text-to-Speech
Sep 18, 2024


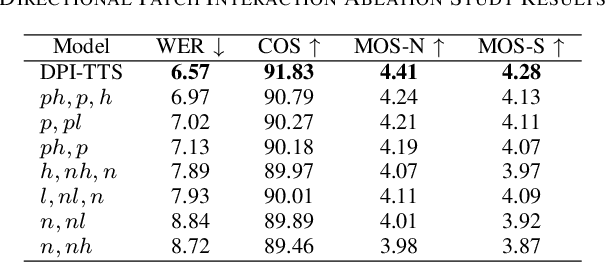
Abstract:In recent years, speech diffusion models have advanced rapidly. Alongside the widely used U-Net architecture, transformer-based models such as the Diffusion Transformer (DiT) have also gained attention. However, current DiT speech models treat Mel spectrograms as general images, which overlooks the specific acoustic properties of speech. To address these limitations, we propose a method called Directional Patch Interaction for Text-to-Speech (DPI-TTS), which builds on DiT and achieves fast training without compromising accuracy. Notably, DPI-TTS employs a low-to-high frequency, frame-by-frame progressive inference approach that aligns more closely with acoustic properties, enhancing the naturalness of the generated speech. Additionally, we introduce a fine-grained style temporal modeling method that further improves speaker style similarity. Experimental results demonstrate that our method increases the training speed by nearly 2 times and significantly outperforms the baseline models.
Text Prompt is Not Enough: Sound Event Enhanced Prompt Adapter for Target Style Audio Generation
Sep 14, 2024



Abstract:Current mainstream audio generation methods primarily rely on simple text prompts, often failing to capture the nuanced details necessary for multi-style audio generation. To address this limitation, the Sound Event Enhanced Prompt Adapter is proposed. Unlike traditional static global style transfer, this method extracts style embedding through cross-attention between text and reference audio for adaptive style control. Adaptive layer normalization is then utilized to enhance the model's capacity to express multiple styles. Additionally, the Sound Event Reference Style Transfer Dataset (SERST) is introduced for the proposed target style audio generation task, enabling dual-prompt audio generation using both text and audio references. Experimental results demonstrate the robustness of the model, achieving state-of-the-art Fr\'echet Distance of 26.94 and KL Divergence of 1.82, surpassing Tango, AudioLDM, and AudioGen. Furthermore, the generated audio shows high similarity to its corresponding audio reference. The demo, code, and dataset are publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge