Mengzhe Geng
MOPSA: Mixture of Prompt-Experts Based Speaker Adaptation for Elderly Speech Recognition
May 30, 2025



Abstract:This paper proposes a novel Mixture of Prompt-Experts based Speaker Adaptation approach (MOPSA) for elderly speech recognition. It allows zero-shot, real-time adaptation to unseen speakers, and leverages domain knowledge tailored to elderly speakers. Top-K most distinctive speaker prompt clusters derived using K-means serve as experts. A router network is trained to dynamically combine clustered prompt-experts. Acoustic and language level variability among elderly speakers are modelled using separate encoder and decoder prompts for Whisper. Experiments on the English DementiaBank Pitt and Cantonese JCCOCC MoCA elderly speech datasets suggest that online MOPSA adaptation outperforms the speaker-independent (SI) model by statistically significant word error rate (WER) or character error rate (CER) reductions of 0.86% and 1.47% absolute (4.21% and 5.40% relative). Real-time factor (RTF) speed-up ratios of up to 16.12 times are obtained over offline batch-mode adaptation.
Towards LLM-Empowered Fine-Grained Speech Descriptors for Explainable Emotion Recognition
May 29, 2025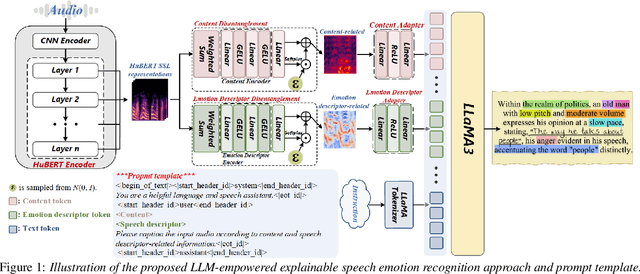
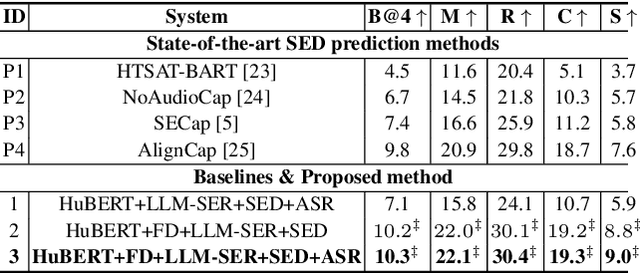
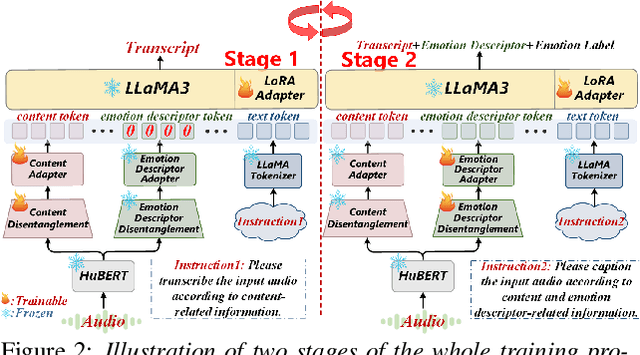
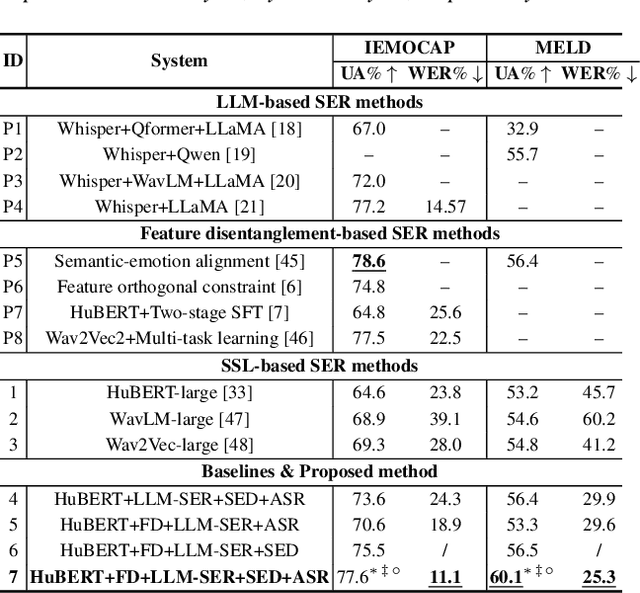
Abstract:This paper presents a novel end-to-end LLM-empowered explainable speech emotion recognition (SER) approach. Fine-grained speech emotion descriptor (SED) features, e.g., pitch, tone and emphasis, are disentangled from HuBERT SSL representations via alternating LLM fine-tuning to joint SER-SED prediction and ASR tasks. VAE compressed HuBERT features derived via Information Bottleneck (IB) are used to adjust feature granularity. Experiments on the IEMOCAP and MELD benchmarks demonstrate that our approach consistently outperforms comparable LLaMA-based SER baselines, including those using either (a) alternating multi-task fine-tuning alone or (b) feature disentanglement only. Statistically significant increase of SER unweighted accuracy by up to 4.0% and 3.7% absolute (5.4% and 6.6% relative) are obtained. More importantly, emotion descriptors offer further explainability for SER.
Effective and Efficient One-pass Compression of Speech Foundation Models Using Sparsity-aware Self-pinching Gates
May 28, 2025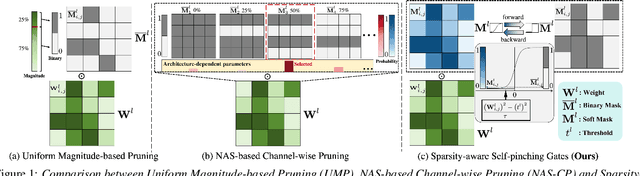
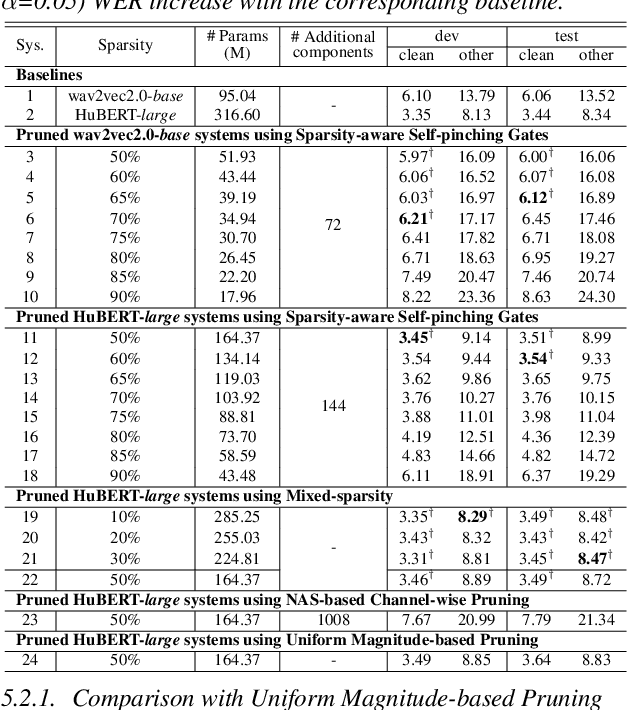
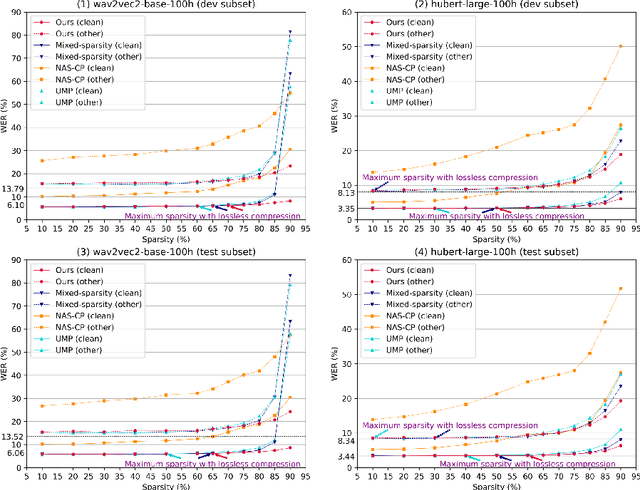
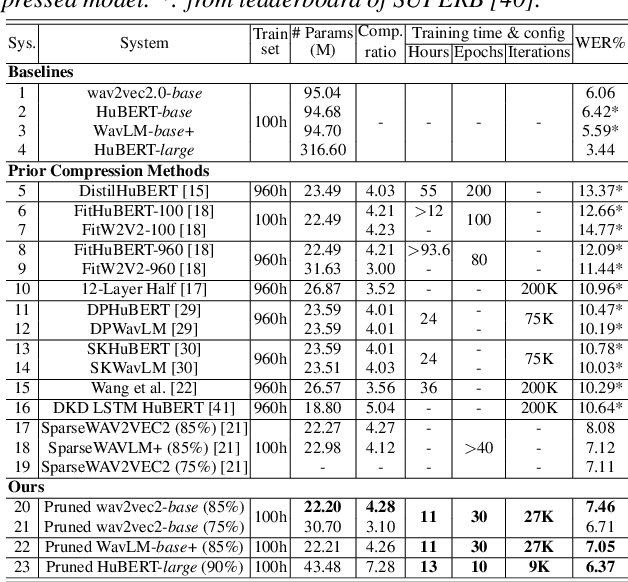
Abstract:This paper presents a novel approach for speech foundation models compression that tightly integrates model pruning and parameter update into a single stage. Highly compact layer-level tied self-pinching gates each containing only a single learnable threshold are jointly trained with uncompressed models and used in fine-grained neuron level pruning. Experiments conducted on the LibriSpeech-100hr corpus suggest that our approach reduces the number of parameters of wav2vec2.0-base and HuBERT-large models by 65% and 60% respectively, while incurring no statistically significant word error rate (WER) increase on the test-clean dataset. Compared to previously published methods on the same task, our approach not only achieves the lowest WER of 7.05% on the test-clean dataset under a comparable model compression ratio of 4.26x, but also operates with at least 25% less model compression time.
On-the-fly Routing for Zero-shot MoE Speaker Adaptation of Speech Foundation Models for Dysarthric Speech Recognition
May 28, 2025



Abstract:This paper proposes a novel MoE-based speaker adaptation framework for foundation models based dysarthric speech recognition. This approach enables zero-shot adaptation and real-time processing while incorporating domain knowledge. Speech impairment severity and gender conditioned adapter experts are dynamically combined using on-the-fly predicted speaker-dependent routing parameters. KL-divergence is used to further enforce diversity among experts and their generalization to unseen speakers. Experimental results on the UASpeech corpus suggest that on-the-fly MoE-based adaptation produces statistically significant WER reductions of up to 1.34% absolute (6.36% relative) over the unadapted baseline HuBERT/WavLM models. Consistent WER reductions of up to 2.55% absolute (11.44% relative) and RTF speedups of up to 7 times are obtained over batch-mode adaptation across varying speaker-level data quantities. The lowest published WER of 16.35% (46.77% on very low intelligibility) is obtained.
Phone-purity Guided Discrete Tokens for Dysarthric Speech Recognition
Jan 08, 2025



Abstract:Discrete tokens extracted provide efficient and domain adaptable speech features. Their application to disordered speech that exhibits articulation imprecision and large mismatch against normal voice remains unexplored. To improve their phonetic discrimination that is weakened during unsupervised K-means or vector quantization of continuous features, this paper proposes novel phone-purity guided (PPG) discrete tokens for dysarthric speech recognition. Phonetic label supervision is used to regularize maximum likelihood and reconstruction error costs used in standard K-means and VAE-VQ based discrete token extraction. Experiments conducted on the UASpeech corpus suggest that the proposed PPG discrete token features extracted from HuBERT consistently outperform hybrid TDNN and End-to-End (E2E) Conformer systems using non-PPG based K-means or VAE-VQ tokens across varying codebook sizes by statistically significant word error rate (WER) reductions up to 0.99\% and 1.77\% absolute (3.21\% and 4.82\% relative) respectively on the UASpeech test set of 16 dysarthric speakers. The lowest WER of 23.25\% was obtained by combining systems using different token features. Consistent improvements on the phone purity metric were also achieved. T-SNE visualization further demonstrates sharper decision boundaries were produced between K-means/VAE-VQ clusters after introducing phone-purity guidance.
Effective and Efficient Mixed Precision Quantization of Speech Foundation Models
Jan 07, 2025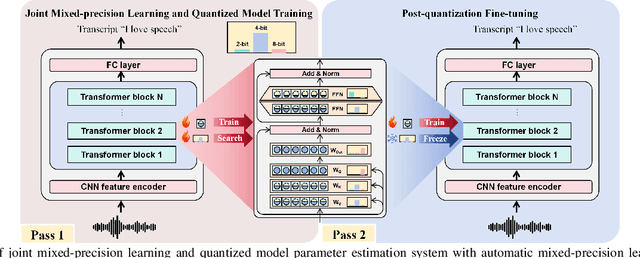
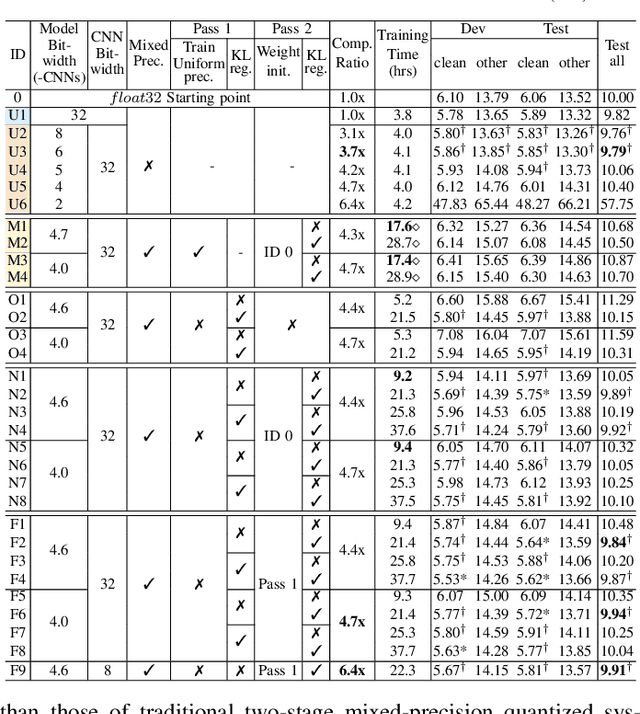
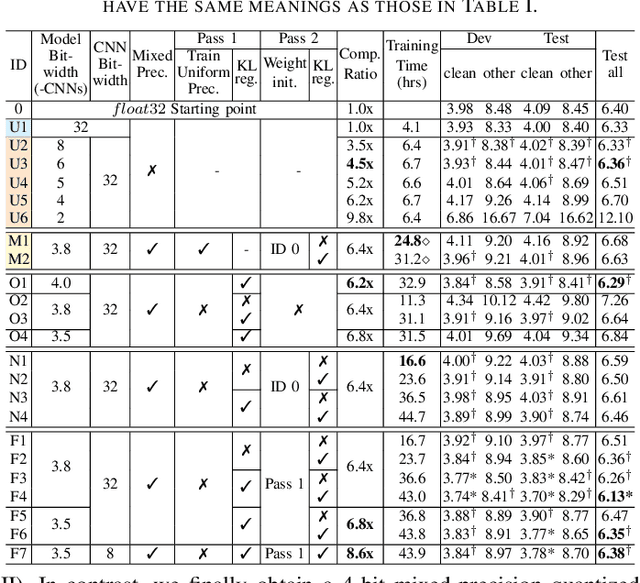
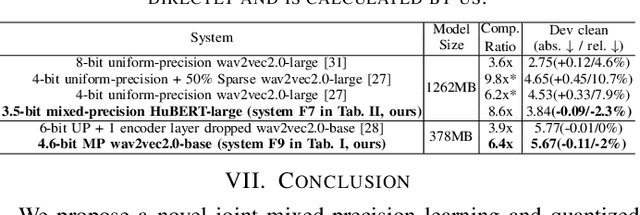
Abstract:This paper presents a novel mixed-precision quantization approach for speech foundation models that tightly integrates mixed-precision learning and quantized model parameter estimation into one single model compression stage. Experiments conducted on LibriSpeech dataset with fine-tuned wav2vec2.0-base and HuBERT-large models suggest the resulting mixed-precision quantized models increased the lossless compression ratio by factors up to 1.7x and 1.9x over the respective uniform-precision and two-stage mixed-precision quantized baselines that perform precision learning and model parameters quantization in separate and disjointed stages, while incurring no statistically word error rate (WER) increase over the 32-bit full-precision models. The system compression time of wav2vec2.0-base and HuBERT-large models is reduced by up to 1.9 and 1.5 times over the two-stage mixed-precision baselines, while both produce lower WERs. The best-performing 3.5-bit mixed-precision quantized HuBERT-large model produces a lossless compression ratio of 8.6x over the 32-bit full-precision system.
Structured Speaker-Deficiency Adaptation of Foundation Models for Dysarthric and Elderly Speech Recognition
Dec 25, 2024



Abstract:Data-intensive fine-tuning of speech foundation models (SFMs) to scarce and diverse dysarthric and elderly speech leads to data bias and poor generalization to unseen speakers. This paper proposes novel structured speaker-deficiency adaptation approaches for SSL pre-trained SFMs on such data. Speaker and speech deficiency invariant SFMs were constructed in their supervised adaptive fine-tuning stage to reduce undue bias to training data speakers, and serves as a more neutral and robust starting point for test time unsupervised adaptation. Speech variability attributed to speaker identity and speech impairment severity, or aging induced neurocognitive decline, are modelled using separate adapters that can be combined together to model any seen or unseen speaker. Experiments on the UASpeech dysarthric and DementiaBank Pitt elderly speech corpora suggest structured speaker-deficiency adaptation of HuBERT and Wav2vec2-conformer models consistently outperforms baseline SFMs using either: a) no adapters; b) global adapters shared among all speakers; or c) single attribute adapters modelling speaker or deficiency labels alone by statistically significant WER reductions up to 3.01% and 1.50% absolute (10.86% and 6.94% relative) on the two tasks respectively. The lowest published WER of 19.45% (49.34% on very low intelligibility, 33.17% on unseen words) is obtained on the UASpeech test set of 16 dysarthric speakers.
Homogeneous Speaker Features for On-the-Fly Dysarthric and Elderly Speaker Adaptation
Jul 08, 2024



Abstract:The application of data-intensive automatic speech recognition (ASR) technologies to dysarthric and elderly adult speech is confronted by their mismatch against healthy and nonaged voices, data scarcity and large speaker-level variability. To this end, this paper proposes two novel data-efficient methods to learn homogeneous dysarthric and elderly speaker-level features for rapid, on-the-fly test-time adaptation of DNN/TDNN and Conformer ASR models. These include: 1) speaker-level variance-regularized spectral basis embedding (VR-SBE) features that exploit a special regularization term to enforce homogeneity of speaker features in adaptation; and 2) feature-based learning hidden unit contributions (f-LHUC) transforms that are conditioned on VR-SBE features. Experiments are conducted on four tasks across two languages: the English UASpeech and TORGO dysarthric speech datasets, the English DementiaBank Pitt and Cantonese JCCOCC MoCA elderly speech corpora. The proposed on-the-fly speaker adaptation techniques consistently outperform baseline iVector and xVector adaptation by statistically significant word or character error rate reductions up to 5.32% absolute (18.57% relative) and batch-mode LHUC speaker adaptation by 2.24% absolute (9.20% relative), while operating with real-time factors speeding up to 33.6 times against xVectors during adaptation. The efficacy of the proposed adaptation techniques is demonstrated in a comparison against current ASR technologies including SSL pre-trained systems on UASpeech, where our best system produces a state-of-the-art WER of 23.33%. Analyses show VR-SBE features and f-LHUC transforms are insensitive to speaker-level data quantity in testtime adaptation. T-SNE visualization reveals they have stronger speaker-level homogeneity than baseline iVectors, xVectors and batch-mode LHUC transforms.
Towards Effective and Efficient Non-autoregressive Decoding Using Block-based Attention Mask
Jun 14, 2024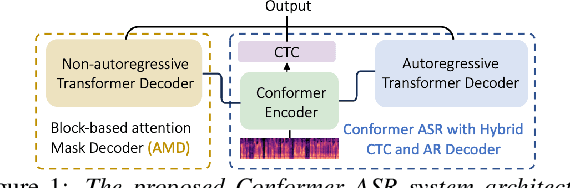
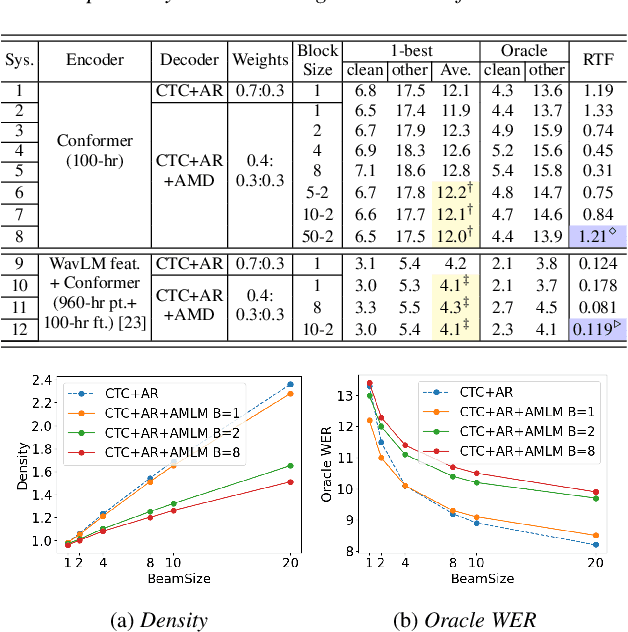
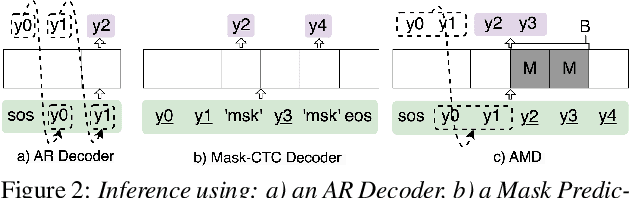
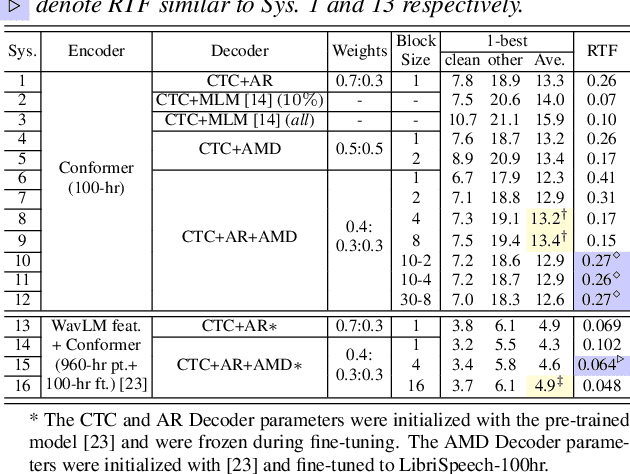
Abstract:This paper proposes a novel non-autoregressive (NAR) block-based Attention Mask Decoder (AMD) that flexibly balances performance-efficiency trade-offs for Conformer ASR systems. AMD performs parallel NAR inference within contiguous blocks of output labels that are concealed using attention masks, while conducting left-to-right AR prediction and history context amalgamation between blocks. A beam search algorithm is designed to leverage a dynamic fusion of CTC, AR Decoder, and AMD probabilities. Experiments on the LibriSpeech-100hr corpus suggest the tripartite Decoder incorporating the AMD module produces a maximum decoding speed-up ratio of 1.73x over the baseline CTC+AR decoding, while incurring no statistically significant word error rate (WER) increase on the test sets. When operating with the same decoding real time factors, statistically significant WER reductions of up to 0.7% and 0.3% absolute (5.3% and 6.1% relative) were obtained over the CTC+AR baseline.
One-pass Multiple Conformer and Foundation Speech Systems Compression and Quantization Using An All-in-one Neural Model
Jun 14, 2024



Abstract:We propose a novel one-pass multiple ASR systems joint compression and quantization approach using an all-in-one neural model. A single compression cycle allows multiple nested systems with varying Encoder depths, widths, and quantization precision settings to be simultaneously constructed without the need to train and store individual target systems separately. Experiments consistently demonstrate the multiple ASR systems compressed in a single all-in-one model produced a word error rate (WER) comparable to, or lower by up to 1.01\% absolute (6.98\% relative) than individually trained systems of equal complexity. A 3.4x overall system compression and training time speed-up was achieved. Maximum model size compression ratios of 12.8x and 3.93x were obtained over the baseline Switchboard-300hr Conformer and LibriSpeech-100hr fine-tuned wav2vec2.0 models, respectively, incurring no statistically significant WER increase.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge