Tianrui Wang
EmoShift: Lightweight Activation Steering for Enhanced Emotion-Aware Speech Synthesis
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Achieving precise and controllable emotional expression is crucial for producing natural and context-appropriate speech in text-to-speech (TTS) synthesis. However, many emotion-aware TTS systems, including large language model (LLM)-based designs, rely on scaling fixed emotion embeddings or external guidance, limiting their ability to model emotion-specific latent characteristics. To address this gap, we present EmoShift, a lightweight activation-steering framework incorporating a EmoSteer layer, which learns a steering vector for each target emotion in the output embedding space to capture its latent offset and maintain stable, appropriate expression across utterances and categories. With only 10M trainable parameters,less than 1/30 of full fine-tuning, EmoShift outperforms zero-shot and fully fine-tuned baselines in objective and subjective evaluations, enhancing emotional expressiveness while preserving naturalness and speaker similarity. Further analysis confirms the proposed EmoSteer layer's effectiveness and reveals its potential for controllable emotional intensity in speech synthesis.
Towards Fine-Grained and Multi-Granular Contrastive Language-Speech Pre-training
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Modeling fine-grained speaking styles remains challenging for language-speech representation pre-training, as existing speech-text models are typically trained with coarse captions or task-specific supervision, and scalable fine-grained style annotations are unavailable. We present FCaps, a large-scale dataset with fine-grained free-text style descriptions, encompassing 47k hours of speech and 19M fine-grained captions annotated via a novel end-to-end pipeline that directly grounds detailed captions in audio, thereby avoiding the error propagation caused by LLM-based rewriting in existing cascaded pipelines. Evaluations using LLM-as-a-judge demonstrate that our annotations surpass existing cascaded annotations in terms of correctness, coverage, and naturalness. Building on FCaps, we propose CLSP, a contrastive language-speech pre-trained model that integrates global and fine-grained supervision, enabling unified representations across multiple granularities. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CLSP learns fine-grained and multi-granular speech-text representations that perform reliably across global and fine-grained speech-text retrieval, zero-shot paralinguistic classification, and speech style similarity scoring, with strong alignment to human judgments. All resources will be made publicly available.
POTSA: A Cross-Lingual Speech Alignment Framework for Low Resource Speech-to-Text Translation
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:Speech Large Language Models (SpeechLLMs) have achieved breakthroughs in multilingual speech-to-text translation (S2TT). However, existing approaches often overlook semantic commonalities across source languages, leading to biased translation performance. In this work, we propose \textbf{POTSA} (Parallel Optimal Transport for Speech Alignment), a new framework based on cross-lingual parallel speech pairs and Optimal Transport (OT), designed to bridge high- and low-resource translation gaps. First, we introduce a Bias Compensation module to coarsely align initial speech representations across languages. Second, we impose token-level OT constraints on a Q-Former using parallel speech pairs to establish fine-grained consistency of representations. Then, we apply a layer scheduling strategy to focus OT constraints on the most semantically beneficial layers. Experiments on the FLEURS dataset show that our method achieves SOTA performance, with +0.93 BLEU on average over five common languages and +5.05 BLEU on zero-shot languages, using only 10 hours of parallel speech per source language.
ASDA: Audio Spectrogram Differential Attention Mechanism for Self-Supervised Representation Learning
Jul 03, 2025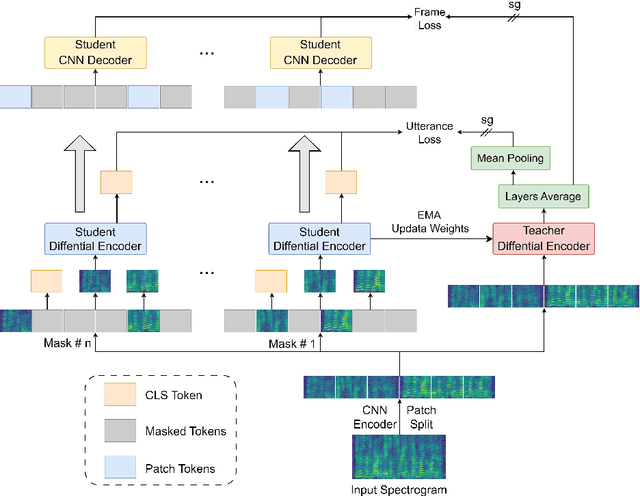



Abstract:In recent advancements in audio self-supervised representation learning, the standard Transformer architecture has emerged as the predominant approach, yet its attention mechanism often allocates a portion of attention weights to irrelevant information, potentially impairing the model's discriminative ability. To address this, we introduce a differential attention mechanism, which effectively mitigates ineffective attention allocation through the integration of dual-softmax operations and appropriately tuned differential coefficients. Experimental results demonstrate that our ASDA model achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance across multiple benchmarks, including audio classification (49.0% mAP on AS-2M, 41.5% mAP on AS20K), keyword spotting (98.3% accuracy on SPC-2), and environmental sound classification (96.1% accuracy on ESC-50). These results highlight ASDA's effectiveness in audio tasks, paving the way for broader applications.
MMAR: A Challenging Benchmark for Deep Reasoning in Speech, Audio, Music, and Their Mix
May 19, 2025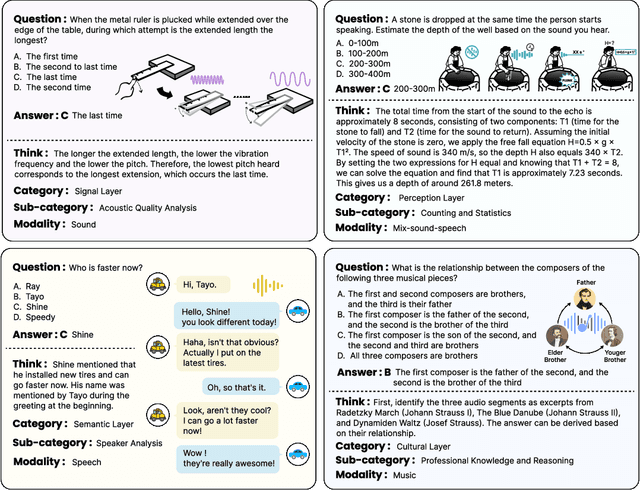
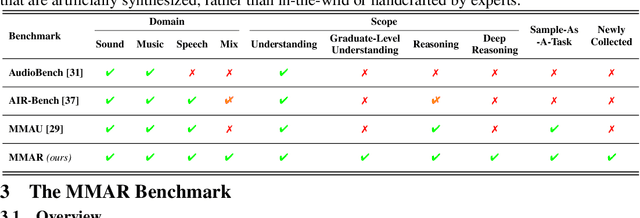
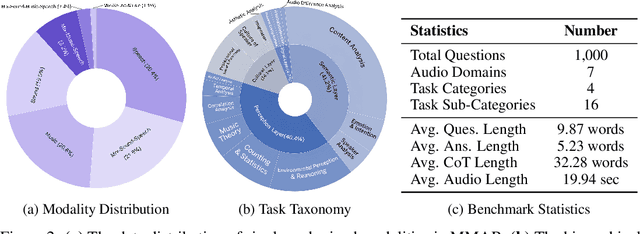
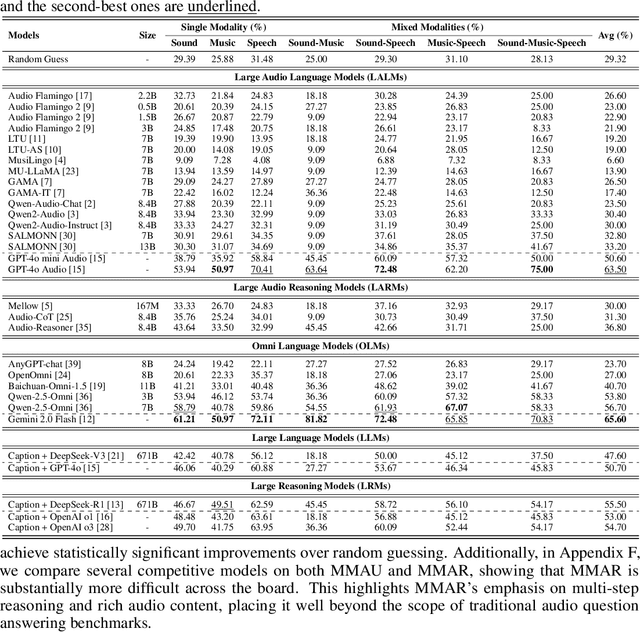
Abstract:We introduce MMAR, a new benchmark designed to evaluate the deep reasoning capabilities of Audio-Language Models (ALMs) across massive multi-disciplinary tasks. MMAR comprises 1,000 meticulously curated audio-question-answer triplets, collected from real-world internet videos and refined through iterative error corrections and quality checks to ensure high quality. Unlike existing benchmarks that are limited to specific domains of sound, music, or speech, MMAR extends them to a broad spectrum of real-world audio scenarios, including mixed-modality combinations of sound, music, and speech. Each question in MMAR is hierarchically categorized across four reasoning layers: Signal, Perception, Semantic, and Cultural, with additional sub-categories within each layer to reflect task diversity and complexity. To further foster research in this area, we annotate every question with a Chain-of-Thought (CoT) rationale to promote future advancements in audio reasoning. Each item in the benchmark demands multi-step deep reasoning beyond surface-level understanding. Moreover, a part of the questions requires graduate-level perceptual and domain-specific knowledge, elevating the benchmark's difficulty and depth. We evaluate MMAR using a broad set of models, including Large Audio-Language Models (LALMs), Large Audio Reasoning Models (LARMs), Omni Language Models (OLMs), Large Language Models (LLMs), and Large Reasoning Models (LRMs), with audio caption inputs. The performance of these models on MMAR highlights the benchmark's challenging nature, and our analysis further reveals critical limitations of understanding and reasoning capabilities among current models. We hope MMAR will serve as a catalyst for future advances in this important but little-explored area.
EmoVoice: LLM-based Emotional Text-To-Speech Model with Freestyle Text Prompting
Apr 22, 2025Abstract:Human speech goes beyond the mere transfer of information; it is a profound exchange of emotions and a connection between individuals. While Text-to-Speech (TTS) models have made huge progress, they still face challenges in controlling the emotional expression in the generated speech. In this work, we propose EmoVoice, a novel emotion-controllable TTS model that exploits large language models (LLMs) to enable fine-grained freestyle natural language emotion control, and a phoneme boost variant design that makes the model output phoneme tokens and audio tokens in parallel to enhance content consistency, inspired by chain-of-thought (CoT) and chain-of-modality (CoM) techniques. Besides, we introduce EmoVoice-DB, a high-quality 40-hour English emotion dataset featuring expressive speech and fine-grained emotion labels with natural language descriptions. EmoVoice achieves state-of-the-art performance on the English EmoVoice-DB test set using only synthetic training data, and on the Chinese Secap test set using our in-house data. We further investigate the reliability of existing emotion evaluation metrics and their alignment with human perceptual preferences, and explore using SOTA multimodal LLMs GPT-4o-audio and Gemini to assess emotional speech. Demo samples are available at https://yanghaha0908.github.io/EmoVoice/. Dataset, code, and checkpoints will be released.
Characteristic-Specific Partial Fine-Tuning for Efficient Emotion and Speaker Adaptation in Codec Language Text-to-Speech Models
Jan 24, 2025



Abstract:Recently, emotional speech generation and speaker cloning have garnered significant interest in text-to-speech (TTS). With the open-sourcing of codec language TTS models trained on massive datasets with large-scale parameters, adapting these general pre-trained TTS models to generate speech with specific emotional expressions and target speaker characteristics has become a topic of great attention. Common approaches, such as full and adapter-based fine-tuning, often overlook the specific contributions of model parameters to emotion and speaker control. Treating all parameters uniformly during fine-tuning, especially when the target data has limited content diversity compared to the pre-training corpus, results in slow training speed and an increased risk of catastrophic forgetting. To address these challenges, we propose a characteristic-specific partial fine-tuning strategy, short as CSP-FT. First, we use a weighted-sum approach to analyze the contributions of different Transformer layers in a pre-trained codec language TTS model for emotion and speaker control in the generated speech. We then selectively fine-tune the layers with the highest and lowest characteristic-specific contributions to generate speech with target emotional expression and speaker identity. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves performance comparable to, or even surpassing, full fine-tuning in generating speech with specific emotional expressions and speaker identities. Additionally, CSP-FT delivers approximately 2x faster training speeds, fine-tunes only around 8% of parameters, and significantly reduces catastrophic forgetting. Furthermore, we show that codec language TTS models perform competitively with self-supervised models in speaker identification and emotion classification tasks, offering valuable insights for developing universal speech processing models.
Reducing the Gap Between Pretrained Speech Enhancement and Recognition Models Using a Real Speech-Trained Bridging Module
Jan 05, 2025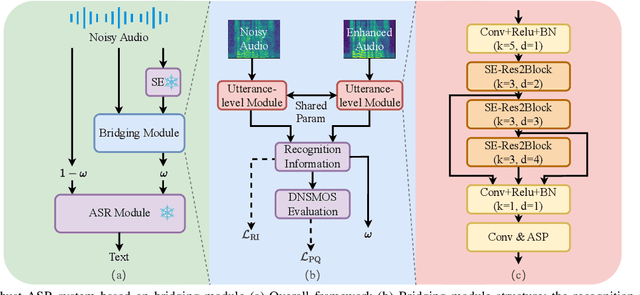
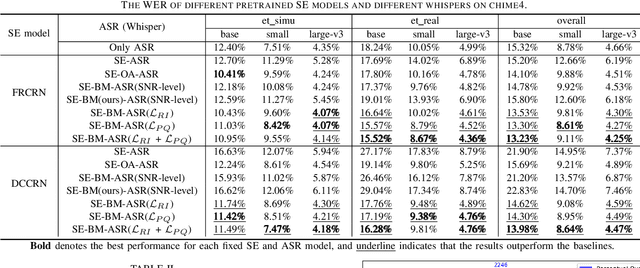
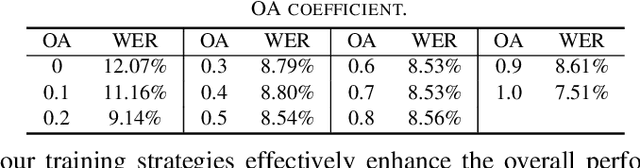
Abstract:The information loss or distortion caused by single-channel speech enhancement (SE) harms the performance of automatic speech recognition (ASR). Observation addition (OA) is an effective post-processing method to improve ASR performance by balancing noisy and enhanced speech. Determining the OA coefficient is crucial. However, the currently supervised OA coefficient module, called the bridging module, only utilizes simulated noisy speech for training, which has a severe mismatch with real noisy speech. In this paper, we propose training strategies to train the bridging module with real noisy speech. First, DNSMOS is selected to evaluate the perceptual quality of real noisy speech with no need for the corresponding clean label to train the bridging module. Additional constraints during training are introduced to enhance the robustness of the bridging module further. Each utterance is evaluated by the ASR back-end using various OA coefficients to obtain the word error rates (WERs). The WERs are used to construct a multidimensional vector. This vector is introduced into the bridging module with multi-task learning and is used to determine the optimal OA coefficients. The experimental results on the CHiME-4 dataset show that the proposed methods all had significant improvement compared with the simulated data trained bridging module, especially under real evaluation sets.
Time-Graph Frequency Representation with Singular Value Decomposition for Neural Speech Enhancement
Dec 24, 2024Abstract:Time-frequency (T-F) domain methods for monaural speech enhancement have benefited from the success of deep learning. Recently, focus has been put on designing two-stream network models to predict amplitude mask and phase separately, or, coupling the amplitude and phase into Cartesian coordinates and constructing real and imaginary pairs. However, most methods suffer from the alignment modeling of amplitude and phase (real and imaginary pairs) in a two-stream network framework, which inevitably incurs performance restrictions. In this paper, we introduce a graph Fourier transform defined with the singular value decomposition (GFT-SVD), resulting in real-valued time-graph representation for neural speech enhancement. This real-valued representation-based GFT-SVD provides an ability to align the modeling of amplitude and phase, leading to avoiding recovering the target speech phase information. Our findings demonstrate the effects of real-valued time-graph representation based on GFT-SVD for neutral speech enhancement. The extensive speech enhancement experiments establish that the combination of GFT-SVD and DNN outperforms the combination of GFT with the eigenvector decomposition (GFT-EVD) and magnitude estimation UNet, and outperforms the short-time Fourier transform (STFT) and DNN, regarding objective intelligibility and perceptual quality. We release our source code at: https://github.com/Wangfighting0015/GFT\_project.
Adapting Whisper for Code-Switching through Encoding Refining and Language-Aware Decoding
Dec 24, 2024


Abstract:Code-switching (CS) automatic speech recognition (ASR) faces challenges due to the language confusion resulting from accents, auditory similarity, and seamless language switches. Adaptation on the pre-trained multi-lingual model has shown promising performance for CS-ASR. In this paper, we adapt Whisper, which is a large-scale multilingual pre-trained speech recognition model, to CS from both encoder and decoder parts. First, we propose an encoder refiner to enhance the encoder's capacity of intra-sentence swithching. Second, we propose using two sets of language-aware adapters with different language prompt embeddings to achieve language-specific decoding information in each decoder layer. Then, a fusion module is added to fuse the language-aware decoding. The experimental results using the SEAME dataset show that, compared with the baseline model, the proposed approach achieves a relative MER reduction of 4.1% and 7.2% on the dev_man and dev_sge test sets, respectively, surpassing state-of-the-art methods. Through experiments, we found that the proposed method significantly improves the performance on non-native language in CS speech, indicating that our approach enables Whisper to better distinguish between the two languages.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge