Chen Yang
University of Science and Technology of China
MOSS Transcribe Diarize: Accurate Transcription with Speaker Diarization
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Speaker-Attributed, Time-Stamped Transcription (SATS) aims to transcribe what is said and to precisely determine the timing of each speaker, which is particularly valuable for meeting transcription. Existing SATS systems rarely adopt an end-to-end formulation and are further constrained by limited context windows, weak long-range speaker memory, and the inability to output timestamps. To address these limitations, we present MOSS Transcribe Diarize, a unified multimodal large language model that jointly performs Speaker-Attributed, Time-Stamped Transcription in an end-to-end paradigm. Trained on extensive real wild data and equipped with a 128k context window for up to 90-minute inputs, MOSS Transcribe Diarize scales well and generalizes robustly. Across comprehensive evaluations, it outperforms state-of-the-art commercial systems on multiple public and in-house benchmarks.
A Platform for Interactive AI Character Experiences
Jan 03, 2026Abstract:From movie characters to modern science fiction - bringing characters into interactive, story-driven conversations has captured imaginations across generations. Achieving this vision is highly challenging and requires much more than just language modeling. It involves numerous complex AI challenges, such as conversational AI, maintaining character integrity, managing personality and emotions, handling knowledge and memory, synthesizing voice, generating animations, enabling real-world interactions, and integration with physical environments. Recent advancements in the development of foundation models, prompt engineering, and fine-tuning for downstream tasks have enabled researchers to address these individual challenges. However, combining these technologies for interactive characters remains an open problem. We present a system and platform for conveniently designing believable digital characters, enabling a conversational and story-driven experience while providing solutions to all of the technical challenges. As a proof-of-concept, we introduce Digital Einstein, which allows users to engage in conversations with a digital representation of Albert Einstein about his life, research, and persona. While Digital Einstein exemplifies our methods for a specific character, our system is flexible and generalizes to any story-driven or conversational character. By unifying these diverse AI components into a single, easy-to-adapt platform, our work paves the way for immersive character experiences, turning the dream of lifelike, story-based interactions into a reality.
Efficient and Robust Video Defense Framework against 3D-field Personalized Talking Face
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:State-of-the-art 3D-field video-referenced Talking Face Generation (TFG) methods synthesize high-fidelity personalized talking-face videos in real time by modeling 3D geometry and appearance from reference portrait video. This capability raises significant privacy concerns regarding malicious misuse of personal portraits. However, no efficient defense framework exists to protect such videos against 3D-field TFG methods. While image-based defenses could apply per-frame 2D perturbations, they incur prohibitive computational costs, severe video quality degradation, failing to disrupt 3D information for video protection. To address this, we propose a novel and efficient video defense framework against 3D-field TFG methods, which protects portrait video by perturbing the 3D information acquisition process while maintain high-fidelity video quality. Specifically, our method introduces: (1) a similarity-guided parameter sharing mechanism for computational efficiency, and (2) a multi-scale dual-domain attention module to jointly optimize spatial-frequency perturbations. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed framework exhibits strong defense capability and achieves a 47x acceleration over the fastest baseline while maintaining high fidelity. Moreover, it remains robust against scaling operations and state-of-the-art purification attacks, and the effectiveness of our design choices is further validated through ablation studies. Our project is available at https://github.com/Richen7418/VDF.
Automated Red-Teaming Framework for Large Language Model Security Assessment: A Comprehensive Attack Generation and Detection System
Dec 21, 2025Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed in high-stakes domains, ensuring their security and alignment has become a critical challenge. Existing red-teaming practices depend heavily on manual testing, which limits scalability and fails to comprehensively cover the vast space of potential adversarial behaviors. This paper introduces an automated red-teaming framework that systematically generates, executes, and evaluates adversarial prompts to uncover security vulnerabilities in LLMs. Our framework integrates meta-prompting-based attack synthesis, multi-modal vulnerability detection, and standardized evaluation protocols spanning six major threat categories -- reward hacking, deceptive alignment, data exfiltration, sandbagging, inappropriate tool use, and chain-of-thought manipulation. Experiments on the GPT-OSS-20B model reveal 47 distinct vulnerabilities, including 21 high-severity and 12 novel attack patterns, achieving a $3.9\times$ improvement in vulnerability discovery rate over manual expert testing while maintaining 89\% detection accuracy. These results demonstrate the framework's effectiveness in enabling scalable, systematic, and reproducible AI safety evaluations. By providing actionable insights for improving alignment robustness, this work advances the state of automated LLM red-teaming and contributes to the broader goal of building secure and trustworthy AI systems.
MalRAG: A Retrieval-Augmented LLM Framework for Open-set Malicious Traffic Identification
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:Fine-grained identification of IDS-flagged suspicious traffic is crucial in cybersecurity. In practice, cyber threats evolve continuously, making the discovery of novel malicious traffic a critical necessity as well as the identification of known classes. Recent studies have advanced this goal with deep models, but they often rely on task-specific architectures that limit transferability and require per-dataset tuning. In this paper we introduce MalRAG, the first LLM driven retrieval-augmented framework for open-set malicious traffic identification. MalRAG freezes the LLM and operates via comprehensive traffic knowledge construction, adaptive retrieval, and prompt engineering. Concretely, we construct a multi-view traffic database by mining prior malicious traffic from content, structural, and temporal perspectives. Furthermore, we introduce a Coverage-Enhanced Retrieval Algorithm that queries across these views to assemble the most probable candidates, thereby improving the inclusion of correct evidence. We then employ Traffic-Aware Adaptive Pruning to select a variable subset of these candidates based on traffic-aware similarity scores, suppressing incorrect matches and yielding reliable retrieved evidence. Moreover, we develop a suite of guidance prompts where task instruction, evidence referencing, and decision guidance are integrated with the retrieved evidence to improve LLM performance. Across diverse real-world datasets and settings, MalRAG delivers state-of-the-art results in both fine-grained identification of known classes and novel malicious traffic discovery. Ablation and deep-dive analyses further show that MalRAG effective leverages LLM capabilities yet achieves open-set malicious traffic identification without relying on a specific LLM.
Ada-FCN: Adaptive Frequency-Coupled Network for fMRI-Based Brain Disorder Classification
Nov 16, 2025Abstract:Resting-state fMRI has become a valuable tool for classifying brain disorders and constructing brain functional connectivity networks by tracking BOLD signals across brain regions. However, existing mod els largely neglect the multi-frequency nature of neuronal oscillations, treating BOLD signals as monolithic time series. This overlooks the cru cial fact that neurological disorders often manifest as disruptions within specific frequency bands, limiting diagnostic sensitivity and specificity. While some methods have attempted to incorporate frequency informa tion, they often rely on predefined frequency bands, which may not be optimal for capturing individual variability or disease-specific alterations. To address this, we propose a novel framework featuring Adaptive Cas cade Decomposition to learn task-relevant frequency sub-bands for each brain region and Frequency-Coupled Connectivity Learning to capture both intra- and nuanced cross-band interactions in a unified functional network. This unified network informs a novel message-passing mecha nism within our Unified-GCN, generating refined node representations for diagnostic prediction. Experimental results on the ADNI and ABIDE datasets demonstrate superior performance over existing methods. The code is available at https://github.com/XXYY20221234/Ada-FCN.
* MICCAI2025
WorldGrow: Generating Infinite 3D World
Oct 24, 2025



Abstract:We tackle the challenge of generating the infinitely extendable 3D world -- large, continuous environments with coherent geometry and realistic appearance. Existing methods face key challenges: 2D-lifting approaches suffer from geometric and appearance inconsistencies across views, 3D implicit representations are hard to scale up, and current 3D foundation models are mostly object-centric, limiting their applicability to scene-level generation. Our key insight is leveraging strong generation priors from pre-trained 3D models for structured scene block generation. To this end, we propose WorldGrow, a hierarchical framework for unbounded 3D scene synthesis. Our method features three core components: (1) a data curation pipeline that extracts high-quality scene blocks for training, making the 3D structured latent representations suitable for scene generation; (2) a 3D block inpainting mechanism that enables context-aware scene extension; and (3) a coarse-to-fine generation strategy that ensures both global layout plausibility and local geometric/textural fidelity. Evaluated on the large-scale 3D-FRONT dataset, WorldGrow achieves SOTA performance in geometry reconstruction, while uniquely supporting infinite scene generation with photorealistic and structurally consistent outputs. These results highlight its capability for constructing large-scale virtual environments and potential for building future world models.
RECALL: REpresentation-aligned Catastrophic-forgetting ALLeviation via Hierarchical Model Merging
Oct 23, 2025Abstract:We unveil that internal representations in large language models (LLMs) serve as reliable proxies of learned knowledge, and propose RECALL, a novel representation-aware model merging framework for continual learning without access to historical data. RECALL computes inter-model similarity from layer-wise hidden representations over clustered typical samples, and performs adaptive, hierarchical parameter fusion to align knowledge across models. This design enables the preservation of domain-general features in shallow layers while allowing task-specific adaptation in deeper layers. Unlike prior methods that require task labels or incur performance trade-offs, RECALL achieves seamless multi-domain integration and strong resistance to catastrophic forgetting. Extensive experiments across five NLP tasks and multiple continual learning scenarios show that RECALL outperforms baselines in both knowledge retention and generalization, providing a scalable and data-free solution for evolving LLMs.
Clarifying Semantics of In-Context Examples for Unit Test Generation
Oct 02, 2025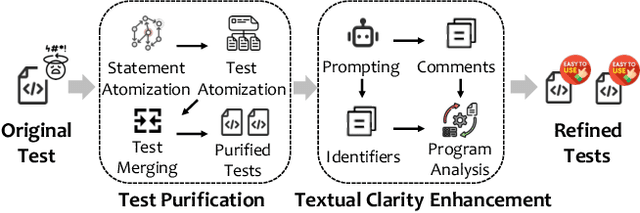
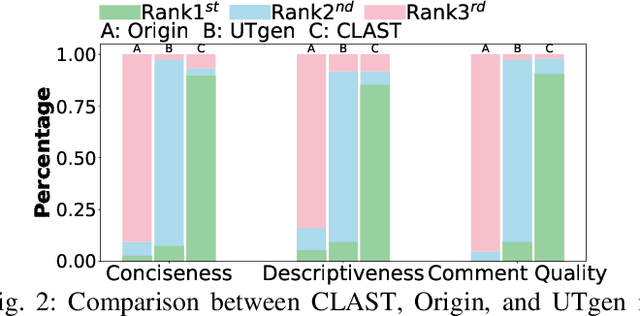
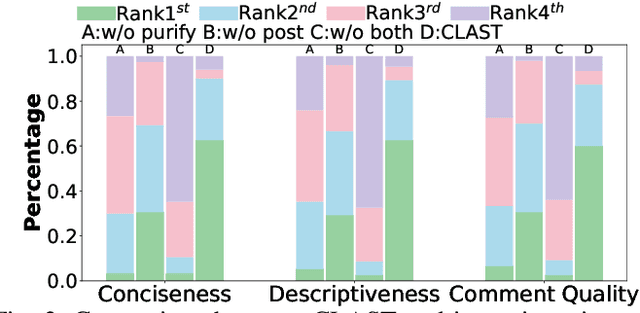
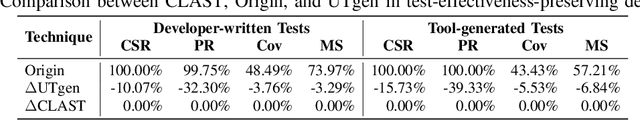
Abstract:Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have enabled promising performance in unit test generation through in-context learning (ICL). However, the quality of in-context examples significantly influences the effectiveness of generated tests-poorly structured or semantically unclear test examples often lead to suboptimal outputs. In this paper, we propose CLAST, a novel technique that systematically refines unit tests to improve their semantic clarity, thereby enhancing their utility as in-context examples. The approach decomposes complex tests into logically clearer ones and improves semantic clarity through a combination of program analysis and LLM-based rewriting. We evaluated CLAST on four open-source and three industrial projects. The results demonstrate that CLAST largely outperforms UTgen, the state-of-the-art refinement technique, in both preserving test effectiveness and enhancing semantic clarity. Specifically, CLAST fully retains the original effectiveness of unit tests, while UTgen reduces compilation success rate (CSR), pass rate (PR), test coverage (Cov), and mutation score (MS) by an average of 12.90%, 35.82%, 4.65%, and 5.07%, respectively. Over 85.33% of participants in our user study preferred the semantic clarity of CLAST-refined tests. Notably, incorporating CLAST-refined tests as examples effectively improves ICL-based unit test generation approaches such as RAGGen and TELPA, resulting in an average increase of 25.97% in CSR, 28.22% in PR, and 45.99% in Cov for generated tests, compared to incorporating UTgen-refined tests. The insights from the follow-up user study not only reinforce CLAST's potential impact in software testing practice but also illuminate avenues for future research.
Few-step Flow for 3D Generation via Marginal-Data Transport Distillation
Sep 04, 2025Abstract:Flow-based 3D generation models typically require dozens of sampling steps during inference. Though few-step distillation methods, particularly Consistency Models (CMs), have achieved substantial advancements in accelerating 2D diffusion models, they remain under-explored for more complex 3D generation tasks. In this study, we propose a novel framework, MDT-dist, for few-step 3D flow distillation. Our approach is built upon a primary objective: distilling the pretrained model to learn the Marginal-Data Transport. Directly learning this objective needs to integrate the velocity fields, while this integral is intractable to be implemented. Therefore, we propose two optimizable objectives, Velocity Matching (VM) and Velocity Distillation (VD), to equivalently convert the optimization target from the transport level to the velocity and the distribution level respectively. Velocity Matching (VM) learns to stably match the velocity fields between the student and the teacher, but inevitably provides biased gradient estimates. Velocity Distillation (VD) further enhances the optimization process by leveraging the learned velocity fields to perform probability density distillation. When evaluated on the pioneer 3D generation framework TRELLIS, our method reduces sampling steps of each flow transformer from 25 to 1 or 2, achieving 0.68s (1 step x 2) and 0.94s (2 steps x 2) latency with 9.0x and 6.5x speedup on A800, while preserving high visual and geometric fidelity. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms existing CM distillation methods, and enables TRELLIS to achieve superior performance in few-step 3D generation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge