Qi Tian
Refer to the report for detailed contributions
Nüwa: Mending the Spatial Integrity Torn by VLM Token Pruning
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Vision token pruning has proven to be an effective acceleration technique for the efficient Vision Language Model (VLM). However, existing pruning methods demonstrate excellent performance preservation in visual question answering (VQA) and suffer substantial degradation on visual grounding (VG) tasks. Our analysis of the VLM's processing pipeline reveals that strategies utilizing global semantic similarity and attention scores lose the global spatial reference frame, which is derived from the interactions of tokens' positional information. Motivated by these findings, we propose $\text{Nüwa}$, a two-stage token pruning framework that enables efficient feature aggregation while maintaining spatial integrity. In the first stage, after the vision encoder, we apply three operations, namely separation, alignment, and aggregation, which are inspired by swarm intelligence algorithms to retain information-rich global spatial anchors. In the second stage, within the LLM, we perform text-guided pruning to retain task-relevant visual tokens. Extensive experiments demonstrate that $\text{Nüwa}$ achieves SOTA performance on multiple VQA benchmarks (from 94% to 95%) and yields substantial improvements on visual grounding tasks (from 7% to 47%).
AI Decodes Historical Chinese Archives to Reveal Lost Climate History
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Historical archives contain qualitative descriptions of climate events, yet converting these into quantitative records has remained a fundamental challenge. Here we introduce a paradigm shift: a generative AI framework that inverts the logic of historical chroniclers by inferring the quantitative climate patterns associated with documented events. Applied to historical Chinese archives, it produces the sub-annual precipitation reconstruction for southeastern China over the period 1368-1911 AD. Our reconstruction not only quantifies iconic extremes like the Ming Dynasty's Great Drought but also, crucially, maps the full spatial and seasonal structure of El Ni$ñ$o influence on precipitation in this region over five centuries, revealing dynamics inaccessible in shorter modern records. Our methodology and high-resolution climate dataset are directly applicable to climate science and have broader implications for the historical and social sciences.
Enhancing Post-Training Quantization via Future Activation Awareness
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Post-training quantization (PTQ) is a widely used method to compress large language models (LLMs) without fine-tuning. It typically sets quantization hyperparameters (e.g., scaling factors) based on current-layer activations. Although this method is efficient, it suffers from quantization bias and error accumulation, resulting in suboptimal and unstable quantization, especially when the calibration data is biased. To overcome these issues, we propose Future-Aware Quantization (FAQ), which leverages future-layer activations to guide quantization. This allows better identification and preservation of important weights, while reducing sensitivity to calibration noise. We further introduce a window-wise preview mechanism to softly aggregate multiple future-layer activations, mitigating over-reliance on any single layer. To avoid expensive greedy search, we use a pre-searched configuration to minimize overhead. Experiments show that FAQ consistently outperforms prior methods with negligible extra cost, requiring no backward passes, data reconstruction, or tuning, making it well-suited for edge deployment.
E^2-LLM: Bridging Neural Signals and Interpretable Affective Analysis
Jan 11, 2026Abstract:Emotion recognition from electroencephalography (EEG) signals remains challenging due to high inter-subject variability, limited labeled data, and the lack of interpretable reasoning in existing approaches. While recent multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have advanced emotion analysis, they have not been adapted to handle the unique spatiotemporal characteristics of neural signals. We present E^2-LLM (EEG-to-Emotion Large Language Model), the first MLLM framework for interpretable emotion analysis from EEG. E^2-LLM integrates a pretrained EEG encoder with Qwen-based LLMs through learnable projection layers, employing a multi-stage training pipeline that encompasses emotion-discriminative pretraining, cross-modal alignment, and instruction tuning with chain-of-thought reasoning. We design a comprehensive evaluation protocol covering basic emotion prediction, multi-task reasoning, and zero-shot scenario understanding. Experiments on the dataset across seven emotion categories demonstrate that E^2-LLM achieves excellent performance on emotion classification, with larger variants showing enhanced reliability and superior zero-shot generalization to complex reasoning scenarios. Our work establishes a new paradigm combining physiological signals with LLM reasoning capabilities, showing that model scaling improves both recognition accuracy and interpretable emotional understanding in affective computing.
Punctuation-aware Hybrid Trainable Sparse Attention for Large Language Models
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Attention serves as the fundamental mechanism for long-context modeling in large language models (LLMs), yet dense attention becomes structurally prohibitive for long sequences due to its quadratic complexity. Consequently, sparse attention has received increasing attention as a scalable alternative. However, existing sparse attention methods rely on coarse-grained semantic representations during block selection, which blur intra-block semantic boundaries and lead to the loss of critical information. To address this issue, we propose \textbf{P}unctuation-aware \textbf{H}ybrid \textbf{S}parse \textbf{A}ttention \textbf{(PHSA)}, a natively trainable sparse attention framework that leverages punctuation tokens as semantic boundary anchors. Specifically, (1) we design a dual-branch aggregation mechanism that fuses global semantic representations with punctuation-enhanced boundary features, preserving the core semantic structure while introducing almost no additional computational overhead; (2) we introduce an extreme-sparsity-adaptive training and inference strategy that stabilizes model behavior under very low token activation ratios; Extensive experiments on general benchmarks and long-context evaluations demonstrate that PHSA consistently outperforms dense attention and state-of-the-art sparse attention baselines, including InfLLM v2. Specifically, for the 0.6B-parameter model with 32k-token input sequences, PHSA can reduce the information loss by 10.8\% at a sparsity ratio of 97.3\%.
CogniEdit: Dense Gradient Flow Optimization for Fine-Grained Image Editing
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:Instruction-based image editing with diffusion models has achieved impressive results, yet existing methods struggle with fine-grained instructions specifying precise attributes such as colors, positions, and quantities. While recent approaches employ Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) for alignment, they optimize only at individual sampling steps, providing sparse feedback that limits trajectory-level control. We propose a unified framework CogniEdit, combining multi-modal reasoning with dense reward optimization that propagates gradients across consecutive denoising steps, enabling trajectory-level gradient flow through the sampling process. Our method comprises three components: (1) Multi-modal Large Language Models for decomposing complex instructions into actionable directives, (2) Dynamic Token Focus Relocation that adaptively emphasizes fine-grained attributes, and (3) Dense GRPO-based optimization that propagates gradients across consecutive steps for trajectory-level supervision. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that our CogniEdit achieves state-of-the-art performance in balancing fine-grained instruction following with visual quality and editability preservation
Bridging the Gap Between Bayesian Deep Learning and Ensemble Weather Forecasts
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:Weather forecasting is fundamentally challenged by the chaotic nature of the atmosphere, necessitating probabilistic approaches to quantify uncertainty. While traditional ensemble prediction (EPS) addresses this through computationally intensive simulations, recent advances in Bayesian Deep Learning (BDL) offer a promising but often disconnected alternative. We bridge these paradigms through a unified hybrid Bayesian Deep Learning framework for ensemble weather forecasting that explicitly decomposes predictive uncertainty into epistemic and aleatoric components, learned via variational inference and a physics-informed stochastic perturbation scheme modeling flow-dependent atmospheric dynamics, respectively. We further establish a unified theoretical framework that rigorously connects BDL and EPS, providing formal theorems that decompose total predictive uncertainty into epistemic and aleatoric components under the hybrid BDL framework. We validate our framework on the large-scale 40-year ERA5 reanalysis dataset (1979-2019) with 0.25° spatial resolution. Experimental results show that our method not only improves forecast accuracy and yields better-calibrated uncertainty quantification but also achieves superior computational efficiency compared to state-of-the-art probabilistic diffusion models. We commit to making our code open-source upon acceptance of this paper.
TheraMind: A Strategic and Adaptive Agent for Longitudinal Psychological Counseling
Oct 29, 2025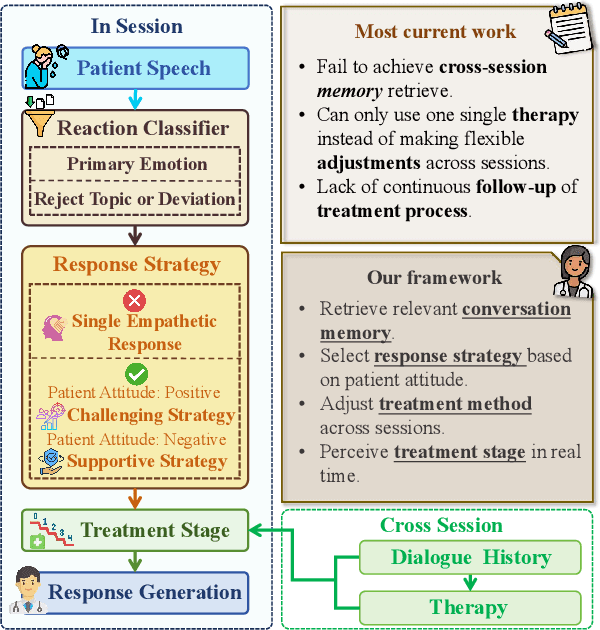
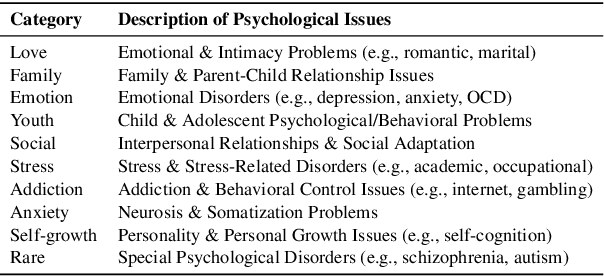
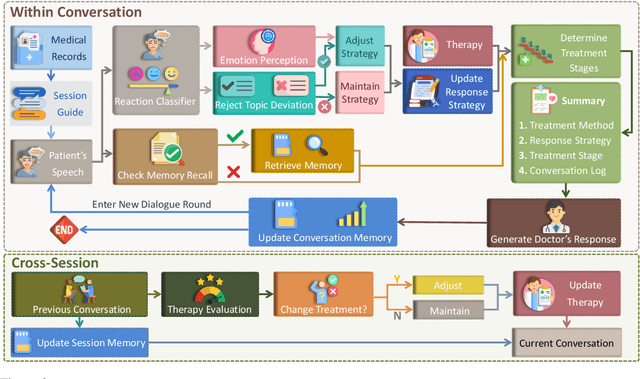
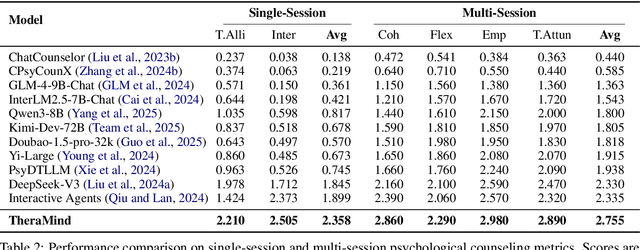
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) in psychological counseling have attracted increasing attention. However, existing approaches often lack emotional understanding, adaptive strategies, and the use of therapeutic methods across multiple sessions with long-term memory, leaving them far from real clinical practice. To address these critical gaps, we introduce TheraMind, a strategic and adaptive agent for longitudinal psychological counseling. The cornerstone of TheraMind is a novel dual-loop architecture that decouples the complex counseling process into an Intra-Session Loop for tactical dialogue management and a Cross-Session Loop for strategic therapeutic planning. The Intra-Session Loop perceives the patient's emotional state to dynamically select response strategies while leveraging cross-session memory to ensure continuity. Crucially, the Cross-Session Loop empowers the agent with long-term adaptability by evaluating the efficacy of the applied therapy after each session and adjusting the method for subsequent interactions. We validate our approach in a high-fidelity simulation environment grounded in real clinical cases. Extensive evaluations show that TheraMind outperforms other methods, especially on multi-session metrics like Coherence, Flexibility, and Therapeutic Attunement, validating the effectiveness of its dual-loop design in emulating strategic, adaptive, and longitudinal therapeutic behavior. The code is publicly available at https://0mwwm0.github.io/TheraMind/.
WorldGrow: Generating Infinite 3D World
Oct 24, 2025



Abstract:We tackle the challenge of generating the infinitely extendable 3D world -- large, continuous environments with coherent geometry and realistic appearance. Existing methods face key challenges: 2D-lifting approaches suffer from geometric and appearance inconsistencies across views, 3D implicit representations are hard to scale up, and current 3D foundation models are mostly object-centric, limiting their applicability to scene-level generation. Our key insight is leveraging strong generation priors from pre-trained 3D models for structured scene block generation. To this end, we propose WorldGrow, a hierarchical framework for unbounded 3D scene synthesis. Our method features three core components: (1) a data curation pipeline that extracts high-quality scene blocks for training, making the 3D structured latent representations suitable for scene generation; (2) a 3D block inpainting mechanism that enables context-aware scene extension; and (3) a coarse-to-fine generation strategy that ensures both global layout plausibility and local geometric/textural fidelity. Evaluated on the large-scale 3D-FRONT dataset, WorldGrow achieves SOTA performance in geometry reconstruction, while uniquely supporting infinite scene generation with photorealistic and structurally consistent outputs. These results highlight its capability for constructing large-scale virtual environments and potential for building future world models.
Few-step Flow for 3D Generation via Marginal-Data Transport Distillation
Sep 04, 2025Abstract:Flow-based 3D generation models typically require dozens of sampling steps during inference. Though few-step distillation methods, particularly Consistency Models (CMs), have achieved substantial advancements in accelerating 2D diffusion models, they remain under-explored for more complex 3D generation tasks. In this study, we propose a novel framework, MDT-dist, for few-step 3D flow distillation. Our approach is built upon a primary objective: distilling the pretrained model to learn the Marginal-Data Transport. Directly learning this objective needs to integrate the velocity fields, while this integral is intractable to be implemented. Therefore, we propose two optimizable objectives, Velocity Matching (VM) and Velocity Distillation (VD), to equivalently convert the optimization target from the transport level to the velocity and the distribution level respectively. Velocity Matching (VM) learns to stably match the velocity fields between the student and the teacher, but inevitably provides biased gradient estimates. Velocity Distillation (VD) further enhances the optimization process by leveraging the learned velocity fields to perform probability density distillation. When evaluated on the pioneer 3D generation framework TRELLIS, our method reduces sampling steps of each flow transformer from 25 to 1 or 2, achieving 0.68s (1 step x 2) and 0.94s (2 steps x 2) latency with 9.0x and 6.5x speedup on A800, while preserving high visual and geometric fidelity. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms existing CM distillation methods, and enables TRELLIS to achieve superior performance in few-step 3D generation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge