Wenzhe Zhao
Follow-Your-Canvas: Higher-Resolution Video Outpainting with Extensive Content Generation
Sep 02, 2024Abstract:This paper explores higher-resolution video outpainting with extensive content generation. We point out common issues faced by existing methods when attempting to largely outpaint videos: the generation of low-quality content and limitations imposed by GPU memory. To address these challenges, we propose a diffusion-based method called \textit{Follow-Your-Canvas}. It builds upon two core designs. First, instead of employing the common practice of "single-shot" outpainting, we distribute the task across spatial windows and seamlessly merge them. It allows us to outpaint videos of any size and resolution without being constrained by GPU memory. Second, the source video and its relative positional relation are injected into the generation process of each window. It makes the generated spatial layout within each window harmonize with the source video. Coupling with these two designs enables us to generate higher-resolution outpainting videos with rich content while keeping spatial and temporal consistency. Follow-Your-Canvas excels in large-scale video outpainting, e.g., from 512X512 to 1152X2048 (9X), while producing high-quality and aesthetically pleasing results. It achieves the best quantitative results across various resolution and scale setups. The code is released on https://github.com/mayuelala/FollowYourCanvas
Follow-Your-Pose v2: Multiple-Condition Guided Character Image Animation for Stable Pose Control
Jun 05, 2024



Abstract:Pose-controllable character video generation is in high demand with extensive applications for fields such as automatic advertising and content creation on social media platforms. While existing character image animation methods using pose sequences and reference images have shown promising performance, they tend to struggle with incoherent animation in complex scenarios, such as multiple character animation and body occlusion. Additionally, current methods request large-scale high-quality videos with stable backgrounds and temporal consistency as training datasets, otherwise, their performance will greatly deteriorate. These two issues hinder the practical utilization of character image animation tools. In this paper, we propose a practical and robust framework Follow-Your-Pose v2, which can be trained on noisy open-sourced videos readily available on the internet. Multi-condition guiders are designed to address the challenges of background stability, body occlusion in multi-character generation, and consistency of character appearance. Moreover, to fill the gap of fair evaluation of multi-character pose animation, we propose a new benchmark comprising approximately 4,000 frames. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach outperforms state-of-the-art methods by a margin of over 35\% across 2 datasets and on 7 metrics. Meanwhile, qualitative assessments reveal a significant improvement in the quality of generated video, particularly in scenarios involving complex backgrounds and body occlusion of multi-character, suggesting the superiority of our approach.
Global and Local Semantic Completion Learning for Vision-Language Pre-training
Jun 12, 2023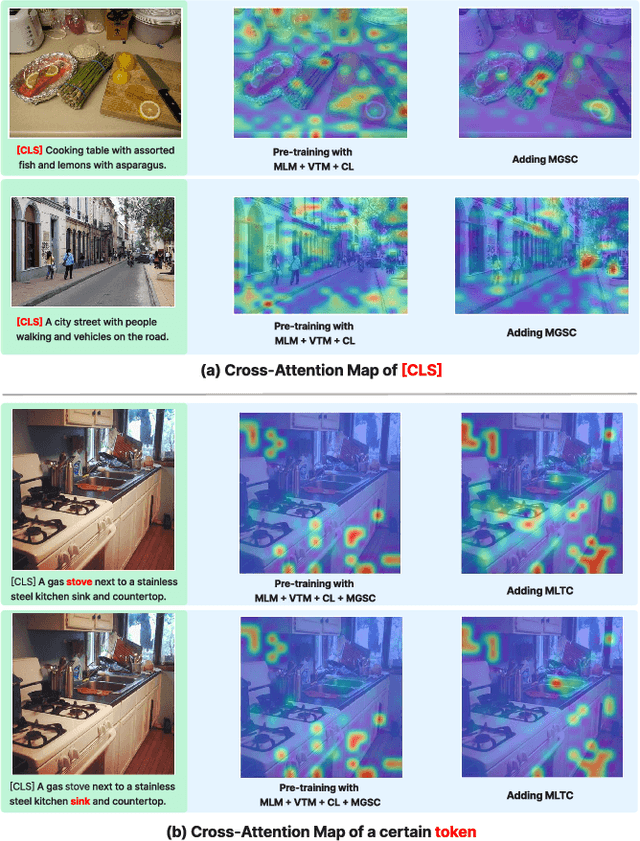
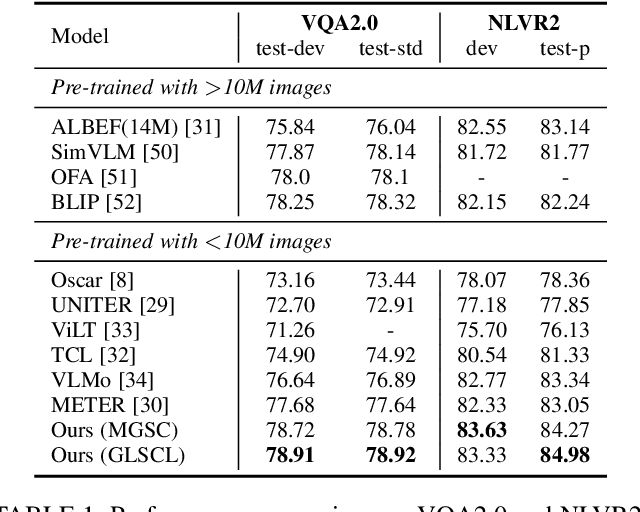
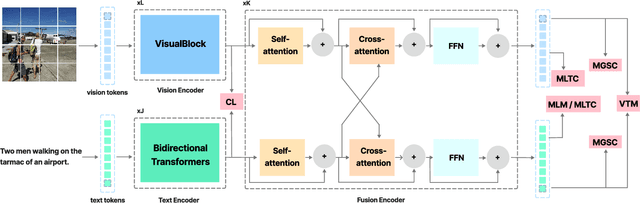
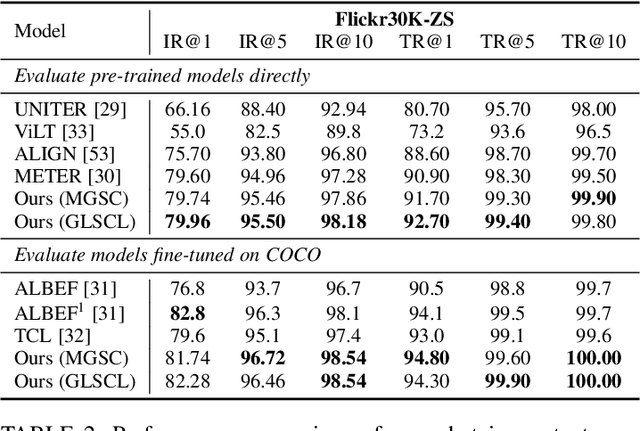
Abstract:Cross-modal alignment plays a crucial role in vision-language pre-training (VLP) models, enabling them to capture meaningful associations across different modalities. For this purpose, inspired by the success of masked language modeling (MLM) tasks in the NLP pre-training area, numerous masked modeling tasks have been proposed for VLP to further promote cross-modal interactions. The core idea of previous masked modeling tasks is to focus on reconstructing the masked tokens based on visible context for learning local-local alignment, i.e., associations between image patches and text tokens. However, most of them pay little attention to the global semantic features generated for the masked data, resulting in a limited cross-modal alignment ability of global representations to local features of the other modality. Therefore, in this paper, we propose a novel Global and Local Semantic Completion Learning (GLSCL) task to facilitate global-local alignment and local-local alignment simultaneously. Specifically, the GLSCL task complements the missing semantics of masked data and recovers global and local features by cross-modal interactions. Our GLSCL consists of masked global semantic completion (MGSC) and masked local token completion (MLTC). MGSC promotes learning more representative global features which have a great impact on the performance of downstream tasks, and MLTC can further enhance accurate comprehension on multimodal data. Moreover, we present a flexible vision encoder, enabling our model to simultaneously perform image-text and video-text multimodal tasks. Experimental results show that our proposed method obtains state-of-the-art performance on various vision-language benchmarks, such as visual question answering, image-text retrieval, and video-text retrieval.
Seeing What You Miss: Vision-Language Pre-training with Semantic Completion Learning
Nov 24, 2022Abstract:Cross-modal alignment is essential for vision-language pre-training (VLP) models to learn the correct corresponding information across different modalities. For this purpose, inspired by the success of masked language modeling (MLM) tasks in the NLP pre-training area, numerous masked modeling tasks have been proposed for VLP to further promote cross-modal interactions. The core idea of previous masked modeling tasks is to focus on reconstructing the masked tokens based on visible context for learning local-to-local alignment. However, most of them pay little attention to the global semantic features generated for the masked data, resulting in the limited cross-modal alignment ability of global representations. Therefore, in this paper, we propose a novel Semantic Completion Learning (SCL) task, complementary to existing masked modeling tasks, to facilitate global-to-local alignment. Specifically, the SCL task complements the missing semantics of masked data by capturing the corresponding information from the other modality, promoting learning more representative global features which have a great impact on the performance of downstream tasks. Moreover, we present a flexible vision encoder, which enables our model to perform image-text and video-text multimodal tasks simultaneously. Experimental results show that our proposed method obtains state-of-the-art performance on various vision-language benchmarks, such as visual question answering, image-text retrieval, and video-text retrieval.
Egocentric Video-Language Pretraining @ Ego4D Challenge 2022
Jul 04, 2022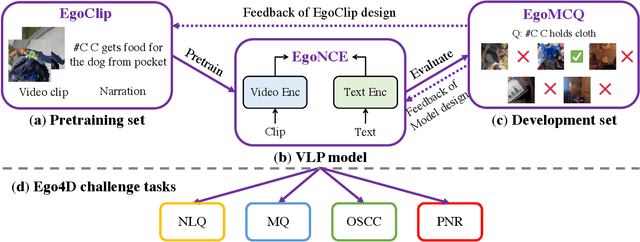
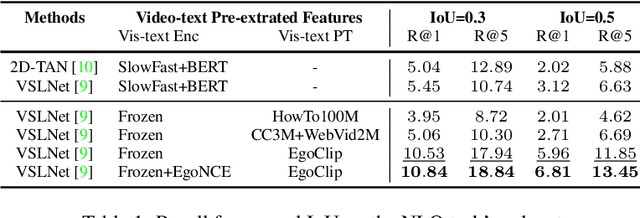
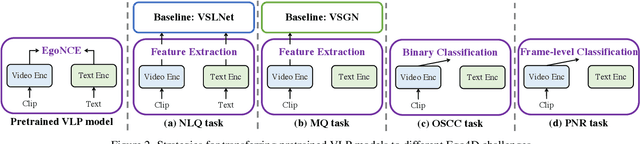
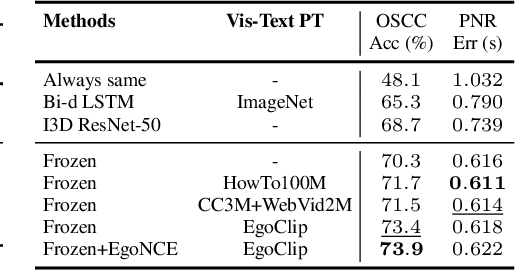
Abstract:In this report, we propose a video-language pretraining (VLP) based solution \cite{kevin2022egovlp} for four Ego4D challenge tasks, including Natural Language Query (NLQ), Moment Query (MQ), Object State Change Classification (OSCC), and PNR Localization (PNR). Especially, we exploit the recently released Ego4D dataset \cite{grauman2021ego4d} to pioneer Egocentric VLP from pretraining dataset, pretraining objective, and development set. Based on the above three designs, we develop a pretrained video-language model that is able to transfer its egocentric video-text representation or video-only representation to several video downstream tasks. Our Egocentric VLP achieves 10.46R@1&IoU @0.3 on NLQ, 10.33 mAP on MQ, 74% Acc on OSCC, 0.67 sec error on PNR. The code is available at https://github.com/showlab/EgoVLP.
Egocentric Video-Language Pretraining @ EPIC-KITCHENS-100 Multi-Instance Retrieval Challenge 2022
Jul 04, 2022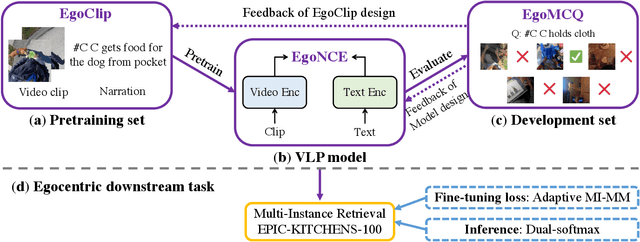
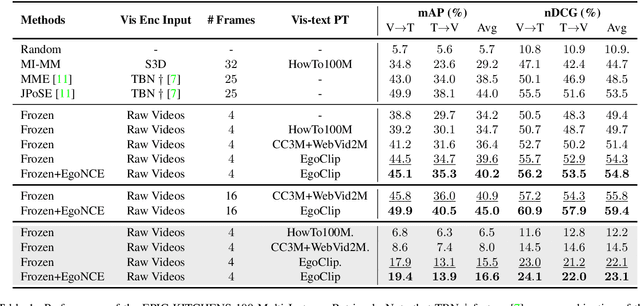
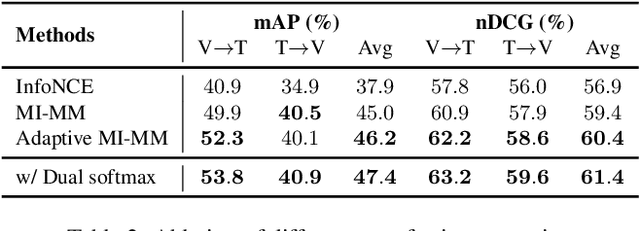
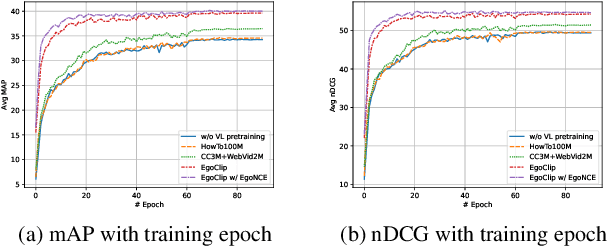
Abstract:In this report, we propose a video-language pretraining (VLP) based solution \cite{kevin2022egovlp} for the EPIC-KITCHENS-100 Multi-Instance Retrieval (MIR) challenge. Especially, we exploit the recently released Ego4D dataset \cite{grauman2021ego4d} to pioneer Egocentric VLP from pretraining dataset, pretraining objective, and development set. Based on the above three designs, we develop a pretrained video-language model that is able to transfer its egocentric video-text representation to MIR benchmark. Furthermore, we devise an adaptive multi-instance max-margin loss to effectively fine-tune the model and equip the dual-softmax technique for reliable inference. Our best single model obtains strong performance on the challenge test set with 47.39% mAP and 61.44% nDCG. The code is available at https://github.com/showlab/EgoVLP.
Egocentric Video-Language Pretraining
Jun 03, 2022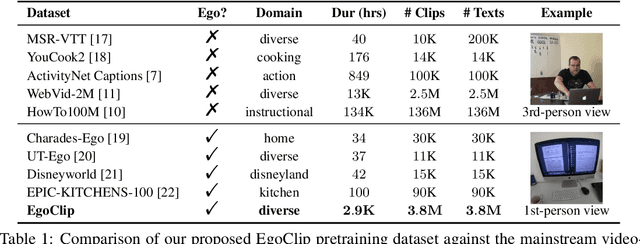
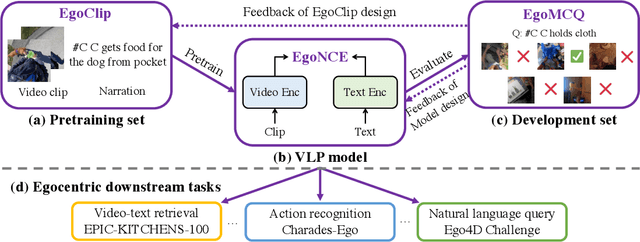
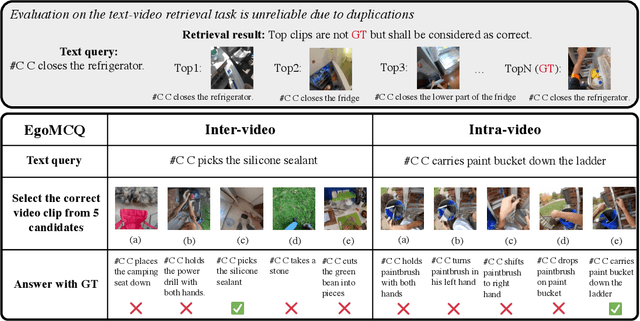
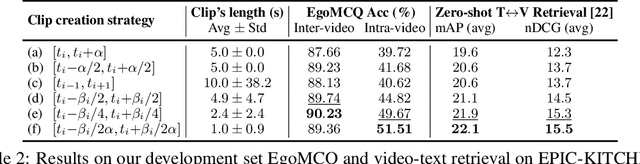
Abstract:Video-Language Pretraining (VLP), aiming to learn transferable representation to advance a wide range of video-text downstream tasks, has recently received increasing attention. Dominant works that achieve strong performance rely on large-scale, 3rd-person video-text datasets, such as HowTo100M. In this work, we exploit the recently released Ego4D dataset to pioneer Egocentric VLP along three directions. (i) We create EgoClip, a 1st-person video-text pretraining dataset comprising 3.8M clip-text pairs well-chosen from Ego4D, covering a large variety of human daily activities. (ii) We propose a novel pretraining objective, dubbed as EgoNCE, which adapts video-text contrastive learning to egocentric domain by mining egocentric-aware positive and negative samples. (iii) We introduce EgoMCQ, a development benchmark that is close to EgoClip and hence can support effective validation and fast exploration of our design decisions regarding EgoClip and EgoNCE. Furthermore, we demonstrate strong performance on five egocentric downstream tasks across three datasets: video-text retrieval on EPIC-KITCHENS-100; action recognition on Charades-Ego; and natural language query, moment query, and object state change classification on Ego4D challenge benchmarks. The dataset and code will be available at https://github.com/showlab/EgoVLP.
HunYuan_tvr for Text-Video Retrivial
Apr 14, 2022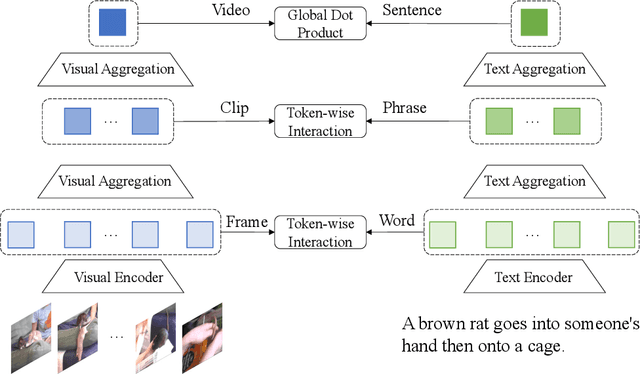
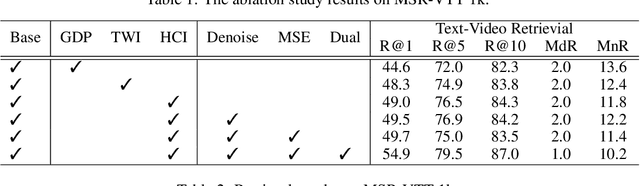
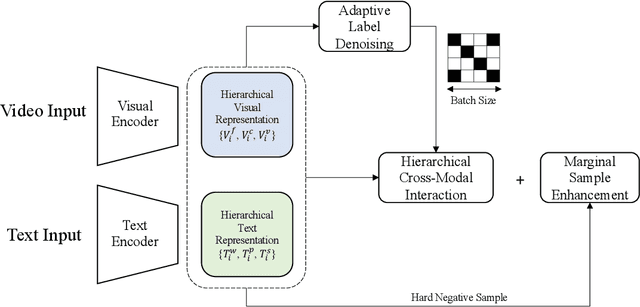
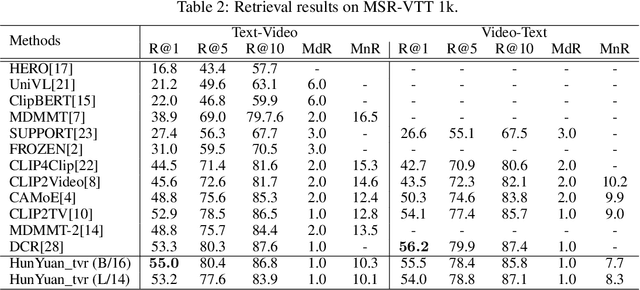
Abstract:Text-Video Retrieval plays an important role in multi-modal understanding and has attracted increasing attention in recent years. Most existing methods focus on constructing contrastive pairs between whole videos and complete caption sentences, while ignoring fine-grained cross-modal relationships, e.g., short clips and phrases or single frame and word. In this paper, we propose a novel method, named HunYuan\_tvr, to explore hierarchical cross-modal interactions by simultaneously exploring video-sentence, clip-phrase, and frame-word relationships. Considering intrinsic semantic relations between frames, HunYuan\_tvr first performs self-attention to explore frame-wise correlations and adaptively clusters correlated frames into clip-level representations. Then, the clip-wise correlation is explored to aggregate clip representations into a compact one to describe the video globally. In this way, we can construct hierarchical video representations for frame-clip-video granularities, and also explore word-wise correlations to form word-phrase-sentence embeddings for the text modality. Finally, hierarchical contrastive learning is designed to explore cross-modal relationships,~\emph{i.e.,} frame-word, clip-phrase, and video-sentence, which enables HunYuan\_tvr to achieve a comprehensive multi-modal understanding. Further boosted by adaptive label denosing and marginal sample enhancement, HunYuan\_tvr obtains new state-of-the-art results on various benchmarks, e.g., Rank@1 of 55.0%, 57.8%, 29.7%, 52.1%, and 57.3% on MSR-VTT, MSVD, LSMDC, DiDemo, and ActivityNet respectively.
Deep Unsupervised Hashing with Latent Semantic Components
Mar 17, 2022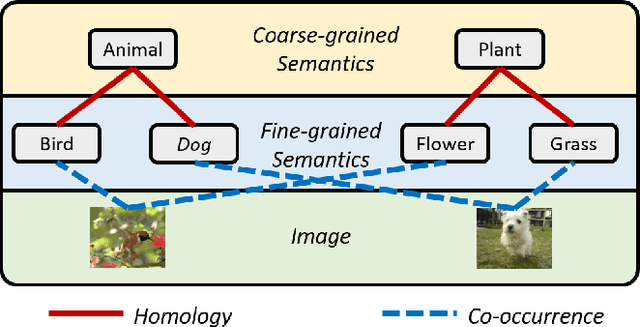
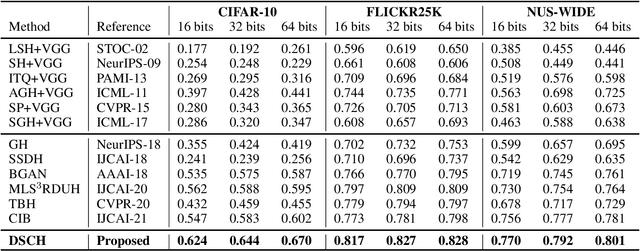
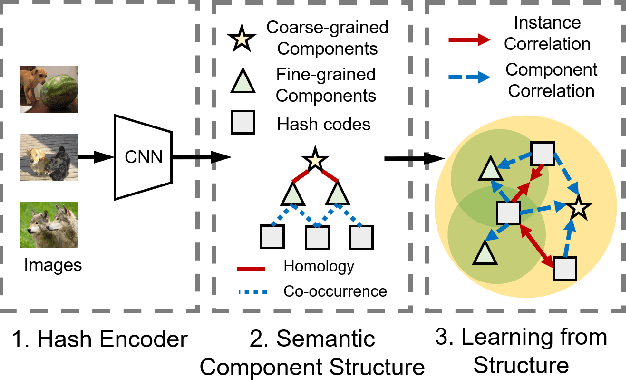
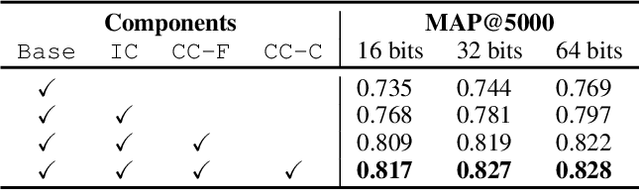
Abstract:Deep unsupervised hashing has been appreciated in the regime of image retrieval. However, most prior arts failed to detect the semantic components and their relationships behind the images, which makes them lack discriminative power. To make up the defect, we propose a novel Deep Semantic Components Hashing (DSCH), which involves a common sense that an image normally contains a bunch of semantic components with homology and co-occurrence relationships. Based on this prior, DSCH regards the semantic components as latent variables under the Expectation-Maximization framework and designs a two-step iterative algorithm with the objective of maximum likelihood of training data. Firstly, DSCH constructs a semantic component structure by uncovering the fine-grained semantics components of images with a Gaussian Mixture Modal~(GMM), where an image is represented as a mixture of multiple components, and the semantics co-occurrence are exploited. Besides, coarse-grained semantics components, are discovered by considering the homology relationships between fine-grained components, and the hierarchy organization is then constructed. Secondly, DSCH makes the images close to their semantic component centers at both fine-grained and coarse-grained levels, and also makes the images share similar semantic components close to each other. Extensive experiments on three benchmark datasets demonstrate that the proposed hierarchical semantic components indeed facilitate the hashing model to achieve superior performance.
Objects detection for remote sensing images based on polar coordinates
Jan 16, 2020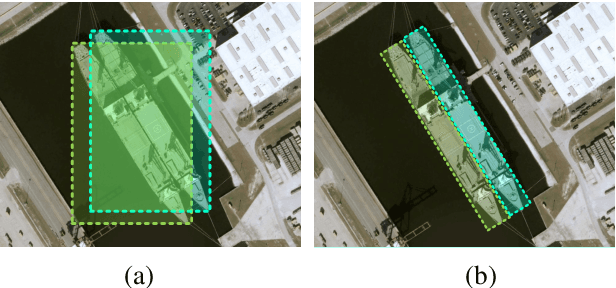
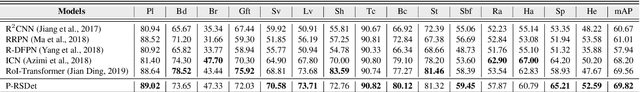
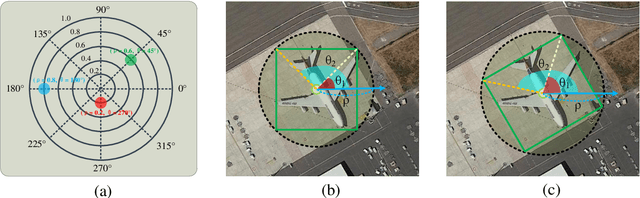
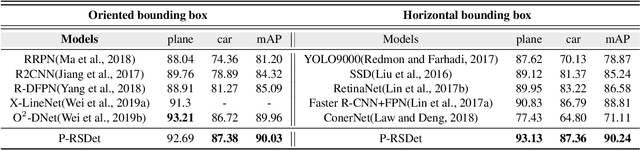
Abstract:Oriented and horizontal bounding box are two typical output forms in the field of remote sensing object detection. In this filed, most present state-of-the-art detectors belong to anchor-based method and perform regression tasks in Cartesian coordinates, which cause the design of oriented detectors is much more complicated than the horizontal ones, because the former usually needs to devise more complex rotated anchors, rotated Intersection-over-Union (IOU) and rotated Non Maximum Supression (NMS). In this paper, we propose a novel anchor-free detector modeled in polar coordinates to detect objects for remote sensing images, which makes the acquisition of oriented output form be as simple as the horizontal one. Our model, named Polar Remote Sensing Object Detector (P-RSDet), takes the center point of each object as the pole point and the horizontal positive direction as the polar axis to establish the polar coordinate system. The detection of one object can be regarded as predictions of one polar radius and two polar angles for both horizontal and oriented bounding box by our model. P-RSDet realizes the combination of two output forms with minimum cost. Experiments show that our P-RSDet achieves competitive performances on DOTA, UCAS-AOD and NWPU VHR-10 datasets on both horizontal and oreinted detection fileds.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge